| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
IKK2 (IC50 = 40 nM); IKK1 (IC50 = 200 nM); IKK (IC50 = 70 nM); LRRK2 (IC50 = 50 nM)
The primary targets of IKK-16 (IKK Inhibitor VII; IKK 16) are the IκB kinase α (IKKα) and IκB kinase β (IKKβ) , key kinases in the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway that regulate IκBα phosphorylation and NF-κB activation. - For human recombinant IKKβ, the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of IKK-16 was 1.3 μM; for human recombinant IKKα, the IC50 was 12 μM, showing higher selectivity for IKKβ [1] - IKK-16 exhibited no significant inhibitory activity against other kinases involved in inflammatory signaling, including c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1, IC50 > 100 μM), p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38α, IC50 > 100 μM), and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 (ERK2, IC50 > 100 μM) [1] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
IKK-16 抑制 HUVEC 细胞中 TNFα 刺激的粘附分子 E-选择素、ICAM-1 和 VCAM-1 的表达。尽管 IKK-16 在 IFNγ 诱导的 β2 微球蛋白或 HLA-DR 表达中显示出活性,但其在这些测定中的效力较弱 4 至 10 倍。激酶测定:IKK 16 是 IKK2、IKK 复合物和 IKK1 的选择性 IκB 激酶 (IKK) 抑制剂,IC50 分别为 40 nM、70 nM 和 200 nM。 IKK16 还抑制富含亮氨酸重复激酶 2 (LRRK2),IC50 为 50 nM。细胞测定:IKK-16(IKK 抑制剂 VII)通过阻断 IκBα 降解来抑制 IKK2,并抑制 HUVEC 细胞中 TNFα 刺激的粘附分子 E-选择素、ICAM-1 和 VCAM-1 的表达。此外,IKK-16 还在 IFNγ 诱导的 MHC 分子 β2 微球蛋白和 HLA-DR 表达中表现出活性,但其在这些测定中的效力比粘附分子测定弱 4 至 10 倍。
1. IKK激酶活性抑制: - IKK-16(0.1~30 μM)以浓度依赖性方式抑制重组人IKKβ活性。3 μM时抑制率约80%,10 μM时抑制率达95%;对IKKα,10 μM IKK-16 的抑制率约60%,证实其优先抑制IKKβ [1] 2. 细胞内NF-κB信号抑制: - NF-κB荧光素酶报告基因实验:在转染NF-κB萤火虫荧光素酶报告质粒及海肾荧光素酶内参质粒的HEK293T细胞中,IKK-16(0.5~20 μM)浓度依赖性抑制TNF-α(10 ng/mL)诱导的NF-κB转录活性,IC50为2.7 μM;20 μM IKK-16 使荧光素酶活性较溶媒对照组降低约90% [1] - IκBα磷酸化抑制:在TNF-α(10 ng/mL)刺激的HeLa细胞中,IKK-16(5 μM)预处理1小时,可在刺激15分钟时使IκBα磷酸化(Ser32/36)降低约75%(Western blot检测);总IκBα蛋白水平无显著变化,表明其特异性抑制IKK介导的磷酸化 [1] 3. 促炎因子分泌减少: - 在脂多糖(LPS,1 μg/mL)刺激的RAW264.7小鼠巨噬细胞中,IKK-16(1~10 μM)浓度依赖性抑制肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)和白细胞介素-6(IL-6)分泌。10 μM时,TNF-α分泌减少约85%,IL-6分泌减少约80%(ELISA检测) [3] - 在原代小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞中,5 μM IKK-16 使LPS诱导的TNF-α和IL-6分泌分别减少约70%和65%,且不影响细胞活力(MTT法检测,20 μM时活力>90%) [3] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
