| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| 25g |
|
||
| 50g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
L-type calcium channel
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在 CLL 细胞中,ephacrynic Acid(50 μM;24 小时)可抑制 Wnt/β-catenin 信号传导 [1]。乙醇酸(1-100 μM;48 小时)对 CLL 细胞具有细胞毒性,IC50 为 8.56 μM [1]。眼睛的房水因利尿酸(0.01-0.25mmol/L;30分钟)而升高,水流出率从28%增加至105%[2]。双尿酸具有抗炎特性,当在 10-100 μM LPS (100 ng/mL) 中使用 30 分钟时,可以降低 RAW264.7 细胞中 NF-κB 染色的活化 [3]。乙醇丙烯酸(20 μM/mL;2 小时)可改善暴露于辐射的 MCF-7 斑点。高 K+ (80 mmol/L) 和乙酰胆碱 (乙酰胆碱,ACh,100 μmol/L) 被乙醇酸 (100 μmol/L;62.5-250 分钟) 抑制。在小鼠中,气管环收缩产生的 EC50 分别为 40.28 µmol/L 和 56.22 µmol/L[8]。依他尼酸(100 µmol/L;500-2500 秒)将高 K+ 和 ACh 引起的细胞内 Ca2+ 浓度分别从 0.40 降低至 0.16 和 0.50 至 0.39 [8]。实时聚合酶链式反应
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Ethacrynic Acid(450 μg/小鼠;口服形式;每天一次,持续 60 天)可抑制小鼠肿瘤生长 [5]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
RT-PCR[1]
细胞类型: 慢性淋巴细胞白血病 (CLL) 测试浓度: 1 μM、10 μM、100 μM 孵育时间:16 h 实验结果:LEF-1、Cyclin D1 和 Fibronectin 表达的抑制呈浓度依赖性。 (LEF-1、Cyclin D1 和 Fibronectin 是 Wnt/b-catenin 途径的既定靶基因)。 蛋白质印迹分析 [3] 细胞类型: RAW 264.7 测试浓度: 10 μM、20 μM、50 μM、100微米; LPS 处理前(100 ng/mL;1 小时) 孵育时间: 30 分钟 实验结果: iNOS mRNA 表达的抑制。抑制 IκBα 和 IκBβ 的降解。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Myeloma Balb/c mouse model [5]
Doses: 450 μg/mouse: po (oral gavage); one time/day for 60 days. balb/c (Bagg ALBino) mouse were injected subcutaneously (sc) (sc) with 5 × 105 MPC11 myeloma cells. Experimental Results: Dramatically inhibited tumor growth. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Onset of action is rapid, usually within 30 minutes after an oral dose of ethacrynic acid or within 5 minutes after an intravenous injection of ethacrynic acid. Thirty-five % or less of ethacrynic acid was excreted in urine of rats and dogs, regardless of mode of admin and 50% or more appeared in feces, suggesting hepatic elimination of the drug. Renal elimination (67%), biliary/fecal (33%), 20% unchanged. /From table/ Ethacrynic acid is rapidly absorbed from the GI tract. Following oral admin, the diuretic effect occurs within 30 min and reaches a peak in approx 2 hr. The duration of action following oral admin is usually 6-8 hr but may continue up to 12 hr. Following IV admin of ethacrynate sodium, diuresis usually occurs within 5 min, reached a max within 15-30 min, and persists for approx 2 hr. In animals, substantial quantities of ethacrynic acid accumulate only in the liver. The drug does not enter the CSF. It is not known whether ethacrynic acid crosses the placenta or is distributed into milk in humans. ... Approx 30-65% of an IV dose of ethacrynate sodium is secreted by the proximal renal tubules and is excreted in urine; approx 35-40% is excreted in bile, partially as the cysteine conjugate. In dogs, approx 30-40% of the drug excreted in urine is unchanged, 20-30% is the cysteine conjugate, and 33-40% is an unstable, unidentified compound. The rate of urinary excretion of ethacrynic acid increases as urinary pH increases and is decreased by probenecid. Metabolism / Metabolites Hepatic. After iv admin (5 or 50 mg/kg) of (14)C-ethacrynic acid to rats 60-70% was excreted into bile within 4 hr; <25% was ethacrynic acid, the remainder was biotransformation products. The 2 major metabolites in bile were identified; one was the glutathione adduct (ethacrynic acid-GSH) and the other was ethacrynic acid-mercapturate. Approx 40% of either dose was excreted as ethacrynic acid-GSH. Ethacrynic acid-mercapturate accounted for 18% of the low dose and 30% of the high dose excreted into bile. Dogs given a 5 mg/kg dose (iv) excreted 25, 11, and 9% of the dose as ethacrynic acid-mercapturate, ethacrynic acid-cysteine and ethacrynic acid-GSH, respectively. Animal studies indicate that ethacrynic acid is metabolized to a cysteine conjugate (which may contribute to the pharmacologic effects of the drug) and to an unstable, unidentified compound. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Because no information is available on the use of ethacrynic acid during breastfeeding and because intense diuresis might decrease lactation, an alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. Low doses of ethacrynic acid may not suppress lactation. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Ethacrynic acid was reportedly used successfully to suppress lactation in 6 postpartum women who did not want to breastfeed and to decrease the intensity of milk production in another. The added contribution of the diuretic to the other measures, which are effective in suppressing lactation, has not been studied. No data exist on the effects of loop diuretics on established, ongoing lactation. Protein Binding > 98% Interactions The high-ceiling diuretics may interact adversely with other drugs. Ethacrynic acid and furosemide are significantly bound to plasma albumin and may compete for sites on the protein with drugs such as warfarin and clofibrate. ...One should be judicious in the use of any cephalosporin in conjunction with...ethacrynic acid. The ototoxic interaction between aminoglycoside antibiotics (Streptomycin, Kanamycin, etc.) and loop-inhibiting diuretics, such as ethacrynic acid, has been well documented. This interaction causes extensive destruction of the hair cells of the cochlea. Viomycin, Capreomycin, and Polymyxin B, when given with ethacrynic acid , were found to produce cochlear hair cell damage that was similar to that produced by aminoglycoside antibiotics admin with ethacrynic acid. Treatment of mice with Neomycin (100 mg/kg bw, IM) 60 min prior to ethacrynic acid led to a 3-5 fold higher accumulation of ethacrynic acid in cochlear structures. It is suggested that Neomycin breaks down hemolabyrinthine or tissue permeability barriers and allows increased penetration of the other drug into the inner ear. The temporal bones of a patient who suffered sudden deafness and ataxia after admin of both furosemide and ethacrynic acid, were examined by light and electron microscopy. There was no loss of hair or supporting cells. Some hair cells, in both the vestibular neuroepithelium and the organ of corti, particularly in the basal turn, were more densely staining and more granular than normal. Membrane whorls also were common within mitochondria of such cells. The endoplasmic reticulum of some spiral ganglion cells was dilated. The major cytologic changes were found in the stria vascularis of the cochlea and dark cell areas of the vestibular system. There was marked dilatation of the intercellular fluid spaces, consistent with the biochemical observation that loop diuretics interfere first with enzyme systems responsible for fluid transport within the inner ear. For more Interactions (Complete) data for ETHACRYNIC ACID (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Mouse iv 175 mg/kg /Ethacrynate sodium/ LD50 Mouse oral 627 mg/kg LD50 Rat oral 1 g/kg LD50 Rat ip 43 mg/kg |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Ethacrynic acid is a white solid. (NTP, 1992)
Etacrynic acid is an aromatic ether that is phenoxyacetic acid in which the phenyl ring is substituted by chlorines at positions 2 and 3, and by a 2-methylidenebutanoyl group at position 4. It is a loop diuretic used to treat high blood pressure resulting from diseases such as congestive heart failure, liver failure, and kidney failure. It is also a glutathione S-transferase (EC 2.5.1.18) inhibitor. It has a role as an ion transport inhibitor, an EC 2.5.1.18 (glutathione transferase) inhibitor and a loop diuretic. It is an aromatic ether, a monocarboxylic acid, an aromatic ketone and a dichlorobenzene. It is functionally related to an acetic acid. A compound that inhibits symport of sodium, potassium, and chloride primarily in the ascending limb of Henle, but also in the proximal and distal tubules. This pharmacological action results in excretion of these ions, increased urinary output, and reduction in extracellular fluid. This compound has been classified as a loop or high ceiling diuretic. Ethacrynic acid is a Loop Diuretic. The physiologic effect of ethacrynic acid is by means of Increased Diuresis at Loop of Henle. Ethacrynic Acid is an unsaturated ketone derivative of aryloxyacetic acid without a sulfonamide substituent belonging to the class of loop diuretics. Ethacrynic acid is extensively bound to plasma proteins; both ethacrynic acid in its unchanged form as well as its metabolites are excreted