| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Cysteine protease
Cysteine proteases: - Cathepsin B (human recombinant): Ki ≈ 0.04 μM (fluorogenic substrate assay) [1] - Cathepsin L (rat liver purified): IC₅₀ ≈ 0.08 μM (azocasein hydrolysis assay) [2] - Cathepsin C (bovine spleen purified): IC₅₀ ≈ 0.2 μM (glycyl-phenylalanyl-4-methoxy-β-naphthylamide cleavage assay) [1] - Selectivity over serine proteases: No inhibition of trypsin or chymotrypsin (10 μM Aloxistatin, casein hydrolysis assay) [1] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Aloxistatin(也称为 E-64d、E-64c 乙酯;Loxistatin;NSC 694281)是一种有效的、选择性的、不可逆的、广谱的、细胞膜可渗透的半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂。 Aloxistatin 可防止体外雨蛙蛋白诱导的胰蛋白酶原激活。阿洛司他汀可以进入完整细胞并抑制钙蛋白酶。 E-64d 已被证明对于治疗人类阿尔茨海默病是安全的。 Aloxistatin 通过调节异常的锌信号转导以及通过海马中的 ApoE/clusterin 途径调节脂质代谢改变,可潜在用于治疗发育性癫痫诱发的脑损伤。阿洛司他汀可以进入完整的血小板,通过抑制钙蛋白酶来抑制蛋白水解。 Aloxistatin 在体外可抑制甲状旁腺激素 (PTH) 诱导的细胞增殖并抑制成骨细胞的分化。激酶测定:在 24 孔板中,用抑制剂 L1 (10-20 μM) 或阿洛司他丁 (20-30 μM) 在 37°C 下处理 CTL 和 NK 细胞 (0.8×106/mL) 24 小时。然后将细胞用于 51 Cr 释放测定或裂解以在蛋白质印迹中检查穿孔素。如所示,在一些 51 Cr 释放测定中,在 4 小时反应期间也以相同浓度添加抑制剂。使用 NP-40 裂解缓冲液(25 mM HEPES、250 mM NaCl、2.5 mM 乙二胺四乙酸、0.1% 体积/体积 Nonidet P-40)制备细胞裂解物,并使用 Bradford 测定法测定总蛋白浓度。等量的蛋白质上样并在 8% SDS-PAGE 凝胶上解析。使用指定的适当抗体检测人或小鼠穿孔素。抗肌动蛋白抗体用作上样对照。细胞测定:用 A23187 加钙激活血小板,已知这种情况会导致钙蛋白酶催化 ABP 和 talin 蛋白水解。在没有抑制剂的情况下,A23187 导致 ABP 和talin 完全降解。 E 64d,渗透抑制剂,确实抑制细胞内蛋白水解。在最低测试浓度 20 μg/ml 下观察到了一些抑制作用,而在 50 μg/ml 下则获得了基本上完全的抑制作用。
半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制活性(文献[1]、[2]): 1. 组织蛋白酶B抑制:Aloxistatin(0.01–1 μM)浓度依赖性抑制人重组组织蛋白酶B。0.1 μM时抑制率达~90%(Z-Arg-Arg-AMC荧光底物实验)[1] 2. 组织蛋白酶L抑制:0.1 μM Aloxistatin抑制大鼠肝脏组织蛋白酶L介导的偶氮酪蛋白降解~85%,IC₅₀≈0.08 μM[2] - 癌细胞自噬调控: 1. 