| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
β-lactam; cephalosporin antibiotic
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:头孢地尼是一种新型口服 2-氨基-5-噻唑基头孢菌素,可抑制 PMA 刺激的人中性粒细胞的鲁米诺放大化学发光 (LACL) 反应,但不抑制调理后的酵母聚糖,且呈浓度依赖性而非时间依赖性。 。头孢地尼抑制由 H2O2、NaI 和辣根过氧化物酶或含淀粉过氧化物酶的中性粒细胞提取物组成的无细胞系统中的 LACL 生成。头孢地尼会损害钙离子载体 A23187 和 FMLP 诱导的 LACL 反应,并且这种损害在细胞松弛素 B 处理的中性粒细胞中会加剧。头孢地尼直接抑制中性粒细胞在可溶性介质刺激过程中释放到细胞外介质中的含有髓过氧化物酶的中性粒细胞提取物的活性,但对吞噬作用过程中释放到吞噬溶酶体中的提取物没有影响。头孢地尼对多种革兰氏阳性和革兰氏阴性细菌表现出优异的活性。头孢地尼对多种 β-内酰胺酶具有抗性,并且表现出的 β-内酰胺稳定性通常优于头孢克洛和头孢呋辛。头孢地尼的消除主要由肾脏介导。头孢地尼与二肽转运蛋白 PEPT1 和 PEPT2 相互作用。头孢地尼肾小管重吸收是显着的,丙磺舒可抑制头孢地尼肾小管分泌,并且这种分泌可能是由肾有机阴离子分泌途径介导的。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
头孢地尼(Omnicef;Abbott Laboratories)是一种主要通过肾脏消除的头孢菌素类抗生素。头孢地尼的非线性肾脏消除已有报道。研究了头孢地尼在无红细胞离体灌流大鼠肾脏中的肾转运机制。用无药物灌注液和单独含头孢地尼的灌注液进行研究,以建立基线生理学并研究头孢地尼肾脏消除特性。为了研究头孢地尼的肾脏转运机制,通过将头孢地尼与肾脏有机阴离子(丙磺舒)、有机阳离子(四乙基铵)或二肽(甘氨酰肌氨酸)转运系统抑制剂共同使用进行了抑制研究。用反相高效液相色谱法测定生物样品中的头孢地尼浓度。使用方差分析和Dunnett检验评估治疗组和对照组之间的差异。头孢地尼的排泄率(ER;根据未结合部分和肾小球滤过率校正的肾清除率)为5.94,该值表示肾小管净分泌。阴离子、阳离子和二肽转运抑制剂均显著影响头孢地尼的ER。使用丙磺舒时,ER降至0.59,清楚地表明头孢地尼肾脏处置具有显著的再吸收成分。甘氨酰肌氨酸研究证实了这一发现,其中ER升高至7.95,表明重吸收至少部分由二肽转运蛋白系统介导。有机阳离子四乙基铵的影响,其中ER被提高到7.53,在性质上可能是次要的。阴离子分泌途径被发现是头孢地尼肾脏排泄的主要机制[2]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
蛋白质结合。对实际IPK实验期间收集的灌注液样品(含和不含抑制剂的头孢地尼)进行超滤。使用一次性微粒分离装置和离心从灌注液中获得不含蛋白质的超滤液。该设备采用各向异性亲水性YMT膜,排除大于-30 kDa的分子。简言之,将475μl等分的灌注液加入装置中,然后将其加盖,在35°C的固定角度转子中于37°C下平衡15分钟,然后在37°C和1800×g下离心25分钟。必要时,在超滤前将灌注液pH调节至样品采集时获得并记录的原始值。通过用CO2对样品放气或通过涡旋样品来去除CO2来调节pH。初步研究(数据未显示)表明,头孢地尼与超滤装置没有明显结合,并且在超滤过程中没有发生蛋白质泄漏。因此,灌流液中未结合头孢地尼(FU)的分数计算为超滤液中头孢地尼浓度与灌流液的浓度之比[2]。
|
| 动物实验 |
Immediately following harvest of a kidney and prior to its transfer to the IPK apparatus, the kidney was carefully trimmed of adhering tissue and rinsed with warm (∼37°C) 10% normal saline to remove abdominal fluids. Care was taken during cleaning not to damage the capsular surface of the kidney. During this time, ∼20 ml of perfusate was allowed to pass through the kidney to remove any residual blood in the organ. The kidney was then transferred to the IPK apparatus, and recirculation was started. The perfusion apparatus was completely enclosed within a Plexiglas chamber maintained at 37°C by thermostatic control. During the experimental period, perfusion pressure at the tip of the renal cannula was kept at 80 ± 10 mm Hg (corrected for the intrinsic apparatus pressure) by way of the pressure and flow restriction valve. Initial perfusion pressure during the equilibration period was slightly higher but fell as hemodynamic equilibration was achieved. Following initiation of perfusion and harvest of the kidney, the organ was placed in the IPK apparatus and a 15-min period for homeostatic equilibration was allowed to pass. The experimental period began (t = 0) with the addition of 150 μl of [14C]inulin to the recirculating perfusion medium (16.7 μCi/ml; specific activity, 2.5 μCi/mg). In all IPK studies, cefdinir (5 μM) and potential transport inhibitors were dissolved separately in a small volume of perfusate and added to the recirculating medium immediately following the addition of [14C]inulin. A 15-min postdose equilibration period was then allowed for drug distribution and hemodynamic stability to occur. Following this period, the remaining 90 min of the experiment was divided into 10-min urine collection intervals for the evaluation of physiologic and clearance parameters. Urine was collected into, and its volume was measured with, a 1-ml tuberculin syringe. Perfusate (1.5 ml) was withdrawn from the sampling port with a 3-ml syringe (21-gauge needle) at the midpoint of each clearance interval (every 10 min). The perfusate and urine pHs were determined immediately after collection. During the experimental period, changes in perfusate composition due to the collection of urine and perfusate samples were minimized by isovolumetric replacement with modified Krebs-Henseleit buffer and blank perfusion medium (no inulin or other compounds present), respectively. Data from the postdose equilibration period (t = 0 to 15 min) were not included in the mean calculations or statistical evaluations.
