| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Natural product; p50; NF-κB
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:发现穿心莲内酯以浓度依赖性方式抑制诱导型一氧化氮合酶的表达。在穿心莲内酯治疗组中,观察到 Akt、c-Jun N 末端激酶和 p65 磷酸化减少。穿心莲内酯还引起 Bcl-2/NF-κb 表达减少和 Cleaved-Caspase3/Bax 蛋白表达剂量依赖性增加。激酶测定:进行体外破骨细胞生成测定以检查穿心莲内酯对破骨细胞分化的影响。制备骨髓巨噬细胞(BMM)。简而言之,将从 6 周龄 C57/BL6 小鼠股骨和胫骨中提取的细胞在 T-75 cm2 烧瓶中的完全细胞培养基和 30 ng/mL M-CSF 中孵育以进行增殖。更换培养基时,洗涤细胞以去除残留的基质细胞。达到90%汇合后,用PBS洗涤细胞3次,并胰蛋白酶消化30分钟以收获BMM。粘附在培养皿底部的细胞被归类为 BMM;将这些 BMM 以每孔 8×103 个细胞的密度一式三份铺在 96 孔板中,并在含有 5% CO2 的加湿培养箱中于 37°C 孵育 24 小时。然后用不同浓度的穿心莲内酯(0、2.5、5 或 10 μM)加 M-CSF (30 ng/mL) 和 RANKL (50 ng/mL) 处理细胞。 5 天后,固定细胞并对其抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶 (TRAP) 活性进行染色。具有超过 5 个细胞核的 TRAP 阳性多核细胞被计为破骨细胞。 细胞测定:用 CCK-8 测定穿心莲内酯对细胞增殖的影响。 BMM 以每孔 3×103 个细胞的密度接种在 96 孔板中,一式三份。 24 小时后,用浓度逐渐增加的穿心莲内酯(0、2.5、5、10 或 20 μM)处理细胞 2 天。接下来,将 10 μL CCK-8 添加到每个孔中,然后将板在 37°C 下再孵育 2 小时。然后使用 ELX800 吸光度酶标仪在 450 nm 波长(650 nm 参考)下测量光密度 (OD)。计算细胞活力
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
穿心莲内酯(5 或 30 毫克/千克)治疗可减少 LPS 引起的骨质流失程度。此外,与 LPS 治疗相比,穿心莲内酯略微增加了 BMD 和皮质厚度。组织学检查证实了穿心莲内酯对 LPS 引起的骨质流失的保护作用。 LPS 注射会导致炎症性骨质侵蚀和 TRAP 阳性破骨细胞数量增加。在一项保肝研究中,连续 5 天给大鼠灌胃穿心莲内酯。结果表明,穿心莲内酯可以上调心脏、肝脏和肾脏中谷氨酸半胱氨酸连接酶催化和修饰亚基、血红素加氧酶-1、超氧化物歧化酶-1、谷胱甘肽S-转移酶蛋白和mRNA的表达。
|
| 酶活实验 |
进行体外破骨细胞生成试验以检查穿心莲内酯对破骨细胞分化的影响。 BMM 细胞或骨髓巨噬细胞被创建。在装有完整细胞培养基和 30 ng/mL M-CSF 的 T-75 cm2 烧瓶中,孵育取自 6 周龄 C57/BL6 小鼠股骨和胫骨的细胞进行增殖。当更换培养基时洗涤细胞以去除可能仍然存在的任何基质细胞。将细胞用 PBS 洗涤 3 次,然后用胰蛋白酶消化 30 分钟,以在细胞达到 90% 汇合后收获 BMM。 BMM 是粘在培养皿底部的细胞。 BMM 以每孔 8×103 个细胞的密度一式三份接种在 96 孔板中,并在含有 5% CO2 的加湿培养箱中于 37°C 下孵育 24 小时。然后,将不同浓度的穿心莲内酯(0、2.5、5 或 10 μM)与 M-CSF (30 ng/mL) 和 RANKL (50 ng/mL) 一起添加到细胞中。五天后对细胞进行固定和染色,以检查抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶 (TRAP) 活性。破骨细胞是 TRAP 阳性的多核细胞,具有 5 个或更多细胞核[1]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
使用 CCK-8 测定穿心莲内酯对细胞增殖的影响。 BMM 以每孔 3×103 个细胞的密度接种在 96 孔板中,一式三份。 24 小时后,将细胞暴露于逐渐增加剂量的穿心莲内酯(0、2.5、5、10 或 20 μM)两天。向每孔添加 10 μL CCK-8 后,将板在 37°C 下再孵育 2 小时。然后使用 ELX800 吸光度酶标仪在 450 nm 波长(650 nm 参考)下测定光密度 (OD)。进行计算以确定细胞活力[1]。
|
| 动物实验 |
Mice: Four groups of seven C57BL/6 mice each are created using 8-week-old mice. One day prior to the injection of LPS (5 g/g body weight), mice are administered i.p. injections of andrographolide (5 or 30 mg/kg body weight) or PBS as a control. Over the course of eight days, either andrographolide or PBS is intraperitoneally injected. On days one and four, LPS is administered intraperitoneally. All mice are euthanized 8 days after receiving the initial LPS injection, and their left femurs are all scanned using a high-resolution micro-CT with a 9-m resolution.
