| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Well absorbed from the GI tract following oral administration. Well absorbed from gastrointestinal tract. Well distributed throughout body fluids. Elimination: Renal- Unchanged, 36 to 65%; as acetamide, 9 to 14%. Respiratory - As carbon dioxide, 20 to 40%. In rodents, about 55% of an intraperitoneal dose is excreted in urine as unchanged drug, 15% as acetamide, and 10% as acetate within 24 hours; approximately 7% of the dose is excreted by the lungs as carbon dioxide and less than 1% is excreted in feces within 24 hours. In mice, highest concentrations of the drug occur in the liver and kidney, while the lowest concentrations occur in the brain. Metabolism / Metabolites 35-65% of oral dose excreted unchanged in urine (which provides the drug's therapeutic effect). ...is metabolized to acetamide. Biological Half-Life 5-10 hours in patients with normal renal function ...increases with increasing dose and reportedly ranges from about 3.5-10 hours in patients with normal renal function. |
|---|---|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
No known binding Interactions Concurrent use of alcoholic beverages with acetohydroxamic acid has resulted in a nonpruritic, reddish, macular skin rash about 30 to 45 minutes after ingestion. The rash may be associated with a general feeling of warmth and tingling, and usually disappears spontaneously in 30 to 60 minutes. Acetohydroxamic acid chelates iron and possibly other heavy metals with concurrent oral administration; this may result in reduced intestinal absorption of both; if iron therapy is indicated, parenteral administration of iron is recommended. In vitro studies indicate that acetohydroxamic acid and methenamine have a synergistic effect in inhibiting increases in pH caused by urease-producing Proteus spp. and that acetohydroxamic acid potentiates the antibacterial effect of methenamine against these bacteria... Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Mouse ip 2.5 g/kg LD50 Mouse oral 5 g/kg LD50 Rat oral 4.8 g/kg |
| 其他信息 |
Acetohydroxamic Acid can cause developmental toxicity according to state or federal government labeling requirements.
Acetohydroxamic acid is a member of the class of acetohydroxamic acids that is acetamide in which one of the amino hydrogens has been replaced by a hydroxy group. It has a role as an EC 3.5.1.5 (urease) inhibitor and an algal metabolite. It is functionally related to an acetamide. It is a tautomer of a N-hydroxyacetimidic acid. Acetohydroxamic Acid, a synthetic drug derived from hydroxylamine and ethyl acetate, is similar in structure to urea. In the urine, it acts as an antagonist of the bacterial enzyme urease. Acetohydroxamic Acid has no direct antimicrobial action and does not acidify urine directly. It is used, in addition to antibiotics or medical procedures, to treat chronic urea-splitting urinary infections. Acetohydroxamic acid is an Urease Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of acetohydroxamic acid is as an Urease Inhibitor. Acetohydroxamic acid has been reported in Arabidopsis thaliana and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with data available. Drug Indication Used, in addition to antibiotics or medical procedures, to treat chronic urea-splitting urinary infections. Mechanism of Action Acetohydroxamic Acid reversibly inhibits the bacterial enzyme urease. This inhibits the hydrolysis of urea and production of ammonia in urine infected with urea-splitting organisms, leading to a decrease in pH and ammonia levels. As antimicrobial agents are more effective in such conditions, the effectiveness of these agents is amplified, resulting in a higher cure rate. Inhibits the hydrolysis of urea and production of ammonia in urine infected with urea-splitting bacteria, by reversible inhibition of the bacterial enzyme urease, and by the chelation of nickel, an essential component of urease enzymes. Such enzyme inhibition results in reduction of both urine alkalinity and ammonia concentration. The effectiveness of antibacterial medication is then enhanced and the formation of urinary calculi reduced. Therapeutic Uses