| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
ionizable cationic lipid; siRNA delivery
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
含LNP质粒的制备[1]
LNP-pDNA的制备如之前在J Phys Chem B,119(28)(2015),第8698-8706页中所述。将氨基脂质、辅助脂质、胆固醇和PEG-DMG以50/10/39/1的摩尔比溶解在乙醇中。将纯化的pCI-FLuc(表达萤火虫荧光素酶)或pCAX-eGFP(表达eGFP)溶解在pH 4至0.116mg/ml的25mM乙酸钠中。使用微型混合器混合溶液。对于大规模制剂,如Pharm Res,22(3)(2005),第362-372页所述,通过T型接头混合器进行混合。除非另有说明,否则所有制剂均以每μmol脂质0.029mg DNA的浓度生产(对应于N/P电荷比为6.0)。 含DNA脂质颗粒分析[1] 粒径、脂质浓度、pDNA包埋和总pDNA浓度如之前在J Phys Chem B,119(28)(2015),第8698-8706页和J Control Release,196(2014),第106-112页中所述进行测量。Zeta电位的测量方法如前所述,见《分子无机酸》,3(2014),第e210页。 含有二硬脂酰磷酸胆碱(DSPC)的脂质纳米粒(LNPs)和可电离的氨基脂质,如二氢吲哚甲基-4-二甲氨基丁酸酯(DLin-MC3-DMA),是体内有效的siRNA递送载体。在这里,我们探索了类似的LNP系统作为质粒DNA(pDNA)转染试剂的实用性。结果表明,用不饱和PC替代DSPC,用相关脂质DLin-KC2-DMA替代DLin-MC3-DMA,可在体外产生高效的HeLa细胞转染试剂。此外,这些制剂在各种哺乳动物细胞系中表现出优异的转染性能,在原代细胞培养中的转染效率接近90%。这些转染水平等于或大于Lipofectamine所达到的水平,毒性大大降低[1]。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
有效的内部 siRNA 递送载体是含有可电离磷酸酯的磷酸盐纳米粒子 (LNP),例如二亚油基甲基-4-二甲基磷酸酯 (DLin-MC3-DMA) 和二硬脂基乙酰磷脂酰胆碱 (DSPC)。 LNP-siRNA 系统程序的摩尔比为 50/10/38.5/1.5 (PEG)-Pallet,经过调整,可在静脉注射后在肝细胞中实现最大的基因沉默功效。它包含DLin-MC3-DMA (MC3)、DSPC、溶液和聚合溶液。 DLin-MC3-DMA 改进的 pKa 值大大提高了功效 [1]。
在小鼠中,当siRNA剂量为1mg/kg时,与MC3的LNPs相比,ALC-0315的LNPs对FVII和ADAMTS13的敲除分别高出2倍和10倍。在高剂量(5mg/kg)下,ALC-0315 LNPs增加了肝毒性标志物(ALT和胆汁酸),而相同剂量的MC3 LNPs则没有。这些结果表明,ALC-0315 LNPs在小鼠肝细胞和HSC中实现了siRNA介导的靶蛋白的有效敲除,尽管在高剂量后可以观察到肝毒性的标志物。本研究提供了一个初步的比较,可能为开发具有最大疗效和有限毒性的可电离阳离子LNP疗法提供信息。[2] |
| 细胞实验 |
培养细胞的体外转染研究[1]
HeLa、HepG2和Hep3B细胞在含有10%FBS的DMEM中培养。PC12和MCF7细胞在含有10%FBS的RPMI 1640中培养。LNPs以0.75-6.0μg/ml pDNA稀释到培养基中。治疗后24小时进行萤光素酶测定。在无血清治疗的情况下,LNP-pDNA系统仅稀释到培养基中。为了研究ApoE的作用,从杰克逊实验室购买了野生型(C57BL/6)和ApoE-/-(B6.129P2-Poetm1Unc/J)小鼠血清。将LNP-pDNA系统稀释到含有每种血清10%的培养基中。将测量的发光归一化为皮尔斯BCA蛋白测定法测量的蛋白质含量。 体外LNP摄取测量[1] 如前所述,进行了LNP制剂的细胞摄取。使用了29个用DiI-C18(总脂质0.2 mol%)标记的LNP pDNA。使用Cellomics Arrayscan VTI HCS阅读器对板进行成像。 |
| 动物实验 |
In vivo transfection by injection of LNP-pDNA[1]
Stage ~19-20 white leghorn chicken embryos were stained with neutral red dye, and a small tear was made in the extraembryonic membranes over the forelimb. LNP formulations mixed with ~0.1% Fast Green dye was injected at the distal forelimb at 10 μg/ml pDNA, using a Picospritzer II microinjector (Parker Hannifin Corp). Eggs were incubated overnight. Embryos were rinsed and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS, and GFP fluorescence was recorded with a Leica MZFLIII stereofluorescence microscope. Transfection of primary embryonic mesenchyme and analysis of reagent toxicity[1] White leghorn chicken embryos at stage 24 were removed and dissected in Hanks buffered saline solution (HBSS). Forelimbs were pooled and treated for 1 h in dispase to remove epithelial ectoderm. Limb mesenchyme was dissociated, and resuspended in DMEM with 5% FBS and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. Cells were plated onto 96-well plates at a density of 2 × 105 or 2 × 107 cells/ml and treated with 0-40 μg/ml LNP-pDNA. Lipofectamine was used as per manufacturer's protocol. Cultures were incubated overnight at 37 °C and resuspended in PBS buffer for expression analysis using a BD LSRII flow cytometer. Cell survival was assessed in low-density cultures after 24 h of treatment, by counting the adherent cells remaining after PBS washes. Viability was determined based on average counts of all adherent cells within a single field of view (100×) normalized to cell counts of untreated cultures. LNP-siRNA injections[2] siFVII, siADAMTS13, and siLuc were encapsulated in LNPs containing either ALC-0315 or MC3 as the ionizable cationic lipid. We injected mice with 1 mg siRNA per kg body weight (mg/kg) for knockdown studies, and 5 mg/kg dose for toxicity studies. A dose of 1 mg/kg siRNA in mice is standard for inducing knockdown of mRNA for proteins made in hepatocytes using siRNA-LNPs, whereas 5 mg/kg is a higher dose than the one that would normally be used in mice.3 The recommended dose of ONPATTRO (the clinically approved siRNA for hATTR) is 0.3 mg/kg, which corresponds to a human equivalent dose (HED) of 3.69 mg/kg in mice when using body surface area conversion. One week after administration, liver tissue and blood were collected to measure target mRNA and protein levels, respectively, and compared to