|
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Andrographolide is a labdane diterpenoid isolated from the leaves and roots of Andrographis paniculata that exhibits anti-HIV, anti-inflammatory and antineoplastic properties. It has a role as a metabolite, an anti-inflammatory drug, an anti-HIV agent and an antineoplastic agent. It is a gamma-lactone, a primary alcohol, a secondary alcohol, a labdane diterpenoid and a carbobicyclic compound.
Andrographolide (HMPL-004) is a botanical product extracted from a herb that occurs naturally in China. The herb has an extensive history of use in TCM for the treatment of upper respiratory tract infections and other inflammatory and infectious diseases. Andrographolide has been reported in Andrographis paniculata, Cymbopogon schoenanthus, and Ginkgo biloba with data available. Andrographolide is a labdane diterpenoid that is produced by the Andrographis paniculata plant, which has a broad range of therapeutic applications including anti-inflammatory and anti-platelet aggregation activities and potential antineoplastic properties. Since andrographolide has multiple therapeutic activities there are several proposed mechanisms of action for this agent. The anti-inflammatory effects of this agent appear to be related to the inhibition of nitric oxide (NO) production by macrophages. This agent may activate the NO/cyclic GMP pathway and inhibit both the phospholipase C gamma 2 (PLC gamma2)/protein kinase C (PKC) and PI3K/AKT-MAPK signaling pathways in activated platelets to inhibit platelet aggregation. In activated platelets, these three signaling pathways are downstream of integrin activation mediated by collagen binding and influence the association of fibrinogen with its receptors. Additionally, andrographolide may exert its anti-cancer activity through the induction of cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 phase and the stimulation of lymphocyte proliferation and activation. These processes could result in decreased proliferation of and increased immunocytotoxicity against tumor cells. Drug Indication Investigated for use/treatment in ulcerative colitis. Mechanism of Action HMPL-004 acts on multiple cellular targets in the inflammatory signal transduction pathways resulting in suppressed inflammation cytokine expression including TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6. HMPL-004 was demonstrated to inhibit TNF-α and IL-1β production in cell-based assays. HMPL-004 is also able to inhibit NF-kB activation. NF-kB is a family of transcriptional factors that regulate a wide spectrum of genes critically involved in host defence and inflammation. The mechanism of action of HMPL-004 was further supported in laboratory IBD animal models. Treatment of IBD rats with HMPL-004 caused a significant drop in plasma cytokine concentrations, including TNF-α and IL-1β. Background and purpose: Osteoclasts play a pivotal role in diseases such as osteoporosis, rheumatoid arthritis and tumour bone metastasis. Thus, searching for natural compounds that may suppress osteoclast formation and/or function is promising for the treatment of osteoclast-related diseases. Here, we examined changes in osteoclastogenesis and LPS-induced osteolysis in response to andrographolide (AP), a diterpenoid lactone isolated from the traditional Chinese and Indian medicinal plant Andrographis paniculata. Experimental approach: Effects of AP on osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption were measured in vitro. Western blots and RT-PCR techniques were used to examine the underlying molecular mechanisms. The bone protective activity of AP in vivo was assessed in a mouse model of osteolysis. Key results: AP concentration-dependently suppressed RANKL-mediated osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption in vitro and reduced the expression of osteoclast-specific markers, including tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase, calcitonin receptors and cathepsin K. Further molecular analysis revealed that AP impaired RANKL-induced NF-κB signalling by inhibiting the phosphorylation of TGF-β-activated kinase 1, suppressing the phosphorylation and degradation of IκBα, and subsequently