| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
HCV 1a (EC50 = 4 nM); HCV 1b (EC50 = 3 nM); HCV 2a (EC50 = 3 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:Elbasvir 对基因型 1a 和 1b 复制子显示出有效的活性,对于野生型 1a_H77 和 1b_con1 复制子的 EC90 均为 0.006 nM。 Elbasvir 抑制基因型 3 复制子,EC90 为 0.12 nM。 Elbasvir(0.06 nM、0.6 nM 和 6 nM)对耐药基因型 1a 复制子具有剂量依赖性抑制作用,高剂量时菌落计数减少即可说明这一点。 Elbasvir 对带有来自 GT1a、-1b、-2a(31L)、-3a、-4a、-5a 和 -6 的 NS5A 序列的 HCV 复制子非常有效,EC50 在低皮摩尔范围内。激酶测定:Elbasvir 是一种 HCV NS5A 抑制剂,可防止丙型肝炎病毒 RNA 复制和病毒粒子组装,根据基因型,EC50 中值范围为 0.2 至 3600 pmol/L。细胞分析:Elbasvir(以前称为 MK-8742;MK8742;商品名 Zepatier)是一种有效的 NS5A(非结构蛋白 5A)抑制剂,具有针对不同 HCV 基因型的抗 HCV(丙型肝炎病毒)活性。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
1b期临床试验结果。(i) Subject accounting。[1]
在一项Elbasvir剂量范围研究中,共有48名患者接受了Elbasvir或安慰剂治疗,其中包括17名基因型1a患者、13名基因型1b患者和18名基因型3患者。所有患者均完成了5天的疗程。测序设施中发生了来自3名患者的7个样本的错误标记(每名患者1个感染基因型1a、1b或3);因此,这些样本被排除在分析之外。另外1名基因型3患者的基线病毒无法扩增。因此,仅使用其他44名患者(包括16名基因型1a、12名基因型1b和16名基因基因型3)的序列数据进行耐药性分析。 在基线检查时,44名患者中有7名(15.9%)在28、30、58和93位检测到NS5A置换的变体(之前已被确定为NS5A抑制剂的潜在RAV)(表6)。除了10 mgElbasvir剂量组中可能有1名感染基因型3的患者外,基线NS5A变异似乎没有影响治疗期间病毒载量减少的幅度。特别是,在基线时,基因型1a中的M28V或Q30R和基因型1b中的Y93H对治疗期间病毒载量减少的幅度影响很小。 (ii)基因型1感染。[1] 在基因型1感染中,所有剂量的Elbasvir均导致HCV RNA快速减少3.7至5.1 log10IU/ml。在相同剂量下,基因型1b感染的病毒载量减少幅度大于基因型1a感染。在相同剂量的elbasvir下,基因型1b患者停止5天的elbasvir单药治疗后的病毒载量下降比基因型1a患者更为持续。总的来说,在每个亚基因型中选择的基线后RAV的类型和患病率在不同剂量水平上是相似的。 在2名具有治疗前M28V或Q30R多态性的基因型1a患者中,分别用5mg和50mg剂量的Elbasvir实现了>3-log的病毒载量减少。在基线M28V(在体外不会产生艾巴斯韦耐药性)接受5mg剂量艾巴斯韦治疗的患者中,在治疗后随访期间,除了M128V/A外,还检测到Q30H/Q和L31L/V。克隆分析确定了M28V和L31V之间以及M28A和Q30H之间的联系,但L31V和Q30H之间没有联系。在第61天的最后一次随访中,通过群体测序仅检测到M28V。在基线Q30R的基因型1a患者中(与体外elbasvir EC90增加24倍相关),用50mg剂量的elbasvirs治疗,从治疗结束到第56天的最后一次随访,用L31V检测到Q30R。该患者未进行克隆测序。一名基因型1b患者在基线时使用Y93H/Y和A92T/A混合物,用50mg剂量的艾巴斯韦治疗,病毒载量降低>4-log(尽管Y93H与体外艾巴斯韦EC90增加67倍有关)。停止治疗后,克隆测序鉴定出与Y93H连锁的L28M和与A92K连锁的L31V,Y93H与L31V或A92K之间没有连锁。在第59天的最后一次就诊时,通过群体测序仅检测到Y93H/Y和L31V/L混合物。 (iii)基因型3感染。[1] 在10 mgElbasvir剂量组中,基因型3的抗病毒反应不如基因型1感染那么强烈,但在50 mg和100 mg剂量下,HCV RNA平均减少了约3 log(3)。在50 mg和100 mg艾巴斯韦剂量组的所有10名患者中都发现了治疗后Y93H,并在每个病例的最后一次随访中持续存在。其中2名患者也检测到L31F。 10mg剂量组中3名基因型3感染的评估患者中有一名携带基线A30A/E/K/T混合物,与10mg剂量组其他2名患者在基线时未检测到RAV的平均病毒血症下降1.43-log10相比,HCV RNA水平在最低点降低了<1-log10IU/ml。群体测序显示,从治疗中断到第61天的最后一次随访,A30A/E/K/T转化为A30K(这使体外ElbasvirEC90增加了41倍)。 |
| 酶活实验 |
Elbasvir 是一种 HCV NS5A 抑制剂,根据基因型的不同,其 EC50 中值范围为 0.2 至 3600 pmol/L。它抑制丙型肝炎病毒的复制和病毒颗粒的组装。
与未治疗相比,HCV复制子用于确定将基因型1a、1b和3变体的HCV RNA水平抑制特定百分比(50%或90%)所需的Elbasvir的有效浓度(EC)。将维持在0.5mg/ml G418中以选择复制细胞的复制子接种在含有5%胎牛血清的Dulbecco改良Eagle培养基(DMEM)的384孔板上。第二天,在0.5%二甲亚砜(DMSO)的存在下,将浓度从1μM到0.002μM的两倍稀释液加入培养基中。孵育72小时后,收获细胞并进行实时逆转录酶PCR(RT-PCR)。对于每种变体,阈值循环数与艾巴韦浓度的对数作图,并使用Prism拟合到S形剂量反应曲线上,以获得EC50和EC90(相对于没有药物的DMSO对照,分别达到50%和90%抑制所需的药物浓度)。作为参考,每天一次50mg艾伯斯韦给药的稳态最低浓度(Cmin)约为22nM[1]。 grazoprevir和Elbasvir在GT1a中的联合动力学分析。[2] 加性反应的“独立效应”定义用于评估抑制剂相互作用的性质(协同、加性或拮抗)。借助MacSynergy软件分析抑制剂相互作用,该软件需要线性尺度的输入数据。为了满足这一要求,使用来自同一测定板的标准曲线将阈值循环数(CT)的对数尺度测量值转换为RNA的相对量。用从复制子细胞分离的总RNA构建标准曲线,然后连续稀释。根据样品的CT和同一平板的标准曲线计算每个样品(每个孔中的处理细胞)的复制子RNA的相对量。 MacSynergy计算每种组合的加性反应,并将协同作用定义为超过加性的反应,将拮抗作用定义为小于加性的响应。然后,应用程序以≥95%的置信区间计算协同/拮抗体积,并将结果分为协同、相加或拮抗。 |
| 细胞实验 |
为了选择Elbasvir敏感性降低的细胞系,在EC90倍数的不同药物浓度下培养复制子细胞的亚融合单层。每60mm板制备2×105个细胞,当细胞达到95%融合时,以1:10的比例只传代一次。首先对选择存活的菌落进行计数,然后合并并扩增进行分析。将艾巴斯韦存在下的菌落计数除以接种的细胞数量,以计算耐药频率。从合并的菌落中分离总细胞RNA,并通过RT-PCR扩增。RT-PCR产物用QIAquick PCR纯化试剂盒纯化,并对全长NS5A基因进行测序。此外,将RT-PCR产物克隆到TOPO TA载体中,并对细菌菌落的质粒DNA进行测序,以寻找连锁变异。在复制子集落形成试验中评估了RAV的复制能力(“适应性”)[1]。
