| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Dynamin-dependent transferrin endocytosis (IC50 = 5.7 μM)
Dyngo-4a specifically targets dynamin GTPase (isoforms dynamin 1, 2, 3) with IC50 values of 1.4 μM (dynamin 1), 2.3 μM (dynamin 2), and 2.7 μM (dynamin 3) for inhibiting GTPase activity [1] Dyngo-4a binds to the GTP-binding pocket of dynamin, blocking GTP hydrolysis without inhibiting other GTPases (e.g., Ras, Rho, Rab) at concentrations up to 50 μM [1] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
大 GTP 酶动力蛋白可裂解膜结合的网格蛋白包被的囊泡。在细胞生理学中,内吞作用(细胞外物质和部分细胞质膜的内化)至关重要。 Hydroxy Dynasore 的 IC50 值为 2.7 μM 和 0.38 μM,在 GTPase 测定中抑制动力蛋白 I (Dyn I) 活性 [1],无论是否存在 0.06% Tween-80。在 U2OS 细胞中,Hydroxy Dynasore 在网格蛋白介导的内吞作用 (CME) 中抑制 Tfn-A594 摄取,IC50 为 5.7 μM [1]。在不存在 Tween -80 的情况下,Hydroxy Dynasore 的 IC50 值分别为 0.38 μM 和 1.1 μM,而在存在 Tween -80 的情况下,IC50 值分别为 4.9 μM 和 30.0 μM。在此 GTPase 实验中,与 Sf21 细胞的 DynII 和 DynII(源自 Sf21 细胞的重组蛋白)相比,Hydroxy Dynasore 对 DynI 的选择性高出 2.1 倍 [1]。在运动神经末梢和培养的海马神经元中,Hydroxy Dynasore 抑制 BoNT/A-Hc 的吸收 [2]。当暴露于 Hydroxy Dynasore(1-100 μM;添加 Alexa Fluor 488-BoNT/A-Hc 前 20 分钟)时,海马神经元会去极化;这种抑制作用具有剂量依赖性,IC50 为 16.0 μM[2]。
5 μM Dyngo-4a 抑制 HeLa 和 COS-7 细胞的网格蛋白介导的内吞作用,使转铁蛋白内化减少 90%, potency 高于 Dynasore(20 μM 仅减少 85%)[1] - 3 μM Dyngo-4a 阻断 NIH 3T3 细胞的小窝蛋白介导的内吞作用,使霍乱毒素 B 亚基内化减少 82% [1] - 2-8 μM Dyngo-4a 阻止大鼠皮质神经元中 A 型肉毒神经毒素(BoNT/A)的内吞,减少 75% 的 SNAP-25 切割,保护神经元活力 [2] - Dyngo-4a(1-10 μM)对正常细胞(HeLa、神经元、NIH 3T3)毒性极低,细胞活力 > 90%,即使在 20 μM 浓度下仍无明显毒性 [1][2] - 5 μM Dyngo-4a 在体外干扰动力蛋白依赖的膜裂变,抑制 88% 的动力蛋白诱导的巨型单层囊泡(GUVs)成管 [1] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在 CD-1 小鼠的膈神经膈肌抽搐模型中,Hydroxy Dynasore(腹腔注射;30 mg/kg;注射 BoNT/A 前 1.5-2 小时)再次提供针对 BoNT/A 诱导的麻痹的保护作用 [2]。
