| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
BAY 85-8501 是一种强效且选择性的人中性粒细胞弹性蛋白酶(HNE)抑制剂。其对 HNE 的抑制常数(Ki)为 0.08 nM。[1]
它表现出物种选择性,对啮齿动物中性粒细胞弹性蛋白酶(RNE)的 Ki 为 8.0 nM,对小鼠中性粒细胞弹性蛋白酶(MNE)的 Ki 为 6.0 nM。[1] 在存在 1 mM 过氧化氢(模拟炎症环境中的氧化应激)的条件下进行的生化抑制实验中,BAY 85-8501 的 IC50 仅偏移 2 倍至 140 pM,表明其具有良好的氧化稳定性。[1] BAY 85-8501 对一组 21 种相关的丝氨酸蛋白酶未显示抑制作用(IC50 > 30,000 nM),证实了其高选择性。[1] 结合动力学分析显示,其结合速率(k_on)为 12.6 x 10^6 M^{-1}s^{-1},解离速率(k_off)为 1.0 x 10^{-3} s^{-1},停留时间约为 0.3 小时(约17分钟)。[1] 该化合物对人细胞色素 P450 亚型 CYP2C9 和 CYP3A4 无抑制效力(IC50 > 50 μM)。[1] |
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在这种情况下,损伤和肺出血的主要来源是外源性 HNE noxa。当在 HNE noxa 前一小时提供时,BAY-85-8501 (29) 完全避免了肺损伤和随后炎症的发展,基于针对 HNE 的皮摩尔效力和针对 MNE 的个位数效力。 0.01mg/kg剂量组的血红蛋白浓度显着降低。 0.1 mg/kg 对中性粒细胞计数有显着影响。在这种情况下,抗 HNE 的效力 (Ki=0.08 nM) 是影响功效的主要因素。在这种情况下,BAY-85-8501(一种高度 HNE 选择性抑制剂)不能预防原发性肺损伤,因为它对 PPE 没有影响。 BAY-85-8501 虽然效力较差,但可以阻断 MNE(炎症和继发性损伤的内源性驱动因素)。因此,BAY-85-8501 现在对炎症和继发性损伤的影响很小,并且只有在高出 30 倍的剂量时才会明显。抗 MNE 的效力 (Ki=6 nM) 是影响第二种情况下疗效的主要因素 [1]。
在小鼠气管内滴注 HNE 诱导的急性肺损伤(ALI)模型中,在攻击前 1 小时口服给予 BAY 85-8501(0.01, 0.03, 0.1 mg/kg)可完全预防肺损伤和随后的炎症。在 0.01 mg/kg 剂量下观察到支气管肺泡灌洗液(BALF)中血红蛋白浓度(指示肺出血)显著降低,在 0.1 mg/kg 剂量下观察到 BALF 中性粒细胞计数(指示炎症)显著减少。[1] 在第二个由猪胰弹性蛋白酶(PPE,BAY 85-8501 不抑制)诱导的 ALI 模型中,该化合物仍然显示出对继发的、MNE 驱动的炎症和损伤的疗效,但剂量需要提高约30倍(1 和 3 mg/kg,口服),这与其对 MNE 的较低效力(Ki = 6 nM)一致。[1] |
| 酶活实验 |
测试化合物对 HNE 的抑制能力通过使用分离酶的功能生化实验进行评估。IC50 值是通过在存在或不存在不同化合物浓度的情况下,使用合适的荧光肽底物 MeOSuc-AAPV-AMC,根据酶活性数据(pH 7.4)推导得出。[1]
对于 Ki 的测定,在不同底物浓度和各种抑制剂浓度下测量酶反应速度,并通过 Dixon 图推算出抑制常数(Ki),证实了竞争性抑制。[1] 弹性蛋白酶抑制剂与靶标结合的速率(k_on)使用带有修饰荧光标记底物(MeOSuc-AAPV-伞形酮基)的功能生化实验测定,该底物允许在毫秒时间尺度上灵敏检测底物水解。对反应进程曲线进行非线性回归得到抑制起始的观察速率常数。[1] 测试化合物抑制人 CYP2C9 和 CYP3A4 的能力是使用混合的人肝微粒体作为酶源和选择性标准底物(CYP2C9 用地氯芬酸,CYP3A4 用咪达唑仑)进行研究的。IC50 值根据存在/不存在不同化合物浓度下的酶活性数据推导得出。[1] |
| 动物实验 |
Acute Lung Injury (ALI) Model in Mice: Mice were administered BAY 85-8501 orally (p.o., gavage) at doses of 0.01, 0.03, 0.1, 1, or 3 mg/kg, formulated in a vehicle (specific vehicle not detailed for efficacy studies). One hour after compound administration, acute lung injury was induced by intratracheal instillation of either human neutrophil elastase (HNE) or porcine pancreatic elastase (PPE). One hour after the elastase challenge, animals were euthanized, and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) was collected. Primary injury was quantified by measuring hemoglobin concentration in BALF, and inflammation was quantified by neutrophil count in BALF. [1]
Pharmacokinetic Studies in Rats: The pharmacokinetic profile was assessed following intravenous (0.25–2 hour infusion) and oral (gavage) administration of BAY 85-8501 at a dose of 0.3 mg/kg. For oral administration, the compound was formulated in vehicles including EtOH/PEG400/H2O or as a suspension in 0.5% Tylose. [1] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
In rats, following intravenous administration (0.3 mg/kg), BAY 85-8501 showed a total plasma clearance (CL) of 0.5 L h^{-1} kg^{-1}, an apparent steady-state volume of distribution (V_ss) of 5.8 L kg^{-1}, and a terminal half-life (t_{1/2}) of 8.5 hours. [1]
Oral bioavailability (F) in rats was 63% when administered as a 0.5% Tylose suspension at a dose of 0.3 mg/kg. [1] Metabolic stability assessed in rat hepatocytes for precursor compounds indicated that the introduction of the electron-withdrawing sulfone substituent at the C2' position in BAY 85-8501 contributed to metabolic stabilization. [1] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
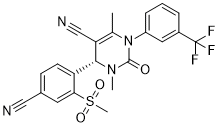
