| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| 50g |
|
||
| 100g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Thymidylate synthase
Thymidylate synthase (TS; Ki=0.05 μM, human recombinant enzyme) [4] - DNA synthesis (inhibition via incorporation of 5-FUTP into DNA; EC50 for human colorectal cancer cell lines: 1-10 μM) [1] - RNA synthesis (interference via 5-FUTP incorporation into RNA) [2] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Adrucil 是尿嘧啶的类似物,在 C-5 位上有一个氟原子取代了氢。它使用与尿嘧啶相同的促进运输机制快速进入细胞。 Adrucil 在细胞内转化为几种活性代谢物:氟脱氧尿苷单磷酸 (FdUMP)、氟脱氧尿苷三磷酸 (FdUTP) 和氟尿苷三磷酸 (FUTP)。 Adrucil代谢物FdUMP与TS的核苷酸结合位点结合,与酶和CH2THF形成稳定的三元复合物,从而阻断正常底物dUMP的结合并抑制dTMP合成。 Adrucil 的代谢物也可能被错误地掺入 DNA,导致 DNA 链断裂和细胞死亡。 Adrucil 的促凋亡作用可能与其激活抑癌基因 p53 有关。 p53 功能的丧失会降低细胞对 Adrucil 的敏感性。 Adrucil 能够抑制多种癌细胞的存活并诱导其凋亡。 Adrucil 抑制鼻咽癌细胞系 CNE2 和 HONE1、胰腺癌细胞系 Capan-1 和人结肠癌细胞系 HT-29 的活力,IC50 分别为 9 μg/mL、3 μg/mL、0.22 μM、2.5 μM 。细胞测定:在96孔板中用Adrucil处理细胞7天后测量生长抑制(4000个HT-29细胞/孔,在含有10%透析胎牛血清的RPMI 1640培养基中);细胞附着过夜后,添加浓度不断增加的 Adrucil。孵育结束后,用磷酸盐缓冲盐水(pH 7.4)冲洗细胞3次,用10%三氯乙酸4℃固定60分钟,用去离子水洗涤5次,用0.4%磺罗丹明B染色溶液在室温下放置 15 分钟。用 1% 冰醋酸冲洗可去除未染色的磺基罗丹明 B。然后,将染色的细胞蛋白干燥并用 10 mM Tris-HCl 溶解。使用检测器在 540 nm 波长处测量光密度值。
72小时暴露后,对人结直肠癌细胞系(HT-29、SW620)具有强效抗增殖活性,IC50分别为3 μM和5 μM;诱导S期细胞周期阻滞和凋亡,表现为caspase-8活性升高和TUNEL染色阳性[1] - 72小时处理对人乳腺癌细胞系MCF-7具有抑制作用,IC50为7 μM;20 μM浓度下克隆形成效率较未处理对照组降低75%[3] - 抑制HT-29细胞中TS活性;10 μM 氟尿嘧啶(Fluorouracil; 5-Fluoracil, 5-FU)处理24小时,TS活性降低80%,导致细胞内胸苷池耗竭[4] - 与亚叶酸联用时抗肿瘤效果增强;5 μM 氟尿嘧啶(Fluorouracil; 5-Fluoracil, 5-FU)联合10 μM亚叶酸,HCT116细胞凋亡率较单药治疗提高60%[5] - 对5-FU耐药的人胃癌细胞系SGC-7901/FU具有细胞毒性,IC50为35 μM;耐药性与TS表达上调相关[2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Adrucil 广泛用于治疗一系列癌症,包括结直肠癌和乳腺癌。 100mg/kg Adrucil 显着抑制小鼠结肠癌 Colon 38 的肿瘤生长,肿瘤倍增时间 (TD)、生长延迟因子 (GDF) 和 T/C 分别为 26.5 天、4.4 和 14%。
抑制裸鼠HT-29结直肠癌异种移植瘤生长;每周腹腔注射(i.p.)50 mg/kg,持续4周,肿瘤生长抑制率(TGI)达70%(相较于溶媒对照组)[1] - 小鼠乳腺癌肺转移模型中有效;每周三次静脉注射30 mg/kg,持续3周,肺转移结节减少55%[3] - 延长L1210白血病小鼠的生存期;每日腹腔注射40 mg/kg,持续7天,中位生存期较未处理小鼠延长14天[5] |
| 酶活实验 |