IKK-16 在大鼠和小鼠中具有口服生物利用度,可抑制 LPS 诱导的体内 TNF-α 释放以及硫代乙醇酸诱导的腹膜炎中的中性粒细胞外渗
1. 盲肠结扎穿孔(CLP)诱导小鼠脓毒症模型(多器官功能障碍综合征MODS模型)中的疗效: - 动物模型与给药方案:8~10周龄雄性C57BL/6小鼠经CLP手术诱导脓毒症,随机分为3组(n=10/组):假手术组(无CLP,无药物)、CLP+溶媒组(CLP+0.5% DMSO/PBS)、CLP+IKK-16组(CLP+10 mg/kg或20 mg/kg IKK-16,腹腔注射)。IKK-16 于CLP后1小时和6小时给药 [3] - 生存率改善:CLP+IKK-16(20 mg/kg)组7天生存率为60%,显著高于CLP+溶媒组的20%(P<0.01);10 mg/kg组生存率中度改善(40%,P<0.05) [3] - 器官损伤减轻: - 肝肾功能:CLP+IKK-16(20 mg/kg)组血清丙氨酸转氨酶(ALT)和天冬氨酸转氨酶(AST,肝损伤标志物)水平分别为CLP+溶媒组的42%和38%;血清肌酐(肾损伤标志物)较溶媒组降低55% [3] - 肺和肠道损伤:组织病理学分析显示,IKK-16(20 mg/kg)减少LPS诱导的肺泡充血及炎症细胞浸润(组织学评分:2.1±0.3 vs 溶媒组4.7±0.5,P<0.01),并减轻肠黏膜糜烂(组织学评分:1.8±0.2 vs 溶媒组4.3±0.4,P<0.01) [3] - 炎症反应及NF-κB活性抑制: - 血清细胞因子:IKK-16(20 mg/kg)在CLP后24小时使血清TNF-α和IL-6水平分别降低约70%和65% [3] - 组织NF-κB活性:肝和肺组织Western blot显示,IKK-16(20 mg/kg)使IKKβ磷酸化(Ser177/181)降低约65%,IκBα磷酸化降低约70%(vs 溶媒组) [3] |
| 酶活实验 |
IKK 16 是 IKK2、IKK 复合物和 IKK1 的选择性 IκB 激酶 (IKK) 抑制剂,IC50 分别为 40 nM、70 nM 和 200 nM。 IKK16 还抑制富含亮氨酸重复激酶 2 (LRRK2),IC50 为 50 nM。
IKKα/IKKβ激酶活性实验: 1. 反应体系制备: - IKKβ实验:将重组人IKKβ(每反应0.1 μg)与GST-IκBα(1 μg,含Ser32/36的底物肽)、ATP(50 μM,含[γ-32P]ATP用于放射性检测)及激酶缓冲液(25 mM Tris-HCl pH7.5、10 mM MgCl2、1 mM DTT、0.1 mM Na3VO4)混合,总体积25 μL。IKK-16 用DMSO溶解,终浓度为0.1、0.3、1、3、10、30 μM(DMSO终浓度≤0.1%),设置溶媒对照组(0.1% DMSO)和阳性对照组(已知IKK抑制剂) [1] - IKKα实验:反应体系与IKKβ实验一致,仅将重组人IKKβ替换为重组人IKKα(每反应0.1 μg) [1] 2. 孵育与检测: - 混合物30°C孵育45分钟,加入5 μL 6×SDS上样缓冲液并95°C加热5分钟终止反应;12% SDS-PAGE分离蛋白后,凝胶真空干燥,采用磷屏成像仪检测磷酸化GST-IκBα的放射性信号 [1] 3. 数据分析: - 图像分析软件定量放射性条带强度,IKK-16 抑制率计算为[(对照组放射性-给药组放射性)/对照组放射性]×100%;采用四参数逻辑模型拟合浓度-抑制曲线,计算IC50值 [1] |
| 细胞实验 |
SH-SY5Y 细胞用 25% (v/v) BacMam LRRK2-GFP G2019S 转导,然后铺板(20 µL/孔,20,000 个细胞/孔)到八个 384 孔测定板上。然后,将 25% BacMam LRRK2-GFP G2019S 转导的 SH-SY5Y 细胞与相应浓度的相应物质(例如 IKK 16、0.01、0.1、1、10 和 100 μM)一起孵育 90 分钟,然后进行 TR -使用 Tb-抗 LRRK2 pSer935 抗体进行 FRET 检测。计算出抑制百分比。
