| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
protein synthesis ( IC50 = 532.5 nM ); RNA synthesis ( IC50 = 2.88 μM )
Eukaryotic ribosomes (reticulocyte ribosomes): Cycloheximide inhibits peptide synthesis on reticulocyte ribosomes [3] - Protein synthesis machinery in eukaryotic cells: Cycloheximide acts as a protein synthesis inhibitor by targeting the translational process [1][4] - TORC1 signaling pathway (indirect effect): Cycloheximide reactivates TORC1 signaling under nutrient-limiting conditions in budding yeast, leading to transcriptional upregulation of ribosome biogenesis genes [4] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:CHX诱导培养的外周血单核细胞凋亡,但对多形核细胞凋亡没有影响,因此其作用取决于细胞类型。对检测细胞凋亡的方法进行评价和比较,结果如下。吉姆萨染色的细胞离心涂片可以识别坏死和凋亡的主要形态特征。台盼蓝染色广泛用于估计细胞活力,但对于检测细胞凋亡毫无价值。两种荧光方法都提供了可靠且可重复的结果,并清楚地区分了凋亡细胞的亚群,并且密切相关。虽然提取 DNA 的琼脂电泳适用于多种细胞类型,但不能适用于所有细胞类型和凋亡条件。一般来说,吖啶橙/溴化乙锭染色细胞的显微镜检查可以被推荐为最可靠的测试方法。激酶测定:Cycloheximide (Naramycin A) 是一种真核生物蛋白质合成抑制剂,体内蛋白质合成和 RNA 合成的 IC50 值分别为 532.5 nM 和 2880 nM。细胞测定:通过将细胞与不同剂量的放线菌酮(CHX)一起孵育或通过312 nm UVB照射来诱导细胞凋亡。用于检测细胞凋亡的方法是光学显微镜(May Grunwald-Giemsa和台盼蓝染色)、荧光显微镜(吖啶橙/溴化乙锭和膜联蛋白V/碘化丙啶染色)和片段化基因组DNA的琼脂糖凝胶电泳。
1. 在感染巨石鲈虹彩病毒(GSIV)的石斑鱼鳍细胞(GF-1)中,Cycloheximide(CHX)处理可减轻凋亡/坏死诱导的磷脂酰丝氨酸(PS)暴露和线粒体膜电位(ΔΨm)丢失;细胞活力实验显示,GSIV感染导致GF-1死亡细胞比例随时间稳步上升(感染后2天11%,5天67%),Annexin V/PI染色显示GSIV诱导的凋亡细胞比例从感染后1天的4%升至5天的29%,感染后4-5天可见凋亡后坏死;Cycloheximide通过抑制新合成蛋白质,抑制了GSIV诱导的这些细胞死亡过程[1] 2. 在营养限制条件下(氨基酸饥饿、酵母代谢周期、减数分裂)的酿酒酵母中,Cycloheximide预处理可快速诱导数百个核糖体生物发生(ribi)基因的转录上调;同时它会阻止这些新转录的ribi mRNA翻译,导致ribi基因的表观翻译效率(TE)下降;若省略Cycloheximide预处理,该效应则消失;Cycloheximide诱导的ribi基因转录上调依赖TORC1信号,并受遗传背景和药物递送溶剂(乙醇vs. DMSO)调控;Cycloheximide导致饥饿酵母细胞中ribi基因的核糖体足迹减少、mRNA水平升高,而非ribi基因受影响较小[4] 3. Cycloheximide抑制网织红细胞核糖体上的肽合成,作用机制与干扰真核翻译过程相关[3] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在进行 200 µA 电击训练之前,小鼠接受 30、60 或 120 mg/kg 放线菌酮注射。放线菌酮对记忆测试试验中的潜伏期有显着影响(P<0.001)。在盐水对照中,这种电击水平导致测试试验的延迟明显高于训练时的延迟。注射最低测试剂量放线菌酮(30 mg/kg)导致测试试验的潜伏期显着高于盐水对照组。接受两种较高剂量放线菌酮中任一种的小鼠在试验中的潜伏期与盐水组相当,即在这些条件下较高剂量既不增强也不损害记忆,导致倒U型剂量反应曲线用于放线菌酮增强记忆。 HI 后 0 小时或 6 小时给予放线菌酮时,通过氯化三苯基四唑 (TTC) 对梗塞区域进行形态测量分析,梗塞体积显着减少 92% 和 61%,但如果给予放线菌酮,则梗死面积减少的趋势不显着。与 HI 对照组相比,在缺氧缺血 (HI) 后 12 小时施用,并且当延迟至 HI 后 24 小时施用时,没有观察到保护作用。