稳定的复制子分析。[2] 对稳定的复制子细胞系进行了化合物敏感性测试。简而言之,将复制子细胞接种在含有0.5mg/ml G-418的Dulbecco修饰的Eagle培养基(DMEM)中的384孔板中。每种化合物的50%有效浓度(EC50)范围内的浓度单独使用,或在格拉唑韦和艾伯斯韦的联合研究中使用。将化合物分别在100%二甲亚砜(DMSO)中连续稀释,然后在接种细胞后的第二天,在5%胎牛血清(FCS)的存在下,将1:200稀释的细胞加入培养基中。DMSO的最终浓度为0.5%(体积比)。孵育72小时后,收获细胞并进行如前所述的实时PCR分析。用于ABI Prism 7900MTS序列检测系统PCR分析的引物/探针组列于补充材料的表S2中。在每个实验(或运行)中,使用三个重复板对独立和组合研究进行了3次测试。 长期病毒动力学研究。[2] 将稳定的复制子细胞以不同的细胞浓度接种在6孔板中,以便在收获时汇合,然后在6小时后以1×EC90的速度独立给药格拉唑普瑞韦和Elbasvir,在不含G418的含10%胎牛血清(FBS)的DMEM中,DMSO的最终浓度为0.5%(体积/体积)。在0、24、48、72、96、168、240和336小时用胰蛋白酶-EDTA(0.25%) 收获处理过的细胞(细胞在72、168和240小时通过),并通过制造商的方案使用RNeasy纯化试剂盒分离RNA。然后使用上述引物和探针对RNA进行实时PCR分析,如前所述。将阈值循环数(CT)归一化为GAPDH(甘油醛-3-磷酸脱氢酶)看家基因,得到ΔCT,并使用Prism绘制对数(1/power)(2,ΔCT-DMSO在第零天的平均ΔCT)随时间的变化图。 针对耐药性的出现,选择复合治疗。[2] 将GT1a亚基因组复制子细胞以2×105个细胞/皿的密度接种到多个6-cm的组织培养皿上。每种处理条件准备了四道菜。接种后24小时,细胞被给予各种组合和倍于格拉唑韦和ElbasvirEC90值的药物(如适当的表格和图表所示)。培养基和化合物每周更新两次。如果单层达到融合(例如,与DMSO处理对照),则以1:10的比例传代这些细胞。在约3至4周后,当抗性复制子细胞形成明确的集落时,将4个培养皿中的3个固定并用结晶紫溶液染色以进行集落计数。扩增剩余培养皿上的细胞以进行进一步分析(即逆转录PCR[RTP]产物的测序和对化合物的表型敏感性)。 |
| 动物实验 |
Phase 1b randomized clinical trial design. [1]
MK-8742 P002 was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, sequential dose-escalating phase 1b study of Elbasvir monotherapy to assess safety, pharmacokinetics, and viral responses in adult men with chronic HCV-1 or HCV-3 infection. Patients between 18 and 60 years of age (up to 65 years old at the discretion of the investigator) with HCV RNA levels of >100,000 IU/ml were eligible. Elbasvir doses were 5, 10, and 50 mg once daily for patients infected with genotype 1a or 1b, and 10, 50, and 100 mg once daily for patients infected with genotype 3. A total of 6 patients were to be enrolled at each dosing level, including 5 patients to receive elbasvir and 1 patient to receive a matching placebo orally for 5 consecutive days, starting at the lowest dose for the infecting genotype. Doses were escalated stepwise once adequate safety data had been reviewed from the previous dosing group. Viral load and resistance testing was to be performed daily and every other day, respectively, for the first 10 days of the study and then at 2 weeks, 3 weeks, 1 month, and 2 months after the last dose of elbasvir. The study was conducted in accordance with good clinical practice guidelines. All participants provided written informed consent. Viral quantification, sequencing, and resistance analyses. [1] In the phase 1b study, HCV RNA levels were measured in plasma specimens obtained at baseline, during and at the end of Elbasvir monotherapy, and at periodic follow-up visits by the TaqMan 2.0 assay with lower limits of quantification and detection of 25 and 9.3 IU/ml, respectively. Blood samples were also collected for viral resistance testing at prespecified time points, including prior to the first elbasvir dose, near the nadir of the HCV RNA level, and up to 2 months after the last elbasvir dose provided that the HCV RNA level remained >1,000 IU/ml. [1] The full-length NS5A gene was amplified from plasma samples using RT-PCR followed by population and selective clonal sequencing. Due to the sensitivity of the assay, resistance analyses were routinely performed only on samples with HCV RNA levels of >1,000 IU/ml. The resultant amino acid sequences were compared to genotype 1a (H77; GenBank no. NC_004102), genotype 1b (con1; GenBank no. AJ238799), or genotype 3 (S52; GenBank no. GU814263) referents. The limit of variant detection in population sequencing was presumed to be ∼20 to 25% of the viral quasispecies. Polymorphisms identified in ≥10% of patients were selected for more detailed analysis. For clonal sequencing, amino acids 1 to 448 of NS5A were amplified by RT-PCR, and the resultant amplicons were cloned into a TOPO TA vector. Approximately 40 clones were sequenced at each time point. Polymorphisms detected in more than a single clone were included in the analysis. [1] In phenotypic analyses to determine the antiviral potency of Elbasvir against detected variants, genotype-specific replicons were constructed to incorporate NS5A polymorphisms. The shift (n-fold) in elbasvir EC for each variant replicon was expressed relative to the EC for the corresponding wild-type replicon. The fitness of resistant variants was evaluated by comparing colony counts to a wild-type referent. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Elbasvir reaches peak plasma concentration 3-6 hours after administration and has an absolute bioavailability of 32%. When co-administered with food, the peak concentration of elbasvir increases 1.5-fold, but this increase in exposure is not likely to be clinically relevant. Elbasvir is mainly eliminated in the feces (90%) with very little eliminated in the urine (<1%). Elbasvir has an estimated apparent volume of distribution of 680 liters. It is thought to distribute into most tissues including the liver. The clearance of elbasvir has not been determined. Metabolism / Metabolites Elbasvir is partially eliminated by oxidative metabolism meditated by CYP3A. No circulating metabolites of elbasvir have been detected in human plasma. Biological Half-Life The geometric mean apparent terminal half-life for elbasvir is 24 hours in HCV-infected subjects. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Elbasvir has not been studied in nursing mothers being treated for hepatitis C infection. Because it is greater than 99.9% bound to maternal plasma proteins, amounts in breastmilk are likely to be very low. Some sources recommend against breastfeeding when elbasvir is used with ribavirin. Hepatitis C is not transmitted through breastmilk and breastmilk has been shown to inactivate hepatitis C virus (HCV). However, the Centers for Disease Control recommends that mothers with HCV infection should consider abstaining from breastfeeding if their nipples are cracked or bleeding. It is not clear if this warning would apply to mothers who are being treated for hepatitis C. Infants born to mothers with HCV infection should be tested for HCV infection; because maternal antibody is present for the first 18 months of life and before the infant mounts an immunologic response, nucleic acid testing is recommended. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Elbasvir is more than 99.9% bound to plasma proteins. It binds both human serum albumin and α1-acid glycoprotein. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Pharmacodynamics
