| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Gwt1 enzyme
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Fosmanogepix (APX001) 的最低有效剂量为 0.008-0.25 μg/ml,可在 40-72 小时内抑制烟曲霉、白色念珠菌、新型梭菌和格特梭菌的生长[1]。
隐球菌性脑膜炎(CM),主要由隐球菌引起的新生,是一致致命的,如果不治疗。治疗选择有限,特别是在资源贫乏的地理区域,尽管有目前的治疗方法,死亡率仍然很高。在这里,我们评估了几种化合物的体外和体内活性,包括APX001A及其前药APX001,目前正在临床开发用于治疗侵袭性真菌感染。这些化合物靶向真菌中糖基磷脂酰肌醇(GPI)锚定细胞壁甘露蛋白定位所需的保守Gwt1酶。Gwt1抑制剂对新生C.和C. gatii的MIC值较低,在0.004 ~ 0.5 μg/ml之间。APX001A和APX2020与氟康唑表现出体外协同作用(分数抑制浓度指数,两者均为0.37)。[1] APX001A抑制烟曲霉生长,最低有效浓度为0.03 μg/ml。[2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Fosmanogepix (APX001)(390 mg/kg,口服,每日 3 次)可降低瑞典隐球菌脑膜炎 (CM) 模型的负担 [1]。 Fosmanogepix (APX001)(100 毫克/公斤)
在CM模型中,APX001和氟康唑单独降低脑组织真菌负荷(分别为0.78和1.04 log10 CFU/g),而联合使用可减少3.52 log10 CFU/g脑组织。另一种Gwt1抑制剂前药APX2096也观察到通过减少脑和肺组织真菌负荷来衡量的疗效,其中真菌负荷的剂量依赖性减少范围为5.91至1.79 log10 CFU/g肺组织和7.00至0.92 log10 CFU/g脑组织,这表明在较高剂量下肺和脑组织几乎完全或完全消毒。这些数据支持这类新型抗真菌药物治疗CM的进一步临床评价。[1] 使用50 mg/kg的1-氨基苯并三唑(ABT),一种细胞色素P450酶的自杀抑制剂,使APX001A暴露(时间-浓度曲线下面积[AUC])增加16至18倍,并将血清半衰期从1至9小时延长,更接近于模拟人类药代动力学。我们比较了APX001(联合ABT)与泊沙康唑治疗小鼠IPA的疗效。与安慰剂相比,每天一次78 mg/kg、每天两次78 mg/kg或104 mg/kg QD的APX001治疗小鼠显著提高了中位生存时间,延长了感染后第21天的总生存期。此外,通过组织病理学检查,与未治疗的对照组相比,施用APX001导致肺部真菌负荷显著降低(4.2至7.6 log10分生孢子当量/g组织),并解决了感染。观察到的生存和组织清除率与临床相关泊沙康唑剂量相当。这些结果保证了APX001作为一种广谱、一流的侵袭性真菌感染治疗药物的继续发展。[2] |
| 酶活实验 |
抗真菌药敏试验。[1]
为了确定APX001A类似物的抑菌活性,根据临床与实验室标准协会(CLSI)指南M27-A3酵母和M38-A2霉菌进行肉汤微稀释药敏试验。APX001A和类似物首先在DMSO中稀释,得到中间稀释度。在微滴板中进一步稀释,最终浓度为2至0.002 μg/ml。在无药对照孔中加入DMSO 1微升。在摇板机上搅拌10 min, 35℃孵育40 ~ 48 h(白色念珠菌、烟曲霉),72 h(新生念珠菌)。与对照组相比,导致真菌生长减少50%的最小浓度(借助阅读镜确定)被确定为白色念珠菌和新生念珠菌的MIC。与DMSO对照孔中菌丝生长相比,导致菌丝缩短的最小浓度被确定为烟曲霉的最小有效浓度(MEC)(与棘白菌素相同)。APX001A(以前的E1210)的MIC和MEC端点分别用于酵母和霉菌,前面已经描述过。对于隐球菌的协同作用研究,APX001A和APX2020的MIC值在50%的抑制下读取。 |
| 细胞实验 |
为了确定APX001A类似物的抑菌活性,按照CLSI指南M38-A2对霉菌进行肉汤微稀释药敏试验。APX001A首先用二甲亚砜(DMSO)稀释,得到中间稀释度。在微滴板中进一步稀释,最终浓度为0.002至2 μg/ml。在“无药”对照孔中加入1 μl DMSO。在平板振动筛上混合10 min,平板在35℃下孵育40 ~ 48 h。与DMSO对照孔中菌丝生长相比,导致菌丝缩短的最小浓度被确定为烟曲霉的MEC(与棘白菌素相同)。类似的方法被用来确定ABT对烟曲霉生长的影响,但由于ABT是一种水溶性分子,所以没有使用DMSO。在一项研究中,ABT浓度范围为0.016 ~ 16 μg/ml,在后续研究中,ABT浓度范围为0.25 ~ 250 μg/ml。APX001A(以前的E1210)的MIC和MEC端点分别用于酵母和霉菌,前面已经描述过。采用标准棋盘法评价ABT与APX001A对烟曲霉MYA3626的协同作用(APX001A浓度范围为0.0005 ~ 0.125 μg/ml;ABT浓度范围为0.016 ~ 16 μg/ml)。使用MEC值读取协同试验的抑制终点,作为评估APX001A抗霉菌活性的读数。[2]
|
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: CD-1 mice [1]
Doses: 100 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip) injection Experimental Results: The half-life of the active part APX001A was extended from 1.3 hrs (hrs (hours)) to 8.8 hrs (hrs (hours)), increasing the area under the curve (AUC) 9 times. Pharmacokinetic analysis. [1] Single-dose PK experiments were performed in healthy male CD-1 mice following i.p. or oral dosing of 26 mg/kg of the prodrugs APX001, APX2096, APX2097, and APX2104. In half of the cohorts, mice received a single oral dose of 100-mg/kg ABT at 2 h prior to prodrug dosing. Plasma was collected at 0.083, 0.5, 2, 4, 8, and 24 h postdose (n = 3 per time point). The area under the curve (AUC) was calculated from time zero to the time of the last measurable concentration. The active metabolite