| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
IP; PGI2 analogue
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
前列环素(PGI2)在输卵管液中合成并促进胚胎发育[1]。伊洛前列素是一种 PGI2 类似物,影响牛卵母细胞的成熟和发育能力[1]。伊洛前列素(0.5 μM;22-24 小时)可增加牛胚胎的囊胚率以及扩张囊胚的比例[1]。伊洛前列素(0.5 μM;22-24 小时)有助于牛卵母细胞的成熟率和卵丘细胞扩张,并增加与卵丘扩张相关基因的 mRNA 表达[1]。伊洛前列素(0.5 μM;22-24 小时)可减少 COC 中细胞凋亡的发生,并促进细胞凋亡相关基因(BAX 和 BCL2)转录的抗细胞凋亡平衡[1]。 RT-PCR[1] 细胞系:牛卵母细胞:卵丘卵母细胞复合物 (COC) 浓度:0.5 μM 孵育时间:22-24 小时 结果:半胱氨酸蛋白酶组织蛋白酶(包括 ADAM17、AREG 和 TNFAIP6 23 和组织蛋白酶)的 mRNA 表达水平增加基因(CTSK 和 CTSS)。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
伊洛前列素(0.3 mg/kg/min;通过皮下微型泵;33 天)在大鼠自发转移肿瘤模型中具有显着的抗转移活性[2]。伊洛前列素(0.2 mg/kg/d;腹腔注射;10 天)可减弱新生小鼠肺部的高氧效应并减少炎症,而环氧合酶-2 (COX-2/PTGS2) 会介导高氧引起的损伤[3]。伊洛前列素(0.2 mg/kg;静脉注射或腹膜内注射)半衰期短,治疗时通常通过频繁(每 2-4 小时)吸入的方式给药[4]。大鼠和小鼠药代动力学参数比较[4] 动物途径 剂量 (mg/kg) AUC (ng•h/mL) F (%) CL (范围) (mL/min/kg) t1/2λi (min) t1/ 2λz (min) 小鼠 iv 0.2 21.9 100 152 3 15 大鼠 ig 0.2 2.2 10 / 4 58 动物模型:Cop 大鼠中自发转移 R 3327 MAT Lu 前列腺癌[2] 剂量:0.3 mg/kg/min 给药方式:通过皮下给药Alzet 迷你泵;连续33天结果:可见肺转移瘤数量减少,但对原发肿瘤的生长没有影响。这种作用是基于减少肿瘤细胞与血小板的附着以及抑制肿瘤细胞-血小板聚集体与内皮衬里的粘附的能力。动物模型:新生C57BL/6小鼠(4日龄)[3] 剂量:0.2 mg/kg 给药方式:腹腔注射;每天一次; 10 天结果:促炎细胞因子 IL-1β 和 TNF-α mRNA 和蛋白质显着减少。抑制肺泡间隔,降低高氧引起的肺总阻力和髓过氧化物酶,防止高氧导致的肺微血管密度降低。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞系:牛卵母细胞:卵丘卵母细胞复合物 (COC)
浓度:0.5 μM 孵育时间:22-24 小时 结果:半胱氨酸蛋白酶组织蛋白酶(包括 ADAM17、AREG 和 TNFAIP6)的 mRNA 表达水平增加23 和组织蛋白酶基因(CTSK 和 CTSS)。 |
| 动物实验 |
Spontaneously metastasizing R 3327 MAT Lu prostate carcinoma in Cop rat
0.3 mg/kg/min Subcutaneous administration via Alzet mini pumps; continuously for 33 days Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2/PTGS2) mediates hyperoxia-induced impairment of lung development in newborn animals and is increased in the lungs of human infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD). COX-2 catalyzes the production of cytoprotective prostaglandins, such as prostacyclin (PGI2), as well as proinflammatory mediators, such as thromboxane A2. Our objective was to determine whether iloprost, a synthetic analog of PGI2, would attenuate hyperoxia effects in the newborn mouse lung. To test this hypothesis, newborn C57BL/6 mice along with their dams were exposed to normoxia (21% O2) or hyperoxia (85% O2) from 4 to 14 days of age in combination with daily intraperitoneal injections of either iloprost 200 µg·kg-1·day-1, nimesulide (selective COX-2 antagonist) 100 mg·kg-1·day-1, or vehicle. Alveolar development was estimated by radial alveolar counts and mean linear intercepts. Lung function was determined on a flexiVent, and multiple cytokines and myeloperoxidase (MPO) were quantitated in lung homogenates. Lung vascular and microvascular morphometry was performed, and right ventricle/left ventricle ratios were determined. We determined that iloprost (but not nimesulide) administration attenuated hyperoxia-induced inhibition of alveolar development and microvascular density in newborn mice. Iloprost and nimesulide both attenuated hyperoxia-induced, increased lung resistance but did not improve lung compliance that was reduced by hyperoxia. Iloprost and nimesulide reduced hyperoxia-induced increases in MPO and some cytokines (IL-1β and TNF-α) but not others (IL-6 and KC/Gro). There were no changes in pulmonary arterial wall thickness or right ventricle/left ventricle ratios. We conclude that iloprost improves lung development and reduces lung inflammation in a newborn mouse model of BPD.