| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
TGF-β receptor type 1/ALK5 (IC50 = 38.2 nM)
Transforming Growth Factor-β type 1 receptor (TGFβRI) (IC50=0.8 nM); exhibits no significant inhibition on TGFβRII (IC50>10000 nM) [2] Transforming Growth Factor-β type 1 receptor (TGFβRI)[1] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
LY3200882 在体外以剂量依赖性方式有效抑制肿瘤和免疫细胞中 TGFβ 诱导的 SMAD 磷酸化[1]。 LY3200882 在三阴性乳腺癌原位 4T1-LP 模型中表现出有效的抗肿瘤作用,这种活性与肿瘤微环境中肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞的增加相关[1]。在体外免疫抑制实验中,LY3200882显示出能够拯救TGFβ1抑制或T调节细胞抑制的幼稚T细胞活性并恢复增殖[1]。 LY3200882 降低 NIH3T3 细胞活力,IC50 为 82.9 nM[2]。
作用机制研究表明LY3200882抑制多种促肿瘤活性。LY3200882在体外肿瘤和免疫细胞中有效抑制TGFβ介导的SMAD磷酸化。在体外免疫抑制实验中,LY3200882显示出挽救TGFβ1抑制或T调节性细胞抑制naïve T细胞活性和恢复增殖的能力。因此,LY3200882作为免疫调节剂具有良好的活性。此外,LY3200882在体外迁移试验中显示出抗转移活性,在体内实验转移性肿瘤模型(静脉注射三阴性乳腺癌EMT6-LM2模型)中也显示出抗转移活性[1]。 抑制TGFβRI激酶活性及下游Smad信号通路:LY3200882强效抑制重组人TGFβRI激酶活性,IC50为0.8 nM,而对TGFβRII及其他激酶抑制活性微弱(对TGFβRI的选择性比率>12500倍)。在A549细胞(IC50=3.2 nM)和MDA-MB-231细胞中,浓度依赖性阻断TGFβ1诱导的Smad2磷酸化(Western blot检测)[2] - 抑制TGFβ介导的细胞应答:在A549细胞中抑制TGFβ1诱导的上皮-间质转化(EMT),Western blot和免疫荧光显示间质标志物(波形蛋白vimentin、N-钙粘蛋白N-cadherin)表达降低,上皮标志物(E-钙粘蛋白E-cadherin)表达升高;在MDA-MB-231和A549细胞中抑制TGFβ1诱导的细胞迁移和侵袭(与单独TGFβ1组相比p<0.01)[2] - 癌细胞增殖抑制活性:通过MTT实验显示,对TGFβ应答型癌细胞系具有浓度依赖性生长抑制作用,A549(IC50=12.5 nM)、MDA-MB-231(IC50=15.8 nM)、HCT116(IC50=18.3 nM);以9.7 nM的IC50抑制A549细胞克隆形成,体现长期增殖抑制效应[2] - 阻断TGFβ诱导的靶基因表达:实时PCR定量显示,在A549细胞中减少TGFβ1诱导的靶基因(PAI-1、CTGF、纤连蛋白fibronectin)表达(与单独TGFβ1组相比p<0.001)[2] - 体外选择性抑制TGFβ信号:在浓度高达10 μM时,不影响骨形态发生蛋白(BMP)信号或其他激酶通路(如EGFR、VEGFR2、PI3K/Akt),证实高靶点选择性[1] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
LY3200882(60 mg/kg;口服灌胃;每天两次;21 天;雌性 BALB/C 小鼠)治疗可显着减缓 CT26 模型中肿瘤的形成[2]。在体内,LY3200882 显着且剂量依赖性地抑制皮下肿瘤中 TGFβ 介导的 SMAD 磷酸化[1]。在实验性转移肿瘤模型(三阴性乳腺癌静脉EMT6-LM2模型)中,LY3200882表现出体内抗转移功效[1]。
在临床前肿瘤模型中,LY3200882在三阴性乳腺癌原位4T1-LP模型中表现出较强的抗肿瘤活性,这种活性与肿瘤微环境中肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞增强有关。在原位4T1-LP模型中观察到持久的肿瘤消退,并在所有小鼠中再次挑战先天性肿瘤导致完全排斥。最后,LY3200882在同基因CT26模型中显示出具有检查点抑制(抗pd - l1)的组合抗肿瘤益处。[1] 抑制异种移植瘤生长:裸鼠皮下接种A549或MDA-MB-231细胞,待肿瘤体积达100–150 mm³时随机分组(每组n=6),实验组每日口服LY3200882 30 mg/kg,连续21天。每周测量两次肿瘤体积,处死时记录肿瘤重量。与溶媒对照组相比,LY3200882显著抑制肿瘤生长,A549模型抑制率65%,MDA-MB-231模型抑制率58%(p<0.01);肿瘤组织Western blot显示p-Smad2水平降低,证实体内TGFβRI信号抑制[1] - 增强抗肿瘤免疫应答:在MC38同源肿瘤模型中,LY3200882(30 mg/kg/天,口服)与抗PD-1抗体联合使用,显著增加肿瘤浸润CD8+ T细胞数量,减少调节性T细胞(Tregs),实现协同肿瘤生长抑制(与溶媒组相比抑制率78%,p<0.001)[1] |
| 酶活实验 |
ALK5抑制活性[2]