Dyngo-4a阻断BoNT/A诱导的瘫痪,延缓肉毒杆菌中毒的发作[2] 研究人员确定了Dyngo-4a是否可用于预防纯化BoNT/A引起的肌肉麻痹。我们使用大鼠半膈肌抽搐模型对此进行了研究。以0.2 Hz的频率刺激肌肉,并在6-8小时内记录收缩力。每种情况下抽搐记录的代表性痕迹如图7A所示。未经治疗和Dyngo-4a治疗的对照肌肉在长达8小时的时间里都没有出现任何收缩下降的迹象。添加BoNT/A后,收缩幅度减小,与BoNT诱导的瘫痪一致。在添加BoNT/A之前,用Dyngo-4a预处理的肌肉收缩强度下降明显较小(图7A和表2)。收缩力以收缩下降百分比表示,与四参数逻辑斯谛曲线非常吻合(R2=0.999和0.994)(表2)。t½和Hill斜率均存在显著差异(分别为p=0.0007和0.0018)。这些结果表明,与BoNT/A对照组相比,Dyngo-4a治疗组的肌肉收缩下降和达到50%下降的时间都显著增加。这些结果共同表明,Dyngo-4a对BoNT/A诱导的肌肉麻痹具有显著的保护作用。 最后,研究人员调查了Dyngo-4a是否可以在体内小鼠模型中预防肉毒中毒的发生。CD-1小鼠腹腔注射Dyngo-4a 在小鼠肉毒中毒模型中,Dyngo-4a 腹腔给药(10 mg/kg)于 BoNT/A 注射后 30 分钟进行,可将瘫痪发作时间延迟 12 小时,48 小时存活率从溶媒组的 0% 提升至 40% [2] - 在体外小鼠膈神经 - 半膈肌制备物中,Dyngo-4a(10 μM,灌流 60 分钟)保护神经肌肉功能免受 BoNT/A 毒性影响,保留 65% 的抽搐张力(溶媒组仅保留 20%)[2] |
| 酶活实验 |
Dynamin GTP酶测定[1]
孔雀石绿比色GTP酶测定如10所述。Dynamin I活性在其SAI活性状态下进行测量,或通过三种不同的方法进行刺激。由于每种刺激在不同程度上激活动力蛋白,因此每种测定都需要不同的动力蛋白浓度。首先,超声波处理的PS脂质体10刺激了最大的动态蛋白活性。纯化的动态蛋白I(10-20nM,稀释于:6mM Tris-HCl、20mM NaCl和0.01%吐温80,pH 7.4)在GTPase缓冲液(5mM Tris-HHCl、10mM NaCl、2mM Mg2+、0.05%吐温80,pH7.4,1µg/mL亮肽和0.1mM PMSF)和GTP 0.3mM的96孔板中,在37°C下在试验化合物存在下孵育30分钟,最终测定体积为150μL。用10μL的0.5 M乙二胺四乙酸(EDTA)(pH 7.4)终止反应,并加入孔雀绿溶液(40μL:2%w/v钼酸铵四水合物、0.15%w/v孔雀绿和4 M HCl)5分钟。第二,使用相同的方案,用10μg/mL紫杉醇稳定的预成型牛脑微管刺激动力蛋白(20 nM)。第三,dynmin I(50 nM)被1μM的重组生长因子受体结合蛋白2(grb2)刺激,grb2是一种含有SH3(Src同源性)的蛋白,其刺激dynmin的效率比脂质体或微管54低5-10倍。测定条件如上所述。最后,使用高浓度的dynamin测量dynamin(500 nM)SAI活性,这促进了其协同自组装成环(但不是螺旋)26。GTP酶或内吞试验中DMSO的最终浓度分别至多为3.3%或1%,但通常为1%。动态蛋白I的GTP酶测定不受DMSO的影响,高达3.3%。将化合物作为30mM原液溶解在100%DMSO中。这些储备溶液可以在-20°C下储存几个月。