| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
glycoprotein labeling reagent
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
对于细胞标记、追踪和蛋白质组分析,Ac4ManNAz (10 μM) 具有足够的标记效率,且对生物系统影响很小[1]。 Ac4ManNAz (50 μM) 会降低主要的细胞过程,例如能量产生、细胞浸润和通道活性 [1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
建议10 μM应作为Ac4ManNAz的最佳浓度,用于体内细胞标记和追踪hUCB-EPCs。此外,我们希望我们的方法可以用于了解基于干细胞的体内治疗的有效性和安全性,并帮助确定干细胞在下游实验中的效用。[2]
|
| 酶活实验 |
根据制造商的说明,使用JC-1染料(5′,6,6′-四氯-1,1′,3,3′-四乙基苯并咪唑基碳菁碘化物)测量线粒体膜电位。简言之,将Ac4MAnNAz处理或未处理的细胞与10µg/mL JC-1染料孵育15分钟,并使用20倍物镜拍摄荧光图像。在图像背景校正之后使用图像J测量红色荧光JC-1聚集体和绿色JC-1单体的比率。[1]
使用10μM Ac4ManNAz测量标记蛋白[1] A549细胞在6孔板中用0和10μM Ac4ManNAz生长。在分析之前,用PBS洗涤细胞并收获。在蛋白质分离之前,将细胞混合,使比例逐渐增加到10μM Ac4ManNAz处理的细胞的100%。每个样品在1 mL中总共有5×105个细胞。混合样品在补充有蛋白酶和磷酸酶抑制剂的全细胞裂解缓冲液(10%甘油、0.5 mM EDTA、1 mM DTT、2 mM氟化钠、0.2%Triton X-100,PBS pH 7.4)中裂解。将总蛋白与DBCO-Cy5(20μM,终浓度)在37°C下孵育1小时,并用乙醇沉淀。将沉淀的蛋白质重新悬浮在PBS中,并在588nm下使用荧光微孔板读数器进行分析。所示数据是三个单独实验的平均值,每个实验重复三次。 活性氧(ROS)产生和线粒体膜电位分析[2] 显微荧光成像用于研究不同浓度Ac4ManNAz处理后hUCB EPC中活性氧(ROS)的产生。接种细胞(每孔1×104个),然后处理至0µM,10微米,在37°C下,将20µM和50µM浓度的Ac4ManNAz保持3天。细胞与2,7-二氯二氢荧光素二乙酸酯(DCF-DA)(10 mM)在37°C下孵育30分钟。吸取反应混合物,并在每个孔中用200µl磷酸缓冲盐水(PBS)代替。将平板在室温下在黑暗中放置在振荡器上10分钟。使用倒置荧光显微镜观察细胞内的荧光并捕获图像。根据制造商的说明,使用JC-1染料(5′,6,6′-四氯-1,1′,3,3′-四乙基苯并咪唑基碳菁碘化物)测量线粒体膜电位。简而言之,hUCB-EPC在24孔板中生长,并用不同浓度的Ac4ManNAz处理。用PBS洗涤Ac4MAnNAz处理或未处理的hUCB EPC,并在37°C下用10µg/mL JC-1染料染色15分钟,然后获取荧光图像。 |
| 细胞实验 |
侵袭和伤口愈合
将无血清培养基中的基质胶(100μL;7-8 mg/mL)加入Transwell Corning Costar板 的每个孔中,并在培养罩中干燥过夜。第二天,将无血清培养基中的2.5×104个细胞移液到Matrigel上,并将完全培养基加入底室。孵育后,用结晶紫对跨膜过滤器进行染色,并计数细胞数。为了伤口愈合,使用无菌移液管尖端,通过A549和Az4MAnNAz处理的A549细胞的融合单层,沿着10cm培养皿的直径清除一小块区域。每8小时从伤口/划痕边缘测量并拍摄细胞迁移。[1] 体外细胞标记和成像[2] hUCB EPCs(5×104个细胞/35mm玻璃底皿)用Ac4ManNAz、Ac4GalNAz或添加了Ac4GlcNAz的培养基(各50µM,终浓度)处理72小时 h.用Dulbecco's磷酸盐缓冲盐水(DPBS)洗涤细胞两次,随后在37°C下用DBCO-Cy5(10µM,终浓度)孵育1小时。然后洗涤细胞并用4%多聚甲醛固定15分钟。固定后,用DAPI溶液染色细胞核 细胞活力和伤口愈合试验[2] 为了测量细胞活力,将hUCB-EPCs接种在96孔板(5×103个细胞/孔)中并孵育1天。细胞与不同浓度的Ac4MAnNAz(0至50µM)在37°C下孵育3天。然后向每个孔中加入细胞计数试剂盒-8溶液(10µL)。在37°C下进一步孵育2小时后,使用酶标仪在450nm处测量每个孔的吸光度。为了促进伤口愈合,使用无菌移液管尖端清除直径为10cm的皿中的一小块区域,其中融合了未经处理或Ac4MAnNAz处理的hUCB EPC单层。18小时后,从伤口/划痕边缘测量细胞迁移并拍照。 |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Metabolic labeling techniques are powerful tools for cell labeling, tracking and proteomic analysis. However, at present, the effects of the metabolic labeling agents on cell metabolism and physiology are not known. To address this question, in this study, we analyzed the effects of cells treated with Ac4ManNAz through microarray analysis and analyses of membrane channel activity, individual bio-physiological properties, and glycolytic flux. According to the results, treatment with 50 μM Ac4ManNAz led to the reduction of major cellular functions, including energy generation capacity, cellular infiltration ability and channel activity. Interestingly, 10 μM Ac4ManNAz showed the least effect on cellular systems and had a sufficient labeling efficiency for cell labeling, tracking and proteomic analysis. Based on our results, we suggest 10 μM as the optimum concentration of Ac4ManNAz for in vivo cell labeling and tracking. Additionally, we expect that our approach could be used for cell-based therapy for monitoring the efficacy of molecule delivery and the fate of recipient cells. [1]
Metabolic labeling is one of the most powerful methods to label the live cell for in vitro and in vivo tracking. However, the cellular mechanisms by modified glycosylation due to metabolic agents are not fully understood. Therefore, metabolic labeling has not yet been widely used in EPC tracking and labeling. In this study, cell functional properties such as proliferation, migration and permeability and gene expression patterns of metabolic labeling agent-treated hUCB-EPCs were analyzed to demonstrate cellular effects of metabolic labeling agents. As the results, 10 μM Ac4ManNAz treatment had no effects on cellular function or gene regulations, however, higher concentration of Ac4ManNAz (>20 μM) led to the inhibition of functional properties (proliferation rate, viability and rate of endocytosis) and down-regulation of genes related to cell adhesion, PI3K/AKT, FGF