| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
事实证明,外用艾芬康唑溶液(0.25 至 1%)对治疗 10 只豚鼠的指间足癣和体癣有益,且呈剂量依赖性。 30天和9天的随访调查显示,用1%艾芬康唑治疗的动物体癣和足癣的复发率分别为30%和20%。当在真菌接种前 48 小时向背部皮肤施用单剂量的 1% 伊夫康唑时,十分之九的小鼠可免受皮肤癣菌病的侵害,这表明活性伊夫康唑在分娩后仍保持活性,并在皮肤组织中保留至少 48 小时[2 ]。
|
|---|---|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Administration of Jublia by the topical route leads to low systemic efinaconazole concentrations. Systemic absorption of efinaconazole in 18 patients with severe onychomycosis was determined after application of Jublia once daily for 28 days to patients' 10 toenails and adjacent skin. The concentration of efinaconazole in plasma was determined at multiple time points over the course of 24-hour periods on days 1, 14, and 28. Efinaconazole mean plasma Cmax on Day 28 was 0.67 ng/mL. The mean plasma concentration versus time profile was generally flat over the course of treatment. In onychomycosis patients, the steady state plasma concentration range was 0.1-1.5 ng/mL for efinaconazole and 0.2-7.5 ng/mL for H3 metabolite. /MILK/ Efinaconazole and or its metabolites were excreted in milk from lactating rats. The radioactivity concentration in milk was higher than that in plasma concentration for 24 hours after the administration of 14C-efinaconazole to lactating rats. However, the elimination half-life of the milk radioactivity was about one half of that of the plasma radioactivity, suggesting that efinaconazole or its metabolites was not retained in milk. /MILK/ It is not known whether efinaconazole is excreted in human milk. Efinaconazole penetrates through nails in vitro after Jublia administration, suggesting drug penetrations to the site of fungal infection in the nail and the nail bed, though clinical relevance is unknown. The penetration of Jublia was evaluated in an in vitro investigation after daily application of radiolabelled efinaconazole (10%) to human nails for 28 days at 55.1 uL/sq cm. After 28 days, the cumulative radioactivity in the receptor fluid and in the nail plate, on a percent basis of total administered radioactivity, was 0.03% and 0.16% (3.11 mg eq/g), respectively. The flux rate was relatively constant from Days 18 to 28, mean 1.40 ug eq/sq cm/day, suggesting steady state attainment. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Efinaconazole (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Efinaconazole is extensively metabolized. It is oxidatively metabolized, cleaved and conjugated to glucuronic acid. The studies have identified 5 metabolites (H1, H2, H3, H4 and H5) of efinaconazole. In rats and minipigs, H3 was the major efinaconazole plasma metabolite, and its levels usually equaled or exceeded those of parent drug. The in vitro and in vivo metabolite profiles in nonclinical species were similar to human with no unique human metabolite(s). Jublia (efinaconazole) is extensively metabolized through oxidative/reductive processes, with the potential of additional metabolite glucuronidation. Analysis of human plasma confirmed that H3 is the only major efinaconazole metabolite. Efinaconazole metabolites, but not parent drug, were excreted in the bile and urine of rats and dogs which suggests complete metabolism of efinaconazole prior to excretion. Most of the absorbed radioactivity was eliminated during the first 72 hours after dermal and SC dosing in urine and feces. Biological Half-Life 29.9 hours in healthy patients. In a ... study of healthy volunteers, the plasma half-life of Jublia at day 10 following repeat treatment applications repeated to all 10 toenails was 29.9 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Efinaconazole is used as antifungal agent. It is indicated for the topical treatment of onychomycosis of the toenail(s) due to Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: Efinaconazole 10% solution did not cause contact sensitization and induced only minimal skin irritation in human studies. ANIMAL STUDIES: Efinaconazole was generally well tolerated in rats with repeated daily doses of up to 30 (males) and 40 (females) mg/kg. In 13 week dermal toxicity in mice, an increase in liver weight and minimal to mild panlobular hepatocellular hypertrophy was observed, the local application of the drug and/or the vehicle alone resulted in higher incidences of hyperkeratosis, epidermal hyperplasia, and mononuclear infiltrates in the treated skin. Higher concentration of the test article were associated with higher severity of these cutaneous changes compared to controls, and a low incidence of the formation of erosion/ulcers at the treated site. Efinaconazole 10% solution applied intratympanically to the guinea pig middle ear caused significant middle ear inflammation and hearing impairment. In dermal toxicity studies, efinaconazole was well tolerated in minipigs at doses up to 150-200 mg /kg/day. Slight to moderate skin reactions were noted macroscopically and microscopically in all test article groups and vehicle control and consisted of hyperkeratosis, acanthosis and localized inflammation. These skin effects were attributed to the vehicle and were not considered adverse due to the mild severity of changes. A 2-year dermal carcinogenicity study in mice was conducted with daily topical administration of 3%, 10% and 30% efinaconazole solution. Severe irritation was noted at the treatment site in all dose groups, which was attributed to the vehicle and confounded