Elbasvir is classified as a direct-acting antiviral (DAA) and prevents viral replication in HCV genotypes 1a, 1b, and 4. Elbasvir is a complex organic heterotetracyclic compound that is a hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5A inhibitor used in combination with grazoprevir (under the brand name Zepatier) for treatment of chronic HCV genotypes 1 or 4 infection in adults. It has a role as an antiviral drug, a hepatoprotective agent and a hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5A inhibitor. It is a L-valine derivative, a member of imidazoles, a carbamate ester, a N-acylpyrrolidine, an organic heterotetracyclic compound and a ring assembly. Elbasvir is a direct-acting antiviral medication used as part of combination therapy to treat chronic hepatitis C, an infectious liver disease caused by infection with hepatitis C virus (HCV). HCV is a single-stranded RNA virus that is categorized into nine distinct genotypes, with genotype 1 being the most common in the United States, affecting 72% of all chronic HCV patients. Treatment options for chronic hepatitis C have advanced significantly since 2011, with the development of direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) such as elbasvir. Elbasvir is an inhibitor of NS5A, a protein essential for viral replication and virion assembly.[synthesis] The barrier to the development of resistance to NS5A inhibitors is lower than that of NS5B inhibitors, another class of DAAs. Substitutions at amino acid positions 28, 30, 31, or 93 are known to confer resistance to elbasvir. Despite this disadvantage elbasvir is still effective against HCV, particularly when paired with [grazoprevir]. Elbasvir is available as a fixed-dose combination product with [grazoprevir] (tradename: Zepatier) used for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Approved in January 2016 by the FDA, Zepatier is indicated for the treatment of HCV genotypes 1 and 4 with or without [ribavirin] depending on the presence of resistance-associated amino acid substitutions in the NS5A protein and previous treatment failure with [ribavirin], [peginterferon alfa-2a], [peginterferon alfa-2b], or other NS3/4A inhibitors like [boceprevir], [simeprevir], or [telaprevir]. Elbasvir and [grazoprevir] are used with or without [ribavirin] with the intent to cure, or achieve a sustained virologic response (SVR), and have been shown to achieve a SVR between 94% and 97% for genotype 1 and 97% and 100% for genotype 4 after 12 weeks of treatment.. SVR and eradication of HCV infection are associated with significant long-term health benefits including reduced liver-related damage, improved quality of life, reduced incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma, and reduced all-cause mortality. In a computational target-based drug repurposing investigation published in April 2020, elbasvir was predicted to bind stably and preferentially to three proteins necessary for viral replication of SARS-CoV-2, the human coronavirus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. While these results are suggestive of antiviral efficacy, follow-up clinical trials are required to validate elbasvir as a potential therapy against SARS-CoV-2. Elbasvir is a Hepatitis C Virus NS5A Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of elbasvir is as a Breast Cancer Resistance Protein Inhibitor. Elbasvir is a small molecule drug with a maximum clinical trial phase of IV (across all indications) that was first approved in 2016 and is indicated