| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:测定了利福平和利福喷丁对驻留在人单核细胞源性巨噬细胞中的结核分枝杆菌的活性。利福喷汀对细胞内细菌的 MIC 和 MBC 比利福平低 2 至 4 倍。对于细胞外细菌来说,这种差异不太明显。细胞测定:Rifapentine 抑制结核分枝杆菌菌株中 DNA 依赖性 RNA 聚合酶的功能,但对哺乳动物细胞没有诱导作用。利福喷汀及其活性代谢物 25-去乙酰利福喷汀均定位于单核细胞衍生的巨噬细胞内,因此与单独的母体或代谢物相比,可以以更高的杀灭率对结核分枝杆菌进行细胞内抑制。利福喷丁在肝脏中被脱乙酰化,诱导细胞色素 P450 的产生比利福平少得多。利福喷丁比 RMP 显示出更高的抑菌和杀菌活性(MIC 和 MBC),特别是针对人类单核细胞来源的巨噬细胞中生长的细胞内细菌。
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Rifapentine 通过与易感物种中 DNA 依赖性 RNA 聚合酶的 β 亚基结合来抑制细菌 RNA 合成。利福喷丁通常比利福平对结核分枝杆菌敏感菌株更有效。利福喷丁显着增加安替比林和戊巴比妥的体内代谢速率。利福喷丁还可以增加肝脏重量、肝微粒体蛋白和细胞色素 P-450 的含量、NADPH-细胞色素 C 还原酶和 NADPH 氧化酶的活性。每天服用利福喷汀与异烟肼 (INH) 和吡嗪酰胺 (PZA) 联合用药,治疗 10 周后,感染小鼠肺和脾中的结核分枝杆菌明显清除
|
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Rapidly and well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Following a single 600 mg oral dose of radiolabeled rifapentine to healthy volunteers (n=4), 87% of the total 14C rifapentine was recovered in the urine (17%) and feces (70%). 70.2 ± 9.1 L Apparent Oral cl=2.51 +/- 0.14 L/h [Male tuberculosis patients who received 600 mg rifapentine in combination with isoniazid, pyrazinamide and ethambutol] Apparent Oral cl=1.69 +/- 0.41 L/h [Female tuberculosis patients who received 600 mg rifapentine in combination with isoniazid, pyrazinamide and ethambutol] Metabolism / Metabolites Hepatic |
||
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Because of its limited use, the effects of rifapentine on the liver have been less well defined than those of rifampin, but they are likely to be similar. Thus, long term therapy with rifapentine is associated with minor, transient elevations in serum aminotransferase levels in 2% to 7% of patients, abnormalities that usually do not require dose adjustment or discontinuation. Clinically apparent liver injury due to rifapentine has not been reported, but it is likely to be similar to rifampin in its potential for causing acute liver injury. Because rifapentine is usually given in combination with isoniazid and/or pyrazinamide, two other known hepatotoxic agents, the cause of the acute liver injury in patients on rifapentine containing regimens may be difficult to relate to a single agent, and some evidence suggests that these combinations are more likely to cause injury than the individual drugs. Typically, the onset of injury due to rifamycins is within 1 to 6 weeks and the serum enzyme pattern is usually hepatocellular at the onset of injury, but can cholestatic and mixed in contrast to isoniazid and pyrazinamide. Extrahepatic manifestations due to rifamycin hepatotoxicity such as fever, rash, arthralgias, edema and eosinophilia are uncommon as is autoantibody formation. This potential for hepatotoxicity has not been specifically demonstrated for rifapentine. Likelihood score: E* (unproven but suspected cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation The amount of rifapentine and its metabolite in milk is insufficient to treat tuberculosis in the breastfed infant. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and other professional organizations state that breastfeeding should not be discouraged in women taking rifapentine. Monitor the infant for signs of liver toxicity. Breastmilk may be stained a red-orange color. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding 97.7% (bound to plasma proteins) |
||
| 参考文献 |
Ann Pharmacother.1999 Nov;33(11):1203-10;Antimicrob Agents Chemother.1995Sep;39(9):2073-7;Drugs.1998 Oct;56(4):607-16; discussion 617.
|
||
| 其他信息 |
Rifapentine is a N-alkylpiperazine, a N-iminopiperazine and a member of rifamycins. It has a role as an antitubercular agent and a leprostatic drug.
