| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
β-lactam
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
对 A 组链球菌、肺炎球菌、敏感葡萄球菌和耐青霉素葡萄球菌的 MIC 分别为 0.05、0.09、0.32 和 0.80 μg/mL,表明苯唑西林抑制革兰氏阳性病原体。其他青霉素对以下菌株具有严重耐药性:对苯唑西林耐药[1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
当用苯唑西林(50-800 mg/kg;皮下注射;一次)治疗时,感染金黄色葡萄球菌 Evans 的小鼠表现出 253.3 mg/kg 的治疗剂量(CD50)。苯唑西林的口服 CD50 为 187.2 mg/kg[2]。
|
| 动物实验 |
Animal Model: S. aureus-infected male albino mice of the CD-1 strain Evans[2]
Dosage: 50, 100, 200, 400 and 800 mg/kg Administration: Subcutaneous injection, once Result: demonstrated therapeutic efficacy at a 253.3 mg/kg CD50. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Oxacillin Sodium is rapidly excreted as unchanged drug in the urine by glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion. Biological Half-Life 20 to 30 minutes |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Oxacillin has been linked to two forms of hepatotoxicity, first an acute and transient elevation in serum aminotransferase levels occurring with high doses of intravenous therapy; and second, a more prolonged, usually cholestatic, idiosyncratic liver injury that is similar to the hepatotoxicity of other second-generation penicillins such as dicloxacillin, flucloxacillin, and nafcillin. High doses of intravenous oxacillin are commonly accompanied by elevations in serum ALT in the range of 2 to 20 times the upper limit of normal arising after 1 to 3 weeks of therapy. Alkaline phosphatase levels are only minimally elevated. Fever and nonspecific symptoms of abdominal pain and nausea can occur, but are often absent. Eosinophilia is present in some patients, but rash and arthralgias are uncommon. Serum aminotransferase levels rapidly fall into the normal range (in 1 to 2 weeks) with discontinuation of oxacillin or switch to lower doses, particularly in oral formulations. Jaundice does not occur. There appears to be no cross reactivity of this response with the natural penicillins, clindamycin or even nafcillin. Intravenous carbenicillin can cause a similar syndrome. This hepatotoxicity may be more common in HIV-positive than noninfected individuals. In addition to the common syndrome of asymptomatic serum aminotransferase elevations during high dose intravenous therapy, oxacillin can also but rarely lead to a more prolonged usually cholestatic hepatitis that appears 1 to 6 weeks after starting therapy and may persist for weeks to months. This form of idiosyncratic liver injury is similar to that described with dicloxacillin and other second generation penicillins. Immunoallergic features of rash, fever and eosinophilia can occur, but are not prominent. Autoantibodies are not found. The liver injury can be prolonged, but generally resolves within 1 to 2 months of onset. Liver biopsy generally shows a cholestatic hepatitis with mixed inflammatory infiltrates. Likelihood score: B (likely rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Limited information indicates that oxacillin produces low levels in milk that are not expected to cause adverse effects in breastfed infants. Occasionally disruption of the infant's gastrointestinal flora, resulting in diarrhea or thrush have been reported with penicillins, but these effects have not been adequately evaluated. Oxacillin is acceptable in nursing mothers. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding 94.2 +/- 2.1% (binds to serum protein, mainly albumin) |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
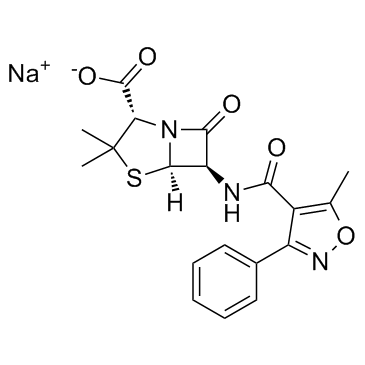
Oxacillin is a penicillin antibiotic carrying a 5-methyl-3-phenylisoxazole-4-carboxamide group at position 6beta. It has a role as an antibacterial agent and an antibacterial drug. It is a conjugate acid of an oxacillin(1-).
