| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
HCV NS3 protease(IC50≈0.2 nM-3.5 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:Asunaprevir (ASV) 抑制基因型 1a(H77 株)和基因型 1b(J4L6S 株)的 NS3 蛋白水解活性,IC50 分别为 0.7 和 0.3 nM。 ASV 针对编码代表基因型 1a、1b 和 4a 的 NS3 蛋白酶结构域的复制子的 EC50 范围为 1.2 至 4.0 nM。使用浓度为 EC50 值的 10 倍和 30 倍(最终浓度分别为 50 或 150 nM)的 asunaprevir 将复制子细胞维持在选择压力下。对于基因型 1b 抗性选择,复制子细胞维持在 EC50 值 10 或 30 倍(最终浓度分别为 30 或 90 nM)的 asunaprevir 存在下。 Asunaprevir 以单剂量或多剂量 200 至 600 mg 每日两次给药,通常具有良好的耐受性,可在慢性感染基因型 1 HCV 的受试者中实现 HCV RNA 水平的快速大幅降低。激酶测定:Asunaprevir (ASV) 抑制基因型 1a(H77 菌株)和基因型 1b(J4L6S 菌株)的 NS3 蛋白水解活性,IC50 分别为 0.7 和 0.3 nM。 ASV 针对编码代表基因型 1a、1b 和 4a 的 NS3 蛋白酶结构域的复制子的 EC50 范围为 1.2 至 4.0 nM。细胞测定:细胞毒性通过将细胞(3,000 至 10,000 个细胞/孔)与连续稀释的测试化合物或 DMSO 一起孵育 5 天(MT-2 细胞)或 4 天(所有其他细胞类型)来确定。使用针对 MT-2 的 MTS 测定或针对 HEK-293、HuH-7、HepG2 和 MRC5 细胞的 Cell-Titer Blue 试剂测定来定量细胞活力,并计算 50% 细胞毒性浓度 (CC50)。对于 HCV 和 BVDV 复制子测定,CC50 是从随后用于确定 EC50 的相同孔中确定的。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
几种动物体内的血浆和组织暴露表明,Asunaprevir/ASV显示出嗜肝倾向(不同物种的肝脏与血浆比率为40至359倍)。给药24小时后,所有受试物种的肝脏暴露量均≥HCV基因型-1复制子观察到的抑制剂EC(50)的110倍。基于这些病毒学和暴露特性,ASV有望与其他抗HCV药物联合治疗HCV感染患者。[4]
Asunaprevir(ASV,3-15 mg/kg,口服)在多种动物中表现出亲肝倾向(不同物种的肝脏与血浆比率范围为 40 至 359 倍)。给药后 24 小时,所有测试物种的肝脏暴露量均高于 HCV 基因型 1 复制子观察到的抑制剂 EC50 的 110 倍以上。 |
| 酶活实验 |
萤光素酶测定[1]
为了监测由ISRE引导的IFN信号传导,将表达萤火虫荧光素酶的质粒pISRE-luc(500 ng/孔)和表达肾肾荧光素酶作为内部对照的pRL-TK(50 ng/孔)共转染到Huh 7.5.1细胞中(1×105)。为了监测IFN-β启动子信号传导,使用表达萤火虫荧光素酶的pGL-4 IFNβ-Luc(pIFNβ/FLuc)(500 ng/孔)和表达肾荧光素酶(Renilla荧光素酶)的pRL-TK(50 ng/孔,Chang等人,20062009)作为内部对照。按照制造商的方案,用Lipofectamine 2000转染试剂转染Huh 7.5.1细胞。简而言之,用含有质粒DNA的DNA沉淀转染在12孔板中培养的细胞(数量如所示,并已由载体对照调整为与实验组样品相同)。转染后5小时,用培养基补充细胞,然后孵育不同时间点。通过Promega双荧光素酶报告检测系统评估相对荧光素酶活性。 基于酶的选择性测定。[2] 为了评估体外选择性,对化合物进行了GBV-B NS3/4A蛋白酶、人中性粒细胞弹性蛋白酶、猪胰腺弹性酶、人α-胰凝乳蛋白酶、人组织蛋白酶A和人肝组织蛋白酶B的复筛。化合物在10%二甲亚砜(DMSO)的测定缓冲液中稀释。如上所述,GBV-B NS3/4A蛋白酶(0.3 nM)在基于FRET的测定中取代了HCV-NS3/4A蛋白酶。所有其他测定均在96孔板中用1%DMSO进行,并在Spectramax平板分光光度计上测量405nm下的连续底物水解。 人中性粒细胞弹性蛋白酶、猪胰腺弹性蛋白酶和人胰腺α-胰凝乳蛋白酶反应混合物分别含有50 mM Tris-HCl(pH 8.0)、50 mM NaCl、0.1 mM EDTA、0.05%吐温20和20 nM人弹性蛋白酶,25 nM猪弹性蛋白酶或1 nM胰凝乳蛋白酶。通过加入底物(弹性蛋白酶、5μM琥珀酰-APV-氨基-4-甲基香豆素(AMC))引发反应;胰凝乳蛋白酶、5μM LLVY-AMC)并在360nm的激发波长(Ex)和480nm的发射波长(Em)下进行荧光监测。组织蛋白酶A测定按照制造商的说明进行,以(7-甲氧基香豆素-4-基)乙酰基RPPGFSAFK(二硝基苯基)-OH为底物;在565/580nm的Ex/Em下监测反应。组织蛋白酶B测定混合物含有50 mM乙酸钠(NaOAc)(pH 5.5)、1 mM三(2-羧乙基)膦、5 nM组织蛋白酶B和2μM Z-FR-AMC作为底物,在360/460 nM的Ex/Em下监测反应。因子XA测定混合物含有100 mM NaPO4(pH 7.5)、0.5%聚乙二醇(PEG)8000、200 mM NaCl、1 nM人因子XA和400μM S-2222作为底物。因子XIA测定混合物含有50 mM HEPES(pH 7.5)、0.1%PEG-8000、5 mM KCl、145 mM NaCl、0.14 nM人因子XIA和250μM S-2366作为底物。因子VIIA测定混合物含有50 mM HEPES(pH 7.5)、150 mM NaCl、5 mM CaCl2、0.1%PEG-8000、1.8 nM因子VIIA 和1 mM S-2288 作为底物。激肽释放酶测定混合物含有50 mM Tris(pH 7.5)、100 mM NaCl、0.5%PEG-8000、0.2 nM激肽释放肽(酶研究实验室)和400μM S-2302 作为底物。凝血酶测定混合物含有100 mM磷酸钠(pH 7.5)、200 mM NaCl、0.5%PEG-8000、0.2 nM凝血酶和200μM S-2366 作为底物。胰蛋白酶测定混合物含有100 mM NaPO4(pH 7.5)、200 mM NaCl、0.5%PEG-8000、0.332 nM胰蛋白酶和200μM S-2222作为底物。 Asunaprevir (ASV) 抑制基因型 1a(H77 菌株)和基因型 1b(J4L6S 菌株)的 NS3 蛋白水解活性,IC50 分别为 0.7 和 0.3 nM。 ASV 针对编码代表基因型 1a、1b 和 4a 的 NS3 蛋白酶结构域的复制子的 EC50 范围为 1.2 至 4.0 nM。 |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞培养病毒学检测。[2]
对于含有RLuc报告子的HCV复制子,如前所述测定化合物抗病毒活性(50%有效浓度[EC50])。对于缺乏报告基因的复制子,如前所述,使用FRET标记的肽底物(10μM)测量活性。如前所述进行BVDV测定(36),不同之处在于孵育保持4天。 通过与一系列稀释的化合物孵育来确定HIV、HRV2和HCoV的抗病毒敏感性。对于表达RLuc的重组HIVs,在感染后5天使用双荧光素酶试剂盒通过荧光素酶测定评估抗病毒活性。将稀释的被动裂解溶液与萤光素酶测定底物和Stop&Glo底物(2:1:1的比例)预混合。向每个抽吸的样品孔中加入40μl混合物,并立即在Wallac TriLux上测量萤光素酶活性。为了测定抗HRV2和HCoV OC43的活性,将化合物和病毒(感染多样性,0.1)与细胞一起孵育96小时,并将细胞保护用作病毒产生的衡量标准。对于细胞保护试验,向每个孔中加入17μl cell Titer Blue试剂。然后将板在室温下孵育2小时,然后使用Spectramax Gemini EM仪器测量荧光,将Ex/EM设置为530/580nm。 细胞毒性是通过用连续稀释的测试化合物或DMSO孵育细胞(3000至10000个细胞/孔)5天(MT-2细胞)或4天(所有其他细胞类型)来确定的。使用MT-2的MTS测定法或HEK-293、HuH-7、HepG2和MRC5细胞的Cell Titer Blue试剂测定法定量细胞存活率,并计算50%的细胞毒性浓度(CC50s)。对于HCV和BVDV复制子检测,CC50是从后来用于确定EC50的相同孔中确定的。 |
