| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Traditional Cytotoxic Agents
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:丝裂霉素 C 通过诱导 DNA 链间交联,以物理方式阻断 DNA 复制、重组和 RNA 转录。 Mitomycin C 可增强 HCT116 (p53-/-) 结肠癌细胞中 TRAIL 诱导的细胞凋亡,并通过不依赖 JNK 的死亡受体上调使 TRAIL 抗性结肠癌细胞 HT-29 对细胞因子敏感。在不同的人类癌细胞系中,如OVCAR-5(卵巢)、HT-29(结肠)、SK-N-MC(神经母细胞瘤)、HEP-2(肝脏)、COLO-205(结肠)、NIH-OVCAR-3 (卵巢)和 A-549(肺)细胞,丝裂霉素 C 显示细胞毒活性。细胞测定:丝裂霉素-C 增强了 p53 缺陷结肠癌 HCT116 细胞中 TRAIL(TNF 相关凋亡诱导配体)诱导的细胞凋亡。在细胞活力测定中,用 5M 丝裂霉素 C 预处理 24 小时,然后暴露于 25ng/ml TRAIL 和 5μM 丝裂霉素 C 12 小时,HCT116 细胞显示出令人惊讶的细胞活力下降。结晶紫染色结果显示5μM丝裂霉素C联合25ng/ml TRAIL可显着增强对HCT116细胞的抑制作用。用 5μM 丝裂霉素 C 预处理可以增强 TRAIL 启动的 caspase-8、-9、-3 加工和 RARP(聚 ADP 核糖聚合酶,caspase-3 底物)的裂解。 Western blot检测显示,在HCT116和HT29细胞中,丝裂霉素C抑制抗凋亡蛋白Mcl-1、Bcl-2、Bcl-XL的表达,下调caspase抑制剂c-IAP-1、XIAP的表达,上调pro凋亡蛋白的表达。 -凋亡蛋白Bax和Bim。
|
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
将NMRI-Fox1nu裸鼠皮下接种,然后随机分为几组:采用电化学疗法并给予5mM丝裂霉素C或仅给予电化学疗法或仅给予5mM丝裂霉素C。结果显示,与对照组相比,电化学联合丝裂霉素C组肿瘤体积缩小,且电化学联合丝裂霉素C组和单独丝裂霉素C组的小鼠存活率较高(p<0.001)。单独使用丝裂霉素 C 的肿瘤缓解率为 53%
|
|
| 酶活实验 |
DNA链间交联(ICL)是丝裂霉素C和顺铂等化疗药物引起的毒性最强的病变。通过共价连接两条DNA链,ICL可以防止DNA熔化、转录和复制。对ICL信号传导和修复的研究有限,因为这些药物会产生额外的DNA损伤,从而触发检查点信号传导。在这里,我们监测来自爪蟾卵和哺乳动物细胞的无细胞提取物中单个位点特异性ICL的传感、信号传导和修复。值得注意的是,我们证明ICL触发检查点反应独立于起源启动的DNA复制以及DNA聚合酶和DNA解旋酶的解偶联。范可尼贫血途径在RPA-ATR-Chk1的上游起作用,产生ICL信号。该系统还可以在涉及广泛、无差错DNA合成的反应中修复ICL。修复通过依赖于原点和独立于原点的机制进行。我们的数据表明,细胞对交联剂的敏感性是由检查点和DNA修复缺陷引起的。[1]
发现化疗药物的分子靶点及其化学足迹可以验证和改善此类药物的使用。在本报告中,我们研究了一种经典的化学治疗剂——mitomycin C(MMC)对TRAIL诱导的癌症细胞凋亡的影响。我们发现MMC不仅增强了HCT116(p53-/-)结肠癌癌症细胞中TRAIL诱导的凋亡,而且在体外和体内都使TRAIL抗性结肠癌癌症细胞HT-29对细胞因子敏感。MMC还增强了两种TRAIL受体激动剂抗体mapatumumab和lexatumumap的促凋亡作用。在机制水平上,MMC下调细胞存活蛋白,包括Bcl2、Mcl-1和Bcl-XL,上调促凋亡蛋白,包括Bax、Bim和TRAIL死亡受体DR4和DR5的细胞表面表达。短发夹RNA对DR5的基因沉默减少了MMC和TRAIL联合治疗诱导的细胞凋亡。DR4和DR5的诱导独立于p53、Bax和Bim,但依赖于c-Jun N末端激酶(JNK),因为JNK的药理学抑制和siRNA消除了MMC对TRAIL受体的诱导[2]。 |
|
| 细胞实验 |
分别使用人结肠癌细胞HT-29和结肠腺癌HCT116。培养物中存在的活细胞数量由 CellTiter-Glo 发光细胞活力测定产生的发光信号指示,该测定使用特殊、稳定形式的荧光素酶来测量 ATP。将细胞暴露于不同浓度的 TRAIL 12 小时后,用 5 μM 丝裂霉素 C 预处理细胞 12 或 24 小时。添加等体积(100 μL)的 CellTiter-GloTM 试剂后,将混合物在定轨摇床上小心混合两分钟。让发光信号在室温下稳定十分钟后,使用 Xenogen IVIS 系统对混合物进行成像以确定细胞的活力。
|
|
| 动物实验 |
|
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Erratic. Approximately 10% of a dose of mitomycin is excreted unchanged in the urine. FOLLOWING IV INJECTION OF 2 MG/KG BODY WT ... WISTAR RATS, 18% WAS RECOVERED UNCHANGED IN URINE WITHIN 24 HR AT ... 8 MG/KG ... 35% WAS RECOVERED IN URINE, BUT NONE IN FECES OR TISSUES. THIRTY MIN AFTER IV INJECTION OF 8 MG/KG BODY WT TO MICE TRACES REMAINED IN BLOOD. IN GUINEA PIGS DRUG WAS CONCN IN KIDNEYS & NOT IN LIVER, SPLEEN OR BRAIN & WAS EXCRETED IN URINE. Mitomycin is absorbed inconsistently from the gastrointestinal tract, and it is therefore administered intravenously. It disappears rapidly from the blood after injection. Peak concentrations in plasma are 0.4 ug/ml after doses of 20 mg/m sq ... The drug is widely distributed throughout the body but is not detected in the brain. In animals, highest mitomycin concentrations are found in the kidneys, followed by muscles, eyes, lung, intestines, and stomach. The drug is not detectable in the liver, spleen, or brain which rapidly inactivate mitomycin. Higher concentrations of the drug are generally present in cancer tissues than in normal tissues. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for MITOMYCIN C (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Primarily hepatic, some in various other tissues. SUGGESTED ALKYLATING METABOLITES OF CARCINOGENS: MITOMYCIN C: REDUCTION PRODUCTS. /FROM TABLE/ Inactivation occurs by metabolism, but the products have not been identified. It is metabolized primarily in the liver, and less than 10% of the active drug is excreted in the urine or the bile. The drug is eliminated primarily by hepatic metabolism with about 20% hepatic extraction and 10-30% recovery of intact drug in the urine. Clearance is 0.3-0.4 l/hr/kg. Mitomycin disappears rapidly from the blood after intravenous injection. It is widely distributed but does not appear to cross the blood-brain barrier. Mitomycin is metabolized mainly in the liver; up to 10% of a dose is excreted unchanged in the urine. MITOMYCIN C WAS PREFERENTIALLY ACTIVATED & METABOLIZED BY SONICATED CELL PREPARATIONS. BIOACTIVATION OF MITOMYCIN TO ALKYLATING AGENT BY EMT6 & SARCOMA 180 CELL SONICATES REQUIRED HYPOXIC CONDITIONS & NADPH-GENERATING SYSTEM. Primarily hepatic, some in various other tissues. Route of Elimination: Approximately 10% of a dose of mitomycin is excreted unchanged in the urine. Half Life: 8-48 min Biological Half-Life 8-48 min After doses of 20 mg/m sq ... Mitomycin is cleared from plasma with a half-time of approximately 1 hour. /Mitomycin/ has an alpha half-life of 5-10 min after IV injection and beta half-life of 46 min. |
|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
Mitomycin is activated in vivo to a bifunctional and trifunctional alkylating agent. Binding to DNA leads to cross-linking and inhibition of DNA synthesis and function. Mitomycin is cell cycle phase-nonspecific. Hepatotoxicity Chemotherapy with mitomycin in combination with other agents is associated with serum enzyme elevations in a proportion of patients, depending upon the dose and other agents used. ALT elevations during mitomycin therapy are usually asymptomatic and transient and may resolve without dose modification. In many instances, it is difficult to attribute the liver test abnormalities to mitomycin, because of the exposure to other potentially hepatotoxic agents. High doses of mitomycin have been linked to cases of sinusoidal obstruction syndrome, typically presenting with right upper quadrant pain 10 to 30 days after the infusion, followed by weight gain, ascites and liver test abnormalities. Fatalities due to hepatic failure have occurred, but most patients recover within 1 to 3 months of onset. The frequency of sinusoidal obstruction syndrome limits the dosage of mitomycin that can be used in cancer chemotherapy and in myeloablation in preparation for bone marrow transplantation. There have been no convincing instances of acute, clinically apparent idiosyncratic liver injury with jaundice associated with mitomycin therapy. Likelihood score: B[H] (very likely but now uncommon cause of sinusoid obstruction syndrome when given in high doses and in combination with other cytotoxic agents). Toxicity Data LD50: 23 mg/kg (Oral, Mouse) (A308) LD50: 30 mg/kg (Oral, Rat) (A308) Interactions IN RATS GIVEN SINGLE DOSES OF 3 MG METHYLCHOLANTHRENE BY SC INJECTION INCIDENCE OF LOCAL SARCOMAS AFTER 120 DAYS WAS REDUCED WHEN WEEKLY IP INJECTIONS OF MITOMYCIN C WERE ALSO GIVEN. IN MICE ... ADMIN 0.2 ML OF 1% SOLN OF METHYLCHOLANTHRENE IN BENZENE ON SKIN DAILY FOR 5-10 DAYS, INCIDENCE OF SKIN PAPILLOMAS WAS GREATLY INCR WHEN MITOMYCIN C WAS GIVEN DAILY BY 20 IP INJECTIONS ... . IN RATS GIVEN 40 UG/KG BODY WT MITOMYCIN C IP & ORAL DOSE DMBA, INCIDENCE OF MAMMARY TUMORS AFTER 120 DAYS WAS SIMILAR TO THAT IN RATS GIVEN DMBA ALONE. Absorption of cephalexin, sulfanilamide, salicylic acid, and D- and L-tryptophan was significantly decreased by the pretreatment with /iv/ mitomycin C /in rats/. Absorption of 6-carboxyfluorescein and fluorescein isothiocyanate conjugated dextran was not significantly affected by mitomycin C pretreatment. Maximal effects, using sulfanilamide as a model, were noted 48 hours after mitomycin C pretreatment. The dosage of mitomycin C ... did not affect the percentage of sulfanilamide absorbed. For more Interactions (Complete) data for MITOMYCIN C (25 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Mouse iv 5 mg/kg LD50 cat iv 1-2.5 mg/kg LD50 dog iv 1-2.5 mg/kg LD50 monkey iv 1-2.5 mg/kg |
