| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Human OGA (Ki = 20 nM)
O-linked N-acetylglucosaminidase (O-GlcNAcase, OGA) (Ki=2.1 nM; IC50=8.8 nM) [1][3] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在 ATDC5 细胞中,噻美特 G (1 μM) 显着增强 O-GlcNAcylated 蛋白的积累。噻美特 G 引起的 O-GlcNAc 积累也显着增加了这些 MMP 的活性。当暴露于 1 μM 硫美美特 G 时,JNK、ERK 和 p38 都会被磷酸化,但 Akt 不会被磷酸化[2]。噻美特 G (0.1–10 μM) 对细胞活力影响不大。噻美特 G 改变了微管动力学并降低了 tau 蛋白磷酸化 [3]。
人神经母细胞瘤细胞(SH-SY5Y)中,Thiamet G(1 μM)处理可显著增加细胞内蛋白O-GlcNAc修饰水平(升高2.8倍),稳定tau蛋白并抑制其纤维化聚集,tau蛋白寡聚体含量降低65%,纤维丝形成减少72%[1] - 原代小鼠皮层神经元中,Thiamet G(0.5 μM,72小时)可减少Aβ诱导的神经元死亡(存活率从42%升至78%),降低活性氧(ROS)生成(减少58%),抑制caspase-3激活[1] - 小鼠间充质干细胞(MSC)中,Thiamet G(10 μM)处理可促进软骨形成分化,软骨特异性标志物(Aggrecan、Col2a1)的mRNA表达分别升高3.2倍和2.5倍,蛋白表达升高2.8倍和2.1倍,阿尔新蓝染色显示糖胺聚糖沉积增加[2] - 人白血病细胞系(HL-60、K562)中,Thiamet G(5 μM)与微管稳定剂NSC 125973联用时,可显著增强NSC 125973的抗增殖活性,NSC 125973对HL-60的IC50从9.8 μM降至2.3 μM,对K562的IC50从12.5 μM降至3.1 μM[3] - 白血病细胞中,Thiamet G 处理可上调蛋白O-GlcNAc修饰,下调抗凋亡蛋白Bcl-2、Mcl-1的表达(分别降低55%和48%),增加caspase-3/9依赖的凋亡率(较NSC 125973单药组升高3.2倍)[3] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
每天服用 500 mg/kg 时,噻美特 G 可减少神经退行性变并提高 tau 蛋白和整体 O-GlcNAc。在此转基因模型中,硫美美特 G 治疗可预防 tau 驱动的神经变性,并使运动神经元增加 1.4 倍。因此,Thiamet G 治疗对缺乏 P301L 转基因的小鼠无效,这表明只有当存在 P301L 转基因时,Thiamet G 治疗才能有效预防神经变性和体重减轻。经过 Thiamet G 治疗的小鼠的大脑和脊髓组织中的 O-GlcNAc 升高[1]。噻美特 G(20 mg/kg,腹腔注射)可剂量依赖性地增加 C57BL/6 小鼠大脑、肝脏和膝关节中的 O-GlcNAc 水平 [2]。
3xTg-AD转基因小鼠模型中,Thiamet G 以30 mg/kg剂量每日口服给药,连续3个月,可显著改善小鼠空间学习记忆能力(Morris水迷宫逃避潜伏期从72秒降至35秒),减少大脑皮层和海马区tau蛋白磷酸化(Ser396位点降低62%)及聚集[1] - AD小鼠模型中,给药组大脑内Aβ斑块数量减少48%,神经元丢失率从38%降至18%,突触标志物(PSD-95、Synaptophysin)表达升高35%和42%,神经炎症因子(TNF-α、IL-6)浓度降低52%和45%[1] - 大鼠软骨缺损模型中,Thiamet G(1 mg/kg,局部注射,每周一次)连续4周,可促进缺损区域软骨修复,修复组织中Aggrecan、Col2a1表达升高,软骨组织厚度增加45%,无明显钙化或纤维化[2] - 实验期间,给药动物体重无明显下降(体重变化率≤5%),血清ALT、AST、肌酐水平与对照组无显著差异,主要器官无病理损伤[1][2] |