An antibiotic similar to [flucloxacillin] used in resistant staphylococci infections. Oxacillin is a Penicillin-class Antibacterial. Oxacillin is a parenteral, second generation penicillin antibiotic that is used to treat moderate-to-severe, penicillinase-resistant staphylococcal infections. Oxacillin has been linked to rare instances of clinically apparent, idiosyncratic liver injury, but it more commonly causes transient elevations in serum aminotransferases without jaundice. Oxacillin has been reported in Bos taurus, Cordyceps farinosa, and Liquidambar formosana with data available. Oxacillin is a semisynthetic penicillinase-resistant and acid-stable penicillin with an antimicrobial activity. Oxacillin binds to penicillin-binding proteins in the bacterial cell wall, thereby blocking the synthesis of peptidoglycan, a critical component of the bacterial cell wall. This leads to inhibition of cell growth and causes cell lysis. Oxacillin Sodium is the sodium salt form of oxacillin, a semisynthetic penicillinase-resistant and acid-stable penicillin with an antimicrobial activity. Oxacillin binds to penicillin-binding proteins in the bacterial cell wall, thereby blocking the synthesis of peptidoglycan, a critical component of the bacterial cell wall. This leads to inhibition of cell growth and causes cell lysis. An antibiotic similar to FLUCLOXACILLIN used in resistant staphylococci infections. See also: Oxacillin Sodium (has salt form); Oxacillin benzathine (is active moiety of). Drug Indication Used in the treatment of resistant staphylococci infections. Mechanism of Action By binding to specific penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located inside the bacterial cell wall, Oxacillin inhibits the third and last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Cell lysis is then mediated by bacterial cell wall autolytic enzymes such as autolysins; it is possible that Oxacillin interferes with an autolysin inhibitor. Pharmacodynamics Oxacillin is a penicillin beta-lactam antibiotic used in the treatment of bacterial infections caused by susceptible, usually gram-positive, organisms. The name "penicillin" can either refer to several variants of penicillin available, or to the group of antibiotics derived from the penicillins. Oxacillin has in vitro activity against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. The bactericidal activity of Oxacillin results from the inhibition of cell wall synthesis and is mediated through Oxacillin binding to penicillin binding proteins (PBPs). Oxacillin is stable against hydrolysis by a variety of beta-lactamases, including penicillinases, and cephalosporinases and extended spectrum beta-lactamases. |
| 分子式 |
C19H18N3NAO5S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
423.4188
|
| 精确质量 |
423.086
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 53.90; H, 4.29; N, 9.92; Na, 5.43; O, 18.89; S, 7.57
|
| CAS号 |
1173-88-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Oxacillin sodium monohydrate;7240-38-2;Oxacillin;66-79-5;Oxacillin-13C6 sodium
|
| PubChem CID |
6196
|
| 外观&性状 |
Solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.49g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
686.8ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
188ºC
|
| 闪点 |
369.2ºC
|
| 蒸汽压 |
8.32E-20mmHg at 25°C
|
| LogP |
0.889
|
| tPSA |
140.87
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
28
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
681
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
3
|
| SMILES |
S1C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])[C@]([H])(C(=O)O[H])N2C([C@]([H])([C@@]12[H])/N=C(/C1=C(C([H])([H])[H])ON=C1C1C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C=1[H])\[O-])=O.[Na+]
|
| InChi Key |
VDUVBBMAXXHEQP-SLINCCQESA-M
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C19H19N3O5S.Na/c1-9-11(12(21-27-9)10-7-5-4-6-8-10)15(23)20-13-16(24)22-14(18(25)26)19(2,3)28-17(13)22/h4-8,13-14,17H,1-3H3,(H,20,23)(H,25,26)/q+1/p-1/t13-,14+,17-/m1./s1
|
| 化学名 |
sodium (2S,5R,6R)-3,3-dimethyl-6-[(5-methyl-3-phenyl-1,2-oxazole-4-carbonyl)amino]-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylate
|
| 别名 |
Oxazocilline;Bactocill,Oxacillin;Oxacillin Sodium;Prostaphlin
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : 85~125 mg/mL ( 200.74~295.22 mM )
Water : ~85 mg/mL Ethanol : ~8 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.90 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.90 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.90 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.90 mM) 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3617 mL | 11.8086 mL | 23.6172 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4723 mL | 2.3617 mL | 4.7234 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2362 mL | 1.1809 mL | 2.3617 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。