采用发光ADP检测法评价化合物与ALK5的结合能力。将10 mM原液在DMSO中连续稀释3倍,得到10点稀释曲线,最终化合物浓度范围为3.333 μM ~ 0.5 nM。测定在1X激酶反应缓冲液中进行,缓冲液中含有40 mM Tris pH 7.5, 20 mM MgCl2, 0.1% BSA, 1 mM DTT,最终测定体积为5 μL。在384孔的实验板中,每孔加入2.5 μL的ALK5蛋白,最终浓度为3 μg/mL,每孔中溶解100 nL每种浓度的测试化合物。2.5 μL TGF-βR1肽,终浓度3 μg/mL, ATP,终浓度1 mM。28℃孵育120 min后,加入5 μL ADP-Glo™试剂终止激酶反应,消耗剩余ATP。28℃孵育120 min后,加入10 μL激酶检测试剂,将ADP转化为ATP,记录发光。 体外p38α酶活性测定[2] 所有酶促反应在28°C下进行,反应时间为40 min。25 μL的反应混合物中含有50 mM HEPES, pH为7.5,0.0015% Brij-35, 25 ng激酶,10 μM ATP和fam标记的肽。化合物在100 μM, 3倍稀释,10倍浓度下进行检测。该检测由ChemPartner进行。它通过定量测定激酶反应后溶液中剩余ATP的量来测量激酶活性。荧光信号与存在的ATP量相关,与激酶活性的量呈负相关。在XLFit excel插件版本5.4.0.8中计算IC50值,使用公式:Y=Bottom +(Top-Bottom)/(1+(IC50/X) ^Hill Slope),其中X为化合物浓度,Y为抑制率(%)。 TGFβRI激酶活性测定:将重组人TGFβRI激酶结构域与ATP、特异性肽底物及系列稀释的LY3200882共同孵育,采用均相时间分辨荧光(HTRF) assay检测底物磷酸化水平。以溶媒处理组为100%活性,通过药物浓度与激酶活性百分比绘制曲线,计算IC50值[2] - 激酶选择性测定:采用放射活性激酶 assay,将10 μM LY3200882与468种人源激酶面板孵育,通过检测放射性ATP掺入底物的量确定每种激酶的抑制率,对比对TGFβRI与其他激酶的抑制作用评估选择性[2] - TGFβRII交叉反应性测定:采用与TGFβRI相同的HTRF assay,使用重组人TGFβRII激酶结构域,加入系列浓度LY3200882(0.1 nM–10 μM),测定IC50以评估交叉反应性[2] |
| 细胞实验 |
基于细胞的荧光素酶报告试验TGF-β 1型受体活性[2]
本实验的目的是在细胞基础上鉴定干扰SMAD 2,3依赖性基因表达的化合物,证明它们在细胞水平上抑制ALK5。以每孔4000个细胞的速度,在96孔板中,用DMEM培养基将已准备好的冷冻原液中的Luc-Smad 2/3-NIH3T3细胞进行平板培养。细胞贴壁过夜后,培养基改为2%胎牛血清。在DMSO中配制试验化合物,制成4mm的原液。将原液在DMSO中连续稀释4倍,得到8点稀释曲线,最终化合物浓度范围为20 μM ~ 1.22 nM,并加入待测化合物。24小时后,在每个孔中加入Glo Lysis Buffer和Bright-Glo Luciferase assay system,使孔体积翻倍。将等分液(180 μL)转移到白色实心底板上,在平板读取器上读取发光(读取1 s)。 Smad磷酸化Western blot实验:A549或MDA-MB-231细胞血清饥饿24小时,用LY3200882(0.1 nM–10 μM)预处理1小时,再用5 ng/ml TGFβ1刺激30分钟。收集细胞提取蛋白,用p-Smad2、总Smad2及内参GAPDH抗体进行Western blot,通过光密度分析定量p-Smad2与总Smad2的比值[2] - 细胞增殖MTT实验:将癌细胞(A549、MDA-MB-231、HCT116)接种于96孔板,用LY3200882(0.1 nM–10 μM)处理72小时,加入MTT试剂孵育4小时后检测吸光度,通过量效曲线计算IC50值[2] - 克隆形成实验:A549细胞低密度接种于6孔板,用LY3200882(0.1 nM–10 μM)处理14天,每3天更换培养基。克隆经固定、染色后计数,以溶媒对照组为基准计算克隆形成率[2] - 细胞迁移和侵袭实验:使用Transwell小室(侵袭实验加Matrigel),将经LY3200882(10 nM–1 μM)预处理1小时的MDA-MB-231或A549细胞接种于上室,下室加入5 ng/ml TGFβ1。迁移实验24小时后、侵袭实验48小时后,固定并染色下室膜上的细胞,计数统计[2] - EMT标志物表达实验:A549细胞用LY3200882(10 nM–1 μM)与5 ng/ml TGFβ1共同处理72小时,Western blot检测E-cadherin、N-cadherin、vimentin表达;免疫荧光染色观察E-cadherin定位[2] - 靶基因表达实时PCR实验:A549细胞用LY3200882(0.1 nM–10 μM)与5 ng/ml TGFβ1共同处理24小时,提取总RNA,实时PCR定量PAI-1、CTGF、fibronectin mRNA水平,以GAPDH为内参归一化[2] |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: BALB/C female mice (5-8 weeks old) injected with CT26 cells[2]
