| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
已证明普达非洛是一种非生物碱木脂素毒素,可抑制多种霉菌的生长。它取自鬼臼属的根和根茎。一种名为 Podofilox 的天然物质可防止微管蛋白聚合,并已被用作创建其他用于治疗应用的抗肿瘤药物的原型。
|
|---|---|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Topical application of 0.05 mL of 0.5% podofilox solution to external genitalia did not result in detectable serum levels. Applications of 0.1 to 1.5 mL resulted in peak serum levels of 1 to 17 ng/mL one to two hours after application. Small amounts of podofilox may be absorbed systemically following topical application. In a study in adults with anogenital warts caused by human papillomavirus, topical application of 0.05 mL of podofilox 0.5% solution to external genitalia did not result in detectable serum concentrations of the drug; however, topical application of 0.1-1.5mL of the solution resulted in peak serum concentrations of 1-17 ng/mL at 1-2 hours after application. Metabolism / Metabolites Half Life: 1.0 to 4.5 hours. Biological Half-Life 1.0 to 4.5 hours. The serum elimination half-life of podofilox is estimated to range from 1-4.5 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
IDENTIFICATION: Podophyllum is a dermatological medication. Origin of the substance: Dried resin from the roots and rhizomes of Podophyllum peltatum (Mandrake or May apple plant) the North American variety; active ingredients are lignans including podophyllotoxins (20%), alpha-peltatin (10%) and beta-peltatin (5%). It is a light brown to greenish yellow solid powder soluble in water, alcohol, chloroform, acetone, warm benzene and glacial acetic acid. Indications: Wart or corn removal preparation. Description: Podophyllum resin has an antimitotic action and is used principally as a topical treatment for ano-genital warts (condylomata acuminata). Podophyllum resin has been used on external genital, perianal and intrameatal warts, but should not be used on cervical or urethral warts. Care must be taken to avoid application to healthy tissue. Podophyllum resin is also used in an ointment for plantar warts. Podophyllum resin has been used as a laxative, but when taken by mouth, it has a marked purging action and it is highly irritating to the intestinal mucosa and produces violent peristalsis. It has been superseded by less toxic laxatives. HUMAN EXPOSURE: Main risk and target organs: Podophyllum resin's major active constituent, podophyllotoxin, is a lipid soluble compound that readily crosses cell membranes. Podophyllotoxin and its derivatives are potent cytotoxic agents that inhibit cell mitosis and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) synthesis in a manner similar to that of colchicine. Cell division is arrested and other cellular processes are impaired, gradually resulting in the disruption of cells and destruction of the tissue. Topical podophyllum is easily absorbed systemically and can cross the placenta. Either local application or oral ingestion may produce multisystem toxic effects. Summary of clinical effects: Features of systemic toxicity include nausea and vomiting (which may be persistent), tachypnea, fever, stupor, coma, tachycardia, hypotension, paralytic ileus, oliguria, renal failure, leukocytosis, leucopenia, peripheral neuropathy and death. Contraindications: Pregnancy: topical podophyllum is absorbed systemically and crosses the placental barrier. It has been associated with the induction of congenital malformations in humans. Routes of exposure: Oral: Easily absorbed even if it induces nausea and vomiting. Dermal: It is absorbed systemically after topical application especially if the skin surface is not intact. Eye: Very well absorbed through mucous membranes. Absorption by route of exposure: Oral absorption: Podophyllum is very well and rapidly absorbed after ingestion. In a fatal case, the patient ingested between 10 and 11 gm of a 25% podophyllum solution in benzoin tincture in the physician's office. He was immediately given syrup of Ipecac and vomited 45 minutes after ingestion. He was also given activated charcoal and magnesium citrate. He died 39 hours after ingestion despite hemoperfusion. Dermal absorption: There are several cases of systemic poisoning following topical application of podophyllum in the literature. In such cases, the onset of symptoms is delayed between two and 24 hours. Distribution by route of exposure: Since podophyllum toxin is water soluble, a small volume of distribution may be predicted. Furthermore, no rebound effects were observed after hemoperfusion. Metabolism: No data available. In a case report, podophyllum toxin in the patient's plasma before, during and after hemoperfusion was examined. A rapid fall in plasma concentration of podophyllum toxin occurred in the period before hemoperfusion was started suggesting rapid metabolism. The delay of onset of symptoms in several case reports may suggest that the metabolized of podophyllum toxin are more toxic than podophyllum toxin itself. This study measured a metabolite during hemoperfusion but several other possible metabolites