| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
H2 receptor
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:法莫替丁(也称为 MK208)是一种组胺 H2 受体拮抗剂,IC50 为 0.6 mM,它抑制胃酸产生,因此常用于治疗胃灼热、GERD、溃疡和其他消化系统疾病。与第一个 H2 拮抗剂西咪替丁不同,法莫替丁对细胞色素 P450 酶系统没有影响,并且似乎不会与其他药物相互作用。
|
||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
法莫替丁 (MK-208) 是一种组胺 H2 受体拮抗剂,可抑制胃酸产生,常用于治疗消化性溃疡病 (PUD) 和胃食管反流病 (GERD/GORD)。法莫替丁(MK-208)组(2 mg/kg/天)在术后第三天和第七天均显着低于对照组的同等参数。 Famotidine (MK-208) 对大鼠结肠吻合口爆裂压和吻合口周围组织的羟脯氨酸含量产生有害影响。法莫替丁 (MK-208) 增加大鼠经胃电位差 (PD),并促进酸化乙醇引起的经胃电位差下降的恢复。法莫替丁对胃病变的预防作用不仅归因于抑制胃酸分泌,还归因于激活胃粘膜防御机制。
|
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Following oral administration, the absorption of famotidine is dose-dependent and incomplete. The oral bioavailability ranges from 40-50%, and the Cmax is reached in 1-4 hours post-dosing. While the bioavailability can be slightly increased with the intake of food and decreased by antacids, there is no clinical significance. About 65-70% of the total administered dose of famotidine undergoes renal elimination, and 30-35% of the dose is cleared by metabolism. Following intravenous administration, about 70% of the drug is eliminated in the urine as an unchanged drug. The steady-state volume of distribution ranges from 1.0 to 1.3 L/kg. Famotidine is found in breast milk; however, it is found in breast milk at the lowest concentrations compared to other H2 receptor antagonists. Renal clearance is 250-450 mL/min, indicating some tubular excretion. Because the renal clearance rate exceeds the glomerular filtration rate, famotidine is thought to be mainly eliminated via both glomerular filtration and renal tubular secretion. All H2-receptor antagonists are distributed in breast milk and cerebral spinal fluid. /Histamine H2-receptor antagonists/ Distribution of famotidine into human body tissues and fluids has not been fully characterized. The apparent volume of distribution of the drug is reported to be 1.1-1.4 l/kg in adults and does not appear to be altered substantially in patients with renal dysfunction. Following oral or IV administration in rats, famotidine is widely distributed, appearing in highest concentrations in the kidney, liver, pancreas, and submandibular gland. The drug is 15-20% protein bound. In rats famotidine appears to distribute only minimally into the CNS, and does not cross the placenta. It is not known whether the drug crosses the placenta in humans. Famotidine is distributed into milk in rats; however, it is not known whether the drug is distributed into milk in humans. Famotidine is excreted principally in urine via glomerular filtration and tubular secretion. Approximately 25-30 or 65-80% of a dose is excreted unchanged in urine within 24 hours following oral or IV administration, respectively, and approximately 13-49 or 52-82% of a single 40 mg oral or IV dose respectively, is excreted within 72 hours. ... The remainder of an orally administered dose is eliminated in feces. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for FAMOTIDINE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Famotidine undergoes minimal first-pass metabolism. About 25-30% of the drug is eliminated through hepatic metabolism. The only metabolite identified in humans is the S-oxide. Famotidine is metabolized in the liver to famotidine S-oxide (S-famotidine). The metabolite does not appear to inhibit gastric acid secretion. Orally administered famotidine undergoes minimal metabolism on first pass through the liver. Biological Half-Life The elimination half-life is about 2 to 4 hours. The half-life is expected to increase nonlinearly in patients with decreased renal function. |
||
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Interactions
Concurrent use /of antacids/ with histamine H2-receptor antagonists in the treatment of peptic ulcer may be indicated for the relief of pain; however, simultaneous administration of antacids of medium to high potency (80 mmol to 150 mmol HCl) is not recommended since absorption of histamine H2-receptor antagonists may be decreased; patients should be advised not to take any antacids within 1/2 to 1 hour of histamine H2-receptor antagonists. /Histamine H2-receptor antagonists/ Concurrent use /of bone marrow depressants/ with H2-receptor antagonists may increase the risk of neutropenia or other blood dyscrasias. /Histamine H2-receptor antagonists/ Histamine H2-receptor antagonists may increase gastrointestinal pH; concurrent administration of ketoconazole with histamine H2-receptor antagonists may result in a marked reduction in absorption of ketoconazole; patients should be advised to take histamine H2-receptor antagonists at least 2 hours after ketoconazole. /Histamine H2-receptor antagonists/ Although a decrease in absorption is only reported in the literature for cimetidine and ranitidine, concurrent use with sucralfate may decrease the absorption of any H2-receptor antagonist; patients should be advised to take an H2-receptor antagonist 2 hours before sucralfate. /Histamine H2-receptor antagonists/ For more Interactions (Complete) data for FAMOTIDINE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