the interpretation of skin effects by efinaconazole. The high dose group was terminated at week 34 due to severe skin reactions. No drug-related neoplasms were noted at doses up to 10% efinaconazole solution (248 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons). In a pre- and post-natal development study in rats, subcutaneous doses of 1, 5 and 25 mg/kg/day efinaconazole were administered from the beginning of organogenesis (gestation day 6) through the end of lactation (lactation day 20). In the presence of maternal toxicity, embryofetal toxicity (increased pre-natal pup mortality, reduced live litter sizes and increased post-natal pup mortality) was noted at 25 mg/kg/day. No embryofetal toxicity was noted at 5 mg/kg/day (17 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons). No effects on post-natal development were noted at 25 mg/kg/day (89 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons). Subcutaneous doses of 1, 5, and 10 mg/kg/day efinaconazole were administered during the period of organogenesis (gestational days 6-19) to pregnant female rabbits. In the presence of maternal toxicity, there was no embryofetal toxicity or malformations at 10 mg/kg/day (154 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons). Efinaconazole revealed no evidence of mutagenic or clastogenic potential based on the results of two in vitro genotoxicity tests (Ames assay and Chinese hamster lung cell chromosome aberration assay) and one in vivo genotoxicity test (mouse peripheral reticulocyte micronucleus assay). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Topical efinaconazole has not been studied during breastfeeding. Because maternal blood levels are very low after topical application to the toenails, it is unlikely that a measurable amount of the drug will enter the breastmilk. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
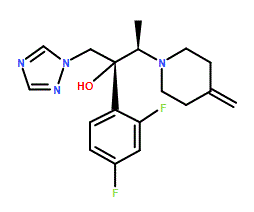
Efinaconazole is a member of the class of triazoles that is butan-2-ol which is substituted at positions 1, 2, and 3 by 1,2,4-triazol-1-yl, 2,4-difluorophenyl, and 4-methylenepiperidin-1-yl groups, respectively (the 2R,3R stereoisomer). It is an antifungal drug used for the topical treatment of onychomycosis (a nail infection caused mainly by dermatophytes). It has a role as an EC 1.14.13.70 (sterol 14alpha-demethylase) inhibitor. It is an organofluorine compound, an olefinic compound, a member of piperidines, a tertiary alcohol, a tertiary amino compound, a conazole antifungal drug and a triazole antifungal drug.
Efinaconazole is a 14 alpha-demethylase inhibitor indicated in the treatment of fungal infection of the nail, known as onychomycosis. It was approved for use in Canada and the USA in 2014 and is marketed by Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America LLC under the name Jublia. Efinaconazole is an Azole Antifungal. Efinaconazole is a triazole compound, with antifungal activity. Upon administration, efinaconazole targets, binds to and inhibits 14-alpha-demethylase, a cytochrome P450-dependent enzyme. Inhibition of 14-alpha-demethylase prevents the conversion of lanosterol to ergosterol, an important component of the fungal cell wall. Inhibition of ergosterol synthesis changes the fungal cell membrane composition and integrity, alters membrane permeability and eventually leads to fungal cell lysis. Drug Indication Indicated in the treatment of fungal infection of the nail, known as onychomycosis. FDA Label Treatment of onychomycosis Mechanism of Action Efinaconazole is an azole antifungal. Efinaconazole inhibits fungal lanosterol 14α-demethylase involved in the biosynthesis of ergosterol, a constituent of fungal cell membranes. Efinaconazole is a triazole antifungal agent. Efinaconazole inhibits fungal lanosterol 14alpha-demethylase involved in ergosterol biosynthesis. The accumulation of 14alpha-methyl sterols and subsequent loss of ergosterol in the fungi cell wall may be responsible for the fungistatic and fungicidal activity of efinaconazole. Efinaconazole is shown in vitro to be substantially adsorbed to keratin but keratin binding is weak. Efinaconazole's low keratin affinity is expected to result in increased availability of free drug to the nail infection site. Therapeutic Uses Antifungal Agents Jublia (efinaconazole) topical solution, 10% is an azole antifungal indicated for the topical treatment of onychomycosis of the toenail(s) due to Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes. /Included in US product label/ We sought to evaluate the efficacy of efinaconazole topical solution, 10%, in patients with onychomycosis and coexisting tinea pedis. We analyzed 1,655 patients, aged 18 to 70 years, randomized (3:1) to receive efinaconazole topical solution, 10%, or vehicle from two identical multicenter, double-blind, vehicle-controlled 48-week studies evaluating safety and efficacy. The primary end point was complete cure rate (0% clinical involvement of the target toenail and negative potassium hydroxide examination and fungal culture findings) at week 52. Three groups were compared: patients with onychomycosis and coexisting interdigital tinea pedis on-study (treated or left untreated) and those with no coexisting tinea pedis. Treatment with efinaconazole topical solution, 10%, was significantly more effective than vehicle use irrespective of the coexistence of tinea pedis or its treatment. Overall, 