Doses: 60 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage); twice a day; for 21 days Experimental Results: A statistically significant tumor growth delay in CT26 model was observed. Pharmacokinetics procedures[2] This study was conducted in BALB/C male subjects to investigate the pharmacokinetic profiles of test compounds. The mice were randomized and divided into two groups consisting of 3 mice/group. Prepare test compounds [15r (a LY3200882 analog)] in PEG200-EtOH-solutol-physiological saline (4:1:1:14) to make 0.5 mg/mL solutions for oral gavage and to make 0.1 mg/mL solutions for intravenous injection. Sample collection was performed as follows: 1) single oral administration (PO) group: 5 mg/kg, 0.2 mL/10 g; 2) single tail vein injection (IV) group: 1 mg/kg, 0.1 mL/10 g. Blood was collected from orbital venous plexus in heparinized EP tube at 5, 15, 30 min, 1, 2, 6, 10, 24 h after intravenous or oral administration, and the contents of the blood were analyzed by LC-MS/MS(API 4500). In vivo tumor xenograft model[2] A well-established tumorigenesis assay was used to evaluate the antitumor effect of compound 15r (a LY3200882 analog) in BALB/C female mice model. All mice were housed under standard specific-pathogen-free (SPF) conditions and the animal experiments strictly complied with protocols approved by the Animal Welfare and Ethics Committee (AWEC). 1 × 106 cells/mouse of CT26 cells were injected subcutaneously into the 5-to-8-week-old BALB/C female mice. All compounds were administrated by oral gavage. Mice were examined thrice a week for the development of tumors by palpation, and tumor volumes calculated using formula V = 0.5 × length × width2. The investigators were not blinded to allocation during experiments and outcome assessment. Mice were randomly allocated to three groups consisting of 6 mice/group by an independent person in the laboratory. No statistical method was used to predetermine sample size. The antitumor effect of the compound was assessed by tumor growth inhibition (TGI) or relative tumor proliferation rate (T/C): TGI(%) = [1-(Vt1-Vt0)/(Vc1-Vc0)] × 100%, where Vc1 and Vt1 are the mean volumes of control and treated groups at time of tumor extraction, while Vc0 and Vt0 are the same groups at the start of dosages; T/C (%) = TRTV/CRTV × 100%, where TRTV is the relative tumor volume (RTV) of treated groups, while CRTV is the RTV of control groups. (RTV = Vt/V0, Vt is the mean volumes of treated groups at time of tumor extraction, V0 is the mean volumes of the same groups at the start of dosages). Xenograft tumor growth inhibition