| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Aquaporin 4 (AQP4) (IC50 = 3.1 μM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
一个配体用于 E3 泛素连接酶,另一个配体用于靶蛋白;这两个配体通过接头连接形成 PROTAC。 PROTAC 利用细胞内泛素-蛋白酶体系统选择性降解靶蛋白[3]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
TGN-020(0.02 mg/μL;2微升玻璃体内注射)可以减轻九周龄雄性Wistar大鼠视网膜的视网膜水肿,这些大鼠已接受STZ诱发糖尿病[2]。 TGN-020(100 mg/kg;腹腔注射;SCI 后立即给予单剂量)可降低水肿程度,抑制 GFAP、PCNA 和 AQP4 的表达,并增强第 3、7、14、21 和 21 天的功能恢复。 28 以下 SCI。在患有 SCI 的成年雌性 Sprague-Dawley 大鼠(180-220 g,9-10 周龄)中,TGN-020 抑制神经胶质疤痕的形成并增加 GAP-43 的表达[4]。
在糖尿病视网膜中,TGN-020抑制了VEGF的免疫反应性和蛋白水平。AQP4免疫反应性高于对照组视网膜,AQP4的表达与GFAP共定位。与VEGF类似,TGN-020也抑制AQP4和GFAP。在伊文思蓝试验中,TGN-020减少了糖尿病视网膜的渗漏。在培养的Müller细胞中,暴露于TGN-020与暴露于贝伐单抗一样,可以抑制高糖条件下细胞体积和细胞内ROS产生的增加。 结论:TGN-020可能对糖尿病视网膜水肿有抑制作用。[2] TGN-020与脊髓损伤(SCI)后第3天脊髓水肿的缓解[4] 我们测量了组织的含水量,以反映SCI部位的水肿程度。SCI后第3天,SCI组和TGN-020组T10脊髓局灶性压迫导致可见损伤,而假手术组则不明显。脊髓损伤中心出血和坏死明显,脊髓损伤组的损伤区域明显多于TGN-020组(图2A)。受伤脊髓的照片与各组脊髓含水量的计算结果相当一致(图2B)。SCI组(76.09±0.93)和TGN-020组(73.07±0.87)第3天损伤部位邻近节段的组织含水量明显高于假手术组(69.02±0.45)(p<0.01)。 0.05),表明TGN-020可以显著降低SCI引起的含水量增加。 TGN-020和SCI后第3天AQP4表达降低[4] 与假手术组相比,SCI组(p<0.01)和TGN-020组(p<0.05)在压缩损伤后3天,AQP4在损伤部位中心及其周围的表达显著增加(图3A、B)。在TGN-020组中,AQP4的表达明显低于SCI组(p<0.05)。用GFAP对AQP4进行免疫荧光染色的结果与蛋白质印迹的结果一致(图3C,D)。在第3天,SCI组和TGN-020组的AQP4荧光强度均显著高于假手术组(p < 0.01), TGN-020组的AQP4表达明显低于SCI组(p<0.05)。这些数据表明,TGN-020可以下调AQP4的表达,从而减轻脊髓水肿的形成。 TGN-020与SCI后第3天星形胶质细胞增殖的抑制作用[4] GFAP是一种细胞骨架中间丝蛋白,被用作特定的星形胶质细胞标志物。增殖细胞核抗原(PCNA)是众所周知的细胞增殖标志物。为了研究AQP4是否与SCI星形胶质细胞增殖有关,我们在SCI后3天检测了PCNA和GFAP的表达。Western印迹表明,假手术组GFAP水平较低,几乎没有PCNA表达(图4A-C)。然而,值得注意的是,与假手术组相比,SCI组和TGN-020组在第3天损伤部位中心周围的GFAP和PCNA表达显著增加(p < 0.01). 在第3天,TGN-020组的GFAP和PCNA表达明显低于SCI组(p < 0.05). TGN-020与SCI后4周胶质瘢痕形成和轴突再生[4] 为了研究TGN-020给药是否可以在SCI后4周保护脊髓组织免受损伤,我们计算了空腔面积的大小,以评估星形胶质细胞瘢痕的形成。4周时,假手术组的脊髓正常,但SCI组和TGN-020组的脊髓都出现了破坏,包括非常大和不规则的空洞(图5A、B)。TGN-020组的空洞面积明显小于SCI组(4.2±0.6 mm2 vs.3.0±0.4 mm2,p<0.01)。这些观察结果表明,TGN-020显著减少了SCI后的继发性脊髓组织退化。 TGN-020与脊髓损伤后4周的神经元存活率[4] SCI诱导的神经元坏死和凋亡导致神经元丢失。脊髓损伤后4周,在横断面上进行尼氏染色,以研究TGN-020的潜在神经保护作用。检测到大量具有延伸细胞体的尼氏阳性神经元,主要位于正常脊髓的腹角(图6B)。因此,在受伤脊髓的前角检测到运动神经元。如图6A所示,在假手术组中,神经元表现出完整的颗粒状形态,以及大而多的尼氏小体,表明神经细胞中有大量的蛋白质合成。在SCI组中,神经元表现出萎缩的细胞体、固缩的核和不规则的形态,病变周围的细胞内甲苯胺蓝染色减少。此外,存活的运动神经元数量明显低于假手术组(图6C,p < 0.01). 在TGN-020组中,存活的运动神经元数量也明显低于假手术组(图6C,p < 0.01), 但神经元形态比SCI组好,细胞质染色更深,尼氏颗粒的损失明显减少(图6C,p<0.01)。这些结果表明,TGN-020给药抑制了神经元的损失。 TGN-020与SCI后功能性运动恢复的促进作用[4] 为了评估TGN-020对SCI后大鼠功能性运动恢复的影响,通过Basso-Beattie-Bresnahan(BBB)量表在第1、3、7、14、21和28天评估行为结果,该量表已被广泛用于评估大鼠SCI后后肢运动功能的恢复情况。假手术组在所有时间点的评分均为21分,反映了正常的运动功能,而脊髓损伤组和TGN-020组的BBB评分在压缩损伤后1天降低,然后随着时间的推移逐渐增加到不同程度(图7)。这表明脊髓损伤后运动功能逐渐恢复。在TGN-020组中,SCI后第3天至第28天的所有时间点,BBB评分均显著高于SCI组(第7天p<0.01;第3、14、12和28天的p<0.05)。这些结果表明,TGN-020给药可以显著促进SCI后大鼠运动功能的恢复。 |
| 细胞实验 |
通过流式细胞术测量细胞体积和ROS产生的细胞内水平[2]
为了检测TR-MUL5细胞体积的变化和高糖条件下细胞内ROS的产生,将细胞在高糖(25 mM)或生理浓度的低血糖(5.5 mM)培养基中孵育2-3天。然后,在生理和高糖条件下,在有或没有TGN-020(100 nM)或贝伐单抗过夜的情况下,使用乙锭荧光流式细胞术分析TR-MUL5的体积变化和细胞内ROS水平。使用荧光探针氢乙啶测量TR-MUL5细胞中的超氧化物水平。氢乙啶被超氧化物氧化形成乙锭,这是一种荧光产物,然后被保留在细胞内,从而可以半定量估计细胞内的超氧化物水平。通过胰蛋白酶消化收集细胞,并在800 g下离心5分钟。用PBS洗涤后,将细胞在37°C下重新悬浮在无酚红的含羟乙基乙胺(1μg/mL)的DMEM中30分钟。将细胞密度调节至2.0×105个细胞/mL。使用488 nm激发和590至610 nm发射波长的流式细胞术分析Müller细胞体积和细胞内超氧化物水平的变化。EC800上的采集和分析软件用于采集和量化荧光强度。我们之前描述了使用EC800流式细胞仪测定TR-MUL5细胞体积变化的细节。 培养的Müller细胞的免疫抑制[2] 为了确定TGN-020对TR-MUL5细胞中VEGF和AQP4表达的影响,通过免疫细胞化学检测了在含有和不含TGN-020>或生理浓度的低血糖(5.5mM)培养基的高糖(25mM)培养基中孵育的细胞。用4%甲醛固定后,将细胞与兔多克隆抗AQP4和小鼠单克隆抗VEGF的一抗在4°C下孵育过夜。用PBS冲洗并阻断后,将这些细胞在室温下在Alexa 594或Alexa 488中孵育2小时,Alexa 594或Alexa 488与1:500稀释的适当二抗结合。细胞核用4′,6-二脒基-2-苯基吲哚染色。用荧光显微镜对处理后的样品进行拍照。 |