采用纯化的人重组TS测定胸苷酸合成酶活性;将0.01-1 μM 氟尿嘧啶(Fluorouracil; 5-Fluoracil, 5-FU)、5,10-亚甲基四氢叶酸(辅因子)和脱氧尿苷一磷酸(dUMP,底物)在37°C下孵育45分钟;通过HPLC测定胸苷一磷酸(dTMP)的生成量,计算Ki值[4]
- 评估二氢嘧啶脱氢酶(DPD)介导的氟尿嘧啶(Fluorouracil; 5-Fluoracil, 5-FU)代谢;将10-100 μM 氟尿嘧啶(Fluorouracil; 5-Fluoracil, 5-FU)与纯化的人DPD和NADPH在37°C下孵育60分钟;通过HPLC定量5-氟-5,6-二氢尿嘧啶(无活性代谢产物),评估代谢速率[5] |
| 细胞实验 |
Adrucil 在 96 孔板中处理 7 天(4000 个 HT-29 细胞/孔,在含有 10% 透析胎牛血清的 RPMI 1640 培养基中),产生生长抑制测量结果;细胞贴壁过夜后,添加 Adrucil 浓度。细胞用去离子水洗涤五次,用10%三氯乙酸4℃固定60分钟,用磷酸盐缓冲盐水漂洗三轮后,用0.4%磺罗丹明B溶液室温染色15分钟( pH 7.4)。用 1% 冰醋酸冲洗,去除未染色的磺基罗丹明 B。之后,干燥并溶解在 10 mM Tris-HCl 中,即为染色的细胞蛋白。使用波长为 540 nm 的检测器测定光密度值。
在96孔板中接种HT-29结直肠癌细胞,每孔3×103个;贴壁24小时后,用0.5-50 μM 氟尿嘧啶(Fluorouracil; 5-Fluoracil, 5-FU)处理72小时;采用MTT法测定细胞活力,碘化丙啶染色后流式细胞术分析细胞周期分布,膜联蛋白V-FITC/PI双染色检测凋亡[1] - 在6孔板中培养MCF-7乳腺癌细胞,每孔5×103个;暴露于2-40 μM 氟尿嘧啶(Fluorouracil; 5-Fluoracil, 5-FU)48小时;洗涤细胞后在无药培养基中培养14天;甲醇固定并结晶紫染色;计数细胞数>50的克隆以确定克隆形成抑制率[3] - 在24孔板中接种SGC-7901/FU耐药细胞;用氟尿嘧啶(Fluorouracil; 5-Fluoracil, 5-FU)(10-80 μM)单独或与TS抑制剂(1 μM)联合处理72小时;通过caspase-8活性测定和PARP裂解免疫印迹检测凋亡细胞;RT-PCR定量TS mRNA表达[2] |
| 动物实验 |
Three times per week, mice are given intraperitoneal injections of 5-FU (23 mg/kg) using a 26 gauge needle. A 1 M/L stock solution is prepared by dissolving 5-FU in 100% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and refrigerating it at −20°C. To prepare 0.1 M/L (10% DMSO) solutions for intraperitoneal injections, the stock is then defrosted and diluted with sterile water. The 5-FU dose is calculated to be equal to one standard human dose per unit of body surface area. In cancerous mouse models, 5-FU at low doses (10–40 mg/kg) has demonstrated antitumor efficacy. Three times a week, a 26 gauge needle was used to inject 10% DMSO in sterile water intraperitoneally into mice that were given sham treatment. The maximum volume per injection is limited to 200 μL, and the injected volumes are determined based on the patient's body weight. Three (2 treatments), seven (3 treatments), and fourteen (6 treatments) days following the initial injection, mice are put to death by cervical dislocation, and their colons are removed for in vitro research.