人乳腺癌MCF-7细胞:10 μM Aloxistatin处理24小时,LC3-II/LC3-I比值上调~3.2倍(Western blot),提示自噬诱导;自噬底物p62水平较对照组降低~60%[6] 2. 小鼠黑色素瘤B16细胞:5 μM Aloxistatin增强自噬流:mRFP-GFP-LC3斑点(自噬体)荧光强度上调~2.8倍(共聚焦显微镜)[6] - 阿尔茨海默病(AD)相关活性: 1. 大鼠原代皮质神经元:2 μM Aloxistatin处理48小时,Aβ₄₂分泌减少~45%(ELISA)。Western blot显示β-分泌酶(BACE1)蛋白水平无变化,而Aβ降解酶组织蛋白酶B活性上调~30%[5] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
E-64d 治疗后,用青霉素治疗小鼠以诱导复发性癫痫发作。结果表明,E-64d显着减少了齿状回颗粒上区和海马CA3亚区的异常苔藓纤维萌芽。在未经E-64d治疗的大鼠中,在齿状回和CA3亚区的锥体层中存在明显的苔藓纤维末端聚集。在用 E-64d 治疗的大鼠中,齿状回颗粒上区域和 CA3 亚区的苔藓纤维末端聚集显着减少。
小鼠AD模型(APP/PS1转基因小鼠,文献[5]): 1. 分组:6月龄小鼠(n=8/组)随机分为2组:(1)溶剂对照组(腹腔注射10% DMSO+90%生理盐水);(2)Aloxistatin 1 mg/kg组[5] 2. 给药方案:腹腔注射,每日1次,持续4周[5] 3. 疗效: - 脑内Aβ₄₂水平:海马区较对照组降低~40%,皮质区降低~35%(ELISA); - 认知功能:Morris水迷宫实验显示逃避潜伏期较对照组缩短~30%; - 小胶质细胞活化:海马区Iba1⁺小胶质细胞数量减少~25%(免疫组织化学)[5] - 小鼠黑色素瘤异种移植模型: 1. 给药方案:B16肿瘤体积达~100 mm³时开始,Aloxistatin 5 mg/kg(腹腔注射,每2天1次),持续14天[6] 2. 疗效: - 肿瘤体积:较溶剂对照组减少~55%; - 肿瘤自噬:肿瘤组织中LC3-II水平上调~2.5倍(Western blot); - 对小鼠体重无显著影响(较基线变化<5%)[6] |
| 酶活实验 |
将抑制剂 L1 (10–20 μM) 或 Aloxistatin (20–30 μM) 应用于 CTL 和 NK 细胞 (0.8×106/mL),在 37°C 下在 24 孔板中持续 24 小时。之后,将细胞用于 51 Cr 释放实验或裂解细胞以在蛋白质印迹分析中观察穿孔素。一些 51Cr 释放测定还在 4 小时反应期间添加相同浓度的抑制剂,如图所示。使用 NP-40 裂解缓冲液(25 mM HEPES、250 mM NaCl、2.5 mM 乙二胺四乙酸、0.1% 体积/体积 Nonidet P-40)制备细胞裂解液,并使用 Bradford 法测定总蛋白浓度。将等量的蛋白质上样并解析到 8% SDS-PAGE 凝胶上。按照指示使用正确的抗体来检测人或小鼠穿孔素。使用抗肌动蛋白抗体作为上样对照。
组织蛋白酶B活性抑制实验: 1. 蛋白制备:人重组组织蛋白酶B在大肠杆菌中表达,镍螯合层析纯化,在50 mM醋酸钠缓冲液(pH5.5)中用10 mM DTT激活[1] 2. 反应体系:100 μL混合物含激活的组织蛋白酶B(0.5 μg)、荧光底物Z-Arg-Arg-AMC(20 μM)、Aloxistatin(0.01–1 μM)及50 mM醋酸钠缓冲液(pH5.5),溶剂(DMSO)作为对照[1] 3. 孵育与检测:37℃孵育60分钟,每10分钟测定荧光强度(激发光360 nm,发射光460 nm)。抑制率=(1–药物组荧光强度/对照组荧光强度)×100%[1] 4. 数据分析:Lineweaver-Burk双倒数作图(竞争性抑制模型)计算Ki值[1] - 组织蛋白酶L活性抑制实验: 1. 蛋白制备:大鼠肝脏中通过离子交换层析纯化组织蛋白酶L,在0.1 M Tris-HCl缓冲液(pH7.5)中用5 mM DTT激活[2] 2. 反应体系:200 μL混合物含组织蛋白酶L(1 μg)、底物偶氮酪蛋白(1%,w/v)、Aloxistatin(0.02–0.5 μM)及0.1 M Tris-HCl缓冲液(pH7.5)[2] 3. 检测:37℃孵育4小时,5%三氯乙酸终止反应,测定上清液366 nm处吸光度,计算抑制率[2] |