[3] Much attention has recently focused on the role of tumor cell-platelet interaction in the metastatic cascade. Prostacyclin and stable prostacyclin analogues have been shown to inhibit specifically the formation of metastases in experimental tumor models. This action is based on their ability to reduce the attachment of tumor cells to platelets and to inhibit adhesion of tumor cells-platelet aggregates to the endothelial lining. To investigate the antimetastatic potential of two prostacyclin analogues (Iloprost and Eptaloprost, Schering AG), we have tested these compounds in the spontaneously metastasizing R 3327 MAT Lu prostate carcinoma of the Cop rat in two types of experiments. Treatment was performed for 33 days, starting one day before s.c. implantation of the tumor. The primary s.c.-implanted tumor remained in situ throughout the experiment. In the first test, Iloprost (0.3 micrograms/kg/min) and Eptaloprost (0.1 micrograms/kg/min) were administered via Alzet mini pumps s.c.. There was a considerable reduction of the number of visible lung metastases by Eptaloprost. In the second test, Eptaloprost was administered p.o. in doses of 0.1 and 0.5 mg/kg daily. The number of lung metastases was significantly reduced. Both compounds had no effect on the growth of the primary tumor in the first as well as in the second test. These data show that the prostacyclin analogue Eptaloprost has a significant antimetastatic activity in a spontaneously metastasizing tumor model and thus merits further investigation.[4] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Following inhalation of iloprost (5 mcg) patients with pulmonary hypertension have iloprost peak plasma levels of approximately 150 pg/mL. Iloprost was generally not detectable in plasma 30 minutes to one hour after inhalation. The absolute bioavailability of inhaled iloprost has not been determined. Unchanged iloprost and its metabolites are mainly excreted in urine. Following intravenous infusion, the apparent steady-state volume of distribution was 0.7 to 0.8 L/kg in healthy subjects. Clearance in normal subjects was approximately 20 mL/min/kg. Metabolism / Metabolites In vitro studies reveal that cytochrome P450-dependent metabolism plays only a minor role in the biotransformation of iloprost. Iloprost is metabolized principally via β-oxidation of the carboxyl side chain. The main metabolite is tetranor-iloprost, which was shown to be pharmacologically inactive in animal experiments. In rabbits, dinor-iloprost has also been identified as a drug metabolite. The chemical structures of iloprost metabolites have not been characterized. Biological Half-Life The half-life of iloprost is 20 to 30 minutes. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the use of iloprost during breastfeeding. The half-life of iloprost is 20 to 30 minutes and iloprost is generally not detectable in plasma 30 to 60 minutes after inhalation. It is unlikely that clinically important amounts of iloprost are excreted into milk after 1 hour following an inhaled dose. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Iloprost is approximately 60% protein-bound, mainly to albumin, and this ratio is concentration-independent in the range of 30 to 3000 pg/mL. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
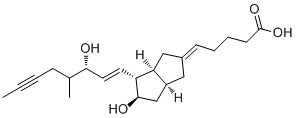
Iloprost is a carbobicyclic compound that is prostaglandin I2 in which the endocyclic oxygen is replaced by a methylene group and in which the (1E,3S)-3-hydroxyoct-1-en-1-yl side chain is replaced by a (3R)-3-hydroxy-4-methyloct-1-en-6-yn-1-yl group. A synthetic analogue of prostacyclin, it is used as the trometamol salt (generally by intravenous infusion) for the treatment of peripheral vascular disease and pulmonary hypertension. It has a role as a platelet aggregation inhibitor and a vasodilator agent. It is a monocarboxylic acid, a secondary alcohol and a carbobicyclic compound.