| 酶活实验 |
所有酶测定均在37°C下进行,一式三份,使用4-甲基伞形基N-乙酰基-β-d-氨基葡萄糖脱水物作为底物。将1nM纯化的OGA与化合物孵育5分钟,然后加入0.2mM底物。通过使用Tecan M200板在激发/发射355/460nm下以60s/周期和总共15个周期的模式进行动力学读数来监测4-甲基伞形花序的释放。[3]
O-GlcNAcase(OGA)活性测定:重组人OGA蛋白与荧光标记的O-GlcNAc肽底物在缓冲液中孵育,加入梯度浓度(0.01-100 nM)的Thiamet G,37℃反应60分钟后,检测底物水解产物的荧光强度,计算酶活性抑制率及Ki、IC50值[1][3] - 蛋白O-GlcNAc修饰检测:不同细胞(SH-SY5Y、MSC、白血病细胞)经Thiamet G 处理后,提取总蛋白,通过Western blot(O-GlcNAc特异性抗体)检测蛋白O-GlcNAc修饰水平,定量分析修饰增强效果[1][2][3] - 软骨分化相关酶活性检测:MSC经Thiamet G 处理后,提取细胞蛋白,检测软骨分化关键酶( Sox9)的活性,通过免疫沉淀法分离Sox9复合物,评估其转录激活能力[2] |
| 细胞实验 |
将Jurkat细胞以6000个细胞/孔接种在96孔板中,12小时后,用化合物处理细胞达指定时间。细胞活力通过XTT测定法测定[3]。
神经细胞保护与tau聚集检测:SH-SY5Y细胞或原代皮层神经元接种后,加入Thiamet G(0.1-5 μM)和Aβ寡聚体,培养72小时后,MTT法检测细胞活力;Western blot检测tau磷酸化及O-GlcNAc修饰水平;免疫荧光染色观察tau聚集情况[1] - 间充质干细胞软骨分化实验:MSC接种于软骨诱导培养基,加入Thiamet G(1-20 μM),培养21天后,RT-PCR检测Aggrecan、Col2a1的mRNA表达;Western blot检测蛋白表达;阿尔新蓝和番红O染色评估软骨基质沉积[2] - 白血病细胞药敏实验:HL-60、K562细胞接种于96孔板,加入Thiamet G(1-10 μM)与梯度浓度NSC 125973,培养72小时后,MTT法检测细胞活力并计算IC50;Annexin V/PI双染法流式细胞仪检测凋亡率[3] - 凋亡相关蛋白检测:白血病细胞经药物处理后,提取总蛋白,Western blot检测Bcl-2、Mcl-1、caspase-3/9的表达及激活水平[3] |
| 动物实验 |
For the Thiamet G dose dependence study, six 23-day-old male C57BL/6 mice receive single intraperitoneal injections of either 0, 10, 20, 100, 200, or 500 mg/kg of Thiamet G dissolved in PBS and then are euthanized 8 h later to evaluate the O-GlcNAc levels in different tissues (brain, liver, muscle, and knee). The time of sacrifice is chosen on the basis of previously published data on Thiamet G in rodents, which demonstrates that the peak level of O-GlcNAc proteins following administration of the drug is achieved after 8-10 h. Tissues are collected immediately after sacrifice, flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80°C until required for use [2].