The parameters evaluated as descriptors of overall renal function included the urine flow rate, urine pH, perfusate flow rate, perfusate pH, perfusion pressure, renal vascular resistance (RVR), glomerular filtration rate (GFR), filtration fraction, and fractional excretion of glucose (FE glucose) and sodium (FE Na+). Cefdinir studies were performed in the absence of inhibitors to characterize the CLR of cefdinir alone in the IPK. Cefdinir inhibition studies were conducted in the presence of known competitive inhibitors of the renal organic anion (probenecid; PRO), organic cation (tetraethylammonium; TEA), and dipeptide (glycylsarcosine [Gly-Sar]) transport systems. Samples of the perfusate and urine were analyzed for concentrations of cefdinir, inulin, glucose, and sodium, as described below [2].
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Maximal plasma cefdinir concentration can be attained between 2-4 hours after an ingested dose. The bioavailability of cefdinir depends on the formulation used. The estimated bioavailability of cefdinir in the capsule form is approximately 16%-21%, depending on the dose. Absolute bioavailability after the administration of a suspension of cefdinir is 25%.. The Cmax of cefdinir is 1.60 μg/mL after a 300 mg dose with an AUC of 7.05. Cmax is 2.87 μg/mL after a 600 mg dose with an AUC of 11. A meal high in fat can reduce the absorption of cefdinir by up to 15%, however, this is not a cause for clinically significant changes, therefore cefdinir may be taken with or without food. When given with aluminum or magnesium-containing antacids or iron, cefdinir absorption may decrease. It is recommended to allow 2 hours between cefdinir administration and the administration of these agents. This drug is mainly excreted by the kidneys. Dose adjustments may be required for patients with renal impairment or patients on dialysis. Approximately 18.4% of a 300 mg dose of cefdinir was found unchanged in the urine after a 300 mg dose was administered during a pharmacokinetic study of 21 individuals. A large proportion of the administered dose is excreted in the feces, although the majority is found in the urine. The average volume of distribution of cefdinir in adults is about 0.35 L/kg and 0.67 L/kg in children. Another resource estimates the volume of distribution in adults at 1.56–2.09 L/kg. Cefdinir is found to be distributed in various tissues at clinically effective concentrations. It may be found in the epithelial lining fluid, bronchial mucosa, tonsils, sinuses, skin blister fluid, as well as the middle ear fluid. Third-generation cephalosporins such as cefdinir cross the blood-brain barrier and are found in high concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid, unlike their first and second generation counterparts. The wide tissue distribution of cefdinir allows it to treat a variety of infections throughout the body. The renal clearance in healthy adults in a pharmacokinetic study was 2.0 (± 1.0) mL/min/kg and the clearance in patients with renal failure was lower, decreasing in proportion to the degree of renal impairment. Dose adjustment is required in patients with renal impairment. Metabolism / Metabolites This drug is not significantly metabolized and its pharmacological actions are mainly attributed to the parent drug. Biological Half-Life The average plasma elimination half-life is about 1.7 hours in adults. In children and healthy infants, plasma elimination half-life ranges from 1.2–1.5 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Although no information is available on the use of cefdinir during breastfeeding, cephalosporins are generally not be expected to cause adverse effects in breastfed infants. Occasionally disruption of the infant's gastrointestinal flora, resulting in diarrhea or thrush have been reported with cephalosporins, but these effects have not been adequately evaluated. Cefdinir is acceptable in nursing mothers. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding The plasma protein binding of cefdinir ranges from 60% to approximately 70%. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
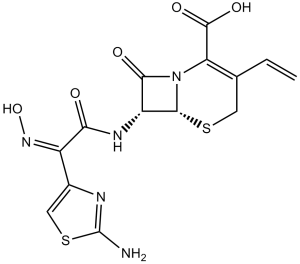
Cefdinir is a cephalosporin compound having 7beta-2-(2-amino-thiazol-4-yl)-2-[(Z)-hydroxyimino]-acetylamino- and 3-vinyl side groups. It has a role as an antibacterial drug. It is a cephalosporin and a ketoxime.