for viral disease and chronic hepatitis c virus infection and has 2 investigational indications. Elbasvir is an investigational NS5A inhibitor with in vitro activity against multiple HCV genotypes. Antiviral activity of elbasvir was measured in replicons derived from wild-type or resistant variants of genotypes 1a, 1b, and 3. The barrier to resistance was assessed by the number of resistant colonies selected by exposure to various elbasvir concentrations. In a phase 1b dose-escalating study, virologic responses were determined in 48 noncirrhotic adult men with chronic genotype 1 or 3 infections randomized to placebo or elbasvir from 5 to 50 mg (genotype 1) or 10 to 100 mg (genotype 3) once daily for 5 days. The NS5A gene was sequenced from plasma specimens obtained before, during, and after treatment. Elbasvir suppressed the emergence of resistance-associated variants (RAVs) in vitro in a dose-dependent manner. Variants selected by exposure to high elbasvir concentrations typically encoded multiple amino acid substitutions (most commonly involving loci 30, 31, and 93), conferring high-level elbasvir resistance. In the monotherapy study, patients with genotype 1b had greater reductions in HCV RNA levels than patients with genotype 1a at all elbasvir doses; responses in patients with genotype 3 were generally less pronounced than for genotype 1, particularly at lower elbasvir doses. M28T, Q30R, L31V, and Y93H in genotype 1a, L31V and Y93H in genotype 1b, and A30K, L31F, and Y93H in genotype 3 were the predominant RAVs selected by elbasvir monotherapy. Virologic findings in patients were consistent with the preclinical observations. NS5A-RAVs emerged most often at amino acid positions 28, 30, 31, and 93 in both the laboratory and clinical trial. (The MK-8742 P002 trial has been registered at ClinicalTrials.gov under identifier NCT01532973.).[1] The selection of resistance-associated variants (RAVs) against single agents administered to patients chronically infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV) necessitates that direct-acting antiviral agents (DAAs) targeting multiple viral proteins be developed to overcome failure resulting from emergence of resistance. The combination of grazoprevir (formerly MK-5172), an NS3/4A protease inhibitor, and Elbasvir (formerly MK-8742), an NS5A inhibitor, was therefore studied in genotype 1a (GT1a) replicon cells. Both compounds were independently highly potent in GT1a wild-type replicon cells, with 90% effective concentration (EC90) values of 0.9 nM and 0.006 nM for grazoprevir and elbasvir, respectively. No cross-resistance was observed when clinically relevant NS5A and NS3 RAVs were profiled against grazoprevir and elbasvir, respectively. Kinetic analyses of HCV RNA reduction over 14 days showed that grazoprevir and elbasvir inhibited prototypic NS5A Y93H and NS3 R155K RAVs, respectively, with kinetics comparable to those for the wild-type GT1a replicon. In combination, grazoprevir and elbasvir interacted additively in GT1a replicon cells. Colony formation assays with a 10-fold multiple of the EC90 values of the grazoprevir-elbasvir inhibitor combination suppressed emergence of resistant colonies, compared to a 100-fold multiple for the independent agents. The selected resistant colonies with the combination harbored