preventing the nuclear translocation of the NF-κB p65 subunit. AP also inhibited the ERK/MAPK signalling pathway without affecting p38 or JNK signalling. Conclusions and implications: AP suppressed RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis through attenuating NF-κB and ERK/MAPK signalling pathways in vitro, thus preventing bone loss in vivo. These data indicated that AP is a promising natural compound for the treatment of osteoclast-related bone diseases. [1] Andrographolide, a diterpenoid, is known for its anti-inflammatory effects. It can be isolated from various plants of the genus Andrographis, commonly known as 'creat'. This purified compound has been tested for its anti-inflammatory effects in various stressful conditions, such as ischemia, pyrogenesis, arthritis, hepatic or neural toxicity, carcinoma, and oxidative stress, Apart from its anti-inflammatory effects, andrographolide also exhibits immunomodulatory effects by effectively enhancing cytotoxic T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, phagocytosis, and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC). All these properties of andrographolide form the foundation for the use of this miraculous compound to restrain virus replication and virus-induced pathogenesis. The present article covers antiviral properties of andrographolide in variety of viral infections, with the hope of developing of a new highly potent antiviral drug with multiple effects. [2] |
| 分子式 |
C20H30O5
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
350.45
|
|
| 精确质量 |
350.209
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 68.54; H, 8.63; O, 22.83
|
|
| CAS号 |
5508-58-7
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
5318517
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
557.3±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
229-232ºC
|
|
| 闪点 |
195.5±23.6 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±3.4 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.568
|
|
| LogP |
1.62
|
|
| tPSA |
86.99
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
25
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
597
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
6
|
|
| SMILES |
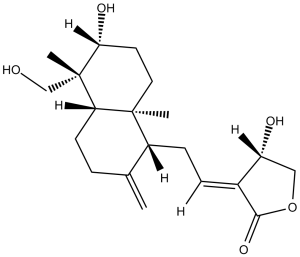
O([H])[C@]1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[C@@]2(C([H])([H])[H])[C@]([H])(C([H])([H])/C(/[H])=C3/C(=O)OC([H])([H])[C@@]/3([H])O[H])C(=C([H])[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[C@]2([H])[C@]1(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])O[H]
|
|
| InChi Key |
BOJKULTULYSRAS-OTESTREVSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C20H30O5/c1-12-4-7-16-19(2,9-8-17(23)20(16,3)11-21)14(12)6-5-13-15(22)10-25-18(13)24/h5,14-17,21-23H,1,4,6-11H2,2-3H3/b13-5+/t14-,15-,16+,17-,19+,20+/m1/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
(3E,4S)-3-[2-[(1R,4aS,5R,6R,8aS)-6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylidene-3,4,4a,6,7,8-hexahydro-1H-naphthalen-1-yl]ethylidene]-4-hydroxyoxolan-2-one
|
|
| 别名 |
Andrographolide
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.13 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.13 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.13 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8535 mL | 14.2674 mL | 28.5347 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5707 mL | 2.8535 mL | 5.7069 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2853 mL | 1.4267 mL | 2.8535 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT04833946 | Recruiting | Other: Andrographis paniculata [150 mg] Other: Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) |
Knee Osteoarthritis (Knee OA) |
Vedic Lifesciences Pvt. Ltd. | March 13, 2021 | Not Applicable |
| NCT03455049 | Completed | Other: Andrographis Paniculata Ext |
Increased Insulin | Indonesia University | October 17, 2017 | Not Applicable |
| NCT04196075 | Completed | Drug: Andrographis Paniculata | Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Esophagus |
Chinese University of Hong Kong |
March 1, 2018 | Phase 3 |
| NCT01993472 | Terminated | Drug: Andrographolides Drug: Capecitabine |
Colorectal Neoplasms | Gu Yanhong | November 2013 | Phase 2 |
|
|---|
|
|