1. NF-κB荧光素酶报告基因实验: - 细胞接种与转染:HEK293T细胞以2×104个/孔接种96孔板,用含10%胎牛血清(FBS)的DMEM过夜培养;将质粒混合物(0.1 μg/孔NF-κB萤火虫荧光素酶报告质粒、0.01 μg/孔海肾荧光素酶内参质粒)与转染试剂共转染细胞,转染24小时后更换为含1% FBS的新鲜DMEM [1] - 药物处理与刺激:向各孔加入IKK-16(0.5、1、5、10、20 μM),预孵育1小时;加入TNF-α(10 ng/mL)刺激NF-κB激活,继续孵育6小时,设置溶媒对照组(0.1% DMSO)和未刺激对照组(无TNF-α) [1] - 荧光素酶活性检测:室温下用被动裂解缓冲液(100 μL/孔)裂解细胞15分钟;取20 μL裂解液与50 μL荧光素酶检测试剂(测萤火虫荧光素酶)及50 μL终止发光试剂(测海肾荧光素酶)混合于96孔发光板,微孔板发光仪检测发光强度;相对荧光素酶活性计算为萤火虫荧光素酶活性与海肾荧光素酶活性的比值 [1] 2. IκBα磷酸化Western blot实验: - 细胞处理:HeLa细胞以2×105个/孔接种6孔板,培养至80%融合;IKK-16(5 μM)预处理1小时后,用TNF-α(10 ng/mL)分别刺激0、15、30、60分钟,设置仅TNF-α刺激的溶媒对照组 [1] - 蛋白提取与检测:冰上用含蛋白酶抑制剂(亮肽素、胃蛋白酶抑制剂)和磷酸酶抑制剂(Na3VO4、NaF)的RIPA缓冲液裂解细胞30分钟;12,000×g 4°C离心15分钟,收集上清;BCA蛋白定量试剂盒测定蛋白浓度;每泳道上样30 μg蛋白,10% SDS-PAGE分离后转PVDF膜;膜用5%脱脂牛奶室温封闭1小时,加入抗磷酸化IκBα(p-IκBα Ser32/36)和总IκBα一抗4°C孵育过夜;TBST洗膜后,加入辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)标记二抗室温孵育1小时;增强化学发光(ECL)系统显影蛋白条带,ImageJ软件定量条带强度 [1] 3. 炎症因子分泌实验: - 细胞培养与处理:RAW264.7小鼠巨噬细胞以5×105个/孔接种24孔板,过夜培养;更换为无血清DMEM,加入IKK-16(1、5、10 μM)预孵育1小时;加入LPS(1 μg/mL)刺激细胞因子分泌,继续孵育24小时 [3] - 细胞因子检测:收集细胞培养上清,1,000×g离心10分钟去除细胞碎片;夹心ELISA试剂盒检测上清中TNF-α和IL-6浓度;酶标仪450 nm测吸光度,根据标准曲线计算细胞因子浓度 [3] |
| 动物实验 |
Rats and Mice: In two animal models, IKK 16 is tested. Its ability to prevent TNF from being released into the bloodstream after LPS challenge in rats is tested first. One hour before the LPS challenge, IKK 16 is dosed subcutaneously (sc) or orally (o) at a dose of 30 mg/kg. Plasma is collected four hours after the challenge, and a commercially available ELISA kit is used to assess the systemic TNFα levels. IKK 16 exhibits a notable 86% (sc) and 75% (p.o.) inhibition when administered via either route and at the recommended dose. IKK 16 is also active in the mouse model of peritonitis caused by thioglycollate in a subsequent experiment. In this model, a dose of 10 mg/kg sc results in an approximately 50% inhibition of neutrophil extravasation.
