| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Luminescent enzyme substrate
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
P-糖蛋白介导的腔肠素外流运输是在瞬时表达海肾荧光素酶 (RLuc) 的 HCT-8 对照细胞中观察到的生物发光不良的原因。另一方面,短暂产生 RLuc 的 HCT-8 细胞显示出强烈的生物发光,这是 shRNAi 下调 P-糖蛋白的一种情况 [3]。
|
||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
给动物静脉注射腔肠素(2 mg/kg),然后暴露在电荷耦合器件(CCD)相机下五分钟,观察HCC1806-RR的体内生长潜力。 Rluc 活性被观察为肿瘤细胞释放的光度,并被捕获为覆盖单色动物照片的伪彩色图像。大多数动物除了在主要位置表现出极高的 Rluc 活性外,还表现出腹股沟 ILN 的转移 [4]。
|
||
| 酶活实验 |
生物发光是一种普遍的自然现象。发光生物存在于细菌、真菌、原生动物、腔肠动物、蠕虫、软体动物、昆虫和鱼类中。对各种生物发光系统的研究揭示了一个有趣的特征——尽管这一生化过程的最终结果相同,但不同分类群的可见光发射机制却有很大不同。在海洋发光生物中发现的几种生物发光反应的底物中,最常用的是咪唑吡嗪酮衍生物,如coelenterazine和Cypridina lucifin。虽然使用的底物是相同的,但在分类上遥远的发光生物中催化发光反应的生物发光蛋白在氨基酸序列或空间结构上都没有显示出相似性。在这篇综述中,我们考虑了各种发光生物的荧光素酶,这些荧光素酶以coelenterazine或Cypridina lucifin为底物,以及这些蛋白质的修饰,以改善它们的物理化学和生物发光特性,从而提高它们在体内生物发光成像中的适用性。[1]
|
||
| 细胞实验 |
研究了超氧阴离子对游离腔肠嗪的氧化作用,并与将合成腔肠嗪掺入载脂蛋白中制备的半合成光蛋白obelin的氧化作用进行了比较。钙与重组的光蛋白结合,引发结合的腔肠嗪氧化。在不含载脂蛋白的情况下,超氧阴离子触发了游离合成银肠嗪的氧化。采用人工合成胆肠嗪的发光方法,研究了fMet-Leu-Phe-和4b-phorbol - 12b-肉豆酸酯- 13a-acetate刺激中性粒细胞产生活性氧代谢物的过程。将该探针的化学发光特性与鲁米诺的化学发光特性进行了比较,总结如下:(a)超氧化物歧化酶抑制了coelenterazine依赖性的化学发光;(b) coelenterazine检测中性粒细胞氧化爆发的敏感性与鲁米诺相当;(c)叠氮化物对异肠菌嗪的化学发光没有抑制作用;(d)与需要催化去除过氧化氢的鲁米诺不同,coelenterazine的化学发光不依赖于细胞源性髓过氧化物酶的活性。这些结果表明,coelenterazine作为超氧阴离子非常敏感和特异的化学发光探针是有用的。[2]
|
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 参考文献 | |||
| 其他信息 |
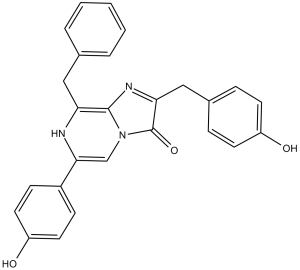
Oplophorus luciferin is an imidazopyrazine that is imidazo[1,2-a]pyrazin-3(7H)-one in which positions 2, 6, and 8 are substituted by 4-hydroxybenzyl, 4-hydroxyphenyl, and benzyl groups, respectively. It has a role as a luciferin. It is a member of phenols and an imidazopyrazine. It derives from a hydride of an imidazo[1,2-a]pyrazine.
Coelenterazine has been reported in Pandalus danae, Pandalus borealis, and other organisms with data available. Multidrug resistance (MDR) remains a major obstacle to successful chemotherapeutic treatment of cancer and can be caused by overexpression of P-glycoprotein, the MDR1 gene product. To further validate a knockdown approach for circumventing MDR, we developed a P-glycoprotein inhibition strategy using short hairpin RNA interference (shRNAi) and now show efficacy and target specificity in vivo. Two of eight tested shRNAi constructs targeted against human MDR1 mRNA inhibited expression of P-glycoprotein by >90%, whereas control shRNAi had no effect. Ablation of P-glycoprotein in cells stably transduced with retroviral-mediated shRNAi was documented by Western blot and functionally confirmed by increased sensitivity of MDR1-transfected cells toward the cytotoxic drugs vincristine, paclitaxel, and doxorubicin as well as by transport of (99m)Tc-Sestamibi. shRNAi-mediated down-regulation of P-glycoprotein transport activity both in cultured cells and in tumor implants in living animals could be followed by direct noninvasive bioluminescence imaging using the Renilla luciferase fluorophore, coelenterazine, a known P-glycoprotein transport substrate. Furthermore, after somatic gene transfer by hydrodynamic infusion of a MDR1-Firefly luciferase (MDR1-FLuc) fusion construct into mouse liver, the effect of shRNAi delivered in vivo on P-glycoprotein-FLuc protein levels was documented with bioluminescence imaging using d-luciferin. ShRNAi against MDR1 reduced bioluminescence output of the P-glycoprotein-FLuc reporter 4-fold in vivo compared with mice treated with control or scrambled shRNAi. Targeted down-regulation of a somatically transferred P-glycoprotein-eGFP fusion reporter also was observed using fluorescence microscopy. Our results show that shRNAi effectively inhibited MDR1 expression and function in cultured cells, tumor implants and mammalian liver, documenting the feasibility of a knockdown approach to reversing MDR in vivo.[3] |
| 分子式 |
C26H21N3O3
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
423.46
|
|
| 精确质量 |
423.158
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 73.74; H, 5.00; N, 9.92; O, 11.33
|
|
| CAS号 |
55779-48-1
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Coelenteramide;50611-86-4
|
|
| PubChem CID |
135445694
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to khaki solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
641.4±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
341.7±34.3 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.689
|
|
| LogP |
3.87
|
|
| tPSA |
90.62
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
32
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
585
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| InChi Key |
LNCOEGVEEQDKGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C26H21N3O3/c30-20-10-6-18(7-11-20)15-23-26(32)29-16-24(19-8-12-21(31)13-9-19)27-22(25(29)28-23)14-17-4-2-1-3-5-17/h1-13,16,30-32H,14-15H2
|
|
| 化学名 |
8-benzyl-6-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-[(4-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]imidazo[1,2-a]pyrazin-3-ol
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: (1). 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 (2). 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮。 (3). 该产品在溶液状态不稳定,请现配现用。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 0.2 mg/mL (0.47 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% EtOH + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 2.0 mg/mL 澄清 EtOH 储备液加入400 μL PEG300 中,混匀;再向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;然后加入450 μL 生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 0.2 mg/mL (0.47 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% EtOH + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 2.0mg/mL澄清EtOH储备液加入到900μL 20%SBE-β-CD生理盐水中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 0.2 mg/mL (0.47 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% EtOH + 90% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3615 mL | 11.8075 mL | 23.6150 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4723 mL | 2.3615 mL | 4.7230 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2361 mL | 1.1807 mL | 2.3615 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。