随后将化合物稀释到由20 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.4配制的50%DMSO溶液中,并再次稀释到最终测定中。为了分析Dyngo-4a抑制的动力学,在浓度范围为0.5至6μM的Dyngo-4a存在下,将终浓度为17 nM的动态蛋白I与含有PS(2µg/mL)和不同量GTP(50-250μM)的GTP酶缓冲液一起孵育。30分钟后,通过加入EDTA(0.5mM,pH 7.4)停止反应。 突触体释放谷氨酸[1] 突触体中谷氨酸的释放如前60所述进行,但变化很小。该测定在37°C下在Perkin-Elmer LS50荧光计中进行。在刺激谷氨酸释放之前,将对照(1%DMSO)和经Dyngo-4a处理的样品在化合物存在下孵育30分钟。 使用FM1-43[1]对SV周转进行荧光成像 将神经元培养物从培养基中取出,在培养基[170 mM NaCl、3.5 mM KCl、0.4 mM KH2PO4、20 mM TES(N-三[羟基甲基]-甲基-2-氨基乙烷磺酸)、5 mM NaHCO3、5 mM葡萄糖、1.2 mM Na2SO4、1.2 mM MgCl2和1.3 mM CaCl2(pH 7.4)]中放置10分钟。然后将培养物安装在华纳成像室(RC‐21BRFS)中。通过一系列短暂的动作电位(80 Hz持续10秒,100 mA和1毫秒脉冲宽度,使用嵌入成像室的铂线输送)引发SV翻转,在阴道膜上加载FM1-43(10μM)。刺激后,染料保持存在1分钟,以确保所有回收膜都被标记(S1负载)。在10分钟的休息期后,使用两个连续的最大刺激从神经末梢卸载积聚的染料,培养基中补充有50 mM KCl(去除50 mM NaCl以保持渗透压)。由于染料损失导致的荧光减少提供了刺激期间翻转的突触小泡总数的估计(S1)。休息20分钟后,重复S1方案(S2加载和卸载)。因此,对于任何选定的神经末梢,S2响应都具有匹配的个体内部控制(S1)。Dyngo化合物Dyngo-4a(30μM)在S2加载(监测对内吞作用的影响)或S2卸载(胞吐作用)之前存在15分钟。 辣根过氧化物酶标记内吞作用途径[1] 如前所述,对颗粒神经元进行电子显微镜处理40。简而言之,将细胞转移到培养基中10分钟,随后在有或没有30μM的Dyngo-4a的情况下培养15分钟。接下来,在添加了HRP(10mg/mL)的培养基中,在有或无Dyngo-4a的条件下,用800个动作电位(80Hz)刺激培养物。 Dynamin II GTP酶测定[1] 测定条件基于动态蛋白I测定,但包含修改。重组动力蛋白II以50 nM的浓度使用,受10µg/mL PS刺激。在终止前,允许GTP酶反应在37°C下发生90分钟。 血浆蛋白结合[1] 使用基于先前发表的方法56的梯度洗脱固定化人血清白蛋白柱(ChromTech手性-HSA,50×3.0 mm,5µm)估算血浆蛋白结合。 葡聚糖摄取的荧光成像[1] 如前所述,监测四甲基罗丹明葡聚糖(40kDa)在CGN神经末梢的摄取情况。简而言之,将细胞在培养基中放置10分钟,然后在四甲基罗丹明葡聚糖(50μM)的存在下用800个动作电位(80 Hz,10秒)刺激。Dyngo化合物Dyngo-4a(30μM)在动作电位刺激前存在15分钟,包括动作电位刺激。 动力蛋白 GTP 酶活性测定:重组动力蛋白(亚型 1/2/3)与 [γ-32P]GTP 底物共孵育。加入系列浓度的 Dyngo-4a(0.1 μM 至 20 μM),37°C 孵育 60 分钟。通过检测释放的 32Pi 定量 GTP 水解,从抑制作用的剂量 - 反应曲线计算 IC50 值 [1] - 动力蛋白 -GTP 结合测定:荧光标记的 mant-GTP 与重组 dynamin 2 共孵育。加入系列浓度的 Dyngo-4a(0.5 μM 至 30 μM),25°C 下测量荧光偏振。推导 Dyngo-4a 与动力蛋白结合的解离常数(Kd)为 1.8 μM [1] |
