| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
HIV[1]
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
以类似的方式,dimercaprol(10-100 μM;4 小时)可以显着保护 PC-12 细胞免遭甲醛介导的细胞死亡 [2]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Dimercaprol(2,3-Dimercapto-1-丙醇;12.5-75 mg/kg;皮下注射;一次)可增加药物浓度并降低肝脏和水中的汞含量[3]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定[2]
细胞类型: PC-12 细胞 测试浓度: 10、25、50 和 100 μM 孵育持续时间:4小时 实验结果:显着保护PC-12细胞免受丙烯醛介导的细胞损伤,并以剂量依赖性方式死亡。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Wistar rats (13 days old)) injected with HgCl2[3]
Doses: 12.5 mg/kg, 25 mg/kg, 50 mg/kg or 75 mg/kg Route of Administration: subcutaneous injection; primary Experimental Results:diminished liver function and mercury levels in the kidneys. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
After intra-muscular injection. Urine. Because it is a lipophilic drug, dimercaprol penetrates rapidly the intracellular spaces. The highest concentrations are found in the liver, kidneys, brain and small intestine. Due to its lipophilic characteristic, the complexes formed with mercury and other metals may be redistributed into sensitive cells in the brain following dimercaprol treatment. It is readily absorbed through the skin after topical application. Percutaneous absorption in rats and humans equals 3 millimol (124 mg)/sq cm per hour. Following absorption, dimercaprol is distributed to all tissues (mainly in the intracellular space) including the brain, with highest concentrations in the liver and kidneys. Following IM injection of therapeutic doses of dimercaprol, peak blood concentrations are attained in 30-60 minutes. Dimercaprol is slowly absorbed through the skin following topical application. Dimercaprol is not absorbed orally. It is rapidly absorbed after intramuscular injection and persists for at least 12 hours. Approximately 80% of the dose is absorbed after 1 hours and 90% after 6 hours. Maximal blood concentrations are attained within 1 hour. Hepatic metabolism (by glucuronidation) and excretion are essentially complete within 4 hours. Dimercaprol is the only commonly used chelating agent that readily crosses cellular membranes; as a result, the concentration in certain organs (liver, kidney, small intestine) can be up to five times that in the blood. Metabolism / Metabolites ... Metabolic degradation and excretion are essentially complete within 4 hours. Dimercaprol not excreted as dimercaprol-metal complex is quickly metabolized by the liver and excreted as an inactive product in the urine. Biological Half-Life The drug has a short half life. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
IDENTIFICATION: Dimercaprol is a therapeutic compound developed as an antidote against the vesicant arsenic was gases such as Lewisite. It is clear to slightly yellow liquid with a pungent odor of mercaptan. It is slightly soluble in water and vegetable oils. Arachis or peanut oil is used in pharmaceutical preparations. It is miscible in alcohol, benzyl benzoate, ether, methyl alcogol and other solvents. Dimercaprol is useful in the treatment of arsenic (organic and inorganic), gold and inorganic mercury poisoning. HUMAN EXPOSURE: The main risks are hypertension, tachycardia, cardiovascular collapse, convulsions, excitation, hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia. Special care should be taken in case of oliguria, hypertension and impaired hepatic function when the antidote is administered. The target organs are the kidneys, the cardiovascular and central nervous systems. The clinical effects are nausea, vomiting, headache, burning sensation of the lips, throat, mouth and eyes; lacrimation and salivation; sweating, rhinorrhea and burning sensation of the penis; a feeling of constriction or pain in the throat or chest, muscle pains and spasms and tingling of the skin of the hands; abdominal pain, anxiety, nervousness and weakness, uticaria and hyperpyrexia. Pain and sterile abscesses can result. Irritation of the skin and mucous membranes can be observed after local contact. This drug should always be administered as soon as possible by deep IM injection and never by IV or SC routes. Dimercaprol is well tolerated in children. The drug cannot be used in poisonings due to iron, cadmium, tellurium, selenium, vanadium and uranium. It is contraindicated in poisonings due to elemental mercury vapor, because it can further increase the metal in the brain. This drug should not be administered in case of renal and hepatic