| 动物实验 |
In vivo exposure studies.[2]
The amorphous free acid form of Asunaprevir (ASV) was used in all studies. Plasma and tissue exposures were characterized in male FVB mice (20 to 25 g), male Sprague-Dawley rats (300 to 350 g; Hilltop Lab Animals, Scottsdale, PA) with indwelling cannulas implanted in the jugular vein or common bile duct, male beagles (ca. 9 to 12 kg) bearing vascular access ports, and male cynomolgus monkeys bearing vascular access ports (3.1 to 5.7 kg). All animal procedures were performed under protocols approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the test facility. In all studies, coagulated blood samples taken after dosing were centrifuged at 4°C (1,500 to 2,000 × g); plasma samples were stored at −20°C until analyzed. Tissue samples were rinsed, blotted dry, weighed, and stored frozen. ASV in plasma and tissue samples was analyzed by LC-MS/MS. The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) of ASV was 1 nM in plasma samples from all species, 5 nM in mouse and rat tissues, and 50 nM in dog and monkey tissues.[2] Mice (n = 9 per group; overnight fast) received ASV by oral gavage (5 mg/kg; vehicle of PEG-400–ethanol, 9:1). Blood samples (∼0.2 ml) were obtained by retro-orbital bleeding at 0.25, 0.5, 1, 3, 6, 8, and 24 h after dosing. Within each group, three animals were bled at 0.25, 3, and 24 h, three at 0.5 and 6 h, and three at 1 and 8 h, resulting in a composite pharmacokinetic profile. Livers and brains were also removed from mice at the terminal sampling points.[2] Rats (n = 3 per group; overnight fast) received ASV (amorphous free acid) by oral gavage (3, 5, 10, and 15 mg/kg) in PEG-400–ethanol (9:1). Serial blood samples (∼0.3 ml) were obtained from the jugular vein predosing (0 h) and at 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 24, and 48 h postdosing. To assess tissue exposure, rats were orally administered ASV (5 or 15 mg/kg, same vehicle as above), and blood, liver, and heart samples from two rats/group were obtained at 0.17, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 24, 48, and 72 h after dosing.[2] Dogs (n = 3; overnight fast) were administered ASV by oral gavage at 3 or 6 mg/kg (3 mg/ml in 85% PEG-400–15% water). Serial blood samples were collected from vascular access ports at 0.08, 0.167, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 24, and 48 h postdose. To assess tissue exposure, six male dogs (8.4 to 12.5 kg) were orally administered ASV (6 mg/kg), and blood, liver, and spleen samples were obtained from one dog each at 1, 3, 7, 24, 48, and 72 h postdosing.[2] Monkeys (n = 3 males; overnight fast) were administered ASV by oral gavage at 3 mg/kg (3 mg/ml in 85% PEG-400–15% water). Blood samples were collected at 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 24 h postdose. To assess tissue exposure, three male and six female cynomolgus monkeys (2 to 5 kg) were orally administered ASV (10 mg/kg), and blood, liver, and spleen samples were obtained from one male each at 2, 8, and 24 h postdosing and from one female each at 0.5, 2, 4, 8, 24, and 30 h postdosing.