| 细胞实验 |
基于细胞的内吞作用[1]
如10所述,对大量血清饥饿的细胞进行了U2OS细胞中Alexa 594-Tfn内吞作用抑制的定量分析。如57所述,使用FM1-43监测培养的CGN中的突触囊泡循环(见支持信息)。如前58所述,使用NIH3T3细胞中的CT内化(使用Tfn作为对照)测量了动态非依赖性内吞作用,但略有变化(见支持信息)。每个数据点的平均单元格数量约为1200。使用GraphPad Prism 5计算IC50值,数据表示为三个孔和约1200个细胞的平均值±95%置信区间(CI)。 内化研究[2] 培养的海马神经元由18岁C57BL/6胚胎制备,并与星形胶质细胞共培养,如前所述。在使用前,让神经元在体外成熟至少14天。从共培养物中取出神经元,在37°C下与100 nm Alexa Fluor 488 BoNT/A-Hc在低K+缓冲液(15 mm HEPES、145 mm NaCl、5.6 mm KCl、2.2 mm CaCl2、0.5 mm MgCl2、5.6 mm d-葡萄糖、0.5 mm抗坏血酸、0.1%牛血清白蛋白(BSA)、pH 7.4)或高K+缓冲溶液(改性为含有95 mm NaCl和56 mm KCl)中孵育5分钟,如所示,有或没有Dyngo-4a或Dynasore。用4%多聚甲醛固定细胞,进行免疫细胞化学处理,成像,并使用Zen软件或LaserPix进行分析。 SNAP25裂解试验[2] 从共培养中取出培养的海马神经元,用低K+缓冲液洗涤一次。然后用DMSO或Dyngo-4a(30μm)处理20分钟。在DMSO或Dyngo-4a持续存在的情况下,用含和不含BoNT/A的高K+缓冲液(100 pm)刺激神经元5分钟。用含DMSO或Dyango-4a的低K+缓冲溶液洗涤细胞五次,静置90分钟,然后转移回与星形胶质细胞和条件培养基共培养24小时。然后将神经元从共培养中取出,进行蛋白质印迹处理,如下:用冰冷的PBS洗涤细胞两次,然后刮入20 mm HEPES,150毫米氯化钠,pH 7.5,含有蛋白酶抑制剂。收集细胞膜并将其重新悬浮在含有10%β-巯基乙醇的Laemmli样品缓冲液中。样品在SDS-PAGE上运行,然后转移到PVDF膜上。使用针对SNAP25切割产物设计的抗体探测膜上切割的SNAP25,该抗体不识别全长SNAP25。将条带的强度归一化为β-肌动蛋白,并使用积分强度来确定相对于对照的切割量。 网格蛋白介导的内吞实验:HeLa 细胞与 Alexa Fluor 488 标记的转铁蛋白及 Dyngo-4a(0.5-10 μM)共孵育 30 分钟。流式细胞术定量内化的转铁蛋白,相对于溶媒对照组计算抑制率 [1] - 小窝蛋白介导的内吞实验:NIH 3T3 细胞与 FITC 标记的霍乱毒素 B 亚基及 Dyngo-4a(1-15 μM)共孵育 45 分钟。荧光显微镜计数内化的毒素,确定抑制率 [1] - BoNT/A 毒性实验:大鼠皮质神经元用 Dyngo-4a(2-8 μM)预处理 30 分钟,随后暴露于 BoNT/A(1 nM)24 小时。Western blot 检测 SNAP-25 切割,MTT 法评估神经元活力 [2] - 动力蛋白诱导的膜成管实验:巨型单层囊泡(GUVs)与重组 dynamin 2 及 Dyngo-4a(1-10 μM)共孵育 20 分钟。相差显微镜观察成管情况,定量成管 GUVs 的百分比 [1] |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: CD-1 mice[2].