Cefdinir, also known as Omnicef, is a semi-synthetic, broad-spectrum antibiotic belonging to the third generation of the cephalosporin class. It has been proven to be effective for the treatment of common bacterial infections in the ear, sinus, throat, lungs, and skin. Cefdinir was approved by the FDA in 1997 to treat a variety of mild to moderate infections and was initially marketed by Abbvie. Because of its chemical structure, it is effective against organisms that are resistant to first-line cephalosporin therapy due to the production of beta-lactamase enzymes. Cefdinir is a Cephalosporin Antibacterial. Cefdinir has been reported in Apis cerana with data available. Cefdinir is a semi-synthetic cephalosporin and a beta-lactam antibiotic with bactericidal activity. Cefdinir's effect is dependent on its binding to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located in the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane. Binding results in the inhibition of the transpeptidase enzymes, thereby preventing cross-linking of the pentaglycine bridge with the fourth residue of the pentapeptide and interrupting consequent synthesis of peptidoglycan chains. As a result, cefdinir inhibits bacterial septum and cell wall synthesis formation. A third-generation oral cephalosporin antibacterial agent that is used to treat bacterial infections of the respiratory tract and skin. See also: Cefdinir monohydrate (active moiety of). Drug Indication Cefdinir is indicated to treat acute bacterial otitis media, acute maxillary sinusitis, community-acquired (CA) pneumonia, acute bacterial exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, pharyngitis/tonsillitis, and uncomplicated skin and skin structure infections in children and adults. The organisms susceptible to cefdinir have been listed below in addition to their associated clinical condition that may be treated with cefdinir. Various beta-lactamase producing organisms may be treated, as indicated in certain sections below. **Respiratory** Acute bacterial exacerbations of chronic bronchitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible only), and Moraxella catarrhalis Community-acquired pneumonia caused by Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible only), and Moraxella catarrhalis **Ear, nose, and throat** Acute bacterial otitis media caused by Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, and Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible only) Tonsillitis caused by Streptococcus pyogenes Pharyngitis caused by Streptococcus pyogenes Acute maxillary sinusitis caused by Haemophilus pneumoniae and Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible only), and Moraxella catarrhalis **Skin and skin structure infections** Uncomplicated skin and skin structure infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes Mechanism of Action Five-member thiazolidine rings that make up penicillins are replaced in cephalosporins by a six-member dihydrothiazine ring, conferring greater bactericidal activity. This This 6-member ring enables cefdinir and other cephalosporins to resist inactivation by certain bacterial enzymes. With a mechanism similar to other beta-lactam antibiotics, the bactericidal activity of cefdinir is caused by the inhibition of cell wall synthesis via binding to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs). Cefdinir, like other cephalosporins, penetrates the bacterial cell wall, combats inactivation by beta-lactamase enzymes, and inactivates penicillin-binding proteins. This interferes with the final step of transpeptidation in cell walls, eventually leading to cell lysis, which eventually leads to the death of bacteria that are susceptible to this drug. Cefdinir has shown affinity to penicillin protein binding proteins 2 and 3. It has also been shown to inhibit transpeptidase enzymes of various bacteria, which may play a role in its bactericidal action. One in vitro study suggests that cefdinir inhibits myeloperoxidase release extracellularly. The impact of this potential drug target in relation to its mechanism of action is unknown. |
| 分子式 |
C14H13N5O5S2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
395.41
|
| 精确质量 |
395.035
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 42.53; H, 3.31; N, 17.71; O, 20.23; S, 16.22
|
| CAS号 |
91832-40-5
|
| 相关CAS号 |
91832-40-5;213978-34-8 (salt);
|
| PubChem CID |
6915944
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to yellow solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.9±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 熔点 |
>180°C dec.
|
| 折射率 |
1.862
|
| LogP |
-0.63
|
| tPSA |
211.75
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
10
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
26
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
739
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
| SMILES |
O=C(C(N12)=C(C=C)CS[C@]2([H])[C@H](NC(/C(C3=CSC(N)=N3)=N\O)=O)C1=O)O
|
| InChi Key |
RTXOFQZKPXMALH-GHXIOONMSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C14H13N5O5S2/c1-2-5-3-25-12-8(11(21)19(12)9(5)13(22)23)17-10(20)7(18-24)6-4-26-14(15)16-6/h2,4,8,12,24H,1,3H2,(H2,15,16)(H,17,20)(H,22,23)/b18-7-/t8-,12-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(6R,7R)-7-[[(2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-hydroxyiminoacetyl]amino]-3-ethenyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid
|
| 别名 |
PD 134393; PD-134393; PD134393; Cefdinir; Omnicef; CFDN; Cefdinirum; Cefdinyl; CI 983; CI-983; FK 482; FK-482; Omnicef.
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : 33.33~79 mg/mL (84.29~199.79 mM )
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.32 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.32 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.32 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.32 mM) 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5290 mL | 12.6451 mL | 25.2902 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5058 mL | 2.5290 mL | 5.0580 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2529 mL | 1.2645 mL | 2.5290 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
|
|
|