[2] Asunaprevir (ASV) is administered orally to mice (n = 9 per group; overnight fast; vehicle: PEG-400-ethanol, 9:1). Retro-orbital bleeding is used to obtain blood samples (-0.2 mL) at 0.25, 0.5, 1, 3, 6, 8, and 24 hours following dosing. To create a composite pharmacokinetic profile, three animals in each group are bled at 0.25, 3, and 24 hours, three at 0.5 and 6 hours, and three at 1 and 8 hours. At the terminal sampling points, mice are also deprived of their livers and brains.Amorphous free acid (ASV) is given orally to rats (n=3 per group; overnight fast) at doses of 3, 5, 10, and 15 mg/kg in PEG-400-ethanol (9:1). The jugular vein is used to draw serial blood samples (-0.3 mL) prior to dosing (0 h) and at 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 24, and 48 h after dosing. Rats are given ASV (5 or 15 mg/kg, same vehicle as above) orally in order to measure tissue exposure. Samples of the rats' liver, heart, and blood are taken at intervals of 0.17, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 24, 48, and 72 hours following dosing. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
In preclinical studies, asunaprevir showed a high liver-to-plasma AUC ratio. It is rapidly absorbed within 30 minutes of administration. Clinical pharmacokinetic studies showed a Tmax of 2-4 hours. The pharmacokinetic profile act in a dose-proportional manner and in a dose of 100 mg the steady-state Cmax and AUC was 572 ng/ml and 1887 ng x h/mL. The absolute bioavailability is reported to be 9.3%. The absorption of asunaprevir is increased with food. Asunaprevir is primarily eliminated via the feces. From the administered dose, 84% is excreted by feces mainly as metabolites and less than 1% of the dose is recovered as metabolites in the urine. The proportion of unchanged asunaprevir recovered in feces represents only 7.5% of the dose. The registered volume of distribution at steady state is 194 L. Clinical pharmacokinetic studies showed a mean oral clearance of 302-491 L/h. Metabolism / Metabolites Asunaprevir is metabolized by the liver. The metabolism is mainly marked by oxidative reactions mediated by the activity of CYP3A. Asunaprevir seems to weakly induce its own metabolism and from the circulating dose, just about 5% of the administered dose is formed by metabolites. The metabolites of asunaprevir are formed after mono- and bis-oxidation, N-dealkylation, loss of isoquinoline ring and O-demethylation. All the metabolic reactions form about 15 metabolites and studies have reported that the main metabolic activity is performed by CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 with some minor activity from CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19 and CYP2D6. Biological Half-Life Clinical pharmacokinetic studies showed a mean terminal half-life of 15-20 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
Protein binding of asunaprevir is very high and it can reach more than 99% of the administered dose independently of the dose. _In vitro_ studies with human Caco-2 cells indicated that asunaprevir is a substrate of P-gp, OATP1B1 and OATP2B1. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Asunaprevir is an oligopeptide.
Asunaprevir, also named BMS-650032, is a potent hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS3 protease inhibitor. It has been shown to have a very high efficacy in dual-combination regimens with daclatasvir in patients chronically infected with HCV genotype 1b. It was developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb Canada and approved by Health Canada on April 22, 2016. The commercialization of asunaprevir was cancelled one year later on October 16, 2017. Asunaprevir is an orally bioavailable inhibitor of the nonstructural protein 3 (NS3), with potential activity against hepatitis C