|
| 参考文献 | ||
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Antibiotics, Antineoplastic; Nucleic Acid Synthesis Inhibitors Mitomycin is useful for the palliative treatment of gastric adenocarcinoma, in conjunction with fluorouracil and doxorubicin. It has produced temporary beneficial effects in carcinomas of the cervix, colon, rectum, pancreas, breast, bladder, head and neck, and lung, and in melanoma. It has also shown activity against lymphomas and leukemia, particularly chronic granulocytic leukemia, but not in myeloma. Thirty patients with advanced colorectal adenocarcinoma were treated by chemotherapy with an alternating regimen consisting of 5-fluorouracil mitomycin C and 5-fluorouracil dacarbazine at 3 wk intervals. ... The toxicity of this regimen was essentially digestive with 30% of grade 3 or 4 nausea and vomiting. In spite of the reported active and synergistic action of drug association in colorectal carcinoma, this treatment schedule is not better than 5-fluorouracil alone. Gastrointestinal toxicity was incr. Forty-two patients with metastatic breast cancer refractory to first line therapies were treated with combination chemotherapy with mitomycin-C and vinblastine. ... The toxicity was acceptable with 20 episodes of moderate myelosuppression (58.8%) and 2 cases with congestive heart failure that responded to medical treatment. For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for MITOMYCIN C (19 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings Mitomycin is contraindicated in patients with pre-existing myelosupression & anemia. Because normal defense mechanisms may be suppressed by mitomycin therapy, the patient's antibody response to the vaccine may be decreased. The interval between discontinuation of medications that cause immunosuppression and restoration of the patient's ability to respond to the vaccine depends on the intensity and type of immunosuppression-causing medication used, the underlying disease, and other factors; estimates vary from 3 months to 1 year. cBecause normal defense mechanisms may be suppressed by mitomycin therapy, concurrent use with a live virus vaccine may potentiate the replication of the vaccine virus, may increase the side/adverse effects of the vaccine virus, and/or may decrease the patient's antibody response to the vaccine; immunization of these patients should be undertaken only with extreme caution after careful review of the patient's hematologic status and only with the knowledge and consent of the physician managing the cytarabine therapy. The interval between discontinuation of medication that cause immunosuppression and restoration of the patient's ability to respond to the vaccine depends on the intensity and type of immunosuppression-causing medications used, the underlying disease, and other factors; estimates vary from 3 months to 1 year. Patients with leukemia in remission should not receive live virus vaccine until at least 3 months after their last chemotherapy. In addition, immunization with oral