were found on analysis and removed by hemoperfusion. Mode of action: Toxicodynamics: Podophyllum resin is a potent spindle poison that blocks mitosis metaphase in a manner similar to colchicine. Human poisoning results from either topical application or ingestion of the commercial extract. Overexposure causes neurological, gastrointestinal and hematological toxicity that occasionally results in fatalities. Rarely, poisoning results from consumption of unripe fruit or plant parts and causes primarily diarrhea. The ripe fruit does not produce toxicity. Podophyllum is a keratolytic agent with caustic and cathartic actions. Podophyllum is an antimitotic agent. It binds to tubulin, the protein subunit of the spindle micro-tubules, at the same site or greatly overlapping the same site as colchicine. The antimitotic action of podophyllum toxin probably results from interference with the movement of the chromosomes. The molecular mechanism of mitosis blockade is the disruption of the micro-tubules of the mitotic spindle via binding of podophyllum toxin to tubulin. Podophyllum is caustic but its action differs from those of most caustics in that its effect is neither direct nor immediate: rather, the disruption of cells and erosion of tissue occur slowly subsequent to arrest of cell division and impairment of other cellular processes. Human toxicity: Adults: Most systemic poisoning cases following topical application of podophyllum involved women and some of these were fatal. Serious systemic toxicity has occurred following topical application of podophyllum to large areas or in excessive amounts, or when the medication was allowed to remain in contact with the skin or mucous membranes for a prolonged period of time. The risk of systemic toxicity may be increased when podophyllum is applied to friable bleeding, or recently biopsied warts, or when the medication is inadvertently applied to normal skin or mucous membranes surrounding the affected area. Renal failure and hepatotoxicity (increased serum concentrations of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), aspartate aminotransferase (AST; SGOT) and alkaline phosphase have occurred following topical application or ingestion of podophyllum. Podophyllum can cause severe systemic toxicity, which may result from topical application and ingestion. The toxic effects are usually reversible but in some instances, they have been fatal. Children: Fever and convulsions seem to be more frequent in children. Most reported cases followed accidental ingestion. Carcinogenicity: Podophyllum is a suspected human carcinogen. Teratogenicity: Podophyllum may be a teratogenic agent in humans. At least two cases of possible teratogenic effects of podophyllum have been described. Interactions: Other keratolytic agents may stimulate dermal absorption of podophyllum. Main adverse effects: The risk of systemic toxicity may be increased when podophyllum is applied to friable, bleeding or recently biopsied warts, or when the medication is inadvertently applied to normal skin or mucous membranes surrounding the affected area. Adverse effects on the nervous system may occur following topical application of podophyllum; these are usually delayed in onset and prolonged in duration. Cerebral toxicity (manifested by altered sensorium ranging from mild confusion to coma) may occur following topical application of podophyllum and continue for 7 to 10 days during which the electorencephalogram (EEG) may show generalized slowing. The following side/adverse effects have been selected on the basis of their potential clinical significance. Skin rash or itching: allergic reaction to benzoin, which may be present in some preparations. Redness, burning or other irritation of the skin has been noted. Abdominal pain, nausea or vomiting. Diarrhea, sometimes severe and prolonged. Clumsiness or unsteadiness. Confusion and reduced reflexes. Excitement, irritability, nervousness and hallucinations. Muscle weakness, leucopenia (sore throat and fever) and thrombocytopenia Autonomic neuropathy (difficult or painful urination; dizziness or lightheadedness, especially when getting from a lying or sitting position; fast heartbeat). Difficulty in breathing. Drowsiness. Paralytic ileus (constipation, nausea and vomiting; pain in upper abdomen or stomach, mild dull and continuing) Peripheral neuropathy (numbness, tingling, pain or weakness in hands or feet). If peripheral neuropathy occurs, it usually appears about 2 weeks after podophyllum application, may worsen progressively for up to 3 months and may persist for up to 9 months or longer. Seizures have been noted. Clinical effects: Acute poisoning: Ingestion: Ingestion may cause: nausea and vomiting, which may be severe and persistent and occur rapidly after ingestion. Abdominal pain, ileus (paralytic), lethargy, coma, tachypnea, respiratory failure, tachycardia, hypotension, cardiac arrhythmia, cardiovascular collapse, oliguria, renal failure, fever, metabolic