virus (HCV). Upon administration, asunaprevir binds to the active center of the HCV NS3 and prevents NS3 protease-mediated polyprotein maturation. This disrupts the processing of viral proteins required for HCV replication. NS3, a serine protease, is essential for the proteolytic cleavages within the HCV polyprotein and plays a key role during HCV viral RNA replication. HCV is a small, enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus belonging to the Flaviviridae family. Drug Indication Asunaprevir is indicated in combination with other agents for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C in adult patients with hepatitis C virus genotypes 1 or 4 and compensated liver cirrhosis. Hepatitis C is a liver disease caused by the hepatitis C virus. The chronic state of this condition accounts for 60-80% of the cases from which the risk of cirrhosis of the liver within 20 years is of around 15-30%. The genotype 1 is the most common type of hepatitis C in the United States and the most difficult to treat. Treatment of chronic hepatitis C Mechanism of Action Asunaprevir is a highly active HCV NS3 protease inhibitor. The genome of HCV has a positive polarity which allows it to be translated into a protein in the host cell without further transformation steps. However, the resultant protein needs to be divided by the enzyme NS3 protease into single proteins in order to be able to exert its enzymatic activity or structural role. Therefore, due to NS3 vital importance for viral replication, the inhibiting action of asunaprevir causes a robust antiviral activity. Pharmacodynamics Studies in vitro demonstrated a significant antiviral activity in HCV replicon cell systems with an EC50 of 4nm and 1nm against the HCV genotype 1a and 1b respectively. These studies showed a limited activity against the genotypes 2 and 3. This property makes asunaprevir a highly selective anti-HCV agent that is not effective against HCV closely related virus. Asunaprevir produce robust declines in HCV RNA levels in patients with HCV genotype 1 infection.In clinical studies, it has been shown that asunaprevir is well-tolerated and the mean maximum HCV RNA level reduction from baseline was of approximately 2.87 log10 IU/ml. Monotherapy clinical studies with asunaprevir showed a mean maximum decline of HCV RNA in the range of 0.28-2.87 log10 IU/ml when administered in increasing doses from 10-600 mg. When asunaprevir was used as a combination product, it was possible to obtain a sustained virological response (aviremia 24 weeks after completion of therapy) in 83-92% of the patients. |
| 分子式 |
C35H46CLN5O9S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
748.29
|
|
| 精确质量 |
747.27
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 56.18; H, 6.20; Cl, 4.74; N, 9.36; O, 19.24; S, 4.28
|
|
| CAS号 |
630420-16-5
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
16076883
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 熔点 |
145-155 ºC
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.616
|
|
| LogP |
4.02
|
|
| tPSA |
201.18
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
10
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
14
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
51
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1470
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
5
|
|
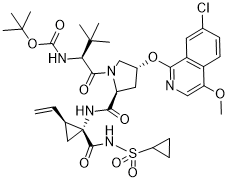
| SMILES |