siLuc-treated mice; half-lives of plasma FVII and ADAMTS13 are 3–6 hours, and 2–3 days, respectively.23,24 mRNA and protein quantification, and toxicity studies are described further below. Toxicological analysis[2] Mice were injected IV with either PBS, or with siLuc encapsulated in LNPs with ALC-0315 (siLuc-ALC-0315) or MC3 (siLuc-MC3) at 5 mg/kg (N = 4). While a dose of any LNP at 10 mg/kg usually causes severe toxicity, such as inflammation and liver necrosis, the toxicity after a 5 mg/kg dose depends on the lipid formulation.26,27 Five hours after the injection, mice were sacrificed, and serum samples were collected as described above. Serum samples were submitted to Idexx BioAnalytics for a toxicology panel. Aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), bile acids, total bilirubin (TBIL), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatine (CREA), gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) levels were analyzed. To note, data regarding bile acid levels in mice treated with PBS and with siLuc-ALC-0315 had N = 3 due to the presence of an outlier in each group (data not shown). The presence of the outliers would have not altered the conclusion, siLuc-ALC-0315 treated mice would have had an even higher bile acid mean and would have been more statistically significant from the PBS-treated mice. Outliers were determined via the ROUT method using GraphPad Prism although limitations such as our small sample size were considered. Bile acid levels commonly range from 0 to 6 μmol/L; however, our results were likely not biologically possible (>130 μmol/L). |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) containing distearoylphosphatidlycholine (DSPC), and ionizable amino-lipids such as dilinoleylmethyl-4-dimethylaminobutyrate (DLin-MC3-DMA) are potent siRNA delivery vehicles in vivo. Here we explore the utility of similar LNP systems as transfection reagents for plasmid DNA (pDNA). It is shown that replacement of DSPC by unsaturated PCs and DLin-MC3-DMA by the related lipid DLin-KC2-DMA resulted in highly potent transfection reagents for HeLa cells in vitro. Further, these formulations exhibited excellent transfection properties in a variety of mammalian cell lines and transfection efficiencies approaching 90% in primary cell cultures. These transfection levels were equal or greater than achieved by Lipofectamine, with much reduced toxicity. Finally, microinjection of LNP-eGFP into the limb bud of a chick embryo resulted in robust reporter-gene expression. It is concluded that LNP systems containing ionizable amino lipids can be highly effective, non-toxic pDNA delivery systems for gene expression both in vitro and in vivo.In summary, the results presented in this study show that LNP formulations of pDNA containing ionizable cationic lipids can be highly effective transfection reagents in vitro that are significantly less toxic than commercial reagents such as Lipofectamine. LNP systems containing DLin-KC2-DMA and unsaturated helper lipids are also potent systems for transfecting primary cells in vitro and in vivo. It is anticipated that these systems will be of considerable utility for transfection of developing tissues in vitro with attendant potential for gene editing applications.[1]
Ionizable cationic lipids are essential for efficient in vivo delivery of RNA by lipid nanoparticles (LNPs). DLin-MC3-DMA (MC3), ALC-0315, and SM-102 are the only ionizable cationic lipids currently clinically approved for RNA therapies. ALC-0315 and SM-102 are structurally similar lipids used in SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines, while MC3 is used in siRNA therapy to knock down transthyretin in hepatocytes. Hepatocytes and hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are particularly attractive targets for RNA therapy because they synthesize many plasma proteins, including those that influence blood coagulation. While LNPs preferentially accumulate in the liver, evaluating the ability of different ionizable cationic lipids to deliver RNA cargo into distinct cell populations is important for designing RNA-LNP therapies with minimal hepatotoxicity. Here, we directly compared LNPs containing either ALC-0315 or MC3 to knock-down coagulation factor VII (FVII) in