||
| 参考文献 | |||
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Anti-Ulcer Agents; Histamine H2 Antagonists Famotidine is currently the drug of choice for initial treatment and maintenance therapy in most patients with uncomplicated gastric or duodenal ulcer. ... A single bedtime dose of famotidine 40 mg is as efficatious as previously recommended multidose regimens and increases compliance. Histamine H2-receptor antagonists are indicated in the short-term treatment of active duodenal ulcer. They are also indicated (at reduce dosage) in the prevention of duodenal ulcer recurrence in selected patients. /Histamine H2-receptor antagonists; Included in US product labeling/ Famotidine ... /is/ indicated in the short-term treatment of active benign gastric ulcer. /Included in US product labeling/ For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for FAMOTIDINE (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings Although appropriate studies on the relationship of age to the effects of these medicines /cimetidine, famotidine, and ranitidine/ have not been performed in the geriatric population, no geriatrics-specific problems have been documented to date. However, confusion is more likely to occur in elderly patients with impaired hepatic or renal function. Adverse nervous system effects (eg, headache, dizziness) and GI effects (eg, constipation, diarrhea) occur most frequently during famotidine therapy. Although adverse effects of the drug generally are not severe, discontinuance of famotidine therapy has been necessary in up to 14% of patients. Adverse effects generally are similar when famotidine is administered orally or IV. Fever, hypertension, flushing, musculoskeletal pain, arthralgia, and tinnitus have been reported in 1% or less of patients receiving famotidine, but a causal relationship to the drug has not been established in many cases. An acute episode of gout occurred in one patient during therapy with the drug. Leukocytosis, leukopenia, neutropenia, pancytopenia, agranulocytosis, eosinophilia, prolonged erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and thrombocytopenia have occurred rarely in patients receiving famotidine. Changes in serum protein or cholesterol concentrations also have occurred. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for FAMOTIDINE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Famotidine decreases the production of gastric acid, suppresses acid concentration and pepsin content, and decreases the volume of gastric secretion. Famotidine inhibits both basal and nocturnal gastric acid secretion, as well as acid secretion stimulated by food, caffeine, insulin, and pentagastrin. Famotidine has a dose-dependent therapeutic action, with the highest dose having the most extended duration of action and the highest inhibitory effect on gastric acid secretion. Following oral administration, the onset of action is within one hour, and the peak effect is reached within 1-3 hours. The duration of effect is about 10-12 hours. |
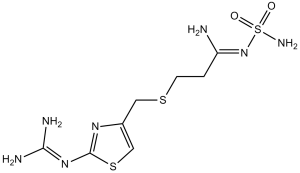
| 分子式 |
C8H15N7O2S3
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
337.45
|
|
| 精确质量 |
337.044
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 28.47; H, 4.48; N, 29.06; O, 9.48; S, 28.51
|
|
| CAS号 |
76824-35-6
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Famotidine-13C,d3; 2744683-81-4
|
|
| PubChem CID |
5702160
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.8±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
662.4±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
163-164°C
|
|
| 闪点 |
354.4±34.3 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.808
|
|
| LogP |
-0.4
|
|
| tPSA |
235.25
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
20
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
469
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
S(C([H])([H])C1=C([H])SC(/N=C(\N([H])[H])/N([H])[H])=N1)C([H])([H])C([H])([H])/C(/N([H])[H])=N/S(N([H])[H])(=O)=O
|
|
| InChi Key |
XUFQPHANEAPEMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C8H15N7O2S3/c9-6(15-20(12,16)17)1-2-18-3-5-4-19-8(13-5)14-7(10)11/h4H,1-3H2,(H2,9,15)(H2,12,16,17)(H4,10,11,13,14)
|
|
| 化学名 |
3-[[2-(diaminomethylideneamino)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]methylsulfanyl]-N'-sulfamoylpropanimidamide
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.41 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.41 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.41 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9634 mL | 14.8170 mL | 29.6340 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5927 mL | 2.9634 mL | 5.9268 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2963 mL | 1.4817 mL | 2.9634 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Chemotherapy and Locor
Histamiini H2 salpaus liitännäishoitona puutteellisen hoitovasteen skitsofreniassa
CTID: null
Phase: Phase 4 Status: Completed
Date: 2007-04-05