| 细胞实验 |
增殖标记物 Ki67 或凋亡标记物 cleaved caspase 3 染色可用于评估细胞增殖和凋亡。极性标记的过程与之前相同。四天后,MCF10 变体在 3D rBM 覆盖培养物中生长,并用 5 μM CA074Me、5 μM Aloxistatin 或 0.1% DMSO 处理。通过使用 Zeiss Axiophot 落射荧光显微镜对两个不同盖玻片上总共 100 个结构进行计数,可以确定 Ki67 或裂解的 caspase 3 呈阳性的结构的百分比。如果一个结构至少有一个 Ki67 染色细胞,则被认为是 Ki67 阳性。当某个结构具有一个或多个裂解 caspase 3 阳性的细胞,并且这些细胞不位于发育管腔的中心时,该结构被称为 caspase 3 阳性[3]。
MCF-7细胞自噬实验: 1. 细胞接种:MCF-7细胞以2×10⁵个细胞/孔接种于6孔板,使用含10% FBS的RPMI 1640培养基[6] 2. 药物处理:加入Aloxistatin(1–20 μM),37℃、5% CO₂孵育24小时。检测自噬流时,最后4小时共孵育100 nM巴弗洛霉素A1[6] 3. 检测: - Western blot:含蛋白酶抑制剂的RIPA缓冲液裂解细胞,30 μg蛋白进行免疫印迹(一抗:抗LC3、抗p62、抗β-actin); - 免疫荧光:药物处理前24小时转染mRFP-GFP-LC3质粒,共聚焦显微镜计数荧光斑点[6] - 原代皮质神经元Aβ分泌实验: 1. 细胞培养:大鼠胚胎(E18)皮质神经元以1×10⁵个细胞/孔接种于24孔板,使用含2% B27添加剂的神经基础培养基[5] 2. 药物处理:加入Aloxistatin(0.5–5 μM),孵育48小时[5] 3. 检测:收集上清液,夹心ELISA量化Aβ₄₂水平;细胞裂解后进行Western blot(一抗:抗BACE1、抗组织蛋白酶B)[5] |
| 动物实验 |
Mice and Pigs: Male Hartley strain guinea pigs, weighing an average of 400 g, or approximately six weeks old, are used. The London mutant β-secretase site sequences and the wt β-secretase site-containing human AβPP are expressed in male transgenic mice. Although accurate dosage can be achieved by gavage delivery, this method is traumatic and should only be used for brief dosage intervals (up to approximately one week). In the studies using guinea pigs, gavage delivery is utilized. The recommended dosages of aloxistatin (0.1, 1.0, 5, and 10 mg/kg) are suspended in Me2SO and given orally once a day through a feeding tube. Me2SO alone is administered by gavage to vehicle control animals.
