| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
100 ppm 时菌丁腈将细胞活力降低至 50% 以下,500 ppm 时细胞活力降低至 10% 以下。腈菌唑在 1 至 100 ppm 的剂量范围内会轻微但显着地升高脂肪酸 (FA) 诱导的脂肪变性。腈菌唑显着降低抗凋亡指标[1]。
|
|---|---|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Rapidly absorbed and excreted. Completely eliminated by 96 hrs. Extensively metabolized prior to excretion. Metabolic patterns similar for both sexes. Disposition & metabolism after pulse administration is linear over dose range. ... Elimination of label from plasma biphasic and evenly distribution between urine and feces. No tissue accumulation after 96 hours. At least 7 major metabolites recovered and identified. Highest amounts of radioactivity found in liver, kidneys, large and small intestines. No tissue accumulation. Metabolism / Metabolites 1,2,4-Triazole (1,2,4-T); triazole alanine (TA); and triazole acetic acid (TAA) are common metabolites to the class of compounds known as triazoles. In plants, 1,2,4-T is rapidly conjugated with serine to form TA. The TA can then be oxidized to form TAA. The extent to which 1,2,4-T, TA, and/or TAA forms in a given plant or animal is primarily dependent on the parent triazole-derivative fungicide. Across the various parent compounds, maximum formation of 1,2 4-T in plants ranges from 0% of the total radioactive residue (TRR) to 17% TRR, with the majority of compounds yielding 1,2,4-T at around 5-10% TRR. In rats, goats, and hens, maximum 1,2,4-T formation ranges from 0 to 77% TRR. Formation of 1,2,4-T in the rat is less than 20% TRR for the majority (approximately 80%) of the triazole-derivative fungicides for which data are available. Formation of TA ranges from 0 to 89% TRR in plants. Triazole acetic acid formation in plants ranges from 0 to 76% TRR. Triazole alanine and triazole acetic acid have generally not been found to be significant metabolites in rats, lactating goats, or laying hens. The exception to this appears to be fenbuconazole. In studies with radio-labeled fenbuconazole fed to goats and hens, TA formation ranges from 0 to 35% TRR; formation of TA from fenbuconazole was not noted in the rat metabolism studies. There is evidence from toxicological studies that there can be limited reduction of TA to 1,2,4-T following oral exposure to TA. /Triazole-derivative fungicide compounds/ Metabolism of two triazole-containing antifungal azoles was studied using expressed human and rat cytochrome P450s (CYP) and liver microsomes. Substrate depletion methods were used due to the complex array of metabolites produced from myclobutanil and triadimefon. Myclobutanil was metabolized more rapidly than triadimefon, which is consistent with metabolism of the n-butyl side-chain in the former and the t-butyl group in the latter compound. Human and rat CYP2C and CYP3A enzymes were the most active. Metabolism was similar in microsomes prepared from livers of control and low-dose rats. High-dose (115 mg/kg/day of triadimefon or 150 mg/kg/day of myclobutanil) rats showed increased liver weight, induction of total CYP, and increased metabolism of the two triazoles, though the apparent Km appeared unchanged relative to the control. Myclobutanil metabolizes into 1,2,4-triazole, which has a lower acute toxicity than the parent compound (L2093). Organic nitriles are converted into cyanide ions through the action of cytochrome P450 enzymes in the liver. Cyanide is rapidly absorbed and distributed throughout the body. Cyanide is mainly metabolized into thiocyanate by either rhodanese or 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfur transferase. Cyanide metabolites are excreted in the urine. (L96) |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