RAVs that required two or more nucleotide changes in the codons. Mutations in the cognate gene caused greater potency losses for elbasvir than for grazoprevir. Replicons bearing RAVs identified from resistant colonies showed reduced fitness for several cell lines and may contribute to the activity of the combination. These studies demonstrate that the combination of grazoprevir and elbasvir exerts a potent effect on HCV RNA replication and presents a high genetic barrier to resistance. The combination of grazoprevir and elbasvir is currently approved for chronic HCV infection.[2] Elbasvir plus grazoprevir (an investigational NS3/4A protease inhibitor) as a once-daily, oral, single fixed-dose combination tablet is currently being developed for treatment of chronic HCV infection. Further analyses of the phase 3 trials of grazoprevir-elbasvir will soon provide more critical data concerning the safety and efficacy of this novel double direct-acting antiviral combination.[1] Collectively, these results demonstrate that the combination of grazoprevir, an NS3/4A inhibitor, and Elbasvir, an NS5A inhibitor, potently inhibits HCV RNA synthesis, with no evidence of antagonism, and present a high genetic barrier to resistance. The inhibitor combination presents an attractive alternative as an oral, interferon-free DAA for patients chronically infected with HCV. In recent clinical studies, the in vitro activities translated to robust clinical efficacy for the combination. In treatment-naive GT1a patients given a once-daily dose of 50 mg/100 mg elbasvir-grazoprevir, an SVR rate of 95% was achieved in patients. The RAVs and dominant resistance pathways observed in clinical studies of GT1a-infected subjects largely mirrored what was observed in vitro. The most common treatment-emergent (TE) NS5A RAV in virologic failures was at Q30. Similarly, D168 amino acid substitutions accounted for most TE NS3 RAVs in virologic failures. The combination has been approved (January 2016) for the treatment of chronic HCV infections.[2] |
| 分子式 |
C49H55N9O7
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
882.02
|
|
| 精确质量 |
881.422
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 66.72; H, 6.29; N, 14.29; O, 12.70
|
|
| CAS号 |
1370468-36-2
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
71661251
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to yellow solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.701
|
|
| LogP |
6.98
|
|
| tPSA |
188.8
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
9
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
13
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
65
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1680
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
5
|
|
| SMILES |
O=C([C@]([H])(C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])N([H])C(=O)OC([H])([H])[H])N1C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C1([H])C1=NC([H])=C(C2C([H])=C([H])C3=C(C=2[H])C([H])=C2C4C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=4O[C@@]([H])(C4C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C=4[H])N23)C2=C([H])N=C([C@]3([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N3C([C@]([H])(C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])N([H])C(=O)OC([H])([H])[H])=O)N2[H])N1[H]
|
|
| InChi Key |
