| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| 25g |
|
||
| 50g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) [1]
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
加合物形成随着地奥司明治疗的增加而增加,且呈剂量依赖性(5 μM 地奥司明时加合物形成增加至 7 倍)。 5 μM 地奥司明会增加 7,12-二甲基苯并(a)蒽的细胞毒性,导致 IC50 从估计的 1.2 μM 变为 400 nM。在研究浓度下,地奥司明本身不具有细胞毒性。在 MCF-7 细胞中,地奥司明以剂量和时间依赖性方式增加 CYPIAI 活性。孵育 24 小时后,地奥司明会产生剂量依赖性的 CYPIAI mRNA 升高,从而导致 CYPIAI mRNA 积累持续增加,并在孵育 48 小时后达到峰值[1]。
对致癌物激活途径的影响:在MCF - 7人乳腺上皮癌细胞中,用地奥司明处理后,乳腺致癌物7,12 - 二甲基苯并(a)蒽(DMBA)的代谢呈剂量依赖性增加。这通过DMBA - DNA加合物形成的增加以及DMBA诱导的细胞毒性来评估。地奥司明还使完整细胞中细胞色素P450 1A1(CYP1A1)的活性呈剂量和时间依赖性增加,与DMBA或芳基烃苯并(a)芘诱导的效果相当。它增加了CYP1A1基因的转录,通过CYP1A1 mRNA水平的升高来衡量,并激活了AhR对CYP1A1的外源性反应元件的DNA结合能力 [1] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在大鼠视网膜中,与缺血组相比,地奥司明显着提高了谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH)和总超氧化物歧化酶(T-SOD)水平,并显着降低了丙二醛(MDA)水平。 P<0.05)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性以及缺血/再灌注(I/R)引起的视网膜电图(ERG)a波和b波振幅的降低均受到抑制。 I/R损伤后整个视网膜厚度、内核层、内丛状层、视网膜外层和神经节细胞层细胞数量均显着减少(P<0.05),地奥辛显着改善了这些改变。视网膜的形状。在大鼠视网膜中,地奥司明还可以减少I/R引起的视网膜神经节细胞(RGC)的损失(P<0.05)[2]。
对视网膜缺血/再灌注损伤的保护作用:在大鼠视网膜缺血/再灌注损伤模型中,地奥司明对大鼠视网膜具有保护作用。它降低了氧化应激标志物丙二醛(MDA)的水平,增加了抗氧化酶超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GPx)的活性。它还降低了细胞凋亡关键酶半胱天冬酶 - 3的表达,并减少了视网膜中TUNEL阳性凋亡细胞的数量 [2] |
| 酶活实验 |
CYP1A1活性测定:从DMBA处理的MCF - 7细胞中分离微粒体。通过乙氧基试卤灵 - O - 脱乙基酶活性测定CYP1A1的活性。用地奥司明处理完整的MCF - 7细胞,导致CYP1A1活性呈剂量和时间依赖性增加。然而,与它的糖苷配基形式地奥司亭不同,地奥司明在微粒体中不直接抑制CYP1A1的活性 [1]
|
| 动物实验 |
Retina ischemia/reperfusion injury model: Rats were anesthetized. Retina ischemia was induced by increasing the intraocular pressure. After a certain period of ischemia, the intraocular pressure was released to allow reperfusion. Diosmin was dissolved in an appropriate vehicle (not specified in detail in the literature) and administered to rats by intragastric gavage at a certain dose (not clearly given in the literature) once a day for a specific number of days (not clearly stated in the literature). After the treatment period, the rats were sacrificed, and the retinas were collected for further analysis, including measurement of MDA, SOD, GPx, caspase - 3, and TUNEL assay [2]
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Diosmin is rapidly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. After a 900 mg single oral dose in a study using liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method, Cmax was 4.2±3.8 ng·mL-1, Tmax was 18.7±9.9 hours, and AUC0~96 was 185.4±166.2 ng·mL-1 in healthy volunteers. Another pharmacokinetic study of 5 adults revealed a Cmax of 417±94.1 ng/dL. Pharmacokinetic data show absence of urinary elimination for diosmin and its aglycone diosmetin. Minor metabolites are found to be eliminated in the urine as glucuronic acid conjugates. A pharmacokinetic study of 5 adults revealed a volume of distribution of 62.1±7.9 L. Metabolism / Metabolites Degradation products of diosmin such as alkyl-phenolic acids confirm a metabolic pattern similar to that of other flavonoids. Biological Half-Life Diosmin half-life ranges from 26 to 43 hours. One study using a liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method after a single 900 mg dose of diosmin demonstrated a half-life of 60.2±85.7 hours in healthy volunteers. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
Diosmin binds to serum albumin. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Diosmin is a flavone glycoside. It has been investigated for its effects on the carcinogen activation pathway mediated by the AhR in cancer cells and for its protective effect against retina ischemia/reperfusion injury. It is a natural dietary agonist of the AhR, which can increase CYP1A1 transcription and activity, potentially affecting the metabolism of carcinogens. In the context of retina ischemia/reperfusion injury, it exerts its protective effect through antioxidant and anti - apoptotic mechanisms [1][2]
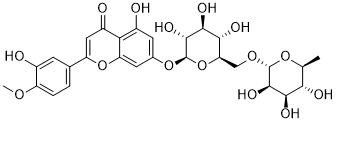