Organic nitriles decompose into cyanide ions both in vivo and in vitro. Consequently the primary mechanism of toxicity for organic nitriles is their production of toxic cyanide ions or hydrogen cyanide. Cyanide is an inhibitor of cytochrome c oxidase in the fourth complex of the electron transport chain (found in the membrane of the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells). It complexes with the ferric iron atom in this enzyme. The binding of cyanide to this cytochrome prevents transport of electrons from cytochrome c oxidase to oxygen. As a result, the electron transport chain is disrupted and the cell can no longer aerobically produce ATP for energy. Tissues that mainly depend on aerobic respiration, such as the central nervous system and the heart, are particularly affected. Cyanide is also known produce some of its toxic effects by binding to catalase, glutathione peroxidase, methemoglobin, hydroxocobalamin, phosphatase, tyrosinase, ascorbic acid oxidase, xanthine oxidase, succinic dehydrogenase, and Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase. Cyanide binds to the ferric ion of methemoglobin to form inactive cyanmethemoglobin. (L97) Toxicity Data LC50 (rat) > 5,000 mg/m3 LD50: 1.75 to 1.8 g/kg (rats, oral) (L2093) Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Rat (male) oral 1600 mg/kg LD50 Rat (female) oral 2290 mg/kg |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Stellavato A, et al. Myclobutanil worsens nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: An in vitro study of toxicity and apoptosis on HepG2 cells. Toxicol Lett. 2016 Nov 16;262:100-104
|
| 其他信息 |
Myclobutanil can cause developmental toxicity and male reproductive toxicity according to The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
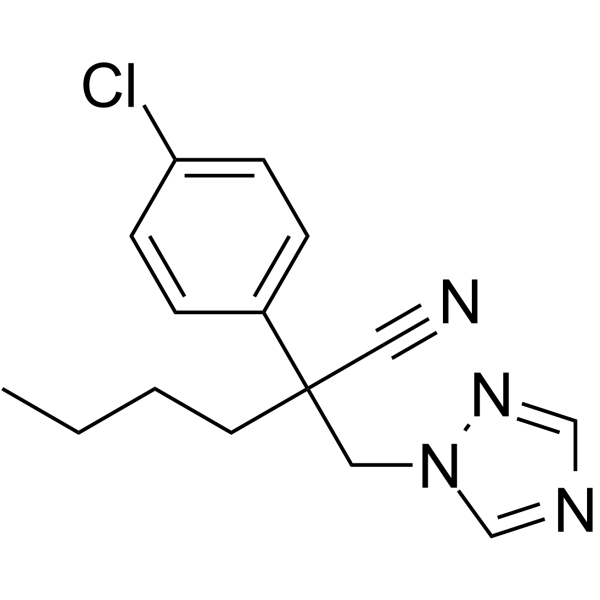
Myclobutanil is a light yellow solid used as a fungicide. 2-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)hexanenitrile is a nitrile that is hexanenitrile substituted at the 2-position by p-chlorophenyl and (1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl groups. It is a nitrile, a member of triazoles and a member of monochlorobenzenes. Myclobutanil is a triazole chemical used as a fungicide. It is a steroid demethylation inhibitor, specifically inhibiting ergosterol biosynthesis. Ergosterol is a critical component of fungal cell membranes. |
| 分子式 |
C15H17CLN4
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
288.77
|
| 精确质量 |
288.114
|
| CAS号 |
88671-89-0
|
| PubChem CID |
6336
|
| 外观&性状 |
Pale yellow solid.
Light yellow crystals |
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
465.2±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
63-68°C
|
| 闪点 |
235.2±31.5 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.589
|
| LogP |
2.82
|
| tPSA |
54.5
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
20
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
345
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
N#CC(CCCC)(CN1C=NC=N1)C1C=CC(Cl)=CC=1
|
| InChi Key |
HZJKXKUJVSEEFU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C15H17ClN4/c1-2-3-8-15(9-17,10-20-12-18-11-19-20)13-4-6-14(16)7-5-13/h4-7,11-12H,2-3,8,10H2,1H3
|
| 化学名 |
2-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)hexanenitrile
|
| 别名 |
HOE39304F; HOE 39304F; Myclobutanil
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (~346.28 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.66 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.66 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.66 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4630 mL | 17.3148 mL | 34.6296 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6926 mL | 3.4630 mL | 6.9259 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3463 mL | 1.7315 mL | 3.4630 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。