acidosis, leukocytosis, leucopenia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, peripheral neuropathy, death. Skin exposure: In contrast to ingestion, there will be a delay of up to 24 hours before appearance of signs. These are similar to those occurring after ingestion. Eye contact: Podophyllum may be absorbed through this route but severe systemic poisoning seldom occurs. Local irritation and lesions of cornea and conjunctiva may occur. Chronic poisoning: Ingestion: This type of poisoning occurred when podophyllum was used as a cathartic or slimming aid. It has not been reported in recent years. In such cases, poisoning was sometimes difficult to diagnose since the clinical picture did not resemble that of acute poisoning. The first clinical signs are either hematological, gastro-intestinal or peripheral neuropathy. Skin exposure: Repeated local treatment of warts or condyloma may produce systemic poisoning or local lesions of the skin (erosion, pain, bleeding, infection). Course, prognosis, cause of death: The precise course following overdose is difficult to predict since we seldom have good indicators of the absorbed dose. It should be noted that some severely intoxicated patients (especially children) have survived while others either died or developed permanent sequelae (peripheral neuropathy) with lower doses. Death generally results from the cerebral; cardiovascular; renal; or hematological complications. Systematic description of clinical effects: Cardiovascular: Tachycardia, cardiac, arrhythmias, hypotension and cardiovascular collapse. Respiratory: Tachypnea and respiratory failure. Pneumonitis (resembling chemical pneumonitis) and pulmonary edema (rarely). Neurological: Central Nervous System (CNS): Confusion, lethargy, coma and convulsions. Peripheral nervous system: Peripheral neuropathy which develops over several days and may take weeks or months to regress. There may be permanent sequelae. Autonomic nervous system: Paralytic ileus. Skeletal and smooth muscle: Rhabdomyolysis may occur with myoglobinuria. This may aggravate the renal failure. Phosphokinase (CPK) should be monitored. Gastrointestinal: Nausea and vomiting which may be persistent and severe; abdominal pain; paralytic ileus and diarrhea which may produce water and electrolyte imbalance. Hepatic: Elevation of hepatic enzymes. Urinary: Renal: Oliguria and renal insufficiency. Other: Cystitis and painful micturition. Endocrine and reproductive system: Fetal death, abortion, premature labor and fetal malformations. Dermatologic: Pruritus around the treated sites especially if the skin has not been protected by petroleum jelly. Irritation, urticaria, skin necrosis and bleeding. Scarring of tissue, especially of anogenital regions, paraphimosis that may require circumcision and pseudo epitheliomatosis hyperplasia. Eye, ear, nose, throat: local effects: Irritation of skin or mucous membrane, necrosis, scarring of tissues, bleeding and corneal erosion. Hematological: Leucocytosis followed by leucopenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia and pancytopenia. Special risks: The use of podophyllum is contraindicated in pregnant or lactating women. ANIMAL STUDIES: Mutagenicity: Podophyllum is mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium. /Podophyllum/ Etoposide, a semisynthetic derivative of podofilox, induces DNA breakage through its inhibition of topoisomerase II. The drug is most active in the late S and early G2 phases of the cell cycle. Teniposide is an analog with very similar pharmacologic characteristics. Podofilox derivatives display binding activity to the enzyme topoisomerase II during the late S and early G2 stage. For instance, etoposide binds and stabilizes the temporary break caused by the enzyme, disrupts the reparation of the break through which the double-stranded DNA passes, and consequently stops DNA unwinding and replication. Mutants resistant to either podofilox, or to its topoisomerase II inhibitory derivatives such as etoposide (VP-16), have been described in Chinese hamster cells. The mutually exclusive cross-resistance patterns of these mutants provide a highly specific mean to distinguish the two kinds of podofilox derivatives. Mutant Chinese hamster cells resistant to podofilox are affected in a protein P1 that was later identified as the mammalian HSP60 or chaperonin protein. (Wikipedia) Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Rat iv 8.7 mg/kg LD50 Rat ip 15 mg/kg |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Podophyllotoxin is an organic heterotetracyclic compound that has a furonaphthodioxole skeleton bearing a 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl substituent. It is found in the roots and rhizomes of Podophyllum species and is used for the topical treatment of genital warts. It has a role as an antineoplastic agent, a keratolytic drug, a tubulin modulator, a microtubule-destabilising agent, an antimitotic and a plant metabolite. It is a furonaphthodioxole, a lignan and an organic heterotetracyclic compound.