BVAZQCUMNICBAQ-PZHYSIFUSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C49H55N9O7/c1-27(2)41(54-48(61)63-5)45(59)56-20-10-14-37(56)43-50-25-34(52-43)30-17-19-36-32(22-30)23-39-33-18-16-31(24-40(33)65-47(58(36)39)29-12-8-7-9-13-29)35-26-51-44(53-35)38-15-11-21-57(38)46(60)42(28(3)4)55-49(62)64-6/h7-9,12-13,16-19,22-28,37-38,41-42,47H,10-11,14-15,20-21H2,1-6H3,(H,50,52)(H,51,53)(H,54,61)(H,55,62)/t37-,38-,41-,42-,47-/m0/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
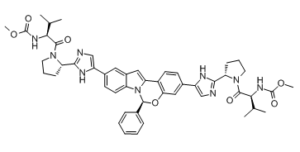
methyl N-[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[5-[(6S)-3-[2-[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-(methoxycarbonylamino)-3-methylbutanoyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl]-1H-imidazol-5-yl]-6-phenyl-6H-indolo[1,2-c][1,3]benzoxazin-10-yl]-1H-imidazol-2-yl]pyrrolidin-1-yl]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]carbamate
|
|
| 别名 |
Elbasvir; Zepatier; MK8742; MK 8742; Elbasvir; 1370468-36-2; Elbasvir [USAN]; Elbasvir [USAN:INN]; UNII-632L571YDK; 632L571YDK; MK-8742
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (2.83 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 +5% Tween-80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80+,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.1338 mL | 5.6688 mL | 11.3376 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2268 mL | 1.1338 mL | 2.2675 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1134 mL | 0.5669 mL | 1.1338 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT04048850 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Elbasvir/Grazoprevir 50 MG-100 MG Oral Tablet [ZEPATIER] |
Hepatitis C Hiv |
University of Illinois at Chicago |
September 20, 2019 | |
| NCT02251990 | Completed | Drug: Grazoprevir/Elbasvir Drug: Placebo |
Hepatitis C | Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC | January 28, 2015 | Phase 3 |
| NCT01797536 | Completed | Drug: Elbasvir | Hepatic Insufficiency | Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC | Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC | Phase 1 |
Kinetics of HCV RNA reduction in GT1a(H77) replicons bearing NS3 and NS5A RAVs treated with elbasvir and grazoprevir. (A) Inhibition of GT1a_R155K (□, ■) and wild-type GT1a (○, ●) with DMSO (open symbols) and 6 pM elbasvir (closed symbols) over 14 days. (B) Inhibition of Q30D (□, ■), Y93H (▽, ▼), and wild-type GT1a (○, ●) with DMSO (open symbols) and 15 nM grazoprevir (closed symbols) over 14 days.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2016 Apr 22;60(5):2954-64. |
|---|
The combination of grazoprevir and elbasvir additively inhibits HCV RNA replication in GT1a(H77) replicon cells.Synergy plots of three independent runs (performed in triplicate) were analyzed by MacSynergy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2016 Apr 22;60(5):2954-64. |
Representative images of a colony formation assay for the combination of grazoprevir and elbasvir in GT1a(H77) replicon cells. Multiples of the EC90values of both inhibitors were titrated in a matrix and scored for the emergence of resistant colonies. Higher concentrations of the combination were evaluated in panel A than in panel B to finely map the combinatorial effect. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2016 Apr 22;60(5):2954-64. |