Iloprost is a mimetic of prostacyclin (PGI2; epoprostenol). Iloprost consists of a mixture of the 4R and 4S diastereoisomers at a ratio of approximately 53:47. It is a potent vasodilator with reported anti-thrombotic properties. Iloprost is a Prostacycline. Iloprost is a prostacyclin analogue with potential chemopreventive activity. Iloprost binds to the prostacyclin receptor in various target cells, thereby causing vasodilation, inhibition of platelet aggregation, and decreased tumor cell adhesion to endothelium among other effects. Prostacyclin is a naturally occurring eicosanoid with anti-inflammatory, antineoplastic, and anti-metastatic properties. (NCI05) An eicosanoid, derived from the cyclooxygenase pathway of arachidonic acid metabolism. It is a stable and synthetic analog of EPOPROSTENOL, but with a longer half-life than the parent compound. Its actions are similar to prostacyclin. Iloprost produces vasodilation and inhibits platelet aggregation. See also: Iloprost tromethamine (is active moiety of). Drug Indication Iloprost is indicated for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) (WHO Group 1) to improve a composite endpoint consisting of exercise tolerance, symptoms (NYHA Class), and lack of deterioration. Studies establishing effectiveness included predominately patients with NYHA Functional Class III–IV symptoms and etiologies of idiopathic or heritable PAH (65%) or PAH associated with connective tissue diseases (23%). It is also indicated for the treatment of severe frostbite in adults to reduce the risk of digit amputations. Effectiveness was established in young, healthy adults who suffered frostbite at high altitudes. Treatment of patients with primary pulmonary hypertension, classified as New York Heart Association functional class III, to improve exercise capacity and symptoms. Mechanism of Action In pulmonary arterial hypertension, endothelial vasoactive mediators such as nitric oxide and prostacyclin are released to induce vasoconstriction. Iloprost mimics the biological actions of prostacyclin, a prostanoid and potent vasodilator produced in the vascular endothelium. Pharmacodynamics Iloprost is a synthetic analogue of prostacyclin PGI2 that dilates systemic and pulmonary arterial vascular beds. It was shown to inhibit platelet aggregation, but whether this effect contributes to its vasodilatory action has not been elucidated. There are two diastereoisomers of iloprost and the 4S isomer is reported to exhibit a higher potency in dilating blood vessels compared to the 4R isomer. When administered intravenously in patients with peripheral vascular conditions such as critical leg ischemia and delayed amputation, iloprost was shown to promote cytoprotection. |
| 分子式 |
C22H32O4
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
360.4871
|
| 精确质量 |
360.23
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 73.30; H, 8.95; O, 17.75
|
| CAS号 |
78919-13-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Iloprost-d4; 1035094-10-0
|
| PubChem CID |
5311181
|
| 外观&性状 |
Clear solution in acetone (white Oily or waxy solid in pure form)
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
539.2±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
115.7ºC
|
| 闪点 |
294.0±26.6 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±3.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.629
|
| LogP |
2.94
|
| tPSA |
77.76
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
| 重原子数目 |
26
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
606
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
5
|
| SMILES |
C(/[C@H]1[C@H](O)C[C@@H]2C/C(/C[C@H]12)=C\CCCC(=O)O)=C\[C@@H](O)C(C)CC#CC
|
| InChi Key |
HIFJCPQKFCZDDL-ACWOEMLNSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H32O4/c1-3-4-7-15(2)20(23)11-10-18-19-13-16(8-5-6-9-22(25)26)12-17(19)14-21(18)24/h8,10-11,15,17-21,23-24H,5-7,9,12-14H2,1-2H3,(H,25,26)/b11-10+,16-8+/t15?,17-,18+,19-,20+,21+/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(5E)-5-[(3aS,4R,5R,6aS)-5-hydroxy-4-[(E,3S)-3-hydroxy-4-methyloct-1-en-6-ynyl]-3,3a,4,5,6,6a-hexahydro-1H-pentalen-2-ylidene]pentanoic acid
|
| 别名 |
ZK-36374; Endoprost; ZK36374; Iloprost; ZK00036374; ZK 36374; Ilomedin; BAYQ6256; ZK-00036374; BAY-Q6256; Ciloprost; Ventavis; CHEMBL494; 78919-13-8; Endoprost; Ilomedin; Iloprostum; UNII-JED5K35YGL;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~100 mg/mL (~277.4 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.94 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.94 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.94 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7740 mL | 13.8700 mL | 27.7400 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5548 mL | 2.7740 mL | 5.5480 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2774 mL | 1.3870 mL | 2.7740 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Infusion of Prostacyclin (Iloprost) vs Placebo for 72-hours in Patients With Septic Shock Suffering From Organ Failure
CTID: NCT04123444
Phase: Phase 2/Phase 3 Status: Completed
Date: 2024-05-07
|
|
|