Nude mice (6-7 weeks old) were implanted subcutaneously with 2×106 HT-29 colorectal cancer cells; when tumors reached 100 mm3, Fluorouracil (5-Fluoracil, 5-FU) was dissolved in 0.9% normal saline and administered i.p. at 50 mg/kg once weekly for 4 weeks; control mice received normal saline; tumor volume was measured every 3 days, and TGI was calculated [1] - BALB/c mice with breast cancer lung metastasis (intravenous inoculation of 1×106 MCF-7 cells) were treated with i.v. Fluorouracil (5-Fluoracil, 5-FU) at 30 mg/kg three times weekly for 3 weeks; the drug was dissolved in phosphate-buffered saline; mice were sacrificed to count lung metastatic nodules [3] - DBA/2 mice inoculated with L1210 leukemia cells (intraperitoneal injection of 1×105 cells) received i.p. Fluorouracil (5-Fluoracil, 5-FU) at 40 mg/kg daily for 7 days; the drug was suspended in 0.5% carboxymethylcellulose sodium; mice were monitored for survival [5] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
28-100% Seven percent to 20% of the parent drug is excreted unchanged in the urine in 6 hours; of this over 90% is excreted in the first hour. The remaining percentage of the administered dose is metabolized, primarily in the liver. Given by continuous iv infusion for 24 hr, plasma concn in range of 0.5 to 3.0 uM are obtained and urinary excretion of fluorouracil is only 4%. Fluorouracil readily enters cerebrospinal fluid, and concn of about 7 uM are reached within 30 min after iv admin; values are sustained for approx 3 hr and subside slowly during period of 9 hr. Fluorouracil crosses the placenta in rats. Following iv administration of fluorouracil, no intact drug is detected in plasma after 3 hours. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for FLUOROURACIL (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Hepatic. The catabolic metabolism of fluorouracil results in degradation products ( e.g., CO2, urea and α-fluoro-ß-alanine) which are inactive. A small portion of fluorouracil is anabolized in the tissues to 5-fluoro-2'-deoxyuridine and then to 5-fluoro-2'-deoxyuridine-5'-monophosphate, the active metabolite of the drug. The major portion of the drug is degraded in the liver. The metabolites are excreted as respiratory carbon dioxide and as urea, alpha-fluoro-beta-alanine, alpha-fluoro-beta-guanidopropionic acid, and alpha-fluoro-beta-ureidopropionic acid in urine. Following a single iv dose of fluorouracil, approximately 15% of the dose is excreted in urine as intact drug within 6 hours; over 90% of this is excreted in the first hour. ... Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase /is/ an NADPH-requiring homodimeric protein (Mr ~210 kDa) containing FMN/FAD, and an iron-sulfur cluster in each subunit. The enzyme is located mainly in liver cytosol, where it catalyzes the reduction of 5-fluorouracil and related pyrimidines ... ... Several routes are available for the formation of the 5'-monophosphate nucleotide (F-UMP) in animal cells. 5-FU may be converted to fluorouridine by uridine phosphorylase and then to F-UMP by uridine kinase, or it may react directly with 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP), in a reaction catalyzed by ... orotate phosphoribosyl transferase, to form F-UMP. Many metabolic pathways are available to F-UMP, including incorporation into RNA. A reaction sequence crucial for antineoplastic activity involves reduction of the diphosphate nucleotide by the enzyme ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase to the deoxynucleotide level and the eventual formation of 5-fluoro-2'-deoxyuridine-5'-phosphate (F-dUMP). 5-FU also may be converted directly to the deoxyriboside 5-FUdR by the enzyme thymidine phosphorylase and further to F-dUMP, a potent inhibitor of thymidylate synthesis, by thymidine kinase ... The folate cofactor, 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate, and F-dUMP form a covalently bound ternary complex with the enzyme /thymidylate synthase/ ... ... Metabolic degradation /of 5-FU and floxuridine/ occurs in many tissues, particularly in liver. Floxuridine is converted by thymidine or deoxyuridine phosphorylases into 5-FU. 5-FU is inactivated by reduction of the pyrimidine ring; this reaction is carried out by dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD), which is found in liver, intestinal mucosa, tumor cells, and other tissues ... Its metabolite, 5-fluoro-5,6-dihydrouracil ... is ultimately degraded to alpha-fluoro-beta-alanine ... Although the liver contains high concn of DPD, dosage does not have to be modified in patients with hepatic dysfunction, presumably because of degradation of the drug at extrahepatic sites or by vast excess of this enzyme in the liver ... 