Diosmin is a disaccharide derivative that consists of diosmetin substituted by a 6-O-(alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl moiety at position 7 via a glycosidic linkage. It has a role as an antioxidant and an anti-inflammatory agent. It is a glycosyloxyflavone, a rutinoside, a disaccharide derivative, a monomethoxyflavone and a dihydroxyflavanone. It is functionally related to a diosmetin. Chronic venous insufficiency is a common condition the western population. Compression and pharmacotherapy are frequently used to manage chronic venous insufficiency, improving circulation and symptoms of venous disease. Diosmin is a bioflavonoid isolated from various plants or synthesized from [hesperidin]. It is used for the improvement of capillary fragility or venous insufficiency, including chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) and hemorrhoids. Diosmin is widely available over-the-counter and demonstrates a favourable a favorable safety profile. Diosmin has been reported in Angelica gigas, Abies nephrolepis, and other organisms with data available. A bioflavonoid that strengthens vascular walls. See also: Agathosma betulina leaf (part of). Drug Indication Diosmin is used over-the-counter alone or with ingredients such as [hesperidin] and [diosmetin] to support vein and capillary function. Mechanism of Action Diosmin helps to maintain circulatory system structure and function, particularly vein strength and competence. The molecular mechanism of action of diosmin has not been established. Several resources indicate that diosmin binds to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor, however clinical relevance to vascular function is unknown. One study demonstrates that oral diosmin exerts effects on the in vitro metabolism of noradrenaline by varicose veins, potentially benefitting vascular health. Pharmacodynamics Diosmin is a venoactive drug supporting circulatory health through various actions on blood vessels; it supports lymphatic drainage and improves microcirculation while increasing venous tone and elasticity. For these reasons, diosmin is frequently taken by individuals with chronic venous disease to support vascular health and has been demonstrated to improve quality of life. In addition to the above effects, diosmin exerts antioxidant activity and scavenges oxygen free radicals, reducing levels of oxidative stress normally detected through biomarkers such as prostaglandins isoprostane precursors. In one clinical study, mean content of TNF alpha, VEGF-C, VEGF-A IL-6, in addition to FGF2 were decreased by after the therapy with diosmin; findings were statistically significant. Additionally, a decrease in edema and mean leg circumference of patients taking diosmin for three months was observed in a clinical study. Diosmin has been demonstrated to enhance the metabolism of glucose in diabetic disorders. |
| 分子式 |
C28H32O15
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
608.54
|
| 精确质量 |
608.174
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 55.26; H, 5.30; O, 39.44
|
| CAS号 |
520-27-4
|
| PubChem CID |
5281613
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to light brown solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.7±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
926.8±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
277-278°C
|
| 闪点 |
305.2±27.8 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.712
|
| LogP |
2.05
|
| tPSA |
238.2
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
8
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
15
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
43
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
995
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
10
|
| SMILES |
C[C@H]1[C@@H]([C@H]([C@H]([C@@H](O1)OC[C@@H]2[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H](O2)OC3=CC(=C4C(=C3)OC(=CC4=O)C5=CC(=C(C=C5)OC)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O
|
| InChi Key |
GZSOSUNBTXMUFQ-YFAPSIMESA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C28H32O15/c1-10-21(32)23(34)25(36)27(40-10)39-9-19-22(33)24(35)26(37)28(43-19)41-12-6-14(30)20-15(31)8-17(42-18(20)7-12)11-3-4-16(38-2)13(29)5-11/h3-8,10,19,21-30,32-37H,9H2,1-2H3/t10-,19+,21-,22+,23+,24-,25+,26+,27+,28+/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
5-hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-7-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-[[(2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxymethyl]oxan-2-yl]oxychromen-4-one
|
| 别名 |
diosmin; 520-27-4; Barosmin; Diosmine; Venosmine; Flebosten; Tovene; Ven-Detrex;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~164.33 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.11 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (4.11 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液添加到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.6433 mL | 8.2164 mL | 16.4328 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3287 mL | 1.6433 mL | 3.2866 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1643 mL | 0.8216 mL | 1.6433 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
|