| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
β-lactam
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在脂多糖刺激的 C8-B4 细胞上,头孢唑啉(0-300 μg/mL;6 或 24 小时)表现出直接的抗炎作用 [2]。用头孢唑林(0-400 μM;72 小时)处理可减少 IL-2、IL-4 和 IL-15 刺激的细胞生长 [3]。使用头孢唑林(100–400 μM;30 分钟)治疗可防止 JAK3 因 IL-2、IL-4、IL-15 和 IL-21 刺激而磷酸化 [3]。头孢唑啉
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
手术后,用五水头孢唑啉钠(皮下注射;300-500 mg/kg;每天一次;5 d)治疗的小鼠学习和记忆能力得到改善[2]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定[2]
细胞类型: C8-B4 细胞 测试浓度: 0、50、100、150、200、250 或 300 µg/ml 孵育时间:6 或 24 小时 实验结果:在所有剂量下均抑制 IL-1β 的增加,但抑制IL-6 仅在 200 μg/ml 时增加。细胞增殖测定[3] 细胞类型: PBMC 和 TF-1 细胞 测试浓度: 0、100、200 和 400 μM 孵育持续时间:72 小时 实验结果:减少 IL-2、IL-4 和 IL-15 诱导的细胞增殖,表明头孢唑啉会干扰不仅与IL-15Rα有关,而且与IL-2/IL-15Rβ和/或γc有关。细胞增殖测定[3] 细胞类型: PBMC、NK-92 和 TF-1 细胞 测试浓度:0、100、200 和400 μM 孵育时间: 30 分钟 实验结果:减少了细胞因子处理后 JAK3 的磷酸化,得出抑制 γc 受体信号转导的结论。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: 6- to 8weeks old male CD-1 mice underwent clinical exploratory laparotomy[2]
Doses: 300-500 mg/kg Route of Administration: subcutaneous (sc)injection; 300-500 mg/kg; one time/day; 5 days Experimental Results: Attenuated learning and memory dysfunction induced by the surgery. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Not absorbed from GI tract. Must be administered parenterally. Peak serum concentrations attained 1-2 hours post intramuscular injection. Cefazolin is present in very low concentrations in the milk of nursing mothers. Cefazolin is excreted unchanged in the urine. In the first six hours approximately 60% of the drug is excreted in the urine and this increases to 70%-80% within 24 hours. CEFAZOLIN CROSSES INFLAMED SYNOVIAL MEMBRANES, YIELDING SYNOVIAL FLUID ANTIBIOTIC CONCN GREATER THAN THOSE IN SERUM WITHIN 2 HR OF IM DOSE... CLEARANCE OF CEFAZOLIN BY KIDNEY IS PREDOMINANTLY BY GLOMERULAR FILTRATION, & CLEARANCE RATES ARE LINEARLY RELATED TO CREATININE CLEARANCE... CEFAZOLIN RAPIDLY PENETRATES BODY TISSUES IN RATS, & DECLINE OF TISSUE ANTIBIOTIC LEVELS AFTER DOSING IS FIRST-ORDER. VERY SMALL AMT OF DRUG CROSS BLOOD-BRAIN BARRIER & PLACENTAL TRANSFER APPEARS NEGLIGIBLE... ...DURING STUDIES OF CEFAZOLIN TRANSFERENCE IN MAN, 92-100% OF ADMIN DOSE WAS ACCOUNTED FOR BY URINARY EXCRETION... ... About 80% of cefazolin is reversibly bound to plasma protein ... is excreted in bile even when there is gallbladder disease ... concn may normally exceed that in plasma by 3 times. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for CEFAZOLIN (13 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Not metabolized. Metabolism of cefazolin is very limited in most of the animal species tested and in /humans/. After parenteral administration of cefazolin nearly 100% is excreted unchanged in urine with 24 hours in /humans/, dog and horse. No major metabolites seem to occur. Biological Half-Life The serum half-life is approximately 1.8 hours following IV administration and approximately 2.0 hours following IM administration. The serum half-life of cefazolin is 1.2-2.2 hr in adults with normal renal function. In one study, half-life was 6.8 hr in 1 adult with a creatinine clearance of 26 ml/min, 12 hr in 3 adults with creatinine clearances of 12-17 ml/min, and 57 hr in 3 adults with creatinine clearances less than 5 ml/min. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Limited information indicates cefazolin produces low levels in milk that are not expected to cause adverse effects in breastfed infants. Occasionally disruption of the infant's gastrointestinal flora, resulting in diarrhea or thrush have been reported with cephalosporins, but these effects have not been adequately evaluated. Cefazolin is acceptable in nursing mothers. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding 74-86% Interactions Hypoprothrombinemia induced by large doses of salicylates and/or cephalosporins, and the gastrointestinal ulcerative or hemorrhagic potential of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), salicylates, or sulfinpyrazone may increase the risk of hemorrhage. /Cephalosporins/ Probenecid decreases renal tubular secretion of those cephalosporins excreted by this mechanism, resulting in increased and prolonged cephalosporin serum concentrations, prolonged elimination half-life, and increased risk of toxicity; probenecid has no effect on the excretion of cefoperazone, ceftazidime, or ceftriaxone; however, other cephalosporins and probenecid might be used concurrently in the treatment of infections, such as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) or other infections, in which high and/or prolonged antibiotic serum and tissue concentrations are required. /Cephalosporins/ Concomitant admin of oral probenecid competitively inhibits tubular secretion resulting in higher and more prolonged serum concn of most cephalosporins. /Cephalosporins/ Concurrent use of nephrotoxic agents such as aminoglycosides, colistin, polymyxin B, or vancomycin may increase the risk of nephrotoxicity with some cephalosporins ... . /Cephalosporins/ For more Interactions (Complete) data for CEFAZOLIN (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Mouse oral (acute) >11000 mg/kg bw LD50 Mouse intravenous >2000 mg/kg bw LD50 Rat intravenous >2000 mg/kg bw LD50 Rat oral (acute) >11000 mg/kg bw |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. R Quintiliani, et al. Cefazolin. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Nov;89(5 Pt 1):650-6.
[2]. Peng Liang, et al. Perioperative use of cefazolin ameliorates postoperative cognitive dysfunction but induces gut inflammation in mice. J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Aug 22;15(1):235. [3]. Barbara Żyżyńska-Granica, et al. The anti-inflammatory potential of cefazolin as common gamma chain cytokine inhibitor. Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 19;10(1):2886. |
| 其他信息 |
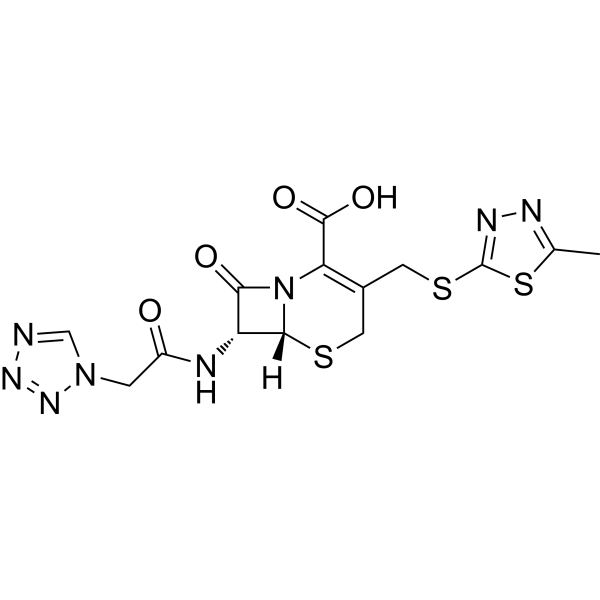
Cefazolin is a first-generation cephalosporin compound having [(5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)sulfanyl]methyl and (1H-tetrazol-1-ylacetyl)amino side-groups at positions 3 and 7 respectively. It has a role as an antibacterial drug. It is a cephalosporin, a member of thiadiazoles, a member of tetrazoles and a beta-lactam antibiotic allergen. It is a conjugate acid of a cefazolin(1-).