5-Fluorouracil is a known human metabolite of Tegafur. Hepatic. The catabolic metabolism of fluorouracil results in degradation products ( e.g., CO2, urea and alpha-fluoro-beta-alanine) which are inactive. Route of Elimination: Seven percent to 20% of the parent drug is excreted unchanged in the urine in 6 hours; of this over 90% is excreted in the first hour. The remaining percentage of the administered dose is metabolized, primarily in the liver. Half Life: 10-20 minutes Biological Half-Life 10-20 minutes Following iv administration, the plasma elimination half-life averages about 16 minutes (range: 8-20 minutes) and is dose dependent. Rapid iv admin of 5-FU produces plasma concn of 0.1 to 1.0 mM; plasma clearance is rapid (half-life 10 to 20 min) ... Oral bioavailability in humans is 15-20% due to first-pass metabolism by dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) in the liver [5] - Plasma half-life (t1/2) in humans is 10-20 minutes; volume of distribution (Vd) is 0.7-1.0 L/kg [5] - Metabolized by DPD to inactive metabolites; active metabolites (5-FUTP, 5-FdUMP) are formed via intracellular phosphorylation [4] - Plasma protein binding rate is 10-15% in humans [3] - 70-80% of the dose is excreted in urine within 24 hours, primarily as inactive metabolites [5] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
The precise mechanism of action has not been fully determined, but the main mechanism of fluorouracil is thought to be the binding of the deoxyribonucleotide of the drug (FdUMP) and the folate cofactor, N5дус10-methylenetetrahydrofolate, to thymidylate synthase (TS) to form a covalently bound ternary complex. This results in the inhibition of the formation of thymidylate from uracil, which leads to the inhibition of DNA and RNA synthesis and cell death. Fluorouracil can also be incorporated into RNA in place of uridine triphosphate (UTP), producing a fraudulent RNA and interfering with RNA processing and protein synthesis. Toxicity Data LD50=230mg/kg (orally in mice) Interactions To incr the complete response rate of patients with locally advanced head and neck cancer after 3 cycles of neoadjuvant chemotherapy, sequential methotrexate was added to the combination of cis-platin and continuous infusion fluorouracil. The feasibility of administering 3 additional cycles of the same regimen as adjuvant chemotherapy was examined. Thirty eight patients were treated; the median age was 53 yr and 36 patients had stage IV disease. Chemotherapy consisted of methotrexate 120 mg/sq m followed 24 hr later by cis-platin 100 mg/sq m and a 5 day continuous infusion of fluorouracil at 1000 mg/sq m/day. Of 34 patients evaluable for response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy, 9 had a complete response, 21 a partial response, 2 a minimal response, and 1 patient each stable disease and no response. Of 31 patients who received local therapy, 15 were treated with surgery and radiotherapy and 16 with radiotherapy alone. Of 25 patients eligible to receive adjuvant chemotherapy only 10 received all 3 intended cycles, while 15 received less or no adjuvant chemotherapy because of patient refusal, cumulative toxicity, or early disease progression. With a median follow up time of 39 mo, the median survival is estimated to be 20 mo. Of 8 patients with nasopharyngeal or paranasal sinus cancer, none had disease recurrence. Patients with good initial performance status and low N-stage also had a significant survival advantage. Chemotherapy-related toxicities consisted mainly of mucositis, requiring fluorouracil dose reduction in the majority of patients; similar toxicities were exacerbated in the adjuvant setting. The addition of methotrexate did not incr the complete response rate over what has been reported for the combination of cis-platin and fluorouracil alone. Leukopenic and/or thrombocytopenic effects fluorouracil may be increased with concurrent or recent therapy with blood dyscrasia causing medications. Concurrent use /with leucovorin/ may increase the therapeutic and toxic