ClC1C([H])=C([H])C2C(=C([H])N=C(C=2C=1[H])O[C@@]1([H])C([H])([H])N(C([C@]([H])(C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])N([H])C(=O)OC(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])=O)[C@@]([H])(C1([H])[H])C(N([H])[C@]1(C(N([H])S(C2([H])C([H])([H])C2([H])[H])(=O)=O)=O)C([H])([H])[C@@]1([H])C([H])=C([H])[H])=O)OC([H])([H])[H]
|
|
| InChi Key |
XRWSZZJLZRKHHD-WVWIJVSJSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C35H46ClN5O9S/c1-9-19-16-35(19,31(44)40-51(46,47)22-11-12-22)39-28(42)25-15-21(49-29-24-14-20(36)10-13-23(24)26(48-8)17-37-29)18-41(25)30(43)27(33(2,3)4)38-32(45)50-34(5,6)7/h9-10,13-14,17,19,21-22,25,27H,1,11-12,15-16,18H2,2-8H3,(H,38,45)(H,39,42)(H,40,44)/t19-,21-,25+,27-,35-/m1/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
1,1-dimethylethyl ((1S)-1-{((2S,4R)-4-(7-chloro-4-methoxyisoquinolin-1-yloxy)-2-({(1R,2S)-1-((cyclopropylsulfonyl)carbamoyl)-2-ethenylcyclopropyl}carbamoyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl)carbonyl}-2,2-dimethylpropyl)carbamate
|
|
| 别名 |
BMS-650032; BMS 650032; BMS650032; S9X0KRJ00S; 1,1-dimethylethyl ((1S)-1-{((2S,4R)-4-(7-chloro-4-methoxyisoquinolin-1-yloxy)-2-({(1R,2S)-1-((cyclopropylsulfonyl)carbamoyl)-2-ethenylcyclopropyl}carbamoyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl)carbonyl}-2,2-dimethylpropyl)carbamate; trade name in Japan and Russia: Sunvepra
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL ( ~133.63 mM )
Ethanol : 20~100 mg/mL(~26.73 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.34 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.34 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.34 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (3.34 mM) in 5% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 50% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 5 中的溶解度: 2 mg/mL (2.67 mM) in 10% EtOH + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,将100 μL 20.0 mg/mL澄清乙醇储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中并混合均匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 6 中的溶解度: ≥ 2 mg/mL (2.67 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% EtOH + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.0 mg/mL 澄清乙醇储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 配方 7 中的溶解度: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.34 mM) 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.3364 mL | 6.6819 mL | 13.3638 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2673 mL | 1.3364 mL | 2.6728 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1336 mL | 0.6682 mL | 1.3364 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Asunaprevir activates ISRE activity and type I IFN and TLR3/RIG-I antiviral signaling pathway.Front Microbiol. 2017; 8: 668. |
|---|
 Effects of Asunaprevir on TLR3/RIG-I signaling pathway in Huh. 7.5.1 cells with MAVS and TRIF knockdown. Huh 7.5.1 cells were transfected by siRNA of MAVS and TRIF for 48 h and then treated with asunaprevir for 24 h. The key signaling proteins such as MAVS, TRIF, IRF3, and phosphorylated IRF-3 were determined by immunoblotting analysis (left panel).Front Microbiol. 2017; 8: 668. |
Effects of Asunaprevir on replication of DENV and HCV. (A)Huh 7.5.1 cells were treated with different doses of asunaprevir for 24 h and immunoblotting analysis for NS3 protein of DENV, and real-time PCR for RNA level of DENV were performed(B).Front Microbiol. 2017; 8: 668. |
 Asunaprevir inhibits DENV-2 and HCV virus production.Front Microbiol. 2017; 8: 668. |
|---|
Effects of asunaprevir on replication of HCV in JFH-1- infected.Front Microbiol. 2017; 8: 668. |
 Effects of asunaprevir on replication of DENV in Huh 7.5.1 cells after knockdown of MAVS and TRIF by siRNA.Front Microbiol. 2017; 8: 668. |