Podofilox is a prescription medicine approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of external genital warts and perianal warts. Podofilox gel and solution are for topicalcutaneous use only. External genital and perianal warts are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV can be an opportunistic infection (OI) of HIV. A lignan found in podophyllin resin from the roots of podophyllum plants. It is a potent spindle poison, toxic if taken internally, and has been used as a cathartic. It is very irritating to skin and mucous membranes, has keratolytic actions, has been used to treat warts and keratoses, and may have antineoplastic properties, as do some of its congeners and derivatives. The physiologic effect of podofilox is by means of Decreased Mitosis. Podofilox has been reported in Phialocephala fortinii, Dysosma aurantiocaulis, and other organisms with data available. Podofilox is a pure, stabilized form of podophyllin, in which only the biologically active portion of the compound is present. Podophyllotoxin is a toxic, polycyclic antimitotic agent isolated primarily from the rhizome of the plant Podophyllum peltatum. This agent is formulated for topical applications. (NCI04) A lignan (lignans) found in podophyllin resin from the roots of podophyllum plants. It is a potent spindle poison, toxic if taken internally, and has been used as a cathartic. It is very irritating to skin and mucous membranes, has keratolytic actions, has been used to treat warts and keratoses, and may have antineoplastic properties, as do some of its congeners and derivatives. A lignan (LIGNANS) found in PODOPHYLLIN resin from the roots of PODOPHYLLUM plants. It is a potent spindle poison, toxic if taken internally, and has been used as a cathartic. It is very irritating to skin and mucous membranes, has keratolytic actions, has been used to treat warts and keratoses, and may have antineoplastic properties, as do some of its congeners and derivatives. See also: Podophyllum (annotation moved to). Drug Indication For treatment of external genital warts (Condyloma acuminatum). Mechanism of Action The exact mechanism of action is not well understood. It does appear, however, that it and its derivatives may bind and inhibit topoisomerase II during the late S and early G2 stage. The drug may bind and stabilize the temporary break caused by the enzyme. This disrupts the reparation of the break through which the double-stranded DNA passes, and consequently stops DNA unwinding and replication The exact mechanism of action for podofilox is unknown. Podofilox is a potent mitotoxic agent that inhibits cell mitosis; cell division stops, other cellular processes are impaired, necrosis occurs, and the affected tissues gradually erode. Therapeutic Uses Antiviral (topical) Podofilox is indicated for the treatment of condyloma acuminatum of the external genital areas; the gel, but not the solution, may be used for perianal warts. Neither the gel nor the solution should be used to treat warts on mucous membranes, including membranous areas of the urethra, rectum, and vagina. /Included in US product labeling/ Drug Warnings Because of the potential for adverse local reactions, the recommended dose, frequency of application, and duration of treatment of topical podofilox should not be exceeded. There is no evidence that applying podofilox more frequently than recommended would increase efficacy; however, more frequent application would be expected to increase the risk of local adverse reactions and increase systemic absorption of the drug. Pregnancy risk category: C /RISK CANNOT BE RULED OUT. Adequate, well controlled human studies are lacking, and animal studies have shown risk to the fetus or are lacking as well. There is a chance of fetal harm if the drug is given during pregnancy; but the potential benefits may outweigh the potential risk./ Podofilox generally is well tolerated when applied topically. In clinical studies evaluating topical podofilox in otherwise healthy adults 18 years of age or older with external genital and/or perianal warts caused by human papillomavirus, up to 6% of patients discontinued the drug because of adverse local reactions; however, serious systemic effects have not been reported to date. Adverse local reactions, including burning, pain, inflammation, erosion, and pruritus, commonly occur at the site of application of podofilox 0.5% gel or 0.5% solution. These reactions usually are mild to moderate in severity; however, severe local reactions have been reported, especially during the first 2 weeks of therapy. Adverse local reactions generally resolve within 4 weeks following completion of topical podofilox therapy. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for PODOFILOX (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Podofilox, also called podophyllotoxin, is a purer and more stable form of podophyllin in which only the biologically active portion of the compound is present. Podofilox is used to remove certain types of warts on the outside skin of the genital areas. |
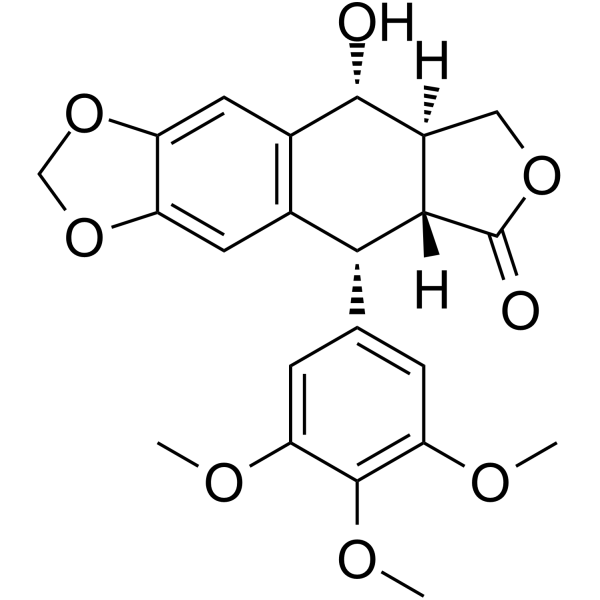
| 分子式 |
C22H22O8
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
414.41188
|
| 精确质量 |
414.131
|
| CAS号 |
518-28-5
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Podofilox-d6
|
| PubChem CID |
10607
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
597.9±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
183-184 °C(lit.)
|
| 闪点 |
210.2±23.6 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.606
|
| LogP |
1.6
|
| tPSA |
92.68
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
30
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
629
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
4
|
| SMILES |
COC1=CC(=CC(=C1OC)OC)[C@H]2[C@@H]3[C@H](COC3=O)[C@H](C4=CC5=C(C=C24)OCO5)O
|
| InChi Key |
YJGVMLPVUAXIQN-XVVDYKMHSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H22O8/c1-25-16-4-10(5-17(26-2)21(16)27-3)18-11-6-14-15(30-9-29-14)7-12(11)20(23)13-8-28-22(24)19(13)18/h4-7,13,18-20,23H,8-9H2,1-3H3/t13-,18+,19-,20-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(5R,5aR,8aR,9R)-5-hydroxy-9-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-5a,6,8a,9-tetrahydro-5H-[2]benzofuro[5,6-f][1,3]benzodioxol-8-one
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~241.31 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 1.25 mg/mL (3.02 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 12.5 mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;再向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;然后加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 1.25 mg/mL (3.02 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 12.5 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 1.25 mg/mL (3.02 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4131 mL | 12.0653 mL | 24.1307 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4826 mL | 2.4131 mL | 4.8261 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2413 mL | 1.2065 mL | 2.4131 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。