| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Probably excreted as phthalic acid. /From table/ Metabolism / Metabolites Yields 4,5-dihydroxyphthalic acid in Pseudomonas. /FROM TABLE/ Dose effects of di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate distribution, excretion, and binding to macromolecules were studied in rodents. The urinary di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate metabolite profile was similar for all doses, except that free phthalic acid was 6 times greater on days 3 and 10 at the highest compared to the lowest dose. The metabolism of di-(5-hexenyl)phthalate and di-(9-decenyl)phthalate was investigated in rats. Male CD rats received two oral doses of 3 to 12 uM/kg radiolabeled or unlabeled di-(5-hexenyl)phthalate and di-(decenyl)phthalate in cottonseed oil 24 hr apart. One third of the radioactivity was found in the urine. The metabolites were identified as mono-5-hexenyl-phthalate. Mono-5-hexenyl-phthalate comprised 21% of the total urinary phthalates while 5-hexenyl-phthalate glucuronide amounted to 13.2% and free 5-hexenyl-phthalate to 7.8%. In contrast no metabolites of di-(9-decenyl)phthalate were excreted as glucuronide conjugates and only a trace of free phthalic acid was detected although 40 to 50% of the compound was recovered in the urine. The distribution of the metabolic phthalates indicated a different metabolic pathway for di-(9-decenyl)phthalate and di-(5-hexenyl)phthalate. /It was/ concluded that the chemically reactive epoxide metabolite of phthalate with unsaturated side chains may play a role in the acute toxicity of di-(5-hexenyl)phthalate and di-(9-decenyl)phthalate. Phthalate grown cells readily oxidized dibutylphthalate, phthalate, 3,4-dihydroxyphthalate and protocatechuate. Phthalate-3,4-dioxygenase (and possibly the dihydrodiol dehydrogenase) was induced by phthalate or a metabolite and subsequent enzymes were inducible by protocatechuate or a subsequent metabolic product. During growth at 37 °C, strain 12B gave clones at high frequency that had lost the ability to grow with phthalate esters. For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for PHTHALIC ACID (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
|---|---|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Non-Human Toxicity Values
LD50 Mouse ip 550 mg/kg LD50 Mouse oral 2,530 mg/kg LD50 Rat oral 7.9 g/kg |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Phthalic acid appears as white crystals or fine white powder. (NTP, 1992)
Phthalic acid is a benzenedicarboxylic acid cosisting of two carboxy groups at ortho positions. It has a role as a human xenobiotic metabolite. It is a conjugate acid of a phthalate(1-). Phthalic acid has been reported in Papaver somniferum, Cocos nucifera, and other organisms with data available. Mechanism of Action Although it is well established that high dose administration of di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate and its monoester metabolite induces severe testicular atrophy in rats the mechanisms of this testicular injury Is not clear. The present experiment was undertaken to examine the effects of di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate and mono(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate on mitochondrial functions of rat testis. Di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate and di-n-octyl phthalate, a di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate isomer which causes less severe testicular injury did not inhibit the state 3 oxygen consumption up to 0.65 umol/mL in vitro. On the other hand, mono(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate and mono-n-octyl phthalate a metabolite of di-n-octyl phthalate inhibited the state 3 oxygen-consumption down to a concentration of 0.065 amble/mL. Testicular mitochondrial respiratory functions of rats administered 2 g/kg di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate were lower than those of control or di-n-octyl phthalate treated rats. These differences were verified by characteristics of pharmacokinetic parameters and testicular concentrations of mono(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate and mono-n-octyl phthalate. It nay be suggested that a possible mechanism of testicular atrophy induced by di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate may be due to direct inhibition by mono(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (and partially di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate) of the respiratory functions of Sertoli cell mitochondria in rat testis. ... phthalic acid and nonylphenol stimulated PXR-mediated transcription at concentrations comparable to those at which they activate estrogen receptor-mediated transcription using a transient reporter gene expression assay in COS-7 cells. |
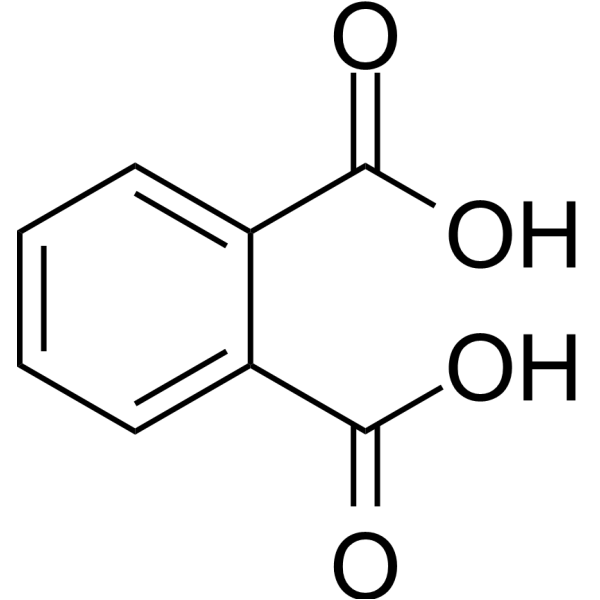
| 分子式 |
C8H6O4
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
166.13
|
| 精确质量 |
166.026
|
| CAS号 |
88-99-3
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Phthalic acid-d4;87976-26-9
|
| PubChem CID |
1017
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.5±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
378.3±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
210-211 °C (dec.)(lit.)
|
| 闪点 |
196.7±19.7 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.618
|
| LogP |
0.81
|
| tPSA |
74.6
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
| 重原子数目 |
12
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
177
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
XNGIFLGASWRNHJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C8H6O4/c9-7(10)5-3-1-2-4-6(5)8(11)12/h1-4H,(H,9,10)(H,11,12)
|
| 化学名 |
phthalic acid
|
| 别名 |
NSC-5348; NSC 5348; Phthalic acid
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~601.94 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (15.05 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (15.05 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (15.05 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.0194 mL | 30.0969 mL | 60.1938 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.2039 mL | 6.0194 mL | 12.0388 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.6019 mL | 3.0097 mL | 6.0194 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。