assay: Female nude mice (6–8 weeks old) were subcutaneously implanted with 5×10^6 A549 or MDA-MB-231 cells. When tumors reached 100–150 mm³, mice were randomized into vehicle and LY3200882 groups (n=6/group). LY3200882 was administered via oral gavage at 30 mg/kg once daily for 21 days. Tumor volume was measured twice weekly using calipers, and tumor weight was recorded at sacrifice. Tumor tissues were collected for Western blot analysis of p-Smad2 [1] - Syngeneic tumor immunotherapy assay: C57BL/6 mice were subcutaneously implanted with 1×10^6 MC38 colon cancer cells. When tumors reached 80–100 mm³, mice were randomized into four groups: vehicle, LY3200882 (30 mg/kg/day, oral), anti-PD-1 antibody (10 mg/kg, intraperitoneal, twice weekly), or combination. Treatment lasted for 14 days, and tumor volume was measured thrice weekly. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes were analyzed by flow cytometry at sacrifice [1] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Oral bioavailability: In rats, oral administration of LY3200882 (10 mg/kg) resulted in an oral bioavailability of 52%, with a Cmax of 1.8 μg/ml and AUC0–24h of 12.6 μg·h/ml [1]
- Half-life and clearance: In dogs, intravenous administration of LY3200882 (5 mg/kg) showed a terminal half-life (t1/2) of 4.8 hours and total body clearance of 1.2 ml/min/kg. Oral administration (10 mg/kg) yielded a Cmax of 2.3 μg/ml and AUC0–24h of 18.9 μg·h/ml [1] - Plasma protein binding: LY3200882 exhibited high plasma protein binding (>95%) in human, rat, and dog plasma, as determined by equilibrium dialysis [2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
In vitro toxicity: LY3200882 showed no significant cytotoxicity in normal human bronchial epithelial cells (BEAS-2B) at concentrations up to 10 μM (cell viability >85% vs control) [2]
- In vivo toxicity: Mice treated with LY3200882 (30 mg/kg/day, oral) for 21 days showed no significant weight loss, hematological abnormalities, or histopathological changes in major organs (liver, kidney, heart, lung) [1] - No drug-drug interaction potential: Did not inhibit cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP3A4) at concentrations up to 10 μM, indicating low potential for drug-drug interactions [2] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
LY-3200882 is under investigation in clinical trial NCT04158700 (A Study of LY3200882 and Pembrolizumab in Participants With Advanced Cancer).
