| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
3CLPRO (SARS-CoV 3C-like protease)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
3CLPRO 裂解 SARS-CoV-2.1 的多蛋白 1a 和 1ab。如果没有 SARS-CoV-2 3CLPRO 的帮助,包括蛋白质在内的非结构蛋白就无法释放以发挥其作用,SARS-CoV-2 3CLPRO 会抑制病毒复制 [1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
用PF-332(250 mg/kg,每天两次)治疗叙利亚金仓鼠,可以完全保护动物免受β(B.1.351)和德尔塔(B.1.617.2)严重急性呼吸系统综合征冠状病毒2变种的鼻内感染。此外,用PF-332治疗严重急性呼吸系统综合征冠状病毒2型(B.1.617.2)感染的动物完全防止了传播给未经治疗的共居哨兵。[2]
|
| 酶活实验 |
蛋白质结合[2]
通过快速平衡透析(RED)方法测量血浆蛋白结合,以确定不同物种的PF-332的游离部分和未结合百分比。对每个样品进行两次平衡透析。在血浆室中加入200μl掺有PF-332的血浆,在缓冲室中加入350μl pH=7.4的PBS。然后将透析块在37°C下孵育6小时,并在400rpm下持续振荡。6小时后,收集血浆和缓冲室的等分试样,加标以获得匹配的均匀基质,并通过LC–MS/MS进行定量。[2] 微粒体代谢稳定性[2] 小鼠肝微粒体(CD-1雄性品系)购自GIBCO。仓鼠(叙利亚雌性品系)和人肝微粒体购自Xenotech。将20mg/ml的1ml肝微粒体(LM)悬浮液与19ml 100mM磷酸盐缓冲液混合。后者是含有1(M)KH2PO4和1(M。使用13mM NADP、33mM葡萄糖-6-磷酸、33mMMgCl2和4U/ml葡萄糖-6-磷酸脱氢酶缓冲溶液制备NADPH再生系统(NRS)的溶液 包括尖端在内的所有塑料材料均在37°C下孵育过夜。使用前,将LM悬浮液和NRS溶液在37°C下孵育约15分钟。将48μl缓冲液加入空白板的孔中。将40μl 1μM的化合物添加到工作板中,将8μl NRS溶液添加到0、5、10、20、30和60分钟的板中。然后通过向每个板中加入32μl 1 mg/ml的LM悬浮液来引发反应。在指定的时间点加入240μl冰冷的乙腈终止反应。在T=0时,在LM溶液之前加入乙腈 将板离心(3500 rpm,20分钟,15°C);然后将110μl蒸馏水加入110μl上清液中,并使用LC–MS/MS进行分析。 |
| 细胞实验 |
严重急性呼吸系统综合征冠状病毒2型体外抗病毒试验[2]
使用Vero E6细胞的测定来源于先前建立的SARS-CoV测定。在该测定中,由于病毒诱导的细胞致病作用,感染严重急性呼吸系统综合征冠状病毒2型后,Vero E6 eGFP细胞的荧光下降。在抗病毒化合物存在的情况下,细胞致病性被抑制并维持荧光信号。Vero E6细胞维持在补充有热灭活的10%v/v胎牛血清(FCS)和500μg/ml Geneticin的Dulbecco改良Eagle培养基(DMEM)中,并在37°C下保持在5%CO2下。[2] 将试验化合物在测定培养基(补充有2%v/vFCS的DMEM)中连续稀释。然后将稀释的化合物与Vero E6-eGFP细胞混合,对应于96孔黑视野板中25000个细胞/孔的最终密度。第二天,细胞以约0.05TCID50/细胞的最终MOI感染严重急性呼吸系统综合征冠状病毒2型。对不同菌株的最终稀释进行调整,以便在所有感兴趣的变体之间获得相似的MOI。将平板在37°C和5%CO2的湿润培养箱中培养。在感染后4天(pi),使用氩激光扫描显微镜检查孔的eGFP表达。显微镜设置为488nm激发和510nm发射,并且将孔的荧光图像转换为信号值。如前所述,在没有病毒的情况下,在标准MTS测定中评估化合物的毒性。[2] A549 Dual™hACE2-TMPRSS2细胞在补充有10µg/ml杀菌素、100µg/ml潮霉素、0.5µg/ml嘌呤霉素和100µg/ml zeocin的DMEM 10%FCS中培养。对于抗病毒测定,将细胞以15000个细胞/孔的密度接种在测定培养基(DMEM 2%)中。一天后,将化合物在测定培养基(补充有2%v/v FCS的DMEM)中连续稀释,并用其各自的SARS-CoV-2菌株以约0.05的MOI感染细胞。在不同的实验中,变异菌株的MOI保持可比性。在第4天π。,如前所述,使用MTS分析由病毒诱导的CPE或由化合物特异性副作用引起的细胞活力的差异。[2] 体外抗病毒实验的结果表示为EC50值,EC50值定义为与未处理的病毒感染的对照细胞相比,实现50%的病毒抑制的eGFP信号的化合物的浓度。 |
| 动物实验 |
SARS-CoV-2 infection model in hamsters[2]
The hamster infection model of SARS-CoV-2 has been described before16,20. Female Syrian hamsters were purchased from Janvier Laboratories and kept per two in individually ventilated isolator cages at 21 °C, 55% humidity and 12:12 day/night cycles. Housing conditions and experimental procedures were approved by the ethics committee of animal experimentation of KU Leuven (license P065-2020). For infection, female hamsters of 6–8 weeks old were anesthetized with ketamine/xylazine/atropine and inoculated intranasally with 50 µL containing 104 TCID50 of SARS-CoV-2 Beta variant B.1.351 (day 0). On day 4 pi, animals were euthanized for the sampling of the lungs and further analysis by i.p. injection of 500 μl Dolethal (200 mg/ml sodium pentobarbital). All caretakers and technicians were blinded to group allocation in the animal facility.[2] Treatment regimen (beta variant study) Hamsters were treated by oral gavage with either the vehicle (n = 12) or PF-332 at 125 (n = 10) or 250 (n = 12) mg/kg/dose twice daily starting from D0, just before the infection with the Beta variant. All the treatments continued until day 3 pi. Hamsters were monitored for appearance, behavior, and weight. At day 4 pi, hamsters were euthanized by i.p. injection of 500 μl Dolethal (200 mg/ml sodium pentobarbital). Lungs were collected and viral RNA and infectious virus were quantified by RT-qPCR and end-point virus titration, respectively as described before17.