Doses: 30 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip)injection; 1.5–2 h before BoNT/A injection Experimental Results: Protected BoNT/A-induced paralysis in vivo. Rat Phrenic Nerve-Hemidiaphragm Twitch Experiments[2] The hemidiaphragm and innervating phrenic nerve were dissected from 5-week-old male Wistar rats. The nerve muscle preparation was suspended in an organ bath containing carbogen-bubbled Tyrode's solution (136.7 mm NaCl, 2.68 mm KCl, 1.75 mm NaH2PO4, 16.3 mm NaHCO3, 1 mm MgCl2, 1 mm CaCl2, 7.8 mm d-glucose). The nerve was stimulated with 0.1-ms square pulses of 10 V at 0.2 Hz and the force of contractions (mN) was recorded through Powerlab and Bridge Amp Systems with Chart software. Upon reaching stable contractions, 30 μm Dyngo-4a or vehicle was added for 1 h prior to the addition of BoNT/A (100 pm). Control preparations were as indicated. Contractions were recorded over 6–8 h and analyzed by converting contractile strength to percentage decline. In Vivo Assay[2] BoNT/A was diluted in 0.9% saline containing 0.1 mg/ml BSA, immediately prior to use. Female CD-1 mice (30–40 g) were injected intraperitoneally with 1 mg of Dyngo-4a (which is 30 mg/kg body weight) or vehicle (1/9 NMP/PEG300 (1 part NMP to 9 parts PEG300) in PBS). 1.5–2 h later, mice were injected with 2LD50 BoNT/A via the tail vein. A top-up of 1 mg of Dyngo-4a or vehicle was administered 4.5–8 h after the initial intraperitoneal injection. Mice were constantly monitored for signs of botulism and euthanized upon development of acute respiratory distress. Dyngo-4a was made up in DMSO (30 mm) for in vitro experiments and dissolved in a formulation containing 1-methyl-2-pyrrolidione (NMP) and polyethylene glycol 300 (PEG300) (1 part NMP to 9 parts PEG300), then diluted 1/9 in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) for in vivo experiments. Mouse botulism model: Female CD-1 mice (20-25 g) were injected intraperitoneally with BoNT/A (1 LD50). Thirty minutes later, mice were randomized into groups (n=10/group) and treated with: (1) vehicle (DMSO + saline) i.p., (2) Dyngo-4a (10 mg/kg) i.p. Mice were monitored for paralysis and survival every 2 hours for 48 hours [2] - Ex vivo phrenic nerve-hemidiaphragm preparation: Male C57BL/6 mice (8-10 weeks old) were euthanized, and phrenic nerve-hemidiaphragm complexes were dissected. Tissues were perfused with Krebs solution containing Dyngo-4a (10 μM) for 60 minutes, then exposed to BoNT/A (0.5 nM). Twitch tension was measured by a force transducer for 24 hours [2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Dyngo-4a showed low in vitro cytotoxicity: HeLa cells (IC50 > 50 μM), rat cortical neurons (IC50 > 40 μM), and NIH 3T3 cells (IC50 > 60 μM) [1][2]
- In acute toxicity studies in mice (single i.p. dose up to 20 mg/kg), Dyngo-4a caused no significant weight loss, convulsions, or organ abnormalities [2] - Dyngo-4a (10 μM) did not inhibit human cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP3A4) in vitro [1] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Dyngo-4a is dynamin inhibitor. It has a role as an EC 3.6.5.5 (dynamin GTPase) inhibitor.