polio-virus vaccine should be postponed in persons in close contact with the patient, especially family members. Gonadal suppression, resulting in amenorrhea or azoospermia, may occur in patients taking antineoplastic therapy, especially with the alkylating agents. In general, these effects appear to be related to dose and length of therapy and may be irreversible. Prediction of the degree of testicular or ovarian function impairment is complicated by the common use of combinations of several antineoplastics, which makes it difficult to assess the effects of individual agents. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for MITOMYCIN C (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Mitomycin is one of the older chemotherapy drugs, which has been around and in use for decades. It is an antibiotic which has been shown to have antitumor activity. Mitomycin selectively inhibits the synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). The guanine and cytosine content correlates with the degree of mitomycin-induced cross-linking. At high concentrations of the drug, cellular RNA and protein synthesis are also suppressed. Mitomycin has been shown in vitro to inhibit B cell, T cell, and macrophage proliferation and impair antigen presentation, as well as the secretion of interferon gamma, TNFa, and IL-2. |
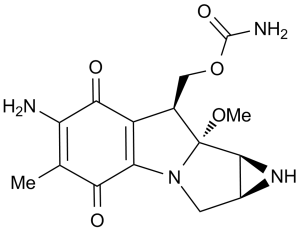
| 分子式 |
C15H18N4O5
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
334.37
|
|
| 精确质量 |
334.127
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 53.89; H, 5.43; N, 16.76; O, 23.93
|
|
| CAS号 |
50-07-7
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
5746
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Black solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.9±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
532.0±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
360 °C
|
|
| 闪点 |
275.5±32.9 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±3.2 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.828
|
|
| LogP |
-0.27
|
|
| tPSA |
146.89
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
24
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
757
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
4
|
|
| SMILES |
NC1=C(C(C2=C(C1=O)[C@@H](COC(N)=O)[C@]3(OC)N2C[C@H]4[C@@H]3N4)=O)C
|
|
| InChi Key |
NWIBSHFKIJFRCO-WUDYKRTCSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C15H18N4O5/c1-5-9(16)12(21)8-6(4-24-14(17)22)15(23-2)13-7(18-13)3-19(15)10(8)11(5)20/h6-7,13,18H,3-4,16H2,1-2H3,(H2,17,22)/t6-,7+,13+,15-/m1/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
[(4S,6S,7R,8S)-11-amino-7-methoxy-12-methyl-10,13-dioxo-2,5-diazatetracyclo[7.4.0.02,7.04,6]trideca-1(9),11-dien-8-yl]methyl carbamate
|
|
| 别名 |
Ametycine; mitomycine C; Mitomycin; 50-07-7; Ametycine; Mutamycin; Mitomycin-C; Mitocin-C; Ametycin; mitomycinX. US trade names: Mitozytrex; Mutamycin. Foreign brand names: Ametycine; MitocinC; Mitolem; MitoMedac; Mutamycine. Abbreviations: MITC; MITO; MITOC; MTC; NCIC04706
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (6.22 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (6.22 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9907 mL | 14.9535 mL | 29.9070 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5981 mL | 2.9907 mL | 5.9814 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2991 mL | 1.4953 mL | 2.9907 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Therapy Adapted for High Risk and Low Risk HIV-Associated Anal Cancer
CTID: NCT04929028
Phase: Phase 2 Status: Recruiting
Date: 2024-11-13