[2] Efficacy-transmission study (delta variant study) Two groups of index hamsters were infected intranasally with 50 µl containing 104 TCID50 of SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant and treated with either vehicle or PF-332 at 250 mg/kg/dose twice daily starting from D0. On day 1 pi (just after the morning dose), each index hamster was co-housed with a contact hamster (non-infected, non-treated hamsters) in one cage and the co-housing continued until day 3 pi The treatment of index hamsters was continued until day 2 pi. At day 3 pi, all the index hamsters were euthanized whereas all the contact hamsters were euthanized the day after (i.e., day 4 pi of index) as mentioned before and lungs were collected to assess viral loads. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
The median Tmax of nirmatrelvir, when given with ritonavir, is 3 hours. After a single oral dose of 300mg nirmatrelvir and 100mg ritonavir in healthy subjects, the Cmax and AUCinf of nirmatrelvir were 2.21 µg/mL and 23.01 µg*hr/mL, respectively. The major route of nirmaltrevir elimination is via renal elimination, due in part to its coadministration with ritonavir which inhibits its metabolism. Following oral administration alongside ritonavir, approximately 49.6% of drug-related material was recovered in the feces and 35.3% was recovered in the urine. The mean volume of distribution of nirmatrelvir, when given with ritonavir, is 104.7 liters. The mean oral clearance of nirmatrelvir, administered with ritonavir, is 8.99 L/h. Metabolism / Metabolites Nirmatrelvir is a substrate of CYP3A4, but undergoes minimal metabolism when administered alongside ritonavir. Biological Half-Life The mean half-life of nirmatrelvir, administered alongside ritonavir, is 6.05 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In preregistration clinical trials, serum aminotransferase elevations were uncommon and mild, and were no more frequent with Paxlovid than with placebo. Furthermore, among more than 1000 patients treated with Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir 300 mg with ritonavir 100 mg twice daily) for 5 days in prelicensure studies, there were no reported episodes of clinically apparent liver injury. Confounding the issue is that serum aminotransferase elevations are common during symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection, present in up to 70% of patients and are more frequent in patients with severe disease and in those with the known risk factors for COVID-19 severity such as male sex, older age, higher body mass index and diabetes. Thus, Paxlovid has not been shown to cause liver injury, but the total clinical experience with its use is limited. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Nirmatrelvir is given in combination with ritonavir, which enhances its bioavailability. The concentration of nirmatrelvir in breastmilk is low. Ritonavir is excreted into milk in measurable concentrations and low levels can be found in the blood of some breastfed infants. No adverse reactions in breastfed infants have been reported. For more information, refer to the LactMed record on ritonavir. Because of the poor oral bioavailability of nirmatrelvir and small amounts of both drugs in milk, this combination is unlikely to adversely affect the nursing infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants In a cross-sectional study of women who had COVID-19 and received nirmatrelvir in combination ritonavir, two women breastfed their infants. No adverse effects were reported in the infants. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Nirmatrelvir, when given with ritonavir, is 69% protein-bound in plasma. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Pharmacodynamics
Nirmatrelvir is administered alongside ritonavir, a potent inhibitor of CYP3A enzymes, in order to inhibit its metabolism and increase plasma nirmatrelvir concentrations. While therapeutically beneficial, the use of ritonavir poses a significant risk of drug interaction due to its potent inhibition profile - patients and clinicians should consult the prescribing information for Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir and ritonavir) to evaluate any potential for drug interaction with existing medications prior to the initiation of Paxlovid. |
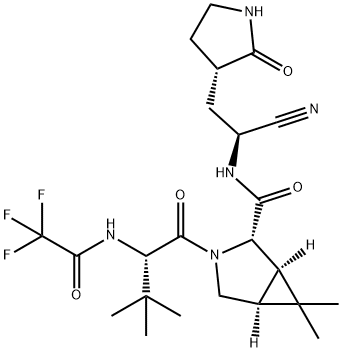
| 分子式 |
C23H32F3N5O4
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
499.5265
|
| 精确质量 |
499.24
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 55.30; H, 6.46; F, 11.41; N, 14.02; O, 12.81
|
| CAS号 |
2628280-40-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Nirmatrelvir-d9;2861202-76-6
|
| PubChem CID |
155903259
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| LogP |
2.2
|
| tPSA |
131Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
35
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
964
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
6
|
| SMILES |
CC1([C@@H]2[C@H]1[C@H](N(C2)C(=O)[C@H](C(C)(C)C)NC(=O)C(F)(F)F)C(=O)N[C@@H](C[C@@H]3CCNC3=O)C#N)C
|
| InChi Key |
LIENCHBZNNMNKG-OJFNHCPVSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C23H32F3N5O4/c1-21(2,3)16(30-20(35)23(24,25)26)19(34)31-10-13-14(22(13,4)5)15(31)18(33)29-12(9-27)8-11-6-7-28-17(11)32/h11-16H,6-8,10H2,1-5H3,(H,28,32)(H,29,33)(H,30,35)/t11-,12-,13-,14-,15-,16+/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(1R,2S,5S)-N-((S)-1-cyano-2-((S)-2-oxopyrrolidin-3-yl)ethyl)-3-((S)-3,3-dimethyl-2-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetamido)butanoyl)-6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-2-carboxamide
|
| 别名 |
Nirmatrelvir; PF-07321332; PF 07321332; P7R9A5P7H32; Nirmatrelvir; Paxlovid; PF-07321332; PF07321332; Nirmatrelvir [USAN]; UNII-7R9A5P7H32; F07321332; brand name Paxlovid;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : 100~140 mg/mL ( 200.18~280.26 mM )
Ethanol : 50 ~100 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.16 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.16 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.16 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 10% DMSO+90% Corn Oil: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.16 mM) 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0019 mL | 10.0094 mL | 20.0188 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4004 mL | 2.0019 mL | 4.0038 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2002 mL | 1.0009 mL | 2.0019 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
 |
|
 |