| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在原代小鼠胰腺 β 细胞中,格列吡嗪抑制 ATP 敏感性钾 (KATP) 通道 (IC50= 6.4 nM) [1]。
|
|---|---|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Gastrointestinal absorption of glipizide is uniform, rapid, and essentially complete. The absolute bioavailability of glipizide in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving a single oral dose was 100%. The maximum plasma concentrations are expected to be reached within 6 to 12 hours following initial dosing. The steady-state plasma concentrations of glipizide from extended-release oral formulations are maintained over the 24-hour dosing interval. In healthy volunteers, the absorption of glipizide was delayed by the presence of food but the total absorption was unaffected. Glipizide is mainly eliminated by hepatic biotransformation, where less than 10% of the initial dose of the drug can be detected in the urine and feces as unchanged glipizide. About 80% of the metabolites of glipizide is excreted in the urine while 10% is excreted in the feces. The mean volume of distribution was approximately 10 L following administration of single intravenous doses in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. In mice and rat studies, the presence of the drug and its metabolites was none to minimal in the fetus of pregnant female animals. Other sulfonylurea drugs were shown to cross the placenta and enter breast milk thus the potential risk of glipizide in fetus or infants cannot be excluded. The mean total body clearance of glipizide was approximately 3 L/hr following administration of single intravenous doses in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism / Metabolites Glipizide is subject to hepatic metabolism, in which its major metabolites are formed from aromatic hydroxylation. These major metabolites are glipizide are reported to be pharmacologically inactive. In contrast, an acetylaminoethyl benzine derivative is formed as a minor metabolite which accounts for less than 2% of the initial dose and is reported to have one-tenth to one-third as much hypoglycemic activity as the parent compound. Glipizide has known human metabolites that include 4-trans-hydroxy-glipizide. Hepatic. The major metabolites of glipizide are products of aromatic hydroxylation and have no hypoglycemic activity. A minor metabolite which accounts for less than 2% of a dose, an acetylaminoethyl benzine derivatives, is reported to have 1/10 to 1/3 as much hypoglycemic activity as the parent compound. Route of Elimination: The primary metabolites are inactive hydroxylation products and polar conjugates and are excreted mainly in the urine. Half Life: 2-5 hours Biological Half-Life The mean terminal elimination half-life of glipizide ranged from 2 to 5 hours after single or multiple doses in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
Sulfonylureas likely bind to ATP-sensitive potassium-channel receptors on the pancreatic cell surface, reducing potassium conductance and causing depolarization of the membrane. Depolarization stimulates calcium ion influx through voltage-sensitive calcium channels, raising intracellular concentrations of calcium ions, which induces the secretion, or exocytosis, of insulin. Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Limited data indicate that the levels of glipizide in milk are low. However, an alternate drug for which there is more information may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. Monitor breastfed infants for signs of hypoglycemia such as jitteriness, excessive sleepiness, poor feeding, seizures cyanosis, apnea, or hypothermia. If there is concern, monitoring of the breastfed infant's blood glucose is advisable during maternal therapy with hypoglycemic agents. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Blood glucose levels were normal in 2 breastfed infants whose mothers were taking oral glipizide 5 mg daily. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Glipizide is about 98-99% bound to serum proteins, with albumin being the main plasma protein. Toxicity Data The acute oral toxicity was extremely low in all species tested (LD50 greater than 4 g/kg). |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Pharmacodynamics