Dynamin GTPase activity increases when it oligomerizes either into helices in the presence of lipid templates or into rings in the presence of SH3 domain proteins. Dynasore is a dynamin inhibitor of moderate potency (IC₅₀ ~ 15 μM in vitro). We show that dynasore binds stoichiometrically to detergents used for in vitro drug screening, drastically reducing its potency (IC₅₀ = 479 μM) and research tool utility. We synthesized a focused set of dihydroxyl and trihydroxyl dynasore analogs called the Dyngo™ compounds, five of which had improved potency, reduced detergent binding and reduced cytotoxicity, conferred by changes in the position and/or number of hydroxyl substituents. The Dyngo compound 4a was the most potent compound, exhibiting a 37-fold improvement in potency over dynasore for liposome-stimulated helical dynamin activity. In contrast, while dynasore about equally inhibited dynamin assembled in its helical or ring states, 4a and 6a exhibited >36-fold reduced activity against rings, suggesting that they can discriminate between helical or ring oligomerization states. 4a and 6a inhibited dynamin-dependent endocytosis of transferrin in multiple cell types (IC₅₀ of 5.7 and 5.8 μM, respectively), at least sixfold more potently than dynasore, but had no effect on dynamin-independent endocytosis of cholera toxin. 4a also reduced synaptic vesicle endocytosis and activity-dependent bulk endocytosis in cultured neurons and synaptosomes. Overall, 4a and 6a are improved and versatile helical dynamin and endocytosis inhibitors in terms of potency, non-specific binding and cytotoxicity. The data further suggest that the ring oligomerization state of dynamin is not required for clathrin-mediated endocytosis.[1] The botulinum neurotoxins (BoNTs) are di-chain bacterial proteins responsible for the paralytic disease botulism. Following binding to the plasma membrane of cholinergic motor nerve terminals, BoNTs are internalized into an endocytic compartment. Although several endocytic pathways have been characterized in neurons, the molecular mechanism underpinning the uptake of BoNTs at the presynaptic nerve terminal is still unclear. Here, a recombinant BoNT/A heavy chain binding domain (Hc) was used to unravel the internalization pathway by fluorescence and electron microscopy. BoNT/A-Hc initially enters cultured hippocampal neurons in an activity-dependent manner into synaptic vesicles and clathrin-coated vesicles before also entering endosomal structures and multivesicular bodies. We found that inhibiting dynamin with the novel potent Dynasore analog, Dyngo-4a(TM), was sufficient to abolish BoNT/A-Hc internalization and BoNT/A-induced SNAP25 cleavage in hippocampal neurons. Dyngo-4a also interfered with BoNT/A-Hc internalization into motor nerve terminals. Furthermore, Dyngo-4a afforded protection against BoNT/A-induced paralysis at the rat hemidiaphragm. A significant delay of >30% in the onset of botulism was observed in mice injected with Dyngo-4a. Dynamin inhibition therefore provides a therapeutic avenue for the treatment of botulism and other diseases caused by pathogens sharing dynamin-dependent uptake mechanisms.[2] Dyngo-4a is a second-generation, potent inhibitor of dynamin GTPase, optimized from Dynasore with higher affinity and specificity [1] The mechanism of Dyngo-4a involves blocking dynamin-dependent membrane fission events by inhibiting GTP hydrolysis, disrupting both clathrin- and caveolin-mediated endocytosis [1] Dyngo-4a exhibits therapeutic potential for botulism by preventing BoNT/A endocytosis into neurons [2] Dyngo-4a is a valuable tool compound for studying dynamin-dependent cellular processes, with improved potency and lower off-target effects compared to first-generation dynamin inhibitors [1] |
| 分子式 |
C18H14N2O5
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
338.31
|
|
| 精确质量 |
338.09
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 63.90; H, 4.17; N, 8.28; O, 23.64
|
|
| CAS号 |
1256493-34-1
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
136227923
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light brown to brown solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.5±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.683
|
|
| LogP |
5.12
|
|
| tPSA |
122.38
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
5
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
25
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
500
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
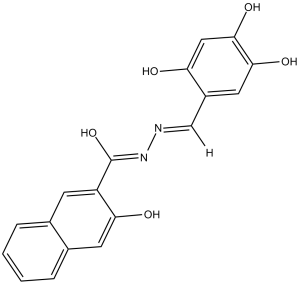
C1=CC=C2C=C(C(=CC2=C1)C(=O)N/N=C/C3=CC(=C(C=C3O)O)O)O
|
|
| InChi Key |
UAXHPUSKEWEOAP-DJKKODMXSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H14N2O5/c21-14-8-17(24)16(23)7-12(14)9-19-20-18(25)13-5-10-3-1-2-4-11(10)6-15(13)22/h1-9,21-24H,(H,20,25)/b19-9+
|
|
| 化学名 |
3-Hydroxynaphthalene-2-carboxylic acid 2-[(2,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)methylene]hydrazide
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (6.15 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 +5% Tween-80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80+,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9559 mL | 14.7793 mL | 29.5587 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5912 mL | 2.9559 mL | 5.9117 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2956 mL | 1.4779 mL | 2.9559 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
|
|---|
|
|