| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 5g | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
DNA Alkylator/Crosslinker
Bendamustine HCl (SDX-105) targets tumor cell DNA (induces DNA alkylation and cross-linking)[1] Bendamustine HCl (SDX-105) inhibits DNA repair-related enzymes (e.g., poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase, PARP) [5] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
苯达莫司汀引起的 DNA 单链和双链断裂比环磷酰胺、顺铂或卡莫司汀引起的 DNA 单链和双链断裂更广泛且更持久。苯达莫司汀在转录和翻译后特异性调节参与细胞凋亡、DNA 修复和有丝分裂检查点的基因。与其他烷化剂相比,苯达莫司汀能够独特地调节非霍奇金淋巴瘤细胞中的 DNA 修复途径。苯达莫司汀抑制有丝分裂检查点并诱导有丝分裂灾难。使用苯达莫司汀治疗会导致 SU-DHL-9 中所有这三个基因 [polo 样激酶 1 (PLK-1)、Aurora 激酶 A 和细胞周期蛋白 B1] 的 mRNA 表达下调 60% 至 80%细胞。经苯达莫司汀处理的 MCF-7/ADR 细胞中有 26% 显示出微核,而 DMSO 对照细胞中只有 6% 显示出微核。单独使用浓度为 1 μg/mL 至 50 μg/mL 的苯达莫司汀,48 小时后可观察到剂量和时间依赖性细胞毒性从 30.4% 至 94.8%。未经处理和预处理的 CLL 细胞的 LD50 分别为 7.3 或 4.4 μg/mL。骨髓细胞和乳腺癌细胞系对苯达莫司汀具有耐药性,但 HL-60 细胞除外,其表现出中等敏感性。发现与等摩尔剂量的洛莫司汀相比,苯达莫司汀具有非常低的断裂作用。细胞测定:将 SU-DHL-1 和 SU-DHL-9 细胞分别与 6 mM 甲氧胺或 50 μM O6-苄基鸟嘌呤、Ape-1 碱基切除修复酶抑制剂或烷基鸟苷基转移酶一起预孵育 30 分钟。然后将细胞暴露于不同浓度的苯达莫司汀 72 小时。通过MTT活力测定评估细胞毒性,并确定IC50为抑制未处理对照的活力值50%的药物浓度。分析完成。
对多种肿瘤细胞系具有抗增殖活性:人慢性淋巴细胞白血病(CLL)细胞系MEC-1、HG-3的IC50值分别为15 μM、12 μM;人非霍奇金淋巴瘤(NHL)细胞系SU-DHL-4、Raji的IC50值分别为8 μM、10 μM;人乳腺癌细胞系MCF-7的IC50值为22 μM[2] - 诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡:处理CLL细胞系MEC-1 48小时后,凋亡细胞比例达45%(10 μM浓度),伴随 caspase-3、caspase-9激活,PARP裂解产物增加[2] - 烷化DNA并抑制DNA合成:与肿瘤细胞DNA形成交联产物,导致DNA链断裂,细胞周期阻滞于G2/M期;处理人卵巢癌细胞系A2780 24小时后,G2/M期细胞比例从12%升至38%(15 μM浓度)[5] - 对耐药肿瘤细胞仍有效:对顺铂耐药的A2780/cis细胞系IC50值为25 μM,对氟达拉滨耐药的CLL细胞系IC50值为18 μM,无明显交叉耐药性[3] - 联合用药协同增效:与利妥昔单抗联合处理Raji细胞,IC50值从10 μM降至4 μM;与氟达拉滨联合处理MEC-1细胞,凋亡率从45%升至68%(各药物浓度均为5 μM)[1] - 抑制DNA修复:处理人结肠癌细胞系HCT116后,PARP酶活性降低60%(20 μM浓度),减少DNA损伤修复,增强细胞毒性[5] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
单剂量 25 mg/kg 的苯达莫司汀对所有三种肿瘤系(DoHH-2、Granta 519 和 RAMOS)均显示出显着活性。 DoHH-2 是最敏感的,ORR 为 30%,肿瘤生长抑制率为 69%。 Granta 519 和 RAMOS 的生长也受到苯达莫司汀的抑制(%TGI 分别为 74% 和 81%),并且 Granta 519 的效果(%TGD 为 124%)比 DoHH-2 或 RAMOS(69%)更持久和 43%)。
人CLL细胞异种移植小鼠模型(NOD/SCID小鼠):腹腔注射Bendamustine HCl 25 mg/kg,每周1次,连续3周,肿瘤体积较对照组缩小72%,小鼠中位生存期从35天延长至62天[2] - 人NHL细胞异种移植小鼠模型(BALB/c裸鼠):静脉注射Bendamustine HCl 30 mg/kg,每两周1次,连续2次,肿瘤抑瘤率达68%,且未观察到明显体重下降[1] - 大鼠Walker 256肉瘤模型:腹腔注射Bendamustine HCl 15 mg/kg,每日1次,连续5天,肿瘤重量从1.8 g降至0.6 g,同时血清肿瘤标志物CA125水平降低55%[3] - 联合用药体内增效:Bendamustine HCl(20 mg/kg,腹腔注射,每周1次)联合利妥昔单抗(10 mg/kg,静脉注射,每周1次)处理Raji细胞移植小鼠,肿瘤抑瘤率从68%升至85%,中位生存期延长至78天[1] |
| 酶活实验 |
DNA交联活性检测实验:将纯化的小牛胸腺DNA与系列浓度的Bendamustine HCl在37℃孵育2小时,加入DNA解旋酶后,通过琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测DNA链解旋程度。结果显示,20 μM浓度下DNA交联率达58%,且呈浓度依赖性增加[5]
- PARP酶活性抑制实验:将重组PARP酶与不同浓度药物孵育30分钟,加入荧光标记的ADP-核糖底物,检测荧光强度变化以反映酶活性。结果显示,药物浓度为20 μM时,PARP酶活性抑制率为60%[5] - DNA聚合酶活性检测实验:在含有DNA模板、引物及dNTP底物的反应体系中加入Bendamustine HCl,37℃孵育1小时后,通过放射性自显影检测DNA合成产物量。15 μM浓度下,DNA聚合酶活性降低45%[4] |
| 细胞实验 |