BAY 85-8501 ((4S)-4-(4-cyano-2-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-3,6-dimethyl-2-oxo-1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-pyrimidine-5-carbonitrile) is a dihydropyrimidinone-based small molecule inhibitor. [1]
Its high potency and selectivity were achieved by strategically locking the bioactive conformation using a methyl group at the N3 position and a methyl sulfone substituent at the C2' position of the northern phenyl ring, which pre-organizes the molecule for optimal binding. [1] The compound binds to HNE via an induced-fit mechanism, where the S2 subsite of the enzyme expands to accommodate the inhibitor's northern cyanophenyl moiety. [1] BAY 85-8501 is described as a clinical candidate and was, at the time of publication, being tested in clinical studies (a safety and efficacy trial, NCT01818544) for the treatment of pulmonary diseases such as bronchiectasis. [1] |
| 分子式 |
C22H17F3N4O3S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
474.455593824387
|
| 精确质量 |
474.097
|
| CAS号 |
1161921-82-9
|
| 相关CAS号 |
(R)-BAY-85-8501;2446175-39-7
|
| PubChem CID |
66601502
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.5±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
626.7±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
332.8±31.5 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.622
|
| LogP |
1.99
|
| tPSA |
114
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
| 重原子数目 |
33
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1030
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
CC1=C([C@H](N(C(=O)N1C2=CC=CC(=C2)C(F)(F)F)C)C3=C(C=C(C=C3)C#N)S(=O)(=O)C)C#N
|
| InChi Key |
YAJWYFPMASPAMM-HXUWFJFHSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H17F3N4O3S/c1-13-18(12-27)20(17-8-7-14(11-26)9-19(17)33(3,31)32)28(2)21(30)29(13)16-6-4-5-15(10-16)22(23,24)25/h4-10,20H,1-3H3/t20-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(S)-4-(4-cyano-2-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-3,6-dimethyl-2-oxo-1-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidine-5-carbonitrile
|
| 别名 |
BAY 858501; BAY858501; BAY-858501; BAY 85-8501; BAY85-8501; BAY-85-8501.
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~200 mg/mL (~421.53 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 5 mg/mL (10.54 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 50.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 5 mg/mL (10.54 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 50.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (5.27 mM) in 5% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 50% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1077 mL | 10.5383 mL | 21.0766 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4215 mL | 2.1077 mL | 4.2153 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2108 mL | 1.0538 mL | 2.1077 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Selection of HNE inhibitors that have reached clinical development.ChemMedChem. 2015 Jul;10(7):1163-73. |
Locking the bioactive conformation with substituents at N3 and C2′. Conformational analysis of free ligands based on modeling. Relaxed coordinate scan of the rotation of the cyanophenyl moiety of 22 and 27 from 0° to 180° in steps of 2°. Depicted is the dihedral angle along N3=C4=C1′=C2′.ChemMedChem. 2015 Jul;10(7):1163-73. |
Acute lung injury (ALI) in vivo model in mice. a) Schematic representation of the experimental rationale.ChemMedChem. 2015 Jul;10(7):1163-73. |