Glipizide is a blood glucose-lowering agent. The initial onset of blood glucose-lowering effect occurs around 30 minutes post-administration with the duration of action lasting for about 12 to 24 hours. While the chronic use of glipizide does not result in elevations in the fasting insulin levels over time, the postprandial insulin response, or insulin response to a meal, is observed to be enhanced, even after 6 months of treatment. The main therapeutic actions of glipizide primarily occur at the pancreas where the insulin release is stimulated, but glipizide also mediates some extrapancreatic effects, such as the promotion of insulin signaling effects on the muscles, fat, or liver cells. Due to its action on the endogenous cells, sulfonylureas including glipizide is associated with a risk for developing hypoglycemia and weight gain in patients receiving the drug. Chronic administration of glipizide may result in down-regulation of the sulfonylurea receptors on pancreatic beta cells, which are molecular targets of the drug, leading to a reduced effect on insulin secretion. Like other sulfonylureas, glipizide may work on pancreatic delta (δ) cells and alpha (α) cells to stimulate the secretion of somatostatin and suppress the secretion of glucagon, which are peptide hormones that regulate neuroendocrine and metabolic pathways. Other than its primary action on the pancreas, glipizide also exerts other biological actions outside of the pancreas, or "extrapancreatic effects", which is similar to other members of the sulfonylurea drug class. Glipizide may enhance the glucose uptake into the skeletal muscles and potentiate the action of insulin in the liver. Other effects include inhibited lipolysis in the liver and adipose tissue, inhibited hepatic glucose output, and increased uptake and oxidation of glucose. It has also been demonstrated by several studies that the chronic therapeutic use of sulfonylureas may result in an increase in insulin receptors expressed on monocytes, adipocytes, and erythrocytes. |
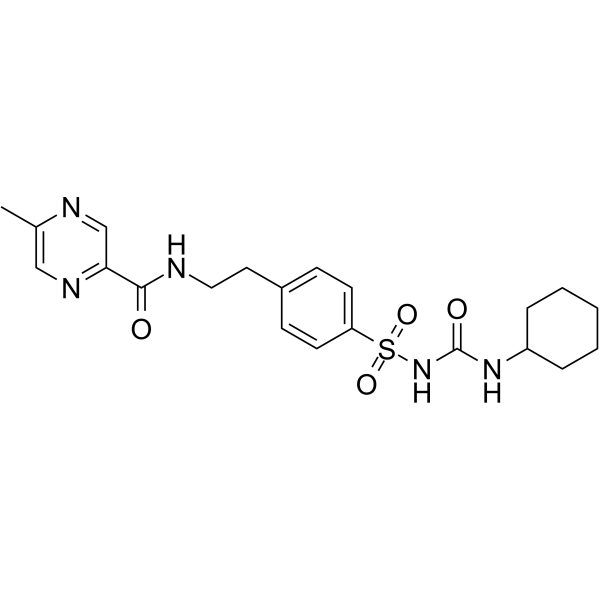
| 分子式 |
C21H27N5O4S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
445.54
|
| 精确质量 |
445.178
|
| CAS号 |
29094-61-9
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Glipizide-d11;1189426-07-0
|
| PubChem CID |
3478
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
676.0±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
208-209°C
|
| 闪点 |
362.6±34.3 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.2 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.654
|
| LogP |
3.37
|
| tPSA |
138.53
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
31
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
697
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
ZJJXGWJIGJFDTL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C21H27N5O4S/c1-15-13-24-19(14-23-15)20(27)22-12-11-16-7-9-18(10-8-16)31(29,30)26-21(28)25-17-5-3-2-4-6-17/h7-10,13-14,17H,2-6,11-12H2,1H3,(H,22,27)(H2,25,26,28)
|
| 化学名 |
N-[2-[4-(cyclohexylcarbamoylsulfamoyl)phenyl]ethyl]-5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxamide
|
| 别名 |
Minidiab; Glucotrol; Glipizide
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~50 mg/mL (~112.22 mM)
H2O : ~0.67 mg/mL (~1.50 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (5.61 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浮液;超声助溶。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.61 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2445 mL | 11.2223 mL | 22.4447 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4489 mL | 2.2445 mL | 4.4889 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2244 mL | 1.1222 mL | 2.2445 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Outpatient Discharge Therapy With Saxagliptin+MetforminXR vs GlipizideXL for Type 2 Diabetes With Severe Hyperglycemia
CTID: NCT01267448
Phase: Phase 4 Status: Completed
Date: 2023-06-26