insufficiency and patients with hypertension. Dermal absorption is possible. Peak concentrations in the blood are obtained 30-60 min after IM injection. Dimercaprol is a lipophilic drug, it penetrates rapidly in intracellular spaces. The highest concentrations are found in the liver, kidneys, brain and small intestine. Glucuronic acid conjugates are excreted by the kidneys. Iron therapy should be given 24 hr or more after the last dose of dimercaprol. It should not be administered at the same time. Breath may smell like odor of a mercaptan. Hemolytic anemia was reported in individuals with G6PD deficiency. In children, dimercaprol may induce a transient reduction in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. ANIMAL STUDIES: In animal studies, the biological half life was short and metabolic degradation and renal excretion is complete within 6-24 hr. In animals a lethal dose of dithiols causes convulsions and severe spasm of the abdominal muscles shortly before death occurs. After injection of sublethal amounts of dimercaprol, the animals become apathetic and develop lacrimation, edema of the conjunctiva, blepharospasms, salivation and vomiting. With increasing doses they develop ataxia, analgesia, muscle tremor, nystagmus, tonic and clonic convulsions and death results during coma. In cats following an IV injection cardiovascular depression as indicated by a fall in systemic and pulmonary artery pressure. After repeated local applications in animals, sensitization dermatitis may develop. Chronic effects in animals include fatty degeneration of the liver and impairment of liver function. In animals, chronic parenteral administration increases white blood cell count by 30%. This drug induced malformations of the skeletal system, growth retardation and increased embryo lethality. Hepatotoxicity In clinical trials conducted in children with Wilson disease, serum aminotransferase levels generally improved or were stable during treatment with dimercaprol. There have been no clinical reports of acute liver injury with jaundice attributed to dimercaprol. Patients with Wilson disease typically have mild-to-moderate serum aminotransferase elevations and may have signs and symptoms of cirrhosis. Improvement in liver injury in Wilson disease typically requires months to years of treatment. The apparent lack of hepatotoxicity of dimercaprol may be due to the infrequency of its use, the typically short courses of therapy and the prominence of other side effects that limit its more prolonged administration. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Drug Class: Chelating Agents, Wilson Disease Agents Other Drugs in the Subclass, Wilson Disease: Penicillamine, Trientine, Zinc Interactions ...GUINEA PIGS ACUTELY POISONED BY IM INJECTION OF TELLURIUM OXIDE SHOWED SEVERE LESIONS OF KIDNEYS & LIVER & HIGHER MORTALITY RATE WHEN RECEIVING BAL... Dimercaprol forms a toxic complex with iron, cadmium, selenium, or uranium. Iron therapy should not be given concurrently with dimercaprol, and it has been suggested that iron therapy be deferred until at least 24 hours after the last dose of dimercaprol. Dimercaprol is a compound used in the treatment of mercury intoxication, however with low therapeutic efficacy. It is assumed that dimercaprol acts by reactivating target sulfhydryl-containing proteins. In the present investigation we studied the inhibitory effect of mercuric chloride treatment (3 days with 2.3 or 4.6 mg/kg HgCl2, sc) in mice on cerebral. renal and hepatic delta-aminolevulinate dehydratase (ALA-D) activity, and a possible reversal of the effect of mercury by dimercaprol (0.25 mmol/kg, 24 hr after the last mercury injection). Mercuric chloride did not inhibit cerebral delta-aminolevulinate dehydratase at the doses injected. Dimercaprol treatment did not restore the normal enzyme activity of the liver after the 25% inhibition caused by 4.6 mg/kg HgCl2. In the kidney, dimercaprol enhanced the inhibitory effect of 4.6 mg/kg mercuric chloride (from 35% after mercury treatment alone to 65% after mercury plus dimercaprol treatment). Mercury content increased in kidney after exposure to 2.3 or 4.6 mg/kg and the levels attained were higher than in any other organ. Mercury accumulated in liver only after exposure to 4.6 mg/kg HgCl2. and dimercaprol further increased mercury deposition. Dimercaprol treatment also increased the levels of mercury in brain of animals exposed to 4.6 mg/kg HgCl2. The enzymes from all sources presented