| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
p110α (IC50 = 5 nM); p110γ (IC50 = 250 nM); p110δ (IC50 = 290 nM); p110β (IC50 = 1200 nM); p110α-H1047R (IC50 = 4 nM); p110α-E545K (IC50 = 4 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
我们研究了阻断ATP位点的新型特异性PI3Kα抑制剂BYL719对骨肉瘤和骨细胞的治疗价值。在人和小鼠骨肉瘤细胞中评估了BYL719对增殖、凋亡和细胞周期的体外影响。使用人间充质干细胞(hMSC)和人CD14+破骨细胞前体测定其对骨细胞的影响。使用两种不同的骨肉瘤小鼠临床前模型来分析BYL719的体内生物活性。BYL719通过阻断G0/G1期细胞周期来降低细胞增殖,对HOS和MOS-J肿瘤细胞的凋亡细胞死亡没有显著影响。BYL719抑制细胞迁移,因此可以被认为是骨肉瘤的细胞生长抑制剂。[4]
BYL719 抑制携带 PIK3CA 突变的乳腺癌细胞系的增殖,与抑制 PI3K/Akt 通路的各种下游信号成分相关。 BYL719/Alpelisib抑制携带PIK3CA突变的乳腺癌症细胞系的增殖,与抑制PI3K/Akt途径的各种下游信号成分有关。 NVP-BYL719在体外有效且选择性地抑制PI3Kα[3] PI3Kα、β、δ和γ酶具有显著的氨基酸残基同源性,在催化激酶结构域中具有特别高的保守性。基于其结合模式,2-氨基噻唑支架被选为开发强效和选择性PI3K抑制剂的起点,这表明有可能使用氨基上的取代基与ATP袋入口处的非共价氨基酸发生相互作用(21)。因此,对关键部分的系统修饰和药物样性质的优化导致了NVP-BYL719的鉴定。 如参考文献18所述,在生化测定中,NVP-BYL719/Alpelisib对野生型PI3Kα(IC50=4.6 nmol/L)的抑制作用比PI3Kδ(IC50=290 nmol/L”)和PI3Kγ(IC50=250 nmol/L“)亚型更强,对PI3Kβ的活性显著降低(IC50=1156 nmol/L。此外,我们发现NVP-BYL719能有效抑制2种最常见的PIK3CA体细胞突变(H1047R,E545K;IC50≈4 nmol/L)。该化合物对III类家族成员Vps34和相关的IV类PIKK蛋白激酶mTOR、DNA-PK和ATR也缺乏活性,对不同的脂质激酶PIK4β的效力明显较低(表1)。 在体外激酶测定面板中进一步检查了NVP-BYL719的激酶选择性特征。在所有测试的激酶中(不包括I类PI3K和PI4Kβ),与PI3Kα相比,它们各自的IC50或Kd值至少高出50倍(补充图1,补充表1-4)。 为了确定NVP-BYL719在细胞检测系统中的效力和选择性,测试了使用活化形式的PI3Kα、PI3Kβ或PI3Kδ转化的Rat1细胞,并使用RPPA定量Akt的磷酸化(S473)作为PI3K途径活性的标志物(17)。如参考文献18所述,NVP-BYL719能有效抑制PI3Kα转化细胞中的Akt磷酸化(IC50=74±15 nmol/L),并在PI3Kβ或PI3Kδ亚型转化细胞中显示出显著降低的抑制活性(与PI3Kα相比≥15倍)。在这里,我们报告了NVP-BYL719全剂量反应曲线及其在Rat1细胞中S473P-Akt的IC80值(补充图S2)。此外,与阳性对照RAD001相比,用NVP-BYL719治疗TSC1缺失的MEF细胞与RPS6磷酸化的减少无关(S235/236)(IC50值<0.5 nmol/L),表明NVP-BYL719不会抑制mTORC1(补充图S3A和S3B)。