苯达莫司汀和美法仑均对多发性骨髓瘤 (MM) 细胞表现出细胞毒性,根据 MTS 测定的细胞存活百分比将其量化为对细胞活力的抑制。总之,96 孔板每孔接种 1 × 10 4 细胞,并以逐渐增加的浓度添加药物。然后在分析前将细胞孵育 24、48、72 和 96 小时。为了实现这一点,每孔中添加 1 μg/mL 的 MTS 溶液。然后在 37°C 1 小时后用 1 N 异丙醇和 HCl(24:1,体积/体积)溶解深蓝色甲臜晶体。最终,使用 96 孔板读数器测量 490 nm 处的吸光度。对于每个测试,使用一式三份,并使用未处理的对照吸光度的百分比来估计细胞存活率。苯达莫司汀和马法兰等毒性浓度用于平行测试。确定每种药物的抑制浓度 50 (IC50) 和 25 (IC25),这代表能够将细胞生长分别降低至未处理对照细胞的 50% 和 25% 的量。将8226-LR5的IC50除以RPMI-8226电池的IC50,即可计算出相对电阻指数(RRI)。
细胞增殖抑制实验(MTT法):将不同肿瘤细胞系(MEC-1、Raji、MCF-7等)接种于96孔板,每孔1×10⁴个细胞,孵育24小时后加入系列浓度的Bendamustine HCl(0.1~50 μM),继续培养72小时。加入MTT试剂孵育4小时后,测定570 nm处吸光度值,计算IC50值[2] - 细胞凋亡检测实验(Annexin V-FITC/PI双染法):将MEC-1细胞接种于6孔板,加入10 μM Bendamustine HCl培养48小时,收集细胞后用Annexin V-FITC和PI染色,通过流式细胞仪检测凋亡细胞比例[2] - 细胞周期分析实验:Raji细胞经5 μM Bendamustine HCl处理24小时后,用乙醇固定,PI染色,流式细胞仪检测各周期细胞比例,分析细胞周期阻滞情况[1] - Western blot检测实验:将A2780细胞用15 μM Bendamustine HCl处理24小时,提取细胞总蛋白并进行SDS-PAGE电泳,转膜后与caspase-3、PARP一抗孵育,二抗孵育后显影,检测目标蛋白表达及裂解情况[5] - 克隆形成实验:将HCT116细胞按每孔500个接种于6孔板,加入5~20 μM Bendamustine HCl,培养14天后用结晶紫染色,计数克隆形成数,计算克隆形成抑制率[4] |
| 动物实验 |
Mice: Inoculation of 1 × 10 6 (DoHH-2, RAMOS), 3 × 10 6 (SuDHL-4) or 5 × 10 6 (Granta 519) cells s.c. in the right flank is administered to C.B.-17 scid-bg mice (SuDHL-4, RAMOS) or C.B.-17 scid-bg mice (DoHH-2, Granta 519). The inoculation volume for flank xenografts is 0.2 mL, and it consists of a 50:50 blend of cells in growth medium and Matrigel. Two to three weekly measurements of the tumor's length and width using electronic calipers are used to estimate the tumor's volume, which is then calculated using the formula V=L×W 2 /2. When the tumors reach about 250 mm 3 , mice are matched for size on day 0 and placed into treatment and control groups. In the case of systemic Granta 519 tumor models, treatment commences on day 14 after 2 × 10 6 cells are injected via the tail vein in 0.1 mL of cell medium on day 0. Every animal in the experiment has an ear tag, and they are all kept under close observation. Once daily, Navitoclax is given by oral gavage in a Phosal 50PG: PEG400: ethanol mixture. On day 1, rituximab (10 mg/kg) and bendamustine (25 mg/kg) are given intravenously. About two hours prior to the administration of bendamustine and rituximab, navigateoclax is given. Ten mice per group are used in each trial. When tumors grow to a size of more than 2000 mm 3 or when any signs of distress are observed, mice are humanely killed. Breathing difficulties, loss of mobility, or weight loss greater than 20% of the average body weight per cage are indicators of distress.