Rats: The rats are inbred male DS rats. Up until the age of seven weeks, weaned rats are given laboratory chow containing 0.3% NaCl. DS rats given an 8% NaCl diet for seven weeks show signs of compensating for concentric left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy, which is related to hypertension at twelve weeks. At nineteen weeks, the rats show signs of a distinct stage of fatal LV failure, accompanied by lung congestion. To that end, DS rats are started on an 8% NaCl diet at 7 weeks of age. From 12 to 19 weeks of age, they are randomized into three groups: HF, Aloxistatin (10 mg per kg of body mass per day, administered intraperitoneally every other day), and RNH-6270 (3 mg/kg per day in chow) (n=10 for each group). Preliminary experiments and prior research determine the doses of aloxistatin and RNH-6270, an ARB. Age-matched controls (control group, n = 10) were DS rats fed a diet containing 0.3% NaCl. All of the rats are killed at 19 weeks of age by injecting an excess of 50 mg/kg of NSC 10816 intraperitoneally, and their hearts are taken out for histological and biological examinations. To measure renin activity, arterial blood is drawn from the abdominal aorta. Every week starting at 7 weeks of age, conscious rats have their heart rate and systolic blood pressure measured using a noninvasive tail-cuff technique. In independent studies, n = 5 per group of 12-week-old DS rats fed a low-salt diet starting at 7 weeks of age are given vehicle, RNH-6270, or Aloxistatin in the same way as in the previous studies. The LV tissues used to measure targeting mRNAs and protein levels are then promptly frozen in liquid nitrogen and kept at -80°C. APP/PS1 transgenic mouse AD model protocol: 1. Animal housing: 6-month-old APP/PS1 transgenic mice (male, 25–30 g) housed in SPF facilities (22–25°C, 12-hour light/dark cycle) with free access to food/water [5] 2. Grouping and treatment: Mice randomized into vehicle control and Aloxistatin groups. Aloxistatin dissolved in 10% DMSO + 90% normal saline, administered via intraperitoneal injection (10 μL/g body weight) at 1 mg/kg, once daily for 4 weeks. Control received solvent alone [5] 3. Monitoring and analysis: - Cognitive function: Morris water maze test performed weekly (escape latency, platform crossing times); - Brain tissue collection: Mice euthanized via CO₂ inhalation; hippocampus and cortex dissected for Aβ ELISA and immunohistochemistry (Iba1 staining) [5] - Mouse B16 melanoma xenograft protocol: 1. Tumor implantation: B16 cells (5×10⁶ cells/mouse) resuspended in 100 μL PBS, subcutaneously injected into right flank of C57BL/6 mice (6–8 weeks old, female) [6] 2. Treatment: Tumors reaching ~100 mm³ (day 0) randomized to groups. Aloxistatin dissolved in 5% DMSO + 95% normal saline, administered via intraperitoneal injection at 5 mg/kg, once every 2 days for 14 days [6] 3. Analysis: Tumor volume measured every 3 days (volume = length × width² / 2); tumors excised at sacrifice for Western blot (LC3, p62) [6] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Intraperitoneal pharmacokinetics in rats:
1. PK parameters (5 mg/kg intraperitoneal dose): - Cmax: ~12 μM (Tmax = 0.5 hours); - AUC₀-24h: ~35 μM·h; - Terminal half-life (t₁/₂): ~2.8 hours; - Clearance (CL): ~140 mL/h/kg [3] 2. Tissue distribution (5 mg/kg intraperitoneal, 1 hour post-dose): - Liver: ~25 μM; - Kidney: ~18 μM; - Brain: ~2.5 μM (low CNS penetration) [3] - Oral pharmacokinetics: 1. Oral bioavailability: ~15% (rat, 10 mg/kg oral dose vs. intraperitoneal dose); significant first-pass metabolism in liver [1] 2. Excretion: ~60% of administered dose excreted in urine (as metabolites) within 72 hours; ~20% excreted in feces (unchanged drug: ~5%) [3] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
In vitro toxicity (literature [1], [6]):
1. Normal human fibroblasts (MRC-5): 20 μM Aloxistatin (72-hour treatment) reduced viability by <10% (MTT assay) [1] 2. Primary rat cortical neurons: 5 μM Aloxistatin showed no significant cytotoxicity; neuron survival rate >90% (NeuN staining) [5] - In vivo toxicity (literature [3], [6]): 1. Acute toxicity (mouse): - Single intraperitoneal LD₅₀ ≈ 80 mg/kg; - Signs of overdose: Transient ataxia and reduced activity, resolved within 24 hours [3] 2. Subchronic toxicity (rat, 5 mg/kg intraperitoneal, daily for 4 weeks): - No mortality; body weight change <5% vs. baseline; - Serum biochemical parameters (ALT, AST, creatinine) within normal ranges [3] - Plasma protein binding: ~85% (human plasma, equilibrium dialysis at 37°C) [1] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
