| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Fluorescent Dye
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
1. 储备液配制
称取 1 mg 5(6)-CFDA,溶于 0.21 mL DMSO 中,配制成 10 mM 的储备液。 注意:储备液需避光保存于 -20℃ 或 -80℃,并尽量减少冻融次数。 2. 工作液配制 使用无血清细胞培养基或 PBS 稀释储备液,配制成 1-10 μM 的 5(6)-CFDA 工作液。 注意:具体工作液浓度需根据实验需求调整。 ________________________________________ 细胞染色步骤 1. 细胞准备 • 悬浮细胞:4℃、1000 g 离心 3-5 分钟,弃上清,PBS 洗涤 2 次(每次 5 分钟)。 • 贴壁细胞:去除培养基,胰酶消化后收集细胞悬液,4℃、1000 g 离心 3-5 分钟,弃上清,PBS 洗涤 2 次(每次 5 分钟)。 2. 染色 • 加入 1 mL 5(6)-CFDA 工作液,室温避光孵育 30 分钟。 3. 洗涤与收集 • 4℃、400 g 离心 3-4 分钟,弃上清。 • PBS 洗涤 2 次(每次 5 分钟)。 • 用无血清培养基或 PBS 重悬细胞,进行荧光显微镜或流式细胞仪检测。 ________________________________________ 注意事项 1. 储备液需避光保存于 -20℃ 或 -80℃,避免反复冻融。 2. 工作液浓度可根据实验体系优化调整。 3. 本产品仅限科研使用,不可用于医药、家用或其他用途。 4. 操作时请穿戴实验服及一次性手套,确保安全。 |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Endothelial progenitor cells (EPC) are believed to be involved in aneurysmal repair and remodeling. The aim of this study was to test this hypothesis and, if true, explore how EPC contribute to aneurysm repair in a rabbit model of elastase-induced carotid aneurysm. Rabbits were divided randomly into an in situ carotid EPC transfusion group (ISCT group, n=5), and an intravenous EPC transfusion group (IVT group, n=5). Autologous EPC were double-labeled with Hoechst 33342 and 5,6-carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester before injection into the animals in either the carotid artery (ISCT group) or marginal ear veins (IVT group). Three weeks later, labeled cells in the aneurysms were observed with respect to location, adhesion, and growth to detect signs of aneurysm repair. Labeled EPC were detected within the neointima in all five aneurysms in the ISCT group and in three of the five aneurysms in the IVT group, but there was no endothelial growth in the aneurysmal neointima in either group. These results show that bone marrow-derived EPC are involved in the process of aneurysm repair in this rabbit model. [1]
Fluorescent dyes were assessed for their ability to stain viable hyphae of the fungi Neotyphodium lolii and N. coenophialum, symbiotic endophytes of the Pooideae grasses Lolium perenne and Festuca arundinacea, respectively. The fluorescein-based fluorophores; fluorescein diacetate (FDA), 5(6)-carboxy-fluorescein diacetate (CFDA), 5-chloromethylfluorescein diacetate (CMFDA) and the chitin-binding stain, Calcofluor while M2R, were assessed for staining of endophyte hyphae in vitro from axenic fungal cultures and in planta, including epidermal leaf sheath peels, nodes, ovaries, embryos and meristems. CMFDA produced the greatest intensity of staining of fungal hyphae and gave excellent contrast in planta compared to the plant cells. Compared to the other dyes, CMFDA was also the least affected by photo bleaching and continued to fluoresce up to 2 h after initial excitation. None of the fluorescent dyes stained fungal hyphae in seed. [2] Endothelial progenitor cells (EPC) are believed to be involved in aneurysmal repair and remodeling. The aim of this study was to test this hypothesis and, if true, explore