Mice: LPS (9 mg/kg body weight) and PepG (3 mg/kg body weight) are administered intraperitoneally to two-month-old male C57BL/6 mice. Sham mice receive the same care but are not exposed to LPS or PepG. Mice are given either IKK 16 (1 mg/kg body weight intravenously) or vehicle (5 mL/kg body weight 10% DMSO intravenously) at one hour after LPS/PepG co-administration. After 24 hours, the experiment is over, and blood and organ samples are taken in order to measure any organ dysfunction or injury. Four groups of mice are randomly assigned: (1) sham+vehicle (n=10); (2) sham+IKK 16 (n=3); (3) LPS/PepG+vehicle (n=9); (4) LPS/PepG+IKK 16 (n=10). CLP-Induced Murine Sepsis Model for Evaluating IKK-16 Efficacy : 1. Animal Preparation: - Male C57BL/6 mice (8-10 weeks old, weighing 22-25 g) were acclimated for 1 week under standard conditions (12-hour light/dark cycle, 22±1°C, free access to food and water). Mice were fasted for 12 hours before surgery but allowed free access to water [3] 2. Sepsis Induction (CLP Surgery): - Mice were anesthetized with isoflurane (inhalation). A 1 cm midline abdominal incision was made, and the cecum was exposed. The cecum was ligated with 4-0 silk suture at 50% of its length from the tip, then punctured twice with a 22-gauge needle. A small amount of fecal material was extruded to ensure patency, and the cecum was returned to the abdominal cavity. The abdomen was closed with 4-0 silk suture (muscle layer) and 5-0 nylon suture (skin layer). Sham-operated mice underwent the same procedure without cecal ligation or puncture [3] 3. Drug Formulation and Administration: - IKK-16 was dissolved in 0.5% DMSO/PBS to prepare dosing solutions of 2 mg/mL (for 10 mg/kg dose) and 4 mg/mL (for 20 mg/kg dose). Mice in the CLP + IKK-16 group received intraperitoneal injections of IKK-16 at 1 hour and 6 hours post-CLP (injection volume: 5 mL/kg). Mice in the CLP + Vehicle group received an equal volume of 0.5% DMSO/PBS [3] 4. Sample Collection and Detection: - Survival Monitoring: Mice were monitored twice daily for 7 days to record survival status [3] - Serum and Tissue Collection: At 24 hours post-CLP, mice were euthanized by CO2 inhalation. Blood was collected via cardiac puncture, centrifuged at 3,000×g for 15 minutes to separate serum, and stored at -80°C for ALT, AST, creatinine, TNF-α, and IL-6 detection [3] - Organ Histology: Lungs, liver, and intestines were excised, fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 24 hours, embedded in paraffin, sectioned (5 μm), and stained with hematoxylin-eosin (HE). Histological scores were evaluated based on the degree of tissue damage and inflammatory infiltration (0-5 scale) [3] - Western Blot for Tissue NF-κB Activity: Liver and lung tissues were homogenized in RIPA buffer containing inhibitors, and protein extracts were used for Western blot analysis of p-IKKβ (Ser177/181) and p-IκBα (Ser32/36) [3] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
1. In Vitro Cytotoxicity:
- In HeLa cells, RAW264.7 macrophages, and primary mouse peritoneal macrophages, IKK-16 (up to 20 μM) had no significant cytotoxicity. Cell viability (assessed by MTT assay) remained >90% compared to the vehicle control after 48 hours of treatment [1, 3] 2. In Vivo Safety in Sepsis Mice: - In the CLP-induced sepsis model, IKK-16 (10 mg/kg and 20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection) did not cause additional toxicity. Mice in the IKK-16 treatment groups showed no significant weight loss (weight change: -5% to -8% vs. -12% in the CLP + Vehicle group at 24 hours post-CLP) or abnormal behavior (e.g., lethargy, ataxia) beyond sepsis-related symptoms [3] - Serum levels of liver and kidney function markers (ALT, AST, creatinine) in the IKK-16 treatment groups were lower than those in the CLP + Vehicle group, indicating no drug-induced liver or kidney damage [3] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
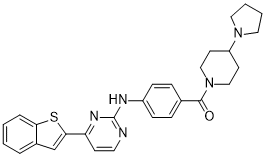
[4-[[4-(1-benzothiophen-2-yl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]-[4-(1-pyrrolidinyl)-1-piperidinyl]methanone is a N-acylpiperidine and a member of benzamides.