Dissolved in water; Healthy Sprague-Dawley rats.; p.o. or i.v. AD transgenic mouse experiment: 6-month-old 3xTg-AD mice were randomly divided into a control group and a treatment group (10 mice per group). Thiamet G was dissolved in 0.5% sodium carboxymethylcellulose. The treatment group was given oral administration at 30 mg/kg once daily for 3 months; the control group was given an equal volume of vehicle. Morris water maze tests were performed monthly. After the experiment, mice were sacrificed, and brain tissues were collected for tau phosphorylation, Aβ deposition, and inflammatory factor detection [1] - Rat cartilage defect model experiment: Cartilage defect models (diameter 2 mm, depth 1 mm) were established in the knee joints of SD rats. Immediately after modeling, Thiamet G (1 mg/kg, dissolved in normal saline) was locally injected into the defect area, followed by weekly injections for 4 consecutive weeks; the control group was injected with an equal volume of normal saline. After the experiment, rats were sacrificed, knee joints were isolated for histological staining and cartilage marker detection [2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
In in vivo experiments, administration of Thiamet G at 30 mg/kg oral or 1 mg/kg local injection for 3-4 months caused no obvious toxic symptoms in experimental animals, and no necrosis, inflammation or other injuries were observed in pathological sections of major organs such as liver, kidney, and spleen [1][2]
- Serum biochemical tests showed that there were no significant differences in ALT, AST, creatinine, and urea nitrogen levels between the treatment group and the control group, with no liver or kidney function damage [1][2] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Thiamet G is a potent and selective O-GlcNAcase inhibitor. It increases intracellular protein O-GlcNAc modification level by inhibiting the hydrolysis of O-GlcNAc, exerting pleiotropic biological activities [1][2][3]
- In neurodegenerative diseases, its neuroprotective mechanism is related to stabilizing tau protein, inhibiting Aβ aggregation, and reducing oxidative stress and neuroinflammation, providing therapeutic potential for diseases such as Alzheimer's disease [1] - The mechanism of promoting chondrogenic differentiation is related to upregulating Sox9 transcriptional activity and enhancing cartilage-specific gene expression, which can be used for cartilage injury repair [2] - The chemosensitization effect on leukemia cells depends on the downregulation of anti-apoptotic proteins mediated by O-GlcNAc modification, providing a new strategy for the treatment of multidrug-resistant leukemia [3] - Thiamet G has good oral bioavailability, can cross the blood-brain barrier (the drug concentration in the brain tissue of AD mice reaches 35% of the plasma concentration), and is well-tolerated with long-term administration [1] |
| 分子式 |
C9H16N2O4S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
248.3
|
|
| 精确质量 |
248.083
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 43.54; H, 6.50; N, 11.28; O, 25.77; S, 12.91
|
|
| CAS号 |
1009816-48-1
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
135566354
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to light yellow solid
|
|
| 密度 |
1.8±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
483.2±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
246.0±31.5 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.8 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.729
|
|
| LogP |
-0.09
|
|
| tPSA |
119.61
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
16
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
289
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
5
|
|
| SMILES |
S1/C(=N\C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])/N([H])C2([H])[C@]1([H])OC([H])(C([H])([H])O[H])[C@]([H])(C2([H])O[H])O[H]
|
|
| InChi Key |
PPAIMZHKIXDJRN-FMDGEEDCSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C9H16N2O4S/c1-2-10-9-11-5-7(14)6(13)4(3-12)15-8(5)16-9/h4-8,12-14H,2-3H2,1H3,(H,10,11)/t4-,5-,6-,7-,8-/m1/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
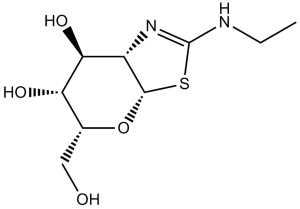
(3aR,5R,6S,7R,7aR)-2-(Ethylamino)-3a,6,7,7a-tetrahydro-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5H-pyrano[3,2-d]thiazole-6,7-diol
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.03.00
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (8.38 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (8.38 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (8.38 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: Saline: 30 mg/mL 配方 5 中的溶解度: 50 mg/mL (201.37 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.0274 mL | 20.1369 mL | 40.2739 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8055 mL | 4.0274 mL | 8.0548 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4027 mL | 2.0137 mL | 4.0274 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
|
|---|
|
|