| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
补骨脂素治疗(10、15、20 和 25 μM;24 小时)对透明乳腺癌细胞 (BCC) 群体(ALDH-细胞、ALDH+细胞和商业 BSCS)敏感,IC50 范围为 18 至 21 μM。另一方面,用补骨脂素(30 μM;24 小时)处理的 MCF-12A 细胞能够显着诱导 ALDH- 细胞、ALDH+ 细胞和商业 BCSC[2]。补骨脂素对治疗 AIDS 中 ALDH- 和 ALDH+ 细胞的作用 [2]
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
补骨脂素 (5 mg/kg) 通过改变在炎症中至关重要的促炎细胞因子的表达来减少 BALB/c 红外线照射肺部的炎症 [1]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定 [2]
细胞类型: ALDH- 细胞、ALDH+ 细胞、商业乳腺癌干细胞 (BSCS) 和正常乳腺上皮细胞 (MCF-12A) 测试浓度:10、15、50 和 25.μM 孵育持续时间:24 小时 实验结果: ALDH- 细胞、ALDH+ 细胞、商业 BCSC 的 IC50 为 18 至 21 μM。 细胞凋亡分析 [2] 细胞类型: ALDH- 细胞、ALDH+ 细胞和商业 BCSC 测试浓度: 20 和 30 μM 孵育时间:24小时 实验结果:20 μM处理死亡诱导后,所有三种细胞类型均未观察到明显的凋亡。然而,在 30 μMin 时,ALDH- 细胞、ALDH+ 细胞和商业 BCSC 的凋亡率分别为 53.60%、44.1% 和 45.9%。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: balb/c (Bagg ALBino) mouse[1]
Doses: 5 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip) injection; 30 minutes before and 1 hour after IR irradiation (20 Gy). Experimental Results: Anti-inflammatory effects on mice irradiated with infrared rays. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Psoralidin is a member of the class of coumestans that is coumestan substituted by hydroxy groups at positions 3 and 9 and a prenyl group at position 2 respectively. It has a role as a plant metabolite and an estrogen receptor agonist. It is a member of coumestans, a polyphenol and a delta-lactone. It is functionally related to a coumestan.
Psoralidin has been reported in Phaseolus lunatus, Dolichos trilobus, and other organisms with data available. See also: Cullen corylifolium fruit (part of). |
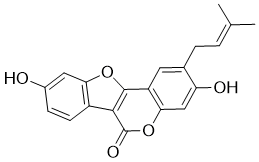
| 分子式 |
C20H16O5
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
336.34
|
| 精确质量 |
336.099
|
| CAS号 |
18642-23-4
|
| PubChem CID |
5281806
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
458.8±34.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
290-292°
|
| 闪点 |
231.3±25.7 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.2 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.689
|
| LogP |
5.03
|
| tPSA |
83.81
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
| 重原子数目 |
25
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
554
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O1C2C([H])=C(C([H])=C([H])C=2C2C(=O)OC3C([H])=C(C(C([H])([H])/C(/[H])=C(\C([H])([H])[H])/C([H])([H])[H])=C([H])C=3C1=2)O[H])O[H]
|
| InChi Key |
YABIJLLNNFURIJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C20H16O5/c1-10(2)3-4-11-7-14-17(9-15(11)22)25-20(23)18-13-6-5-12(21)8-16(13)24-19(14)18/h3,5-9,21-22H,4H2,1-2H3
|
| 化学名 |
3,9-dihydroxy-2-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)-[1]benzofuro[3,2-c]chromen-6-one
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~50 mg/mL (~148.66 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 2.08 mg/mL (6.18 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浮液;超声助溶。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (6.18 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9732 mL | 14.8659 mL | 29.7318 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5946 mL | 2.9732 mL | 5.9464 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2973 mL | 1.4866 mL | 2.9732 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
|
|
|