how EPC contribute to aneurysm repair in a rabbit model of elastase-induced carotid aneurysm. Rabbits were divided randomly into an in situ carotid EPC transfusion group (ISCT group, n=5), and an intravenous EPC transfusion group (IVT group, n=5). Autologous EPC were double-labeled with Hoechst 33342 and 5,6-carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester before injection into the animals in either the carotid artery (ISCT group) or marginal ear veins (IVT group). Three weeks later, labeled cells in the aneurysms were observed with respect to location, adhesion, and growth to detect signs of aneurysm repair. Labeled EPC were detected within the neointima in all five aneurysms in the ISCT group and in three of the five aneurysms in the IVT group, but there was no endothelial growth in the aneurysmal neointima in either group. These results show that bone marrow-derived EPC are involved in the process of aneurysm repair in this rabbit model. [3] |
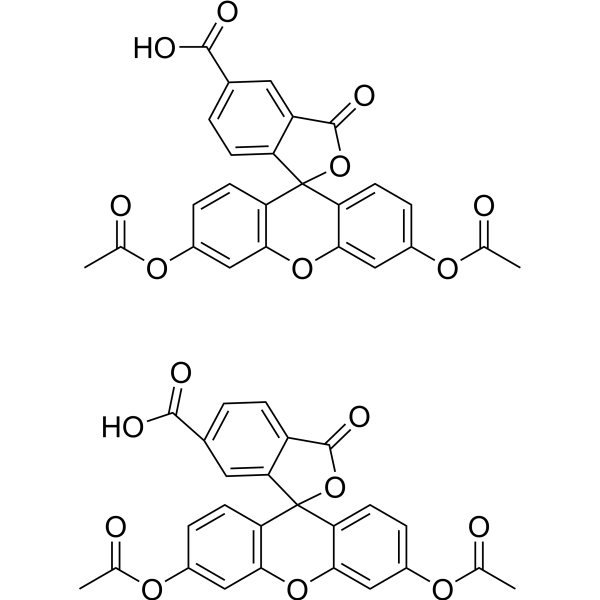
| 分子式 |
2[C25H16O9]
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
920.778280000001
|
| 精确质量 |
920.158
|
| CAS号 |
124387-19-5
|
| 相关CAS号 |
5-CFDA;79955-27-4;6-CFDA;3348-03-6
|
| PubChem CID |
44119974
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to yellow solid powder
|
| LogP |
7.606
|
| tPSA |
250.86
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
18
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
10
|
| 重原子数目 |
68
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1660
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
CC(OC1=CC=C2C(OC3=C(C=CC(OC(C)=O)=C3)C24C5=CC(C(O)=O)=CC=C5C(O4)=O)=C1)=O.CC(OC6=CC=C7C(OC8=C(C=CC(OC(C)=O)=C8)C79C%10=CC=C(C(O)=O)C=C%10C(O9)=O)=C6)=O
|
| InChi Key |
SWRGCNMDGRMQGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/2C25H16O9/c1-12(26)31-15-4-7-18-21(10-15)33-22-11-16(32-13(2)27)5-8-19(22)25(18)20-9-14(23(28)29)3-6-17(20)24(30)34-25;1-12(26)31-14-6-8-18-20(10-14)33-21-11-15(32-13(2)27)7-9-19(21)25(18)22-16(23(28)29)4-3-5-17(22)24(30)34-25/h2*3-11H,1-2H3,(H,28,29)
|
| 化学名 |
3',6'-diacetyloxy-1-oxospiro[2-benzofuran-3,9'-xanthene]-4-carboxylic acid;3',6'-diacetyloxy-1-oxospiro[2-benzofuran-3,9'-xanthene]-5-carboxylic acid
|
| 别名 |
5(6)-Carboxyfluorescein diacetate; 124387-19-5; CFDA; 5-(6)-Carboxyfluorescein diacetate;CFDA; Spiro[isobenzofuran-1(3H),9'-[9H]xanthene]-ar-carboxylic acid, 3',6'-bis(acetyloxy)-3-oxo-; 3',6'-diacetyloxy-1-oxospiro[2-benzofuran-3,9'-xanthene]-4-carboxylic acid;3',6'-diacetyloxy-1-oxospiro[2-benzofuran-3,9'-xanthene]-5-carboxylic acid; 5-6-CFDA; DTXSID70657464;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~125 mg/mL (~271.51 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.52 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.52 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.0860 mL | 5.4302 mL | 10.8604 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2172 mL | 1.0860 mL | 2.1721 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1086 mL | 0.5430 mL | 1.0860 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。