effects of fluorouracil. Because normal defense mechanisms may be suppressed by fluorouracil therapy the patient's antibody responses to vaccine (killed virus) may be decreased. For more Interactions (Complete) data for FLUOROURACIL (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Dog oral 30 mg/kg LD50 Mouse oral 115 mg/kg LD50 Mouse iv 81 mg/kg LD50 Mouse sc 169 mg/kg For more Non-Human Toxicity Values (Complete) data for FLUOROURACIL (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Myelosuppression (leukopenia, thrombocytopenia) is the major dose-limiting toxicity in humans; occurs at i.v. doses ≥500 mg/m² [1] - Gastrointestinal toxicity (mucositis, diarrhea, nausea) was observed in rats receiving i.p. doses >100 mg/kg [3] - Mild hepatotoxicity (elevated serum transaminases) was noted in dogs treated with i.v. doses of 80 mg/kg weekly for 4 weeks; no significant nephrotoxicity was detected [5] - Drug-drug interaction: co-administration with irinotecan increases gastrointestinal toxicity due to synergistic inhibition of intestinal epithelial cell proliferation [1] - Cytotoxicity to normal human intestinal epithelial cells (HIEC) is moderate with CC50 >50 μM [2] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Antimetabolites; Antimetabolites, Antineoplastic; Immunosuppressive Agents Fluorouracil is indicated for palliative treatment of carcinoma of the colon, rectum, breast, stomach, and pancreas in patients considered to be incurable by surgery or other means. /Included in US product update/ Fluorouracil is also indicated for treatment of bladder carcinoma, prostatic carcinoma, epithelial ovarian carcinoma, cervical carcinoma, endometrial carcinoma, anal carcinoma, esophageal carcinoma,metastatic tumors of skin carcinoma, and hepatoblastoma, and is used by intra-arterial injection for treatment of hepatic tumors and head and neck tumors. /Not included in US product label/ Fluorouracil, in combination therapy, is reasonable medical therapy at some point in the management of adrenocortical carcinoma, vulvar carcinoma, penile carcinoma and carcinoid tumors (gastrointestinal and neuroendocrine tumors). /Not included in US product label/ For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for FLUOROURACIL (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings Anorexia and nausea are common adverse effects of fluorouracil, and vomiting occurs frequently. These reactions generally occur during the first week of therapy, can often be alleviated by antiemetics, and generally subside within 2 or 3 days following therapy. Stomatitis is one of the most common and often the earliest sign of specific toxicity, appearing as early as the fourth day but more commonly on the fifth to eighth day of therapy. Diarrhea, which also occurs frequently, usually appears slightly later than stomatitis, but may occur concurrently or even in the absence of stomatitis. Esophagitis, proctitis, and GI ulceration and bleeding have been reported, and paralytic ileus occurred in two patients who received excessive dosage. Patients must be closely monitored for adverse GI effects. Leukopenia, predominantly of the granulocytopenic type, thrombocytopenia, and anemia occur commonly with fluorouracil therapy; leukopenia usually occurs after an adequate course of fluorouracil therapy. Pancytopenia and agranulocytosis also have occurred. The patient's hematologic status must be carefully monitored. The nadir of the white blood cell count usually occurs from the ninth to the fourteenth day after therapy is initiated but may occur as late as the 25th day after the first dose of fluorouracil. Maximum thrombocytopenia has been reported to occur from the seventh to seventeenth day of therapy. Hematopoietic recovery is usually rapid and by the thirtieth day, blood cell counts have usually reached the normal range. Hair loss occurs frequently with fluorouracil therapy, and cosmetically significant alopecia has occurred in a substantial number of patients. Regrowth of hair has been reported even in patients receiving repeated courses of the drug. Partial loss of nails has occurred rarely, and diffuse melanosis of the nails has been reported. The most common type of dermatologic toxicity is a pruritic maculopapular rash which usually appears on the extremities and less frequently on the trunk. This rash is generally reversible and usually responsive to symptomatic treatment. An erythematous, desquamative rash involving the hands and feet has been reported in patients receiving fluorouracil (in some cases, prolonged infusions of high dosages of the drug were administered). The rash may be accompanied by tingling or painful hands and feet, swollen palms and soles, and phalangeal tenderness. These adverse effects, referred to as palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia or hand-foot syndrome, may gradually disappear over 5-7 days after discontinuance of fluorouracil therapy. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for FLUOROURACIL (31 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Fluorouracil is an antineoplastic anti-metabolite. Anti-metabolites masquerade as purine or pyrimidine - which become the building blocks of DNA. They prevent these substances from becoming incorporated into DNA during the \"S\" phase (of the cell cycle), stopping normal development and division. Fluorouracil blocks an enzyme which converts the cytosine nucleotide into the deoxy derivative. In addition, DNA synthesis is further inhibited because Fluorouracil blocks the incorporation of the thymidine nucleotide into the DNA strand. Fluorouracil (5-Fluoracil, 5-FU) is a fluorinated pyrimidine antimetabolite, one of the most widely used chemotherapeutic agents [1] - Its antitumor effect is mediated by multiple mechanisms: inhibition of TS via 5-FdUMP, incorporation of 5-FUTP into RNA, and incorporation of 5-FdUTP into DNA, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis [4] - Approved by the FDA for the treatment of colorectal cancer, breast cancer, gastric cancer, and several other solid tumors [3] - Leucovorin enhances 5-FU efficacy by stabilizing the TS-5-FdUMP-5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate ternary complex [5] - Resistance mechanisms include upregulation of TS, increased DPD activity, and enhanced DNA repair capacity in tumor cells [2] |
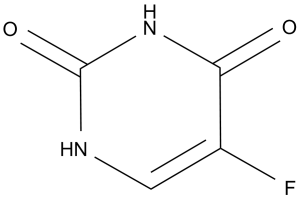
| 分子式 |
C4H3FN2O2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
130.08
|
|
| 精确质量 |
130.017
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 36.93; H, 2.32; F, 14.61; N, 21.54; O, 24.60
|
|
| CAS号 |
51-21-8
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
3385
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.7±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
401.4±48.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
282-286 °C (dec.)(lit.)
|
|
| 闪点 |
196.5±29.6 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.596
|
|
| LogP |
-2.1
|
|
| tPSA |
65.72
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
0
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
9
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
199
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
FC1=C([H])N([H])C(N([H])C1=O)=O
|
|
| InChi Key |
GHASVSINZRGABV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C4H3FN2O2/c5-2-1-6-4(9)7-3(2)8/h1H,(H2,6,7,8,9)
|
|
| 化学名 |
5-fluoro-1H-pyrimidine-2,4-dione
|
|
| 别名 |
NSC 19893; 5-FU; Fluorouracil; NSC-19893; NSC19893; 5-Fluorouracil; 5-Fluorouracil; 5FU; Fluoroplex; Efudex; Adrucil; Carac; Trade name: Adrucil among many others.
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (19.22 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (19.22 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (19.22 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (19.22 mM) (饱和度未知) in 5% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 50% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 5 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (19.22 mM) (饱和度未知) in 5% DMSO + 95% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 6 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (19.22 mM) in 5% DMSO + 95% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 7 中的溶解度: Saline: 10mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 7.6876 mL | 38.4379 mL | 76.8758 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.5375 mL | 7.6876 mL | 15.3752 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.7688 mL | 3.8438 mL | 7.6876 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Testing Immunotherapy (Atezolizumab) With or Without Chemotherapy in Locoregional MSI-H/dMMR Gastric and Gastroesophageal Junction (GEJ) Cancer
CTID: NCT05836584
Phase: Phase 2 Status: Recruiting
Date: 2024-11-19