| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
辅酶 Q10 是每个细胞线粒体呼吸链的重要组成部分。因此,它在三磷酸腺苷 (ATP) 的合成中起着至关重要的作用,而三磷酸腺苷是大多数生物功能的能量来源。在高尔基体、线粒体、溶酶体和质膜内,辅酶 Q10 直接与自由基反应或将生育酚和抗坏血酸从氧化状态恢复,从而产生抗氧化作用 [1]。由于辅酶Q10被广泛认为是促进人类健康的重要成分,因此它是深受人们喜爱的膳食补充剂。由于其在线粒体功能和细胞生物能学中的重要作用,辅酶 Q10 已被提议作为一系列影响心血管系统、退行性神经系统和神经肌肉系统疾病的治疗剂 [2]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
由于其疏水性和大分子量,膳食 CoQ10 吸收缓慢且程度有限。溶解的 CoQ10 配方在膳食补充剂方面表现出卓越的生物利用度。 Tmax 大约为 6 小时,消除半衰期大约为 33 小时。在健康个体中,血浆辅酶 Q10 参考区间为 0.40 至 1.91 mM。血浆CoQ10的增加与CoQ10补充剂的服用剂量之间存在相当显着的关系。对动物的研究表明,所有器官,包括心脏和大脑线粒体,都会吸收大量的 CoQ10 [2]。 CoQ10 治疗导致 12 个月大的大鼠大脑皮质线粒体中 CoQ10 浓度大幅上升。当口服辅酶Q10时,家族性肌萎缩侧索硬化症转基因小鼠模型的寿命更长,并且还显着减少了3-硝基丙酸全身治疗引起的纹状体损伤[3]。
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Ubidecarenone is absorbed from the small intestine into the lymphatics and then it can enter the blood. The hydrophobicity and large molecular weight limit its absorption making it very poor and variable depending on the food intake and the number of lipids presented in the food. The absorption is lower in the presence of an empty stomach and greater in presence of high lipid food diet. The daily dosage of ubidecarenone presents the reach of maximal serum concentration by reaching a plateau after three weeks. The pharmacokinetic properties may vary between different brands but studies have reported an AUC of 11.51 mcg h/ml and a Cmax of 0.32 mcg/ml at a time of 7.9 h. The main elimination route of ubidecarenone is through the bile. After its oral administration, over 60% of the dose is excreted in the feces in the form of unchanged ubidecarenone and a small fraction of the metabolites. In the urine, ubidecarenone is bound to saposin B protein and represents only 8.3% of the total administered dose. Ubidecarenone is distributed to the various tissues of the body and it is able to enter the brain. In preclinical studies with intravenous administration of ubidecarenone, it is reported a volume of distribution of 20.4 L/kg which reflects its ability to penetrate extensively into organs and tissues. AS a general rule, tissues with high-energy requirements or metabolic activity tend to presents higher amounts of ubidecarenone, these organs can be heart, kidney, liver and muscle. In preclinical studies with intravenous administration of ubidecarenone, it is reported a total clearance of 1.18 ml h/kg which was indicative of a prolonged elimination. Metabolism / Metabolites Studies indicate that there is no saturation process during the metabolism of ubidecarenone. It is metabolized in all tissues by the phosphorylation in the cells and transportation to the kidneys for further excretion by the urine. After exerting its action, ubidecarenone is reduced and forms hydroquinone which is capable of recycling and regenerates other antioxidants such as tocopherol and ascorbate. The later metabolism of hydroquinone generates the formation of Q acid I and Q acid II in free and conjugated forms. Biological Half-Life The pharmacokinetic properties may vary between different brands but studies have reported a half-life of ubidecarenone of 21.7 h. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Coenzyme Q10 is generally recognized as safe and has not been linked to elevations in serum aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, or bilirubin levels. Despite wide scale use for several decades, there have been no convincing reports of clinically apparent liver injury due to coenzyme Q10. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Drug Class: Nutritional Supplements Other Names: Ubiquinone, Semiubiquinone, Ubiquinol, CoQ10 Protein Binding In the blood, ubidecarenone is split into the various lipoprotein particles including LDL and VLDL. The plasma concentration of ubidecarenone is highly dependent on the presence of plasma lipoproteins and about 95% of the administered form is found in the reduced form. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Coenzyme Q10 is a ubiquinone having a side chain of 10 isoprenoid units. In the naturally occurring isomer, all isoprenyl double bonds are in the E- configuration. It has a role as a human metabolite, a ferroptosis inhibitor and an antioxidant.