| 动物实验 |
Intravitreal Injection [2]
Two microliter intravitreal injections of TGN-020 (0.02 mg/μL) or bevacizumab (0.025 mg/μL) (Genentech Inc, San Francisco, CA, USA) or vehicle alone (phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4) were performed on STZ-induced diabetic rats using a Hamilton syringe and a 30-gauge needle. Animals received general anesthesia, and perfused fixation was performed 48 h after the intravitreal injections. Evans Blue Assay [2] Retinal blood vessel permeability of the STZ-induced diabetic rats in the presence or absence of TGN-020 was tested by Evans Blue assay. A total of 100 μL of Evans Blue (20 mg/mL) in PBS was injected into the tail vein. After 10 min, retinas were carefully explanted and post-fixed in 4% PFA in PBS overnight. Flat-mounted retinas were created and extravasation was evaluated by epifluorescence analysis at an excitation wavelength of 594 nm with a laser scanning confocal microscope Animals and experimental groups [4] Great effort was made to reduce animal suffering. Animals were then randomly assigned to the following three groups: Sham group (n = 35) which were only subject to laminectomy without compression of spinal cord, SCI group (n = 35) which underwent 35 g impounder compression for 5 min at T10, TGN-020 group (n = 35) which received TGN-020 (100 mg/kg, i.p.) immediately followed SCI. Each group was equally and randomly assigned into four subgroups (n = 5 or 6 and 8/group) for the following experiments: (A) Spinal cord water content determination; (B) Western blotting; (C) Immunofluorescent assay, Hematoxylin-Eosin staining and Nissl staining; and (D) Locomotor function test. These rats in all groups were sacrificed 3 day or 4 weeks after injury. 2.2. Surgical procedures and TGN-020 administration [4] Basic surgical procedures and compression injury were performed as described previously. All surgeries were performed under sterile conditions. Briefly, the rats were anesthetized with 10% chloral hydrate (0.33 mL/kg, i.p.). Once anesthesia took effect, surgical area was clean shaved and sterilized with 75% ethanol, a 3 cm dorsal longitudinal incision was made over the midthoracic spinal cord at T9–T12 and then removed peripheral paraspinal soft tissues to expose the spinal cord, leaving the dura intact. The spinal cord was extradurally compressed with a metal impounder (35 g, 5 min) gently loaded onto T10 level of the spinal cord to achieve a moderate injury (Fig. 1). Following surgery wounds were then closed in layers using 4–0 silk. Postoperativaly, TGN-020 (100 mg/kg, i.p.) diluted in 10% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was administrated to TGN-020 group. The concentration of DMSO was adjusted at 0.1% before injection. The Sham group and SCI group received the equal volume DMSO intraperitoneally at the same time. The animals were returned to individual cages once them were waked. During the postoperative recovery period, ceftriaxone sodium (50 mg/kg, i.p.) was administered on three consecutive days. The bladders were manually pressed three times daily until natural voiding reflex recovery, food and water were available ad libitum. Animals that behaved any abnormal neurological signs would be excluded from experiments. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