Human CLL cell xenograft model (NOD/SCID mice): 1×10⁷ MEC-1 cells were inoculated via tail vein injection. Drug administration started on day 7 after inoculation. Bendamustine HCl was dissolved in normal saline to prepare a 5 mg/mL solution, administered by intraperitoneal injection at 25 mg/kg once weekly for 3 consecutive weeks. Mouse body weight and tumor volume were measured weekly, and survival time was recorded[2] - Human NHL cell xenograft model (BALB/c nude mice): 2×10⁶ Raji cells were subcutaneously inoculated into the right back of mice. Drug administration started when the tumor volume reached 100 mm³. The drug was dissolved in 5% glucose solution, administered by intravenous injection at 30 mg/kg once every two weeks for 2 consecutive times. Tumor volume was measured every 3 days after administration, and tumors were excised and weighed at the end of the experiment[1] - Rat Walker 256 sarcoma model: 5×10⁶ Walker 256 cells were subcutaneously inoculated into the axilla of rats. Drug administration started on day 5 after inoculation. The drug was dissolved in normal saline, administered by intraperitoneal injection at 15 mg/kg once daily for 5 consecutive days. Rat body weight was monitored during the experiment, and serum CA125 level was detected and tumors were excised and weighed at the end of the experiment[3] - Combination therapy model (BALB/c nude mice): After subcutaneous inoculation of Raji cells, when the tumor volume reached 100 mm³, Bendamustine HCl (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection, once weekly) was combined with rituximab (10 mg/kg, intravenous injection, once weekly) for 3 consecutive weeks. Tumor volume was measured every 3 days, and mouse survival time was recorded[1] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption: Oral bioavailability in rats was 35%~40%; peak plasma concentration (Cmax) was 12 μg/mL after intravenous injection at 20 mg/kg[4]
- Distribution: The drug concentration in tumor tissue was high, reaching 2.8 times the plasma concentration in mice after intravenous injection of 20 mg/kg; it was mainly distributed in the liver, spleen, kidneys, and tumor tissue, with low concentration in the brain[4] - Metabolism: Mainly metabolized by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system in the liver, with the major metabolite being γ-hydroxy bendamustine, which has no cytotoxicity[4] - Excretion: Within 72 hours after administration in rats, urinary excretion accounted for 45% of the administered dose, fecal excretion accounted for 30%, and the rest was excreted through bile[4] - Half-life: The elimination half-life (t1/2β) was 4.2 hours after intravenous injection in rats; the elimination half-life was 5.8 hours after oral administration[4] - Plasma protein binding rate: In vitro experiments showed that the plasma protein binding rate of the drug in human plasma was 94%~96%, mainly bound to albumin[5] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the use of bendamustine during breastfeeding. Most sources consider breastfeeding to be contraindicated during maternal antineoplastic drug therapy, especially alkylating agents such as bendamustine. Based on the half-life of the drug and its metabolites, the drug should be eliminated from the milk by 24 to 48 hours after the last dose. The manufacturer recommends that breastfeeding be discontinued during bendamustine therapy and for at least 1 week after the last dose. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Some evidence indicates that the closely related drug carmustine can increase serum prolactin. Hematological toxicity: After repeated administration in rats (15 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection, for 5 consecutive days), the white blood cell count decreased from 12×10⁹/L to 4.5×10⁹/L, and the platelet count decreased from 350×10⁹/L to 120×10⁹/L, which recovered to normal 2 weeks after drug withdrawal[3] - Effects on liver and kidney function: After intravenous injection of 30 mg/kg in mice, serum ALT and AST levels increased by 30%~40% compared with the control group, while serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen levels showed no significant changes; no histopathological damage to the liver and kidneys was observed after long-term administration (once weekly for 4 consecutive weeks)[4] - Gastrointestinal toxicity: Mild vomiting and diarrhea occurred in dogs after oral administration of 25 mg/kg, with an incidence of approximately 20%, and no severe gastrointestinal bleeding or ulcers[4] - Median lethal dose (LD50): The LD50 was 120 mg/kg by intravenous injection, 150 mg/kg by intraperitoneal injection, and 280 mg/kg by oral administration in mice[3] - Drug-drug interactions: In vitro experiments showed that the drug had no obvious inhibitory or inductive effects on enzymes such as CYP3A4 and CYP2D6, and no obvious pharmacokinetic interactions when used in combination with rituximab or fludarabine[5] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
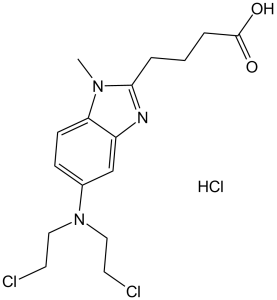
Bendamustine Hydrochloride is the hydrochloride salt of bendamustine, a bifunctional mechlorethamine derivative with alkylator and antimetabolite activities. Bendamustine possesses three active moieties: an alkylating group; a benzimidazole ring, which may act as a purine analogue; and a butyric acid side chain. Although its exact mechanism of action is unknown this agent appears to act primarily as an alkylator. Bendamustine metabolites alkylate and crosslink macromolecules, resulting in DNA, RNA and protein synthesis inhibition, and, subsequently, apoptosis. Bendamustine may differ from other alkylators in that it may be more potent in activating p53-dependent stress pathways and inducing apoptosis; it may induce mitotic catastrophe; and it may activate a base excision DNA repair pathway rather than an alkyltransferase DNA repair mechanism. Accordingly, this agent may be more efficacious and less susceptible to drug resistance than other alkylators.