1. 在ICR小鼠抑制性回避训练模型中: - 以120 mg/kg剂量皮下注射,于训练前30分钟给药,训练足底电击强度为100、150、250或300 μA(持续1秒)时,Cycloheximide以电击强度依赖的方式损害记忆,在最高电击强度(300 μA)下记忆损害最显著;生理盐水对照组小鼠的记忆潜伏期随电击强度升高而延长[2] - 以30、60或120 mg/kg剂量皮下注射,于训练前30分钟给药,训练足底电击强度为200 μA(持续1秒)时,Cycloheximide以倒U型剂量反应方式增强记忆,30 mg/kg剂量下增强效果最显著(与生理盐水对照组相比P<0.05)[2] 2. 除小鼠记忆调控外,指定文献中未发现Cycloheximide其他体内药效学数据(如组织分布、靶点结合)[1][3][4] |
| 酶活实验 |
Cycloheximide(也称为 naramycin A)是一种真核蛋白质合成抑制剂,体内蛋白质合成和 RNA 合成的 IC50 值分别为 532.5 nM 和 2880 nM。
1. 网织红细胞核糖体肽合成抑制实验:制备网织红细胞核糖体样本,将其与不同浓度的Cycloheximide(无具体浓度)在支持肽合成的反应体系中孵育;通过未指定的检测方法测定肽链延伸速率或总肽合成量,评估Cycloheximide对核糖体介导肽合成的抑制作用;实验证实Cycloheximide干扰网织红细胞核糖体的肽合成过程,但该实验未完全阐明其具体抑制机制[3] |
| 细胞实验 |
在 60 毫米培养皿上生长的 GF-1 细胞单层(4.0 mL,105 细胞/mL)培养至少 20 小时,然后用 PBS 冲洗两次。然后用放线菌酮 (CHX, 0.33 µg/mL) 和 BKA (20 µM) ANT 抑制剂处理细胞 0-5 天。最后,GSIV K1 菌株(感染复数 [moi] = 5)在初始步骤 (dpi) 后感染 0-5 天。孵育期结束后,将每个样品从培养基中取出并进行 PBS 清洗。之后,将细胞在 100 µL 染色溶液中孵育 10 至 15 分钟。
1. GSIV感染GF-1细胞的活力与凋亡/坏死实验: - 细胞培养:GF-1细胞在标准条件下培养,以未指定的感染复数(MOI)感染GSIV;感染后合适时间点用Cycloheximide(无具体浓度)或溶媒对照处理细胞。 - 活力评估:在感染后2、3、4、5天(dpi)采用未指定的活力实验检测细胞活力,计算死亡细胞比例(感染未处理组2 dpi 11%至5 dpi 67%)。 - 凋亡/坏死检测:1-5 dpi进行Annexin V/PI染色,通过流式细胞术(FACS)定量凋亡细胞(1 dpi 4%至5 dpi 29%)和凋亡后坏死细胞(4-5 dpi显著)。 - 线粒体膜电位(ΔΨm)检测:采用JC-1染料检测感染细胞1-3 dpi的ΔΨm丢失情况(1 dpi 42%,3 dpi 98%);通过对比处理组和未处理组感染细胞,评估Cycloheximide对ΔΨm丢失和PS暴露的影响[1] 2. 酿酒酵母翻译效率(TE)与mRNA水平实验: - 细胞培养:酿酒酵母在充足营养或营养限制(氨基酸饥饿)培养基中培养;样本采集前用Cycloheximide(无具体浓度)或溶媒对照预处理细胞。 - 核糖体图谱与RNA-seq:在酵母代谢周期、减数分裂或氨基酸饥饿的不同时间点分离酵母细胞的核糖体足迹和总mRNA;通过测序定量ribi和非ribi基因的足迹及mRNA水平,计算翻译效率(TE=核糖体足迹/mRNA)。 - 多聚核糖体梯度分析:评估mRNA在多聚核糖体梯度中的位置以验证TE变化;通过监测NOP2 mRNA随时间的丰度变化(乙醇溶剂组比DMSO组积累更快、更多),评估Cycloheximide对ribi基因转录的影响;采用含NOP2启动子/编码序列/UTR元件的报告基因实验,证实Cycloheximide仅在NOP2启动子驱动表达时,通过转录激活影响ribi基因TE[4] |
| 动物实验 |
Mice: In this experiment, male ICR mice that are around two months old are utilized. IP cycloheximide is given in concentrations of 0, 30, 60, or 120 mg/kg (saline controls). Injections of cycloheximide are given half an hour before training. Mice amnesia is commonly studied at a dose of 120 mg/kg. Observe that rats receive much lower amnestic Cycloheximide doses (1-3 mg/kg) than mice do, which is consistent with a comparable difference in the LD50s of mice and rats. As measured 30–60 minutes after injection, cycloheximide doses of 120–150 mg/kg cause about 95% inhibition of brain protein synthesis, while doses of 30 mg/kg cause about 80% inhibition.