The in vitro inhibitory effects and in silico docking energies of 18 compounds with respect to aquaporin 4 (AQP4) were investigated. More than half of the compounds tested showed inhibitory activity in the in vitro functional assay and included the 5-HT(1B/1D) agonists sumatriptan, and rizatriptan. Moreover, the observed inhibitory activity of the compounds used in this study at 20 microM showed a strong correlation with their in silico docking energies, r(2)=0.64, which was consistent with that found in previous studies. The AQP4 inhibitory IC(50) values of three compounds, 2-(nicotinamido)-1,3,4-thiadiazole, sumatriptan and rizatriptan, were subsequently found to be 3, 11, and 2 microM, respectively.[1]
Purpose: To investigate the effect of a selective aquaporin 4 (AQP4) inhibitor, 2-(nicotinamide)-1,3,4-thiadiazole (TGN-020), on the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, as well as on the retinal edema in diabetic retina. Methods: Intravitreal injections of bevacizumab, TGN-020, or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) were performed on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Retinal sections were immunostained for anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), anti-AQP4, and anti-VEGF. Protein levels of VEGF from collected retinas were determined by Western blot analysis. In addition, retinal vascular leakage of Evans Blue was observed in the flat-mounted retina from the diabetic rats in the presence or absence of TGN-020. Volumetric changes of rat retinal Müller cells (TR-MUL5; transgenic rat Müller cells) and intracellular levels of ROS were determined using flow cytometry analysis of ethidium fluorescence in the presence or absence of TGN-020 or bevacizumab under physiological and high glucose conditions. Results: In the diabetic retina, the immunoreactivity and protein levels of VEGF were suppressed by TGN-020. AQP4 immunoreactivity was higher than in the control retinas and the expressions of AQP4 were co-localized with GFAP. Similarly to VEGF, AQP4 and GFAP were also suppressed by TGN-020. In the Evans Blue assay, TGN-020 decreased leakage in the diabetic retinas. In the cultured Müller cells, the increase in cell volumes and intracellular ROS production under high glucose condition were suppressed by exposure to TGN-020 as much as by exposure to bevacizumab. Conclusion: TGN-020 may have an inhibitory effect on diabetic retinal edema.[2] There are several challenges towards the development and clinical use of small molecule inhibitors, which are currently the main type of targeted therapies towards intracellular proteins. PROteolysis-TArgeting Chimeras (PROTACs) exploit the intracellular ubiquitin-proteasome system to selectively degrade target proteins. Recently, small-molecule PROTACs with high potency have been frequently reported. In this review, we summarize the emerging characteristics of small-molecule PROTACs, such as inducing a rapid, profound and sustained degradation, inducing a robust inhibition of downstream signals, displaying enhanced target selectivity, and overcoming resistance to small molecule inhibitors. In tumor xenografts, small-molecule PROTACs can significantly attenuate tumor progression. In addition, we also introduce recent developments of the PROTAC technology such as homo-PROTACs. The outstanding advantages over traditional small-molecule drugs and the promising preclinical data suggest that small-molecule PROTAC technology has the potential to greatly promote the development of targeted therapy drugs. [3] Aims: Identifying drugs that inhibit edema and glial