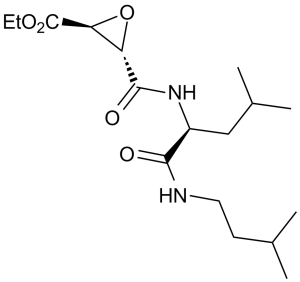
Aloxistatin is an L-leucine derivative that is the amide obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of (2S,3S)-3-(ethoxycarbonyl)oxirane-2-carboxylic acid with the amino group of N-(3-methylbutyl)-L-leucinamide. It has a role as a cathepsin B inhibitor and an anticoronaviral agent. It is a L-leucine derivative, a monocarboxylic acid amide, an epoxide and an ethyl ester.
Aloxistatin is an inhibitor of cysteine protease with blood platelet aggregation inhibiting activity. Aloxistatin is an irreversible, membrane-permeable inhibitor of lysosomal and cytosolic cysteine proteases with the ability to inhibit calpain activity in intact platelets. E-64 isolated from a culture of Aspergillus japonicus is a specific inhibitor of cysteine proteinases. E-64-c, a synthetic analog of E-64, was effective in model animals of muscular dystrophy only when it was given intraperitoneally and by means of osmotic minipump. It showed no effects due to its low absorbability from intestine when it was administered orally. EST, the ethyl ester of E-64-c, was expected to be readily absorbed through intestinal membrane, since it is more lipophilic than E-64-c. Both EST and E-64-c have a high specificity to cysteine proteinase similar to E-64 but E-64-c was 100 to 1000 times stronger than EST in in vitro cathepsin inhibition. However, EST was stronger than E-64-c in cathepsin inhibition when given orally. The cathepsin B&L activities (whole activities of cathepsins B and L) in the skeletal muscle, heart and liver of hamsters were strongly inhibited soon after oral administration of 100 mg/kg body weight of EST. The inhibition continued for at least 3 h and then disappeared gradually. E-64-c was found in plasma of hamster treated with EST, but unchanged EST was not found. These results suggested that EST was converted to E-64-c, a more active form, during the permeation through intestinal membrane. The conversion of EST to E-64-c was also indicated by the absorption experiment using in situ loop method. EST was thus shown to be useful as an oral drug and expected to be effective in therapeutic trials using model animals.[1] E-64d, a membrane permeant derivative of E-64c, a thiol protease inhibitor (Tamai et al. (1986) J. Pharmacobio-Dyn. 9, 672-677), was tested for ability to inhibit calpain activity in intact platelets. Calpain activity was measured by proteolysis of actin-binding protein and talin, two known substrates of calpain. Incubation of platelets with E-64c (not permeant) or E-64d before lysis prevented proteolysis after lysis. When the platelets were incubated with E-64c or E-64d and then washed to remove the drugs before lysis, only E-64d inhibited proteolysis. When platelets were incubated with E-64c or E-64d and then activated with A23187 plus calcium, a treatment that activates intraplatelet calpain, only E-64d inhibited proteolysis. These results indicate that E-64d can enter the intact cell and inhibit calpain.[2] Parathyroid hormone (PTH) activates calpains I and II (calcium-activated papain-like proteases) and stimulates the synthesis and secretion of cathepsin B (a lysosomal cysteine protease) in osteoblastic cells. Anabolic doses of PTH also stimulate osteoprogenitor cell proliferation and differentiation into mature, fully functional osteoblasts capable of elaborating bone matrix, whereas catabolic doses of PTH stimulate calcium mobilization and matrix turnover. Previous investigations in other cell types have demonstrated that calcium-activated calpains play a major role in regulating proliferation and differentiation by catalyzing limited regulatory proteolysis of nuclear proteins, transcription factors, and enzymes. We tested the hypothesis that inhibition of intracellular cysteine proteases such as the calpains will ablate PTH-mediated osteoblast proliferation and differentiation, two fundamental indices of bone anabolism. A