Rats: Methoxyflurane anesthesia is used to perform unilateral carotid artery ligation on 7-day-old Sprague Dawley rat pups. The right common carotid artery is permanently ligated with 4-0 silk after a midline incision in the neck. Every animal received surgery for a maximum of five minutes. Rats are returned to their mother for recovery and feeding for two hours after surgery. The pups are then placed in an airtight chamber that is partially submerged in a temperature-controlled water bath to maintain a constant 36°C inside during the 100-minute hypoxic exposure period (8% O2, 92% N2). The rat pups in the HI with Cycloheximide treatment group receive an intraperitoneal injection of Cycloheximide at a dose of 0.6 mg/kg at0,6,12, or 24 hours of recovery, while the HI control group receives an equal volume of normal saline. Once the rat pups have been returned to their dam, they are sacrificed. The entire brain tissue is removed under deep intraperitoneal pentobarbital anesthesia (60 mg/kg) for triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (TTC) and flow cytometry at 48 and 72 hours after HI, respectively.
1. Inhibitory avoidance training and memory testing in ICR mice: - Experimental animals: Male ICR mice (no specific weight/age provided). - Drug preparation: Cycloheximide was dissolved in a suitable vehicle (not specified) to prepare doses of 30, 60, 120 mg/kg; saline was used as the control vehicle. - Administration route and timing: Subcutaneous injection 30 min prior to inhibitory avoidance training. - Training protocol: Mice were subjected to inhibitory avoidance training with footshock intensities of 100, 150, 200, 250, or 300 μA (1 s duration). - Memory testing: Memory was assessed 48 h after training by measuring avoidance latencies; the effect of Cycloheximide on memory was evaluated by comparing latencies between drug-treated and saline-treated groups[2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Interactions
CHLORDANE IS REPORTED TO CAUSE RAPID LOSS OF ACTIVITY /OF CYCLOHEXIMIDE/. Pretreatment of rats with ... spironolactone & ethylestrenol ... protected against the fungicide cycloheximide. Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Rat oral 2 mg/kg LD50 Rat ip 3700 ug/kg LD50 Rat sc 2500 ug/kg LD50 Rat iv 2 mg/kg For more Non-Human Toxicity Values (Complete) data for CYCLOHEXIMIDE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Cycloheximide can cause developmental toxicity according to state or federal government labeling requirements.
Cycloheximide appears as colorless crystals. Used as a fungicide and as a anticancer drug. (EPA, 1998) Cycloheximide is a dicarboximide that is 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperidine-2,6-dione in which one of the hydrogens attached to the carbon bearing the hydroxy group is replaced by a 3,5-dimethyl-2-oxocyclohexyl group. It is an antibiotic produced by the bacterium Streptomyces griseus. It has a role as a bacterial metabolite, a protein synthesis inhibitor, a neuroprotective agent, an anticoronaviral agent and a ferroptosis inhibitor. It is a member of piperidones, a piperidine antibiotic, an antibiotic fungicide, a dicarboximide, a secondary alcohol and a cyclic ketone. It is functionally related to a piperidine-2,6-dione. Cycloheximide has been reported in Streptomyces, Streptomyces pulveraceus, and Streptomyces griseus with data available. Antibiotic substance isolated from streptomycin-producing strains of Streptomyces griseus. It acts by inhibiting elongation during protein synthesis. Mechanism of Action STIMULATED TRANSPORT OF NUCLEAR RIBONUCLEOPROTEIN COMPLEXES TO CYTOPLASM AFTER ADMIN CYCLOHEXIMIDE TO RATS WAS STUDIED. ADMIN OF 2 MG/KG CYCLOHEXIMIDE CAUSED A DECR IN CONTENT OF TOTAL LIVER NUCLEAR RIBONUCLEOPROTEIN COMPLEX WITHIN 2 HR. THE OVERALL DECR WAS DUE TO AN INCREASED TRANSPORT INTO THE CYTOPLASM, NOT DECREASED SYNTHESIS. OTHER RESULTS SUGGEST THAT DURING INHIBITORY PHASE OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS, GENE TRANSCRIPTION CONTINUES & GENE PRODUCT IS TRANSPORTED TO CYTOPLASM FOR TRANSLATION. CYCLOHEXIMIDE (2-5 MG/KG BODY WT) CAUSED COMPLETE INHIBITION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN RAT LIVER WITHIN 30 MIN, & THE LABELING OF NUCLEAR PROTEINS WAS STRONGLY INHIBITED. UNDER THESE CONDITIONS, THE AMT OF NUCLEOLAR 45 S PRE-rRNA & ITS OROTATE-(14)C LABELING REMAINED UNAFFECTED FOR AT LEAST 4 HR, INDICATING THAT INITIALLY THE RATES OF SYNTHESIS & PROCESSING OF 45 S PRE-rRNA WERE NOT APPRECIABLY ALTERED. DRASTIC ALTERATIONS IN THE 45 S PRE-rRNA PROCESSING PATHWAYS OCCURRED AT THE EARLY STAGES OF CYCLOHEXIMIDE ACTION. THE CHANNELING OF NUCLEAR PRE-rRNA ALONG