1. Mechanism of Action: - IKK-16 exerts its biological effects by selectively inhibiting IKKβ (and weakly inhibiting IKKα). It binds to the ATP-binding pocket of IKKβ, blocking its kinase activity and preventing the phosphorylation and subsequent degradation of IκBα. This traps the NF-κB (p65/p50) dimer in the cytoplasm, inhibiting the transcription of NF-κB target genes (e.g., pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6; genes involved in cell survival and proliferation) [1, 3] 2. Therapeutic Potential: - IKK-16 shows potential for treating NF-κB-overactivated diseases, particularly sepsis-induced multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS). Its ability to reduce inflammatory responses and organ damage while improving survival in sepsis mice supports its development as a candidate for inflammatory and infectious diseases [3] 3. Chemical Class and Development Background: - IKK-16 belongs to the 2-benzamido-pyrimidine class of compounds, a series of small-molecule IKK inhibitors designed and synthesized for targeting the NF-κB pathway. It is widely used as a research tool compound to study IKK/NF-κB signaling in vitro and in vivo, but has not entered clinical development [1] 4. Selectivity Profile: - IKK-16 exhibits high selectivity for IKKβ over other kinases (JNK1, p38α, ERK2) and IKKα, reducing the risk of off-target effects (e.g., unintended inhibition of MAPK signaling) that may cause toxicity [1] |
| 分子式 |
C28H29N5OS
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
483.63
|
| 精确质量 |
483.209
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 69.54; H, 6.04; N, 14.48; O, 3.31; S, 6.63
|
| CAS号 |
873225-46-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
IKK 16 hydrochloride;1186195-62-9
|
| PubChem CID |
9549298
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to yellow solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
721.6±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
390.2±35.7 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.700
|
| LogP |
5.67
|
| tPSA |
89.6
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
35
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
702
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O=C(N1CCC(N2CCCC2)CC1)C1C=CC(NC2N=C(C3=CC4C(=CC=CC=4)S3)C=CN=2)=CC=1
|
| InChi Key |
BWZJBXAPRCVCKQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C28H29N5OS/c34-27(33-17-12-23(13-18-33)32-15-3-4-16-32)20-7-9-22(10-8-20)30-28-29-14-11-24(31-28)26-19-21-5-1-2-6-25(21)35-26/h1-2,5-11,14,19,23H,3-4,12-13,15-18H2,(H,29,30,31)
|
| 化学名 |
[4-[[4-(1-benzothiophen-2-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl]amino]phenyl]-(4-pyrrolidin-1-ylpiperidin-1-yl)methanone
|
| 别名 |
IKK 16; IKK Inhibitor VII; IKK-16; IKK16
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.17 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.17 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.17 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 30% PEG400+0.5% Tween80+5% propylene glycol: 30 mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0677 mL | 10.3385 mL | 20.6770 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4135 mL | 2.0677 mL | 4.1354 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2068 mL | 1.0338 mL | 2.0677 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| Bioorg Med Chem Lett.2006 Jan 1;16(1):108-12. |
|---|