TGFbeta Inhibitor LY3200882 is an orally bioavailable agent that targets transforming growth factor-beta (TGFb), with potential antineoplastic activity. Upon administration, LY3200882 specifically targets and binds to TGFb, which prevents both the binding of TGFb to its receptor TGFbR and TGFb-mediated signal transduction. This may lead to a reduction in TGFb-dependent proliferation of cancer cells. The TGFb signaling pathway is often deregulated in tumors, and plays a key role in the regulation of cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis, motility, invasion, angiogenesis, and various immune responses. The transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) signaling pathway is a pleiotropic cellular pathway that plays a critical role in cancer. In fact, aggressive tumors are typically associated with high ligand levels and thus associated with poor prognosis in various tumor types. Cancer cells use autocrine and paracrine TGFβ signaling to modulate tumor cells and the tumor microenvironment leading to a highly invasive and metastatic phenotype, inducing and increasing tumor vascularization, modulating the extracellular matrix in the stroma, and inhibiting immune surveillance and antitumor immunity. Clinical studies with galunisertib (aka LY2157299 monohydrate), a small molecule inhibitor targeting the TGFβ pathway, have provided proof of concept data supporting the role of TGFβ in cancer and the utility of targeting the TGFβ pathway. Here we describe the identification of LY3200882, a next generation small molecule inhibitor of TGF-β receptor type 1 (TGFβRI). The molecule is a potent, highly selective inhibitor of TGFβRI embodied in a structural platform with a synthetically scalable route. It is an ATP competitive inhibitor of the serine-threonine kinase domain of TGFβRI. In conclusion, we have developed a novel potent and highly selective small molecule inhibitor of TGFβRI for the treatment of cancer.[1] Inhibition of transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) type 1 receptor (ALK5) provides a feasible approach for the treatment of fibrotic diseases and malignant tumors. In this study, we designed and synthesized a new series of 4-(pyridin-4-oxy)-3-(3,3-difluorocyclobutyl)-pyrazole derivatives, and evaluated biologically as TGF-β type 1 receptor inhibitors. The most potent compound 15r inhibited the ALK5 enzyme and NIH3T3 cell viability with IC50 values of 44 and 42.5 nM, respectively. Compound 15r also displayed better oral plasma exposure and excellent bioavailability than LY-3200882, and in vivo inhibited 65.7% of the tumor growth in a CT26 xenograft mouse model.[2] LY3200882 is a novel, highly selective small-molecule inhibitor of TGFβRI, belonging to the 4-(pyridin-4-oxy)-3-(3,3-difluorocyclobutyl)-pyrazole derivative class [2] The mechanism of action involves direct inhibition of TGFβRI kinase activity, thereby blocking the downstream Smad2/3 signaling pathway, which is critical for tumor progression, EMT, metastasis, and immune suppression [1][2] LY3200882 exhibits excellent selectivity for TGFβRI over other kinases (including TGFβRII), minimizing off-target effects [2] In preclinical studies, LY3200882 showed single-agent antitumor activity in TGFβ-responsive xenograft models and synergistic efficacy when combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors (anti-PD-1), highlighting its potential for combination cancer therapy [1] LY3200882 has favorable pharmacokinetic properties, including good oral bioavailability, moderate half-life, and high plasma protein binding, supporting its development as an oral therapeutic agent [1][2] |
| 分子式 |
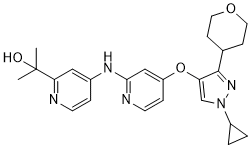
C24H29N5O3
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
435.518765211105
|
|
| 精确质量 |
435.227
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 66.19; H, 6.71; N, 16.08; O, 11.02
|
|
| CAS号 |
1898283-02-7
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
121249291
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Off-white to light yellow solid powder
|
|
| LogP |
2.1
|
|
| tPSA |
94.3
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
32
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
612
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
O1CCC(CC1)C1C(=CN(C2CC2)N=1)OC1C=CN=C(C=1)NC1C=CN=C(C=1)C(C)(C)O
|
|
| InChi Key |
PNPFMWIDAKQFPY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C24H29N5O3/c1-24(2,30)21-13-17(5-9-25-21)27-22-14-19(6-10-26-22)32-20-15-29(18-3-4-18)28-23(20)16-7-11-31-12-8-16/h5-6,9-10,13-16,18,30H,3-4,7-8,11-12H2,1-2H3,(H,25,26,27)
|
|
| 化学名 |
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.74 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.74 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.74 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2961 mL | 11.4805 mL | 22.9611 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4592 mL | 2.2961 mL | 4.5922 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2296 mL | 1.1481 mL | 2.2961 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。