352 patients with onychomycosis (21.3%) had coexisting interdigital tinea pedis, with 215 of these patients (61.1%) receiving investigator-approved topical antifungal agents for their tinea pedis in addition to their randomized onychomycosis treatment. At week 52, efinaconazole complete cure rates of 29.4% were reported in patients with onychomycosis when coexisting tinea pedis was treated compared with 16.1% when coexisting tinea pedis was not treated. Both cure rates were significant compared with vehicle (p = 0.003 and 0.045, respectively), and in the latter subgroup, no patients treated with vehicle achieved a complete cure. Treatment of coexisting tinea pedis in patients with onychomycosis enhances the efficacy of once-daily topical treatment with efinaconazole topical solution, 10%. A number of comorbidities and risk factors complicate the successful management of onychomycosis. Underlying conditions and patient characteristics, such as tinea pedis, age, and obesity, contribute to risk, whereas comorbidities, such as diabetes and psoriasis, can increase susceptibility to the disease. There are limited data on treatment effectiveness in these patients. Here, the authors review post hoc analyses of efinaconazole topical solution, 10%, in mild-to-moderate onychomycosis and present new data in terms of age and obesity. The only post hoc analysis to report significant differences so far is gender, where female patients do much better; however, the reasons are unclear. The authors report significant differences in terms of efficacy in obese patients who do not respond as well as those with normal body mass index (p=0.05) and in patients who have their co-existing tinea pedis treated compared to those in whom co-existing tinea pedis was not treated (p=0.025). Although there is a trend to reduced efficacy in older patients and those with co-existing diabetes, differences were not significant. More research is needed in onychomycosis patients with these important risk factors and comorbidities to fully evaluate the treatment challenges and possible solutions. Onychomycosis is a common fungal infection of the nail unit that results in discoloration, subungual debris, thickening, onycholysis, and often pain and impairment of mobility. Dermatophytomas are characterized by a thick fungal mass within and under the nail plate and are especially resistant to treatment. Here we report a case of a patient with a dermatophytoma who had failed oral terbinafine but was successfully treated with efinaconazole 10% topical solution. Drug Warnings Adverse effects reported in at least 1% of adults treated with efinaconazole 10% topical solution and more frequently than with topical vehicle solution include application site dermatitis, ingrown toenail, application site vesicles, and application site pain. Prior to treatment of onychomycosis, the diagnosis should be confirmed by direct microscopic examination of scrapings from infected toenails mounted in potassium hydroxide (KOH) or by culture. Efinaconazole 10% solution is for topical use only. The topical solution should not be used orally or intravaginally, and should not be applied to the eyes. Efinaconazole 10% topical solution may cause application site irritation (e.g., redness, swelling, burning, itching, blisters); there is no evidence to date that the solution causes contact sensitization. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Efinaconazole (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics mean ± SD plasma Cmax on Day 28 of treatment: 0.67 ± 0.37 ng/mL. mean ± SD AUC was 12.15 ± 6.91 ng*h/mL. |
| 分子式 |
C18H22F2N4O
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
348.39
|
| 精确质量 |
348.176
|
| CAS号 |
164650-44-6
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Efinaconazole-d4
|
| PubChem CID |
489181
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
512.2±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
263.6±32.9 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.590
|
| LogP |
3.46
|
| tPSA |
54.18
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
25
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
470
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
| SMILES |
C[C@H]([C@](CN1C=NC=N1)(C2=C(C=C(C=C2)F)F)O)N3CCC(=C)CC3
|
| InChi Key |
NFEZZTICAUWDHU-RDTXWAMCSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H22F2N4O/c1-13-5-7-23(8-6-13)14(2)18(25,10-24-12-21-11-22-24)16-4-3-15(19)9-17(16)20/h3-4,9,11-12,14,25H,1,5-8,10H2,2H3/t14-,18-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(2R,3R)-2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-3-(4-methylidenepiperidin-1-yl)-1-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)butan-2-ol
|
| 别名 |
AGJ95634; KP103; CTK5J2975; KB145948; AGJ-95634; KP-103; CTK-5J2975; KB-145948; AGJ 95634; KP 103; CTK 5J2975; KB 145948; trade names Jublia; Clenafin
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (~287.03 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.18 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.18 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.18 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8703 mL | 14.3517 mL | 28.7035 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5741 mL | 2.8703 mL | 5.7407 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2870 mL | 1.4352 mL | 2.8703 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。