and EGFR signaling pathways. Interestingly, the new blood vessel formation and angiogenic potential of hUCB-EPCs were not affected by Ac4ManNAz concentration. Based on our results, we suggest 10 μM as the optimal concentration of Ac4ManNAz for in vivo hUCB-EPC labeling and tracking. Additionally, we expect that our approach can be used for understanding the efficacy and safety of stem cell-based therapy in vivo. [2] Sialylated glycans are found at elevated levels in many types of cancer and have been implicated in disease progression. However, the specific glycoproteins that contribute to the cancer cell-surface sialylation are not well characterized, specifically in bona fide human disease tissue. Metabolic and bioorthogonal labeling methods have previously enabled the enrichment and identification of sialoglycoproteins from cultured cells and model organisms. Herein, we report the first application of this glycoproteomic platform to human tissues cultured ex vivo. Both normal and cancerous prostate tissues were sliced and cultured in the presence of the azide-functionalized sialic acid biosynthetic precursor Ac4 ManNAz. The compound was metabolized to the azidosialic acid and incorporated into cell surface and secreted sialoglycoproteins. Chemical biotinylation followed by enrichment and mass spectrometry led to the identification of glycoproteins that were found at elevated levels or uniquely in cancerous prostate tissue. This work therefore extends the use of bioorthogonal labeling strategies to problems of clinical relevance. [3] |
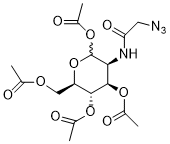
| 分子式 |
C16H22N4O10
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
430.367
|
| 精确质量 |
430.133
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 44.65; H, 5.15; N, 13.02; O, 37.17
|
| CAS号 |
361154-30-5
|
| 相关CAS号 |
361154-30-5;
|
| PubChem CID |
71311757
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to light yellow solid powder
|
| LogP |
1.2
|
| tPSA |
158Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
12
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
12
|
| 重原子数目 |
30
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
736
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
4
|
| SMILES |
CC(=O)OC[C@@H]1[C@H]([C@@H]([C@@H](C(O1)OC(=O)C)NC(=O)CN=[N+]=[N-])OC(=O)C)OC(=O)C
|
| InChi Key |
HGMISDAXLUIXKM-LIADDWGISA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C16H22N4O10/c1-7(21)26-6-11-14(27-8(2)22)15(28-9(3)23)13(16(30-11)29-10(4)24)19-12(25)5-18-20-17/h11,13-16H,5-6H2,1-4H3,(H,19,25)/t11-,13+,14-,15-,16?/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
Peracetylated N-azidoacetyl-d-mannosamine
|
| 别名 |
Ac4ManNAz; Ac 4ManNAz; Ac-4ManNAz; Ac4Man-NAz; Ac4ManNAz; 361154-30-5; 1,3,4,6-Tetra-O-acetyl-N-azidoacetylmannosamine; (3S,4R,5S,6R)-6-(acetoxymethyl)-3-(2-azidoacetamido)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2,4,5-triyl triacetate; MFCD26961126; [(2R,3S,4R,5S)-3,4,6-triacetyloxy-5-[(2-azidoacetyl)amino]oxan-2-yl]methyl acetate; [(2R,3S,4R,5S)-3,4,6-TRIS(ACETYLOXY)-5-(2-AZIDOACETAMIDO)OXAN-2-YL]METHYL ACETATE; Ac4ManAz; Ac4-Man-NAz; Ac4-ManNAz; N-Azidoacetylmannosamine-tetraacylated
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.03.00
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~232.36 mM)
H2O: ~2.5 mg/mL (~5.81 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.81 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.81 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.81 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.50 mg/mL (5.80 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + + 45% Saline ≥ 2.50 mg/mL (5.80 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in saline) ≥ 2.50 mg/mL (5.80 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn oil 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3236 mL | 11.6179 mL | 23.2358 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4647 mL | 2.3236 mL | 4.6472 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2324 mL | 1.1618 mL | 2.3236 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
|
|
|