brief preincubation with the membrane-permeable, irreversible cysteine protease inhibitor E64d (10 micrograms/mL) before short-term PTH treatment blunted PTH-induced cell proliferation in subconfluent cultures and also attenuated proliferation and inhibited differentiation in longer-term confluent cultures. This confirms the hypothesis that cysteine proteases such as the calpains are important in mediating the proliferative and prodifferentiating or anabolic effects of PTH on MC3T3-E1 cells in culture. Immunofluorescent localization demonstrated that calpain I, calpain II, and calpastatin (the endogenous calpain inhibitor) are abundant and widely distributed within actively proliferating MC3T3-E1 preosteoblasts. Since the calpains are active and stable at neutral intracellular pH levels in osteoblasts, whereas cathepsins are not, our results support a role for these calcium-activated regulatory proteases in mediating the anabolic effects of PTH in bone.[3] Background: Aloxistatin (Loxistatin; E64d, NSC-694281) is a cell-permeable, irreversible inhibitor of cysteine proteases (e.g., cathepsins B/L/C), developed for research in protease-related diseases (Alzheimer’s disease, cancer, inflammation) [1][5][6] - Mechanism of action: Covalently binds to the active-site cysteine residue of cysteine proteases, irreversibly inhibiting their activity. In AD, it enhances cathepsin B-mediated Aβ degradation; in cancer, it induces protective autophagy or cytotoxic autophagy depending on cell type [5][6] - Therapeutic potential: Preclinical efficacy in AD transgenic mice (reduced Aβ, improved cognition) and cancer models (tumor growth inhibition) supports its potential for protease-targeted therapies [5][6] |
| 分子式 |
C17H30N2O5
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
342.43
|
|
| 精确质量 |
342.215
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 59.63; H, 8.83; N, 8.18; O, 23.36
|
|
| CAS号 |
88321-09-9
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
65663
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
470.5±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
126.2°C
|
|
| 闪点 |
238.4±31.5 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.6 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.530
|
|
| LogP |
3.64
|
|
| tPSA |
97.03
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
11
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
24
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
450
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
3
|
|
| SMILES |
C([C@H]1O[C@@H]1C(=O)OCC)(=O)N[C@@H](CC(C)C)C(=O)NCCC(C)C
|
|
| InChi Key |
SRVFFFJZQVENJC-IHRRRGAJSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C17H30N2O5/c1-6-23-17(22)14-13(24-14)16(21)19-12(9-11(4)5)15(20)18-8-7-10(2)3/h10-14H,6-9H2,1-5H3,(H,18,20)(H,19,21)/t12-,13-,14-/m0/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
ethyl (2S,3S)-3-[[(2S)-4-methyl-1-(3-methylbutylamino)-1-oxopentan-2-yl]carbamoyl]oxirane-2-carboxylate
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.30 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% EtOH + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 EtOH 储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;再向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;然后加入450 μL 生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.30 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% EtOH + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清乙醇储备液加入 900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.30 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% EtOH + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 2.08 mg/mL (6.07 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;再向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;然后加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 5 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (6.07 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入900 μL 玉米油中,混合均匀。 配方 6 中的溶解度: 2% DMSO+corn oil: 5mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9203 mL | 14.6015 mL | 29.2030 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5841 mL | 2.9203 mL | 5.8406 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2920 mL | 1.4602 mL | 2.9203 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。