Ubidecarenone, also called coenzyme Q10, is a 1,4-benzoquinone. From its name (Q10), the Q refers to the constitutive quinone group, and 10 is related to the number of isoprenyl subunits in its tail. It is a powerful antioxidant, a lipid-soluble and essential cofactor in mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. The ubidecarenone is the coenzyme destined for mitochondrial enzyme complexes involved in oxidative phosphorylation in the production of ATP. It is fundamental for cells that have a high metabolic demand. Ubidecarenone is sold as a dietary supplement and is not FDA approved as a drug - it is not meant to treat, cure or prevent any disease. FDA does not approve this dietary supplements before sold nor regulate the manufacturing process. Ubiquinone-10 is a metabolite found in or produced by Escherichia coli (strain K12, MG1655). Coenzyme Q10, also known as ubiquinone, is an enzyme cofactor found in virtually all cells of the body and participates in many essential energy-producing and antioxidant enzymatic actions. While normally synthesized in the body in adequate amounts, coenzyme Q10 is used as a nutritional supplement for conditions highly dependent upon its actions, some of which are associated with low serum levels of the coenzyme. Coenzyme Q supplements are generally well tolerated and there is no evidence that they cause serum enzyme elevations or clinically apparent liver injury. Coenzyme Q10 has been reported in Fusarium fujikuroi, Cytisus scoparius, and other organisms with data available. Coenzyme Q10 is a naturally occurring benzoquinone important in electron transport in mitochondrial membranes. Coenzyme Q10 functions as an endogenous antioxidant; deficiencies of this enzyme have been observed in patients with many different types of cancer and limited studies have suggested that coenzyme Q10 may induce tumor regression in patients with breast cancer. This agent may have immunostimulatory effects. (NCI04) See also: ... View More ... Drug Indication The diet supplements containing ubidecarenone are indicated, as stated in the product label, to assist individuals with cardiovascular complaints including congestive heart failure and systolic hypertension. In the product, ubidecarenone is used to increase the cardiac input as well as for the prevention of several other diseases like Parkinson, fibromyalgia, migraine, periodontal disease and diabetes, based on preclinical studies. It is important to highlight that these products are not FDA approved and it is recommended to use under discretion. Mechanism of Action Ubidecarenone is an essential cofactor in the mitochondrial electron transport chain. Its functions are the acceptance of electrons from the complex I and II and this activity is vital for the production of ATP. It acts as a mobile redox agent shuttling electrons and protons in the electron transport chain. Ubidecarenone also presents antioxidant activity in mitochondria and cellular membranes, protecting against peroxidation of lipid membranes as well as inhibiting oxidation of LDL-cholesterol. Pharmacodynamics Ubidecarenon has roles in many prysiological process including sulfide oxidation, regulation of mitochondrial permeability transition pore and translocation of protons and calcium ions accross biological membranes. Studies have shown its benefitial effect in treating cancer, statin myopathy, congestive heart failure and hypertension. |
| 分子式 |
C59H90O4
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
863.36
|
| 精确质量 |
862.683
|
| CAS号 |
303-98-0
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Coenzyme Q10-d6;110971-02-3;Coenzyme Q10-d9;2687960-97-8
|
| PubChem CID |
5281915
|
| 外观&性状 |
Yellow to orange solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.0±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
869.0±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
49-51 °C
|
| 闪点 |
324.6±34.3 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±3.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.526
|
| LogP |
20.93
|
| tPSA |
52.6
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
31
|
| 重原子数目 |
63
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1840
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
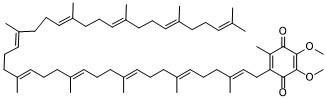
| SMILES |
CC1=C(C(=O)C(=C(C1=O)OC)OC)C/C=C(\C)/CC/C=C(\C)/CC/C=C(\C)/CC/C=C(\C)/CC/C=C(\C)/CC/C=C(\C)/CC/C=C(\C)/CC/C=C(\C)/CC/C=C(\C)/CCC=C(C)C
|
| InChi Key |
ACTIUHUUMQJHFO-UPTCCGCDSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C59H90O4/c1-44(2)24-15-25-45(3)26-16-27-46(4)28-17-29-47(5)30-18-31-48(6)32-19-33-49(7)34-20-35-50(8)36-21-37-51(9)38-22-39-52(10)40-23-41-53(11)42-43-55-54(12)56(60)58(62-13)59(63-14)57(55)61/h24,26,28,30,32,34,36,38,40,42H,15-23,25,27,29,31,33,35,37,39,41,43H2,1-14H3/b45-26+,46-28+,47-30+,48-32+,49-34+,50-36+,51-38+,52-40+,53-42+
|
| 化学名 |
2-[(2E,6E,10E,14E,18E,22E,26E,30E,34E)-3,7,11,15,19,23,27,31,35,39-decamethyltetraconta-2,6,10,14,18,22,26,30,34,38-decaenyl]-5,6-dimethoxy-3-methylcyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione
|
| 别名 |
Ubidecarenone Vitamin Q COQ10 ubiquinone coenzyme Q Coenzyme Q10
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: (1). 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮和光照。 (2). 该产品在溶液状态不稳定,请现配现用。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMF : 20 mg/mL (~23.17 mM)
Ethanol : ~2.5 mg/mL (~2.90 mM) DMSO : ~1 mg/mL (~1.16 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 3 mg/mL (3.47 mM) in 10% DMF 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浮液;超声助溶。
*20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 13.33 mg/mL (15.44 mM) in 20% HP-β-CD in Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.1583 mL | 5.7913 mL | 11.5827 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2317 mL | 1.1583 mL | 2.3165 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1158 mL | 0.5791 mL | 1.1583 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
CoQ10 and Exercise for Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Advance Kidney Disease
CTID: NCT05422534
Phase: Phase 3 Status: Recruiting
Date: 2024-10-26