Enzyme Inhibitors Acetohydroxamic acid is indicated in the prophylaxis of struvite calculi formation that is promoted by urease-producing bacteria such as Proteus. Its use may enhance effectiveness of urinary antibacterials, especially following surgical removal of existing stones. Use of acetohydroxamic acid also improves the possibility of reducing the frequency and rate of new stone formation. /Included in US product labeling/ Acetohydroxamic acid is indicated as an adjunct in the treatment of chronic, urea-splitting urinary tract infections caused by urease-producing bacteria. Its inhibition of urease activity decreases the urinary ammonia and alkalinity produced from the enzyme hydrolysis of urea. /Included in US product labeling/ Drug Warnings Acetohydroxamic acid is not indicated for dissolution of existing calculi, replacement of indicated surgical treatment, urinary tract infections controllable by culture-specific oral antibacterials, or urinary tract infections caused by nonurease producing organisms. Use of acetohydroxamic acid is contraindicated during pregnancy since studies in animals have shown it to cause leg deformities at doses of 750 mg/kg of body weight and above. At doses of 1500 mg/kg, exencephaly and encephalocele occurred. Also, cardiac, coccygeal, and abdominal-wall anomalies developed in pups of beagle dogs given 25 mg/kg a day during pregnancy. It is not known if acetohydroxamic acid is distributed into breast milk. Although problems in humans have not been documented, its use is not recommended in breast-feeding mothers because of the potential for serious adverse effects in the nursing infant. Headache, appearing during the first 48 hours of treatment, reportedly occurs in approximately 30% of patients receiving acetohydroxamic acid; however, several clinicians reported that mild, transient headache occurred in 70-75% of patients during initiation of therapy. Headache is generally mild, responsive to oral salicylate analgesics, and usually disappears spontaneously. Headache has not been associated with vertigo, tinnitus, or visual or auditory disturbances. Malaise occurs in about 20-25% of patients receiving the drug. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for ACETOHYDROXAMIC ACID (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Acetohydroxamic Acid, a synthetic drug derived from hydroxylamine and ethyl acetate, is similar in structure to urea. In the urine, it acts as an antagonist of the bacterial enzyme urease. Acetohydroxamic Acid has no direct antimicrobial action and does not acidify urine directly. |
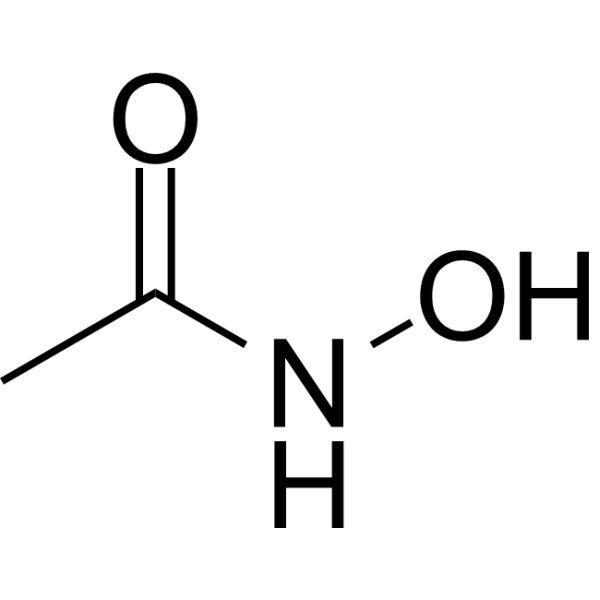
| 分子式 |
C2H5NO2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
75.0666
|
| 精确质量 |
75.032
|
| CAS号 |
546-88-3
|
| PubChem CID |
1990
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
231.4ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
88-90 °C(lit.)
|
| 折射率 |
1.421
|
| LogP |
-1.59
|
| tPSA |
49.33
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
2
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
0
|
| 重原子数目 |
5
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
42.9
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O([H])N([H])C(C([H])([H])[H])=O
|
| InChi Key |
RRUDCFGSUDOHDG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C2H5NO2/c1-2(4)3-5/h5H,1H3,(H,3,4)
|
| 化学名 |
N-hydroxyacetamide
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~250 mg/mL (~3330.23 mM)
H2O : ~100 mg/mL (~1332.09 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (27.71 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (27.71 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (27.71 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 100 mg/mL (1332.09 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 13.3209 mL | 66.6045 mL | 133.2090 mL | |
| 5 mM | 2.6642 mL | 13.3209 mL | 26.6418 mL | |
| 10 mM | 1.3321 mL | 6.6605 mL | 13.3209 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT03181828 | TERMINATEDWITH RESULTS | Drug: Acetohydroxamic Acid Oral Tablet Other: No treatment |
Urea Cycle Disorder | Nicholas Ah Mew | 2017-03-24 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |