| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
DNA-PK; DDR/DNA damage; DSBs (DNA double-strand breaks)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在 U251 和 NSC11 细胞中,VX-984(0-500 nM,30 分钟)抑制辐射引起的 DNA-PKcs 磷酸化 [1]。在 U251 和 NSC11 细胞中,VX-984 (0-500 nM) 以浓度依赖性方式增加 DNA-PKcs 磷酸化 [1]。 VX-984 (0-1 μM) 增强了 DSB 修复的替代机制,包括同源重组 (HR) 和放射重力 [1]。和 mNHEJ,或突变 NHEJ[2]。药物化合物含有氢、碳和其他元素的稳定重同位素。这些同位素主要用作药物开发中的定量示踪剂。由于其药代动力学特性和衍生特征而引起人们的兴趣[4]。黄昏物质可能具有以下好处:(1)延长体内半衰期。导致死亡的化合物可能能够延长化合物的体内半衰期或其药代动力学特性。这可以提高药物的便利性,同时也增强化合物的安全性、有效性和耐受性。增强肠道生物利用度 (2)。在肠壁和脐中,氘化物质会降低所需的代谢(首过代谢),从而增加到达其预期作用部位的不需要的药物的量。低剂量下更好的耐受性和活性取决于高生物利用度。 (3) 性能增强。氘化物质可提高死亡安全性并降低毒性或反应性 (4)。致死物质是无害的,并且能够减轻或消除药物化合物的负面影响。 (5) 保持其治疗特性。先前调查中预测死亡
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在原位脑肿瘤异种移植物中,VX-984(0-100 mg/kg,口服强饲,每日)抑制辐射引起的 DNA-PKcs 磷酸化 [1]。口服 VX-984(0-50 mg/kg),每日两次,持续两天,可改善脑肿瘤异种移植物的放射敏感性[1]。
将这些结果扩展到体内模型,用VX-984治疗小鼠抑制了原位脑肿瘤异种移植物中辐射诱导的DNA-PKcs磷酸化,表明该化合物在足够的浓度下穿过血脑肿瘤屏障。对于携带U251或NSC11脑肿瘤的小鼠,单独使用VX-984治疗对总体生存率没有显著影响;单靠辐射就能提高存活率。与对照组和单独辐射相比,接受联合方案的小鼠的存活率显著提高。这些结果表明,VX-984增强了脑肿瘤异种移植物的放射敏感性,并表明它可能有利于GBM的治疗管理[1]。 |
| 酶活实验 |
Neutral comet assay[1]
根据制造商的建议,使用市售试剂盒进行Neutral comet assay试验,并稍作修改。简而言之,单层被照射(10 Gy)并返回培养箱。在指定时间,产生单细胞悬浮液,用PBS洗涤,与低熔点琼脂糖(1:10)混合,并转移到提供的载玻片上。细胞在4°C下在湿冰上裂解1小时,在室温下电泳20分钟,并用70%乙醇固定。用SYBR Green对DNA进行染色,并用TriTek CometScore分析数字荧光图像。数据以剩余损伤百分比表示,其中在冰上照射并在照射后立即收集的培养物的橄榄尾力矩设置为100%损伤,照射后的剩余时间相应地归一化。通过减去假照射载体或VX-984处理样品的Olive尾矩,对VX-984或单独载体处理的所有时间点进行校正。每种条件下至少测量50个细胞。所提供的数据是3个独立实验的平均值±SEM。 |
| 细胞实验 |
蛋白质印迹分析 [1]
细胞类型: U251 和 NSC11 细胞 测试浓度: 0、100、250 和 500 nM 孵育持续时间:30 分钟 实验结果:所示浓度。当在辐射前 1 小时施用 VX-984 时,在每个神经胶质瘤系中观察到辐射诱导的 DNA-PKcs 磷酸化依赖性减少。单独使用 VX-984 治疗无效。 类别转换重组分析[2] 通过用ACK裂解缓冲液裂解红细胞,然后使用抗CD43 MACS微珠和Mini-MACS柱进行反向选择,分离出B细胞。收集的B细胞在37°C下用5μM CFSE染色10分钟,然后在含有10%FBS、1x青霉素/链霉素、1%L-谷氨酰胺、1x MEM非必需氨基酸、1%丙酮酸钠、1%HEPES和53 mM 2-巯基乙醇的RPMI-1640中培养。培养基中补充了来自大肠杆菌的25μg/ml LPS、50 U/ml白细胞介素-4和1:1000大鼠抗CD180。在37°C和5%CO2的条件下,用VX-984(0.2、0.4和0.8μM)培养细胞72小时。 用5μl抗小鼠CD16/CD32阻断B细胞。一抗生物素大鼠抗小鼠IgG1和FITC大鼠抗鼠CD45R/B220以10μl的1:100稀释液加入,然后加入10μl 1:100稀释的链霉抗生物素-A647。使用Becton Dickinson FACSCalibur测量细胞增殖和IgG+细胞,并通过FlowJo软件分析数据。 终止加入双报告子(EJ-DR)检测[2] 将U2OS EJ-DR细胞铺在含有10%炭剥离FBS和1%抗生素抗真菌剂的DMEM中的6孔板中。72小时后,洗涤细胞,用含有10%无tet FBS和1%抗生素抗真菌剂的DMEM代替培养基,并加入VX-984(0.5、0.7和1.0μM)。为了在I-Sce1位点诱导双链断裂,在药物加入后30分钟加入1μM Shield1和100nM曲安奈德。24小时后,洗涤细胞,加入新鲜的EJ-DR无Tet培养基和药物。72小时后,收集细胞,使用Becton Dickinson FACSCalibur测量HR和NHEJ水平,并通过FlowJo软件分析数据。 免疫荧光分析[2] 该测定用于观察DNA损伤后,有和没有VX-984时,H2AX病灶的存在和随后的分辨率随时间的变化。磷酸化组蛋白变体H2AX(γ-H2AX)的水平是DNA损伤水平的替代标志。双链断裂(DSB)后,γH2AX立即形成明亮的核灶,可以通过免疫荧光显微镜进行染色和可视化。γ-H2AX病灶的存在被广泛认为是细胞中DSB的标志,并已被证明对DSB具有特异性[38]。我们使用γ-H2AX抗体来观察DNA损伤的细胞。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Athymic female nude mice (6-8 weeks old, 7-8 mice/group, U251 intracerebral xenograft) [1]
Doses: 0, 50 and 100 mg/kg Route of Administration: Oral tube Feed, daily, 1 or 4 hrs (hrs (hours)) before irradiation (10 Gy) Experimental Results: DNA-PKcs phosphorylation levels diminished after irradiation. Animal/Disease Models: Athymic female nude mice (6-8 weeks old, 7/group, U251 intracerebral xenograft) [1] Doses: 0, 50 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage), twice a day, before Local tumor irradiation (3Gy) for 30 minutes, followed by 4 hrs (hrs (hours)) for 3 days (3 × 3Gy) Experimental Results: VX-984 alone in U251 tumors had no significant impact on overall survival compared with vehicle; radiation alone improved survival Rate. The combination of VX-984 and radiotherapy increased tumor radiosensitivity and Dramatically improved mouse survival compared with radiotherapy alone. Orthotopic xenografts [1] U251 (2.5 × 105) cells or CD133+ NSC11 cells (1.0 × 105) transduced to express luciferase and GFP with the lentivirus LVpFUGQ-UbC-ffLuc2-eGFP2 were intracranially implanted into the right striatum of 6- to 8-week-old athymic female nude mice (Ncr nu/nu; NCI Animal Production Program) at 1.0 mm anterior and 2.0 mm lateral to the bregma to a depth of 3.0 mm as previously described. Bioluminescent imaging (BLI) and local irradiation were all performed as described previously. VX-984 was dissolved in freshly made 5% methylcellulose and delivered by oral gavage. On day 6 (U251) or day 20 (NSC11) after implantation, consistent BLI was detected in all mice, which were then randomized according to the signal obtained from BLI into four groups: vehicle, VX-984, radiation (3 × 3 Gy), and VX-984 plus radiation (7–8 mice/group), and the treatments initiated the next day. Three Gy was delivered on 3 consecutive days with VX-984 (dissolved in 5% methylcellulose) delivered by oral gavage each day 0.5 hour before and 4 hours after irradiation. For irradiation, mice were anesthetized using a cocktail of keta-mine/xylazine/acepromazine and placed in well-ventilated Plexi glass jigs with shielding for the entire torso of the mouse along with critical normal structures of the head (ears, eyes, and neck). Radiation was delivered using an X-Rad 320 X-irradiator with a 2.0 mm aluminum filtration (300 kV peak; 10 mA) X-ray at a dose rate of 2.9 Gy/minute. All in vivo irradiation experiments were performed using the same instrument located within the animal facility; output and quality assurance are performed annually. Mice were monitored every day until the onset of neurologic symptoms (morbidity). BLI and weights were measured biweekly (U251) or weekly (NSC11) after irradiation until the first mouse of the group was lost. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
DNA-dependent Protein Kinase Inhibitor VX-984 is an ATP-competitive inhibitor of the catalytic subunit of DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK), with potential sensitizing and enhancing activities for both chemo- and radiotherapies. Upon administration, DNA-PK inhibitor VX-984 binds to and inhibits the catalytic subunit of DNA-PK, thereby interfering with the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) process and preventing repair of DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) caused by ionizing radiation or chemotherapeutic treatment. This increases chemo- and radiotherapy cytotoxicity and leads to enhanced tumor cell death. The enhanced ability of tumor cells to repair DSBs plays a major role in the resistance of tumor cells to chemo- and radiotherapy; DNA-PK plays a key role in the NHEJ pathway and DSB repair.
Radiotherapy is a primary treatment modality for glioblastomas (GBM). Because DNA-PKcs is a critical factor in the repair of radiation-induced double strand breaks (DSB), this study evaluated the potential of VX-984, a new DNA-PKcs inhibitor, to enhance the radiosensitivity of GBM cells. Treatment of the established GBM cell line U251 and the GBM stem-like cell (GSC) line NSC11 with VX-984 under in vitro conditions resulted in a concentration-dependent inhibition of radiation-induced DNA-PKcs phosphorylation. In a similar concentration-dependent manner, VX-984 treatment enhanced the radiosensitivity of each GBM cell line as defined by clonogenic analysis. As determined by γH2AX expression and neutral comet analyses, VX-984 inhibited the repair of radiation-induced DNA double-strand break in U251 and NSC11 GBM cells, suggesting that the VX-984-induced radiosensitization is mediated by an inhibition of DNA repair. [1] Purpose: DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) can be repaired by non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) or homologous recombination (HR). We demonstrate the selectivity of VX-984, a DNA-PK inhibitor, using assays not previously reported. Experimental design: The class switch recombination assay (CSR) in primary B cells was used to measure efficiency of NHEJ. A cellular reporter assay (U2OS EJ-DR) was used to assess the efficiency of HR and NHEJ in cells treated with VX-984. Immunofluorescence assays (IF) evaluated γ-H2AX foci for DSB repair kinetics in human astrocytes and T98G glioma cells. Western blotting was used to evaluate phosphorylation of DNA-PKcs substrates. Results: We found a dose-dependent reduction in CSR efficiency with VX-984, and through the EJ-DR assay, dramatic dose-dependent increases in HR and mNHEJ. Immunofluorescence assays showed an inability of malignant cells to resolve γ-H2AX foci in the presence of VX-984. Radiation-induced phosphorylation of DNA-PK substrates was further reduced by treatment with VX-984. Conclusions: VX-984 efficiently inhibits NHEJ, resulting in compensatory increases in alternative repair pathways, increases DSBs, and appears to affect transformed cells preferentially.[2] Ionizing radiation (IR), which is widely used for the treatment of cancer, causes double-strand breaks (DSBs) in DNA. If left unrepaired, these DSBs are lethal to the cell. DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) is a key enzyme in the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway that repairs DSBs caused by IR, or chemotherapeutic agents that cause DSBs such as doxorubicin. The goal of these studies was to characterize the radiation enhancing effects of VX-984, a selective and potent ATP-competitive inhibitor of the catalytic subunit of DNA-PK (DNA-PKcs), with a focus on non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells and tumor xenografts. VX-984 enhances the cytotoxicity of IR in a panel of cancer cell lines including NSCLC cell lines in vitro with dose enhancement factors (DEF) greater than 3. Notably, VX-984 combined with IR in normal human lung fibroblasts minimally enhanced the cytotoxicity compared to IR alone. Additionally, VX-984 decreased DNA-PKcs autophosphorylation on S2056 both in vitro and in vivo in NSCLC cells and attenuated the decay of the DNA damage markers γH2AX and pKAP1 in response to IR. In NSCLC PDX models VX-984, in combination with IR (2 Gy x 3), caused durable complete responses while IR alone only led to a delay in tumor growth, consistent with delayed DNA damage repair. In these models, the combination of VX-984 and IR was well tolerated. These data demonstrate that VX-984 is a potent radiation-enhancing agent and provide a strong rationale for the use of VX-984 in combination with IR for the treatment of NSCLC.[3] |
| 分子式 |
C23H23N7O
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
415.487346887589
|
| 精确质量 |
415.209
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 66.49; H, 6.06; N, 23.60; O, 3.85
|
| CAS号 |
1476074-39-1
|
| 相关CAS号 |
1476071-49-4 (normal);1562396-65-9 (demethyl);1476074-39-1 (deuterium);
|
| PubChem CID |
72188357
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| LogP |
2.7
|
| tPSA |
106
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
31
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
582
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
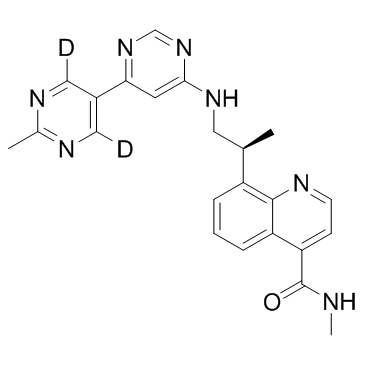
O=C(C1C=CN=C2C=1C=CC=C2[C@H](C)CNC1C=C(C2=C([2H])N=C(C)N=C2[2H])N=CN=1)NC
|
| InChi Key |
PEACIOGDEQRHFA-KIYKJNLWSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C23H23N7O/c1-14(17-5-4-6-18-19(23(31)24-3)7-8-25-22(17)18)10-28-21-9-20(29-13-30-21)16-11-26-15(2)27-12-16/h4-9,11-14H,10H2,1-3H3,(H,24,31)(H,28,29,30)/t14-/m1/s1/i11D,12D
|
| 化学名 |
(S)-N-methyl-8-(1-((2'-methyl-[4,5'-bipyrimidin]-6-yl-4',6'-d2)amino)propan-2-yl)quinoline-4-carboxamide
|
| 别名 |
VX-984; VX 984; 1476074-39-1; UNII-0C33IBK195; 0C33IBK195; VX984; 8-[(2S)-1-[[6-(4,6-dideuterio-2-methylpyrimidin-5-yl)pyrimidin-4-yl]amino]propan-2-yl]-N-methylquinoline-4-carboxamide; VX984; M9831; M-9831; M 9831
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~10 mg/mL (~24.07 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 1 mg/mL (2.41 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 10.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 1 mg/mL (2.41 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 10.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4068 mL | 12.0340 mL | 24.0680 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4814 mL | 2.4068 mL | 4.8136 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2407 mL | 1.2034 mL | 2.4068 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。