Rifapentine is an antibacterial prescription medicine approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of active tuberculosis (TB) of the lungs. (Active TB is also called TB disease.) Rifapentine is also FDA-approved for the treatment of latent TB infection to prevent the infection from advancing to active TB disease. TB can be an opportunistic infection (OI) of HIV. Rifapentine is an antibiotic drug used in the treatment of tuberculosis. It inhibits DNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity in susceptible cells. Specifically, it interacts with bacterial RNA polymerase but does not inhibit the mammalian enzyme. Rifapentine is a Rifamycin Antimycobacterial. Rifapentine is a rifamycin antibiotic that is similar in structure and activity to rifampin and rifabutin and that is used in combination with other agents as therapy of tuberculosis, particularly in once or twice weekly regimens. Rifapentine is associated with transient and asymptomatic elevations in serum aminotransferase and is a likely cause of clinically apparent acute liver injury. Rifapentine is a long-acting, cyclopentyl-substituted derivative of rifamycin used to treat mycobacterium infections. See also: Rifapentine hydrochloride (is active moiety of). Drug Indication For the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. Mechanism of Action Rifapentine has shown higher bacteriostatic and bactericidal activities especially against intracellular bacteria growing in human monocyte-derived macrophages. Rifapentine inhibits DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in susceptible strains of M. tuberculosis. Rifapentine acts via the inhibition of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase, leading to a suppression of RNA synthesis and cell death. Pharmacodynamics Rifapentine is an antibiotic that inhibits DNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity in susceptible cells. Specifically, it interacts with bacterial RNA polymerase but does not inhibit the mammalian enzyme. It is bactericidal and has a very broad spectrum of activity against most gram-positive and gram-negative organisms (including Pseudomonas aeruginosa) and specifically Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Because of rapid emergence of resistant bacteria, use is restricted to treatment of mycobacterial infections and a few other indications. Rifampin is well absorbed when taken orally and is distributed widely in body tissues and fluids, including the CSF. It is metabolized in the liver and eliminated in bile and, to a much lesser extent, in urine, but dose adjustments are unnecessary with renal insufficiency. |
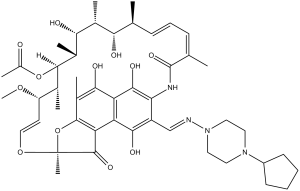
| 分子式 |
C47H64N4O12
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
877.03
|
|
| 精确质量 |
876.452
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 64.37; H, 7.36; N, 6.39; O, 21.89
|
|
| CAS号 |
61379-65-5
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Rifapentine-d9
|
|
| PubChem CID |
135403821
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
969.3±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
179-180ºC
|
|
| 闪点 |
540.0±34.3 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.625
|
|
| LogP |
2.58
|
|
| tPSA |
216.66
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
6
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
15
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
63
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1730
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
9
|
|
| SMILES |
OC(C1=C(C2=O)C(O[C@@]2(O/C=C/[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@]([C@@H]3C)([H])OC(C)=O)C)OC)C)=C(C)C(O)=C1C(O)=C4NC(/C(C)=C\C=C\[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@@H](C)[C@H]3O)O)C)=O)=C4/C=N/N5CCN(C6CCCC6)CC5
|
|
| InChi Key |
WDZCUPBHRAEYDL-GZAUEHORSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C47H64N4O12/c1-24-13-12-14-25(2)46(59)49-37-32(23-48-51-20-18-50(19-21-51)31-15-10-11-16-31)41(56)34-35(42(37)57)40(55)29(6)44-36(34)45(58)47(8,63-44)61-22-17-33(60-9)26(3)43(62-30(7)52)28(5)39(54)27(4)38(24)53/h12-14,17,22-24,26-28,31,33,38-39,43,53-57H,10-11,15-16,18-21H2,1-9H3,(H,49,59)/b13-12+,22-17+,25-14-,48-23+/t24-,26+,27+,28+,33-,38-,39+,43+,47-/m0/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
3-(N-(4-Cyclopentyl-1-piperazinyl)formimidoyl)rifamycin
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.03.00
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : 50 ~100 mg/mL ( 57.01 ~114.02 mM )
H2O : ~0.67 mg/mL (~0.76 mM) Ethanol : ~10 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (2.85 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (2.85 mM) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.1402 mL | 5.7011 mL | 11.4021 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2280 mL | 1.1402 mL | 2.2804 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1140 mL | 0.5701 mL | 1.1402 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。