similar sensitivity to the combined effect of HgCl2 and dimercaprol in vitro. In the absence of preincubation, 0-500 uM dimercaprol potentiated the inhibitory effect of HgCl2 on delta-aminolevulinate dehydratase activity. In the presence of preincubation, and 100 and 250 uM dimercaprol enhanced delta-aminolevulinate dehydratase sensitivity to mercury, whereas 500 uM dimercaprol partially protected the enzyme from mercury inhibition. Dimercaprol (500 uM) inhibited renal and hepatic delta-aminolevulinate dehydratase when preincubated with the enzymes. These data suggested that the dimercaprol-Hg complex may have a more toxic effect on delta-aminolevulinate dehydratase activity than Hg2+. Furthermore, the present data show that dimercaprol did not act by reactivating mercury-inhibited sulfhydryl-containing delta-aminolevulinate dehydratase, and that indeed it may have an inhibitory effect per se depending on the tissue. Dimercaprol decreases insulin effectiveness by reducing disulfide bridges. Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Mouse ip 125 mg/kg (approx) LD50 Rat ip 140 mg/kg (approx) LD50 Rat intramuscular 105 mg/kg (approx) |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Antidotes; Chelating Agents Dimercaprol is the antidote of choice in the treatment of acute arsenic (except arsine), mercury, or gold poisoning resulting from ingestion of salts of these metals or following overdosage of therapeutic agents containing these metals. Dimercaprol administration should be accompanied by appropriate supportive measures and is most effective when administered early in the course of the poisoning. In the treatment of acute poisoning by mercury salts, dimercaprol is most effective if administered within 1-2 hours following ingestion, since extensive mercury-induced renal damage cannot be reversed. Dimercaprol is not effective in the treatment of poisonings resulting from monoalkyl mercury compounds, and the drug is only minimally effective in chronic mercury poisoning. Although dimercaprol is usually of no value in the treatment of hypersensitivity reactions to mercury compounds, mercury-induced acrodynia (pink disease) in infants and children responds to treatment with dimercaprol. Dimercaprol is usually effective in the treatment of chronic poisoning from inorganic or organic arsenicals, but may be of little value if aplastic anemia, hemorrhagic encephalitis, or jaundice has developed. In one patient who experienced protein-loss enteropathy in association with arsenic poisoning, hypoproteinemia and edema improved following dimercaprol therapy. The drug is ineffective in the treatment of poisoning resulting from arsine gas (AsH3). Gold-induced dermatitis and gold-induced thrombocytopenia may improve following dimercaprol therapy. /Use included in US product label/ Dermatologic or ocular manifestations of arsenic poisoning have been effectively treated with topical dimercaprol ointment or oil solution, respectively. /Use NOT included in US product label/ Although dimercaprol chelates lead, other agents (e.g., edetate calcium disodium (calcium EDTA), succimer) generally are preferred for the management of most cases of moderate lead poisoning. However, dimercaprol is useful as an adjunct to edetate calcium disodium and concomitant administration of the drugs is preferred, at least initially, in the management of patients with severe lead poisoning (blood lead concentrations exceeding 70 ug/dL) and/or in those with acute lead encephalopathy (which occurs most often in children). Concomitant administration of dimercaprol and edetate calcium disodium increases the rate of excretion of lead, lowers mortality, and may lower the incidence of brain damage as compared with the use of edetate calcium disodium alone; however, such concomitant therapy does not completely eliminate the risk of permanent severe residual brain damage. Since lead encephalopathy occurs only rarely in adults, experience with the use of the combination in these patients is limited; however, use of dimercaprol and edetate calcium disodium has resulted in prompt relief of symptoms in a few adults with lead encephalopathy. Although concomitant therapy with dimercaprol and edetate calcium disodium also has been recommended in symptomatic patients with blood lead concentrations less than 70 ug/dL, the American Academy of Pediatrics currently states that the toxicity of dimercaprol and the current availability of alternative drugs mandate its use only