ALTERNATIVE PROCESSING PATHWAYS IS UNDER STRINGENT CONTROL BY THE CONTINUOUS SUPPLY OF CRITICAL PROTEINS. CYCLOHEXIMIDE IS A POTENT INHIBITOR OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN FUNGI & ANIMALS. IT CAUSES AN INCREASE IN ADRENAL RNA, INCREASED PRODUCTION OF GLUCOCORTICOIDS ... & DECREASE IN PYRUVATE UTILIZATION IN ISOLATED ADIPOSE TISSUE. Therapeutic Uses Antibiotics, Antifungal; Protein Synthesis Inhibitors MEDICATION (VET): ANTIBIOTIC, ANTIFUNGAL, TRICHOMONACIDAL ... ESPECIALLY EFFECTIVE AGAINST MALIGNANT LYMPHOMAS IN DOGS. Cycloheximide ... was used in the treatment of cryptococcal infections (Cryptococcus neoformans) before the development of amphotericin B. 1. Cycloheximide (CHX) is a glutarimide antibiotic and a classic eukaryotic protein synthesis inhibitor, primarily targeting the translational process on ribosomes; it does not inhibit prokaryotic protein synthesis[3] 2. Cycloheximide suppresses GSIV-induced mitochondria-mediated apoptotic/necrotic cell death in GF-1 fish cells by inhibiting de novo protein synthesis, and its effect is synergistic with bongkrekic acid (BKA, an adenine nucleotide translocase inhibitor) in attenuating PS exposure and ΔΨm loss[1] 3. The effect of Cycloheximide on memory in mice is bidirectional (impairment vs. enhancement) and dependent on dose and training footshock intensity: high doses (120 mg/kg) impair memory at high shock intensities (300 μA), while low doses (30 mg/kg) enhance memory at moderate shock intensities (200 μA) in an inverted-U dose-response manner; this suggests that Cycloheximide modulates memory by altering memory formation modulators as a secondary consequence of protein synthesis inhibition, rather than directly interfering with training-initiated protein synthesis required for memory formation[2] 4. Cycloheximide can distort measurements of mRNA levels and translation efficiency (TE) in budding yeast under nutrient-limiting conditions by inducing TORC1-dependent transcriptional upregulation of ribi genes while preventing their translation; this highlights a critical caveat for using Cycloheximide in experiments measuring TE or mRNA levels, and pretreatment with Cycloheximide should be avoided to obtain accurate TE data[4] 5. Cycloheximide-induced ribi gene transcription in yeast is associated with the nuclear exit of transcription factors (Dot6, Tod6, Stb3) upon drug treatment, with Stb3 showing the most robust response[4] |
| 分子式 |
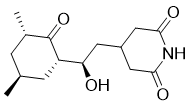
C15H23NO4
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
281.35
|
|
| 精确质量 |
281.162
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 64.04; H, 8.24; N, 4.98; O, 22.75
|
|
| CAS号 |
66-81-9
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
6197
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.1±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
491.8±10.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
111-116 °C
|
|
| 闪点 |
251.2±19.0 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.8 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.499
|
|
| 来源 |
Streptomyces
|
|
| LogP |
0.56
|
|
| tPSA |
83.47
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
20
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
404
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
4
|
|
| SMILES |
O=C(CC(C[C@H]([C@H]1C([C@@H](C)C[C@H](C)C1)=O)O)C2)NC2=O
|
|
| InChi Key |
YPHMISFOHDHNIV-FSZOTQKASA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C15H23NO4/c1-8-3-9(2)15(20)11(4-8)12(17)5-10-6-13(18)16-14(19)7-10/h8-12,17H,3-7H2,1-2H3,(H,16,18,19)/t8-,9-,11-,12+/m0/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
4-[(2R)-2-[(1S,3S,5S)-3,5-dimethyl-2-oxocyclohexyl]-2-hydroxyethyl]piperidine-2,6-dione
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (7.39 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (7.39 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (7.39 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5543 mL | 17.7715 mL | 35.5429 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7109 mL | 3.5543 mL | 7.1086 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3554 mL | 1.7771 mL | 3.5543 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Experimental strategy of GTI-seq using ribosome E-site translation inhibitors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2012 Sep 11;109(37):E2424-32. |
|---|
Impact of uORF features on translational regulation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2012 Sep 11;109(37):E2424-32. |
Cross-species conservation of alternative TIS positions and identification of translated ncRNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2012 Sep 11;109(37):E2424-32. |