hepatocytes and ADAMTS13 in HSCs. At a dose of 1 mg/kg siRNA in mice, LNPs with ALC-0315 achieved a 2- and 10-fold greater knockdown of FVII and ADAMTS13, respectively, compared to LNPs with MC3. At a high dose (5 mg/kg), ALC-0315 LNPs increased markers of liver toxicity (ALT and bile acids), while the same dose of MC3 LNPs did not. These results demonstrate that ALC-0315 LNPs achieves potent siRNA-mediated knockdown of target proteins in hepatocytes and HSCs, in mice, though markers of liver toxicity can be observed after a high dose. This study provides an initial comparison that may inform the development of ionizable cationic LNP therapeutics with maximal efficacy and limited toxicity. This work represents proof-of-concept that ionizable cationic LNPs can be used to access and knockdown HSCs-specific targets like ADAMTS13. It shows there are differences in efficacy of MC3 and ALC-0315, which are two of the three clinically approved ionizable cationic lipids used in the LNP delivery platform. Insights from this head-to-head comparison may enable the optimization of RNA-based agents to modulate expression of proteins that were previously inaccessible in vivo for research and therapeutic purposes.[2] |
| 分子式 |
C43H79NO2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
642.0929
|
| 精确质量 |
641.611
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 80.43; H, 12.40; N, 2.18; O, 4.98
|
| CAS号 |
1224606-06-7
|
| 相关CAS号 |
1224606-06-7 ; 1258299-72-7 (deleted)
|
| PubChem CID |
49785164
|
| 外观&性状 |
Colorless to light yellow liquid
|
| 密度 |
0.886±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
|
| 沸点 |
670.2±43.0 °C(Predicted)
|
| LogP |
13.647
|
| tPSA |
29.54
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
36
|
| 重原子数目 |
46
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
687
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
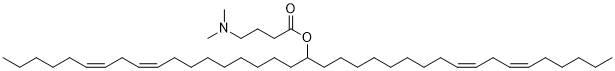
O(C(CCCN(C)C)=O)C(CCCCCCCC/C=C\C/C=C\CCCCC)CCCCCCCC/C=C\C/C=C\CCCCC
|
| InChi Key |
NRLNQCOGCKAESA-KWXKLSQISA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C43H79NO2/c1-5-7-9-11-13-15-17-19-21-23-25-27-29-31-33-35-38-42(46-43(45)40-37-41-44(3)4)39-36-34-32-30-28-26-24-22-20-18-16-14-12-10-8-6-2/h13-16,19-22,42H,5-12,17-18,23-41H2,1-4H3/b15-13-,16-14-,21-19-,22-20-
|
| 化学名 |
(6Z,9Z,28Z,31Z)-Heptatriaconta-6,9,28,31-tetraen-19-yl 4-(dimethylamino)butanoate
|
| 别名 |
D-Lin-MC3-DMA; MC 3; RV-28; MC3; DLin-MC3-DMA; (6Z,9Z,28Z,31Z)-Heptatriaconta-6,9,28,31-tetraen-19-yl 4-(dimethylamino)butanoate; Q0J6FQ6FKP; D-Lin-MC3-DMA (Excipient); RV 28; MC-3; RV28; DLin-MC3-DMA; Dlin-mc3-dma
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
Ethanol : ~125 mg/mL (~194.68 mM)
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~155.74 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 6.25 mg/mL (9.73 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浮液;超声助溶。
*生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 5 mg/mL (7.79 mM) in 5% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 50% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: 5 mg/mL (7.79 mM) in 5% DMSO + 95% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 配方 4 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.89 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;再向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;然后加入450 μL 生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 5 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (3.89 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100μL 25.0mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到900μL 20%SBE-β-CD生理盐水中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 6 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.89 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 配方 7 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.89 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若要配制1 mL工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清DMSO 储备液加入到900 μL 玉米油中,混匀。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.5574 mL | 7.7871 mL | 15.5741 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3115 mL | 1.5574 mL | 3.1148 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1557 mL | 0.7787 mL | 1.5574 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。