in the most serious cases of lead poisoning (i.e., blood lead concentrations exceeding 70 ug/dL or when symptoms suggestive of encephalopathy are present). Edetate calcium disodium generally is used alone (i.e., without dimercaprol) in asymptomatic patients with blood lead concentrations of 45-70 ug/dL. ... Dimercaprol is not useful in acute poisonings resulting from alkyl lead compounds (e.g., tetraethyl lead). /Use included in US product label/ For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Dimercaprol (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings Dimercaprol is potentially nephrotoxic. Since the chelate dissociates in acid medium, the urine should be kept alkaline during dimercaprol therapy to protect the kidneys. Dimercaprol should be used with caution and/or the dosage reduced in patients with oliguria. If acute renal failure develops during therapy, the drug should be discontinued or used very cautiously because serum concentrations of dimercaprol may reach toxic levels. Adverse effects of dimercaprol are usually mild and transitory and occur in about one-half of patients who receive an IM dose of 5 mg/kg. If the dose of dimercaprol exceeds 5 mg/kg, most patients will experience vomiting, seizures, and stupor or coma which may begin within 30 minutes after injection and usually subside in 1-6 hours. Prophylactic or therapeutic administration of ephedrine or an antihistamine may prevent or relieve many of the mild adverse effects of dimercaprol. The most frequent adverse effect, a rise in systolic and diastolic blood pressure which is dose related and may be accompanied by tachycardia, may appear 15-30 minutes following the injection and blood pressure usually returns to normal within 2 hours. Frequently pain and occasionally sterile abscesses occur at the injection site, particularly if the drug is not administered deep IM. Other adverse effects that may occur include nausea, vomiting, headache, sweating, and a feeling of constriction (or pain) in the throat, chest, or hands which may be accompanied by anxiety, nervousness or restlessness, and weakness. Muscular aches and pains, muscle spasms, tingling of extremities, and abdominal pain have also been reported. Dimercaprol has a strong odor and imparts an unpleasant mercaptan-like odor to the patient's breath. The drug may also produce a burning sensation of the lips, mouth, throat, eyes, and penis, and pain in the teeth. Blepharal spasm, conjunctivitis, lacrimation, rhinorrhea, and salivation may also occur. When the drug is applied topically, it produces erythema and edema. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Dimercaprol (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Due to its oily nature, dimercaprol is not absorbed orally and its administration requires a deep intra-muscular injection that is extremely painful and allergenic. It was found to mobilize and relocate lead to the brain, increasing its neurotoxic effects. Despite that fact that dimercaprol increases cadmium excretion, there is an associated increase in kidney cadmium concentration. Because of this, dimercaprol must be avoided in patients with cadmium toxicity. |
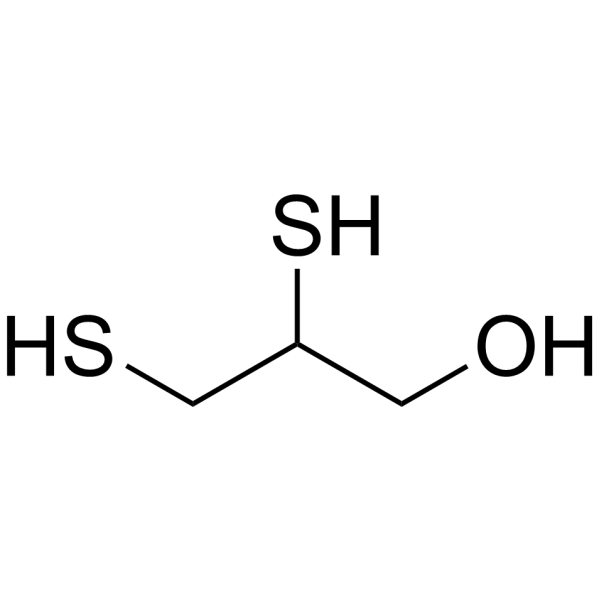
| 分子式 |
C3H8OS2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
124.23
|
| 精确质量 |
124.001
|
| CAS号 |
59-52-9
|
| PubChem CID |
3080
|
| 外观&性状 |
Colorless to light yellow liquid
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
223.4±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
< 25 °C
77 °C |
| 闪点 |
89.1±18.2 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.552
|
| LogP |
0.64
|
| tPSA |
97.83
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
| 重原子数目 |
6
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
32
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
C(C(CS)S)O
|
| InChi Key |
WQABCVAJNWAXTE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C3H8OS2/c4-1-3(6)2-5/h3-6H,1-2H2
|
| 化学名 |
2,3-bis(sulfanyl)propan-1-ol
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
H2O : 41.67 mg/mL (335.43 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 100 mg/mL (804.96 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶。
请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 8.0496 mL | 40.2479 mL | 80.4959 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.6099 mL | 8.0496 mL | 16.0992 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.8050 mL | 4.0248 mL | 8.0496 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。