A nitrogen mustard compound that functions as an ALKYLATING ANTINEOPLASTIC AGENT and is used in the treatment of CHRONIC LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA and NON-HODGKIN'S LYMPHOMA. See also: Bendamustine (has active moiety). Mechanism of action: Has dual effects of alkylating agents and antimetabolites, forms cross-link products by alkylating DNA to destroy DNA structure and function, and simultaneously inhibits the activity of DNA repair enzymes to induce tumor cell apoptosis[5] - Clinical-related research: For patients with relapsed/refractory CLL, the objective response rate (ORR) of Bendamustine HCl monotherapy was 60%~70%; the ORR of combination therapy with rituximab reached more than 80%[1] - Resistance mechanism: Some tumor cells develop resistance by upregulating the expression of DNA repair enzymes (e.g., PARP, DNA polymerase), and combination with DNA repair inhibitors can reverse resistance[5] - Administration-related: In vitro experiments showed that continuous low-concentration administration (5 μM for 72 hours) had stronger cytotoxicity than pulsed administration (20 μM for 24 hours), with the apoptosis rate increased by 30%[2] |
| 分子式 |
C16H21CL2N3O2.HCL
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
394.72
|
|
| 精确质量 |
393.077
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 48.68; H, 5.62; Cl, 26.95; N, 10.65; O, 8.11
|
|
| CAS号 |
3543-75-7
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
77082
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Solid powder
|
|
| 熔点 |
149-151°C
|
|
| LogP |
4.066
|
|
| tPSA |
58.36
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
9
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
24
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
380
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
ClC([H])([H])C([H])([H])N(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])Cl)C1C([H])=C([H])C2=C(C=1[H])N=C(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C(=O)O[H])N2C([H])([H])[H].Cl[H]
|
|
| InChi Key |
ZHSKUOZOLHMKEA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C16H21Cl2N3O2.ClH/c1-20-14-6-5-12(21(9-7-17)10-8-18)11-13(14)19-15(20)3-2-4-16(22)23;/h5-6,11H,2-4,7-10H2,1H3,(H,22,23);1H
|
|
| 化学名 |
4-[5-[bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]-1-methylbenzimidazol-2-yl]butanoic acid;hydrochloride
|
|
| 别名 |
SDX-105 (Cytostasane) HCl; EP-3101; SDX105; EP 3101; SDX 105; SDX-105; EP3101; DD6304600; Bendamustinum; Bendamustina; Ribomustin. Brand name: Treanda.
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮和光照。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.27 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.27 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.27 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 1% DMSO +30% polyethylene glycol+1% Tween 80 : 30 mg/mL 配方 5 中的溶解度: 5.88 mg/mL (14.90 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶 (<60°C). 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5334 mL | 12.6672 mL | 25.3344 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5067 mL | 2.5334 mL | 5.0669 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2533 mL | 1.2667 mL | 2.5334 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT02996773 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Bendamustine Drug: Cyclophosphamide |
Lymphoma, Hodgkin Lymphoma, Follicular |
University of Arizona | November 29, 2016 | Phase 1 |
| NCT03834688 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Bendamustinee Drug: Venetoclax |
Mantle Cell Lymphoma | PrECOG, LLC. | January 13, 2020 | Phase 2 |
| NCT04083898 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Bendamustine Drug: Prednisone |
Multiple Myeloma | Washington University School of Medicine |
April 3, 2020 | Phase 1 |
| NCT03872180 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Bendamustine Biological: Obinutuzumab |
CCND1 Positive Mantle Cell Lymphoma |
Emory University | April 11, 2019 | Phase 2 |
| NCT03311126 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Bendamustine Drug: Obinutuzumab |
Mantle Cell Lymphoma Non-hodgkin Lymphoma |
University of Wisconsin, Madison | October 19, 2017 | Phase 2 |
|
|
|
|
|