in bile and urine. A compound that inhibits symport of sodium, potassium, and chloride primarily in the ascending limb of Henle, but also in the proximal and distal tubules. This pharmacological action results in excretion of these ions, increased urinary output, and reduction in extracellular fluid. This compound has been classified as a loop or high ceiling diuretic. Drug Indication For the treatment of high blood pressure and edema caused by diseases like congestive heart failure, liver failure, and kidney failure. FDA Label Mechanism of Action Ethacrynic acid inhibits symport of sodium, potassium, and chloride primarily in the ascending limb of Henle, but also in the proximal and distal tubules. This pharmacological action results in excretion of these ions, increased urinary output, and reduction in extracellular fluid. Diuretics also lower blood pressure initially by reducing plasma and extracellular fluid volume; cardiac output also decreases, explaining its antihypertensive action. Eventually, cardiac output returns to normal with an accompanying decrease in peripheral resistance. Its mode of action does not involve carbonic anhydrase inhibition. Optimal diuretic activity depends on at least 2 structural requirements: (1) methylene and adjacent ketone groups capable of reacting with sulfhydryl radicals of presumed receptor, and (2) substituents on aromatic nucleus. In vitro, ethacrynic acid inhibits the active transport of chloride in the lumen of the ascending limb of the loop of Henle, thereby diminishing reabsorption of sodium and chloride at that site. Because this inhibition occurred with lower concns of ethacrynic acid in the presence of cysteine, it has been proposed that the ethacrynate-cysteine metabolite is the most active form of the drug. The drug increases potassium excretion in the distal renal tubule. Ethacrynic acid does not inhibit carbonic anhydrase, and it is not an aldosterone antagonist. Aldosterone secretion may incr during therapy with the drug and may contribute to the hypokalemia caused by ethacrynic acid. ...IRREVERSIBLY COMBINES WITH 2 THIOL GROUPS OF GLYCERALDEHYDE 3-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE, THUS INACTIVATING THE ENZYME. HOWEVER, IT IS NOT POSSIBLE TO ATTRIBUTE DIURETIC ACTION TO THIS TYPE OF BIOCHEMICAL REACTION... Therapeutic Uses Diuretics A major use of loop diuretics is in the treatment of acute pulmonary edema. A rapid incr in venous capacitance in conjunction with a brisk natriuresis reduces left ventricular filling pressures and thereby rapidly relieves pulmonary edema. Loop diuretics also are widely used for the treatment of chronic congestive heart failure when diminution of extracellular fluid volume is desirable to minimize venous and pulmonary congestion. Diuretics are widely used for the treatment of hypertension, and controlled clinical trials demonstrating reduced morbidity and mortality have been conducted with Na+-Cl- symport (thiazides and thiazide-like diuretics), but not Na+-K+-2Cl- symport, inhibitors. Nonetheless, Na+-K+-2Cl- symport inhibitors appear to lower blood pressure as effectively as Na+-Cl- symport inhibitors while causing smaller perturbations in the lipid profile. /Loop diuretics/ The edema of nephrotic syndrome often is refractory to other classes of diuretics, and loop diuretics often are the only drugs capable of reducing the massive edema associated with this renal disease. Loop diuretics also are employed in the treatment of edema and ascites of liver cirrhosis; however, care must be taken not to induce encephalopathy or hepatorenal syndrome. In patients with a drug overdose, loop diuretics can be used to induce a forced diuresis to facilitate more rapid renal elimination of the offending drug. /Loop diuretics/ Loop diuretics- combined with isotonic saline admin to prevent volume depletion- are used to treat hypercalcemia. Loop diuretics interfere with the kidney's ability to produce a concentrated urine. Consequently, loop diuretics combined with hypertonic saline are useful for the treatment of life-threatening hyponatremia. /Loop diuretics/ For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for ETHACRYNIC ACID (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings Vet: Rapid ototoxicity in cats. Do not admin in cases of decr renal function. Not recommended for routine use /in pregnancy/. /Loop diuretics/ Geriatric patients may be more sensitive to the effects of the usual adult dose. Ethacrynic acid may cause adverse GI effects, including anorexia, abdominal discomfort or pain, nausea, vomiting, malaise, diarrhea, and dysphagia. Adverse GI effects occur most frequently when large doses are employed or after 1-3 months of continuous therapy and may necessitate discontinuing the drug. Severe, profuse, watery diarrhea may occur; the drug should be permanently discontinued if this occurs. GI bleeding has been reported, most frequently in patients receiving IV ethacrynate sodium therapy and especially in patients receiving heparin sodium concomitiantly. Acute necrotizing pancreatitis, with an incr in serum amylase, has been reported. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for ETHACRYNIC ACID (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Ethacrynic acid is a monosulfonamyl loop or high ceiling diuretic. Ethacrynic acid acts on the ascending limb of the loop of Henle and on the proximal and distal tubules. Urinary output is usually dose dependent and related to the magnitude of fluid accumulation. Water and electrolyte excretion may be increased several times over that observed with thiazide diuretics, since ethacrynic acid inhibits reabsorption of a much greater proportion of filtered sodium than most other diuretic agents. Therefore, ethacrynic acid is effective in many patients who have significant degrees of renal insufficiency. Ethacrynic acid has little or no effect on glomerular filtration or on renal blood flow, except following pronounced reductions in plasma volume when associated with rapid diuresis. |
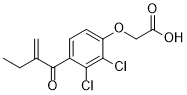
| 分子式 |
C13H12CL2O4
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
303.14
|
| 精确质量 |
302.011
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 51.51; H, 3.99; Cl, 23.39; O, 21.11
|
| CAS号 |
58-54-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Ethacrynic acid sodium;6500-81-8
|
| PubChem CID |
3278
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.35g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
480ºC at 760mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
125 °C
|
| 闪点 |
244.1ºC
|
| LogP |
3.605
|
| tPSA |
63.6
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
19
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
370
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
ClC1C(=C(C([H])=C([H])C=1C(C(=C([H])[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])=O)OC([H])([H])C(=O)O[H])Cl
|
| InChi Key |
AVOLMBLBETYQHX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C13H12Cl2O4/c1-3-7(2)13(18)8-4-5-9(12(15)11(8)14)19-6-10(16)17/h4-5H,2-3,6H2,1H3,(H,16,17)
|
| 化学名 |
2-[2,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylidenebutanoyl)phenoxy]acetic acid
|
| 别名 |
Taladren; Ethacrynic acid; Etacrinic acid; Hydromedin; Otacril Reomax; Crinuryl; MK-595; Mingit; NSC 624008; NSC 85791
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: 61~100 mg/mL (201.2~329.9 mM)
H2O: ~27.5 mg/mL (~90.7 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.25 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.25 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.25 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 1 mg/mL (3.30 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2988 mL | 16.4940 mL | 32.9881 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6598 mL | 3.2988 mL | 6.5976 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3299 mL | 1.6494 mL | 3.2988 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT02852564 | Completed | Drug: Ethacrynic Acid | Bladder Cancer | Eugene Lee, MD | August 2016 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01628731 | Completed | Drug: furosemide Drug: ethacrynic acid |
Fluid Overload | Bambino Gesù Hospital and Research Institute |
October 2012 | Phase 3 |
| NCT02051946 | Completed | Device: Retroject Device Drug: balanced salt solution |
Glaucoma | Molly Walsh | May 2014 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
|