A semisynthetic cephalosporin analog with broad-spectrum antibiotic action due to inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis. It attains high serum levels and is excreted quickly via the urine. Cefazolin is a Cephalosporin Antibacterial. Cefazolin has been reported in Apis cerana with data available. Cefazolin is a beta-lactam antibiotic and first-generation cephalosporin with bactericidal activity. Cefazolin binds to and inactivates penicillin-binding proteins (PBP) located on the inner membrane of the bacterial cell wall. Inactivation of PBPs interferes with the cross-linkage of peptidoglycan chains necessary for bacterial cell wall strength and rigidity. This results in the weakening of the bacterial cell wall and causes cell lysis. A semisynthetic cephalosporin analog with broad-spectrum antibiotic action due to inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis. It attains high serum levels and is excreted quickly via the urine. See also: Cefazolin Sodium (has salt form); Cefazolin benzathine (is active moiety of). Drug Indication Mainly used to treat bacterial infections of the skin. It can also be used to treat moderately severe bacterial infections involving the lung, bone, joint, stomach, blood, heart valve, and urinary tract. It is clinically effective against infections caused by staphylococci and streptococci species of Gram positive bacteria. May be used for surgical prophylaxis; if required metronidazole may be added to cover B. fragilis. FDA Label Mechanism of Action In vitro tests demonstrate that the bactericidal action of cephalosporins results from inhibition of cell wall synthesis. By binding to specific penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located inside the bacterial cell wall, it inhibits the third and last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Cell lysis is then mediated by bacterial cell wall autolytic enzymes such as autolysins. Bactericidal; action depends on ability to reach and bind penicillin-binding proteins located in bacterial cytoplasmic membranes; cephalosporins inhibit bacterial septum and cell wall synthesis, probably by acylation of membrane-bound transpeptidase enzymes. This prevents cross-linkage of peptidoglycan chains, which is necessary for bacterial cell wall strength and rigidity. Also, cell division and growth are inhibited, and lysis and elongation of susceptible bacteria frequently occur. Rapidly dividing bacteria are those most susceptible to the action of cephalosporins. /Cephalosporins/ Therapeutic Uses Mesh Heading: anti-bacterial agents Cephalosporins Cefazolin is indicated in the treatment of biliary tract infections caused by susceptible organisms. /Included in US product labeling/ THERAP CAT: Antibacterial. For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for CEFAZOLIN (17 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings Hypersensitivity reactions to cephalosporins are the most common side effects ... /and/ appear to be identical to those caused by the penicillins ... Patients who are allergic to one class of agents may manifest cross-reactivity when a member of the other class is admin. Immunological studies have demonstrated cross-reactivity in as many as 20% of patients who are allergic to penicillin, but clinical studies indicate a much lower frequency (about 1%) ... There are no skin tests that can reliably predict whether a patient will manifest an allergic reaction to the cephalosporins. /Cephalosporins/ Maternal Medication usually Compatible with Breast-Feeding: Cefazolin: Reported Sign or Symptom in Infant or Effect on Lactation: None. /From table 6/ Positive direct and indirect antiglobulin (Coombs') test results have been reported in 3% or more of patients receiving a cephalosporin. The mechanism of this reaction is usually nonimmunologic in nature; a cephalosporin-globulin complex coats the erythrocytes and reacts nonspecifically with Coombs' serum. Nonimmunologic positive Coombs' test results are most likely to occur in patients who have received large doses of a cephalosporin or who have impaired renal function or hypoalbuminemia. /Cephalosporins/ A positive Coombs reaction appears frequently in patients who receive large doses of a cephalosporin. Hemolysis is not usually associated with this phenomenon, although it has been reported. Cephalosporins have produced rare instances of bone-marrow depression, characterized by granulocytopenia ... Serious bleeding related either to ... thrombocytopenia, and/or platelet dysfunction has been reported with several beta-lactam antibiotics. This appears to be a particular problem with certain patients (elderly, poorly nourished, or those with renal insufficiency) who are receiving moxalactam. /Cephalosporins/ For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for CEFAZOLIN (38 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Cefazolin (also known as cefazoline or cephazolin) is a semi-synthetic first generation cephalosporin for parenteral administration. Cefazolin has broad-spectrum antibiotic action due to inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis. It attains high serum levels and is excreted quickly via the urine. |
| 分子式 |
C14H14N8O4S3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
454.51
|
| 精确质量 |
454.029
|
| CAS号 |
25953-19-9
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Cefazolin sodium;27164-46-1;Cefazolin sodium pentahydrate;115850-11-8
|
| PubChem CID |
33255
|
| 外观&性状 |
Needles from aqueous acetone
|
| 密度 |
2.0±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 熔点 |
198-200ºC
|
| 折射率 |
1.961
|
| LogP |
1.13
|
| tPSA |
234.93
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
12
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
29
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
740
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
| SMILES |
O=C(C(N12)=C(CSC3=NN=C(C)S3)CS[C@]2([H])[C@H](NC(CN4N=NN=C4)=O)C1=O)O
|
| InChi Key |
MLYYVTUWGNIJIB-BXKDBHETSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C14H14N8O4S3/c1-6-17-18-14(29-6)28-4-7-3-27-12-9(11(24)22(12)10(7)13(25)26)16-8(23)2-21-5-15-19-20-21/h5,9,12H,2-4H2,1H3,(H,16,23)(H,25,26)/t9-,12-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(6R,7R)-3-[(5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)sulfanylmethyl]-8-oxo-7-[[2-(tetrazol-1-yl)acetyl]amino]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : 250 mg/mL (550.04 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.58 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.58 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.58 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2002 mL | 11.0009 mL | 22.0017 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4400 mL | 2.2002 mL | 4.4003 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2200 mL | 1.1001 mL | 2.2002 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Pediatric Open Fractures
CTID: NCT06055712
Phase: Phase 4 Status: Enrolling by invitation
Date: 2024-10-08