concentrations in plasma (APX001A, APX2039, APX2020, and APX2041) were determined by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. PK parameters were determined using Phoenix WinNonlin (v7.0) software and a noncompartmental model. Samples with concentrations that were below the limit of quantification (0.5 or 1 ng/ml) were not used in the calculation of averages. IPA model. [2] The IPA model was performed as previously described. Briefly, immunosuppressed mice were challenged with A. fumigatus in an inhalation chamber by aerosolizing 12 ml of a 1 × 109 ml suspension of conidia with a small particle nebulizer driven by compressed air. A standard exposure time of 1 h was used for all experiments. Immediately after infection, a subset of the mice was sacrificed, and the lungs were removed for quantitative culture. Mice were rendered neutropenic using a regimen of 200 mg/kg cyclophosphamide and 500 mg/kg cortisone acetate 2 days before and on day 3 relative to infection. To prevent bacterial infection, mice were given Baytril (50 μg/ml of enrofloxacin; Bayer) added to the drinking water from day –3 to day 0. Ceftazidime (5 μg/dose/0.2 ml) replaced Baytril treatment on day 0 and was administered daily by subcutaneous injection from day 0 until day 8. We administered 50 mg/kg ABT orally 2 h before the administration of APX001 for 7 days. Posaconazole (20 mg/kg QD or 30 mg/kg BID) was administered orally for 7 days. Survival was monitored through day 21. Mice were given free access to water and standard laboratory diet. All drug treatments were initiated 16 h postinfection and continued for 8 consecutive days given by oral gavage. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Analysis of AUC values versus the change in the number of log10 CFU per gram of tissue. The three compounds evaluated in the efficacy model had MIC values for the infecting strain (C. neoformans H99) that differed by 8- to 32-fold: for APX001A, 0.25 μg/ml; for APX2020, 0.031 μg/ml; and for APX2039, 0.008 μg/ml (Table 1). The data in Table 3 show that AUC values after i.p. dosing (plus ABT) ranged from 24.3 to 97.3 μg · h/ml, representing a 4-fold difference. To understand the influence of AUC-versus-MIC differences, we assessed the magnitude of changes in the number of log10 CFU/g of tissue across the three experiments.[1]
AUC values across the three experiments for APX001 (with or without ABT) ranged from 7.0 μg · h/ml (7.5-mg/kg APX001 QD plus ABT) to 196.3 μg · h/ml (390 mg/kg TID). At an AUC of 196.3 μg · h/ml, a modest but significant reduction in the lung burden was observed (1.5 log10 CFU/g). Lower AUC values were not efficacious. AUC values ranged from 10.0 to 116.4 μg · h/ml for APX2097 and from 27 to 224.3 μg · h/ml for APX2096. We compared the efficacy of the three compounds at a dose that gave rise to AUC values of approximately 80 µg · h/ml. In the presence of ABT, doses of 20-mg/kg APX2096, 60-mg/kg APX2097, and 80-mg/kg APX001 resulted in very similar AUC values of 74.8, 82.1, and 79.4 μg · h/ml, respectively. However, the reductions were 2.95, 1.45, and 0.85 log10 CFU/g, respectively, in brain and 3.69, 1.55, and 0.9 log10 CFU/g, respectively, in lung. Thus, despite the same AUC values for the 3 compounds, better efficacy was associated with lower MIC values (0.008 μg/ml, 0.031 μg/ml, and 0.25 μg/ml, respectively), suggesting that improved microbiological activity largely accounts for improved efficacy.