scar formation and increase neuronal survival is crucial to improving outcomes after spinal cord injury (SCI). Here, we used 2-(nicotinamide)-1,3,4-thiadiazole (TGN-020), a potent selective inhibitor of aquaporin 4 (AQP4), to investigate the effects of TGN-020 on SCI in Sprague-Dawley rats. Main methods: We compressed the spinal cord at T10 using a sterile impounder (35 g, 5 min), to induce moderate injury. TGN-020 (100 mg/kg) or an equal volume of 10% dimethyl sulfoxide was then administered via intraperitoneal injection. Neurological function was evaluated using the Basso-Beattie-Bresnahan open-field locomotor scale 1, 3, 7, 14, 21, and 28 days after SCI. The degree of edema was assessed via determination of the precise spinal cord water content 3 days after SCI. Expression levels of AQP4, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), and growth-associated protein-43 (GAP-43) were determined via western blotting and immunofluorescence staining 3 days after SCI and 4 weeks after SCI. Numbers of surviving neurons and glial scar sizes were determined using Nissl and hematoxylin-eosin staining, respectively. Key findings: Our results showed that TGN-020 promoted functional recovery at days 3, 7, 14, 21, and 28, as well as reduced the degree of edema and inhibited the expression of AQP4, GFAP, PCNA at days 3 after SCI. Furthermore, observations 4 weeks after SCI revealed that TGN-020 inhibited the glial scar formation and upregulated GAP-43 expression. Significance: TGN-020 can alleviate spinal cord edema, inhibit glial scar formation, and promote axonal regeneration, conferring beneficial effects on recovery in rats. [4] |
| 分子式 |
C8H6N4OS
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
206.22
|
|
| 精确质量 |
206.026
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 46.59; H, 2.93; N, 27.17; O, 7.76; S, 15.55
|
|
| CAS号 |
51987-99-6
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
1313731-99-5
|
|
| PubChem CID |
4173511
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| LogP |
1.569
|
|
| tPSA |
99.5
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
14
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
214
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
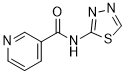
C1=CC(=CN=C1)C(=O)NC2=NN=CS2
|
|
| InChi Key |
AGEGZHOPKZFKBP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C8H6N4OS/c13-7(6-2-1-3-9-4-6)11-8-12-10-5-14-8/h1-5H,(H,11,12,13)
|
|
| 化学名 |
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 25 mg/mL (121.23 mM) in 15% Cremophor EL + 85% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浮液;超声助溶。
*生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 1.67 mg/mL (8.10 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 16.7 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: 5 mg/mL (24.25 mM) in 0.5% MC 0.5% Tween-80 (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.8492 mL | 24.2460 mL | 48.4919 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.9698 mL | 4.8492 mL | 9.6984 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4849 mL | 2.4246 mL | 4.8492 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
PET images. (a) WT and (b) KO mice. |
Ex vivo PET images of the brain. (a) WT and (b) KO mouse brains. (c) MRI images of the corresponding brain slices.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2011 Oct 19; 2(10): 568–571. |
Time course analysis of SUV. Data from WT (n= 6, ○) and KO (n= 4, |