[1] The PK of APX001A after oral administration of 26 mg/kg of the prodrug APX001 (equivalent to 20 mg/kg of the active moiety APX001A using a conversion factor of 1.3 to account for the methyl phosphate group) were compared with and without the administration of ABT given 2 h prior to APX001 dosing. ABT doses were tested at 25, 50, and 100 mg/kg once daily (QD) and at 50 mg/kg twice daily (BID). Consistent with our previous findings (17), administration of ABT at 100 mg/kg QD resulted in a 15-fold increase in the average APX001A AUClast (area under the plasma concentration-time curve from time zero to time of last measurable concentration) in male CD-1 mice when the prodrug APX001 was dosed at 26 mg/kg (Table 1). Interestingly, this increase in AUClast was maintained when ABT was dosed at 50 mg/kg QD or BID (16.3- or 15-fold versus the no-ABT control, P > 0.62 for all ABT comparison regimens) (Table 1), suggesting that this lower dose of ABT is as efficient as the 100-mg/kg ABT dose in enhancing APX001A AUClast. In contrast, the 25-mg/kg QD dose of ABT resulted in a lower APX001A AUC value that was statistically significant from the 50-mg/kg QD dose (P = 0.02), although a 12.8-fold increase in the AUC value versus the no-ABT control was observed (P = 0.0002) (Table 1).[2] Since higher APX001 doses could potentially be utilized in efficacy models, it was important to understand the linearity of AUC values while utilizing ABT. Thus, the PK of APX001A after the administration of 52 mg/kg APX001 prodrug (equivalent to 40 mg/kg of the active moiety APX001A) was evaluated in the presence of different doses of ABT. The data in Table 1 show that the administration of ABT at 50 mg/kg BID and 50 mg/kg QD resulted in similar APX001A AUC values (92.41 ± 7.70 and 94.29 ± 12.43, respectively), which translated into a 17.4- to 17.8-fold increase in AUC versus the no-ABT control (5.30 ± 0.98) (P < 0.0003). In contrast, the 25-mg/kg QD ABT dose resulted in a lower APX001A AUC value (52.00 ± 35.46), representing a 9.8-fold increase versus the no-ABT control (Table 1).[1] The AUC values obtained after dosing 52 mg/kg APX001 plus 50 mg/kg ABT (QD or BID) were ∼2-fold higher than the parallel values obtained when 26 mg/kg APX001 was dosed (P > 0.14), consistent with dose linearity, at least within that dosing range. We chose to use the lowest, optimal dose of ABT at a 50-mg/kg QD dose in conjunction with the oral administration of APX001 in the subsequent A. fumigatus mouse model experiments.[2] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Fosmanogepix is under investigation in clinical trial NCT03604705 (An Efficacy and Safety Study of APX001 in Non-Neutropenic Patients With Candidemia).
Fosmanogepix is an orally available small molecule inhibitor of the Gwt1 fungal enzyme with potential antifungal activity. Upon administration, fosmanogepix, a N-phosphonooxymethyl prodrug, is rapidly and completely metabolized by systemic alkaline phosphatases to its active moiety, APX001A (E1210). The active prodrug targets Gwt1, a highly conserved inositol acylase which catalyzes an essential step in the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchor biosynthesis pathway. Inhibition of Gwt1 prevents localization of cell wall mannoproteins, which compromises cell wall integrity, biofilm formation, germ tube formation, and fungal growth. |
| 分子式 |
C22H21N4O6P
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
468.3991
|
| 精确质量 |
468.119
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 56.41; H, 4.52; N, 11.96; O, 20.49; P, 6.61
|
| CAS号 |
2091769-17-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Manogepix;936339-60-5
|
| PubChem CID |
44123754
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to yellow solid powder
|
| LogP |
1.6
|
| tPSA |
148
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
9
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
9
|
| 重原子数目 |
33
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
644
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
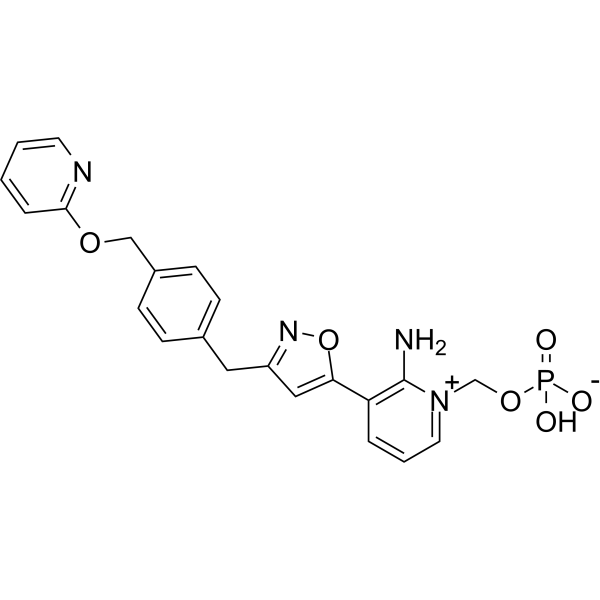
P(=O)([O-])(O[H])OC([H])([H])[N+]1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C(=C1N([H])[H])C1=C([H])C(C([H])([H])C2C([H])=C([H])C(C([H])([H])OC3=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])=N3)=C([H])C=2[H])=NO1
|
| InChi Key |
JQONJQKKVAHONF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H21N4O6P/c23-22-19(4-3-11-26(22)15-31-33(27,28)29)20-13-18(25-32-20)12-16-6-8-17(9-7-16)14-30-21-5-1-2-10-24-21/h1-11,13,23H,12,14-15H2,(H2,27,28,29)
|
| 化学名 |
[2-amino-3-[3-[[4-(pyridin-2-yloxymethyl)phenyl]methyl]-1,2-oxazol-5-yl]pyridin-1-ium-1-yl]methyl hydrogen phosphate
|
| 别名 |
Fosmanogepix; 2091769-17-2; APX001; Fosmanogepix [INN]; Fosmanogepix [USAN]; APX-001; 1XQ871489P; E1211;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~5 mg/mL (~10.67 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.34 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.34 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1349 mL | 10.6746 mL | 21.3493 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4270 mL | 2.1349 mL | 4.2699 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2135 mL | 1.0675 mL | 2.1349 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。