同样,NVP-BYL719似乎不会干扰在ATM和ATR依赖性检测系统中确定的参与DNA损伤修复(ATM和ATR)过程的PIKK(补充图S3C和S3D)。这些数据共同有力地支持了NVP-BYL719具有选择性PI3Kα抑制剂的相关体外特性的观点。 PIK3CA突变细胞系对NVP-BYL719具有选择性敏感性[3] 上述方法有助于确定哪些肿瘤对PI3Kα抑制有反应。当人们考虑哪种治疗方式是最具选择性的,因此在特定的癌症基因型中可能具有最佳的治疗指数时,会提出一个独立的问题。在这里,我们使用一种新的分析方法来定义小分子抑制剂在CCLE中的选择性指数,比较了不同化合物处理(约1000)的选择性特征,包括PIK3CA突变体与野生型细胞系中的200多种作用机制,并根据其在这两组中的作用程度对化合物进行了排名(图6)。与野生型细胞系群体和pan-PI3K抑制剂相比,NVP-BYL719与3种类似物一起在PIK3CA突变体中显示出显著的选择性功效。相反,与突变体相比,MEK抑制剂在PIK3CA野生型细胞系中的选择性更高。 BYL719/Alpelisib抑制骨肉瘤细胞增殖[4] 如图1b所示,BYL719(图1a中的化学结构)迅速抑制了所有评估细胞系中P-AKT和P-mTOR的水平,证实了BYL719对骨肉瘤细胞的功能活性(图1b)。然后进行XTT测定,分析BYL719对骨肉瘤细胞生长的影响(人:MG63,HOS-MNG;小鼠:POS-1,MOS-J和大鼠:OSRGA)(图1c)。治疗72小时后,BYL719以剂量依赖的方式显著抑制了所有骨肉瘤细胞系的细胞生长(图1c和1d),在72小时时IC50范围为6至15µM,IC90范围为24至42µM(图1e)。为了确定BYL719诱导的细胞存活率降低是否与细胞周期改变有关,在添加BYL719后进行了细胞DNA含量的流式细胞术(支持信息数据3)。结果显示,BYL719显著改变了细胞周期阶段的分布,更具体地说,MG-63中G0/G1期的细胞数量从57%增加到70%,HOS中从44%增加到73%(支持信息数据3A),MOS-J中从45-70%增加到58-70%,POS-1细胞中从58%增加到70%(支持信息数据3B)。这些观察结果伴随着S-G2/M期细胞的减少。在大鼠骨肉瘤细胞系OSRGA上获得了类似的结果(支持信息数据4)。 BYL719/Alpelisib作为骨肉瘤细胞的细胞生长抑制剂[4] 为了确定这些影响是否是由于抑制细胞增殖和/或诱导细胞死亡,在台盼蓝排斥染色后通过手动计数活细胞来评估BYL719的影响。BYL719以剂量和时间依赖的方式显著减少活HOS和MOS-J细胞的数量,而不影响死细胞的数量。这支持了BYL719在骨肉瘤细胞中具有细胞生长抑制活性的观点(分别为图1d和支持信息数据5A)。此外,BYL719未能诱导凋亡,如HOS和MOS-J细胞中评估的caspase-3/7活性所示(分别为图1e,左图和支持信息5B),并通过BYL719治疗HOS骨肉瘤细胞后没有切割的PARP表达得到证实(图1e,右图)。MG-63、POS-1(数据未显示)和OSRGA细胞系(支持信息数据4D)也获得了类似的数据。还对HOS和MOS-J细胞进行了迁移测定,以确定BYL719对细胞运动的影响,并证明BYL719降低了细胞运动(支持信息数据6A和B)。然后我们进行了回收分析。令人惊讶的是,处理过的细胞能够以与对照条件相同的方式恢复,这表明BYL719仅在药物存在时具有细胞生长抑制作用(图4c)。所有这些数据表明,BYL719在骨肉瘤细胞中具有细胞生长抑制活性。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在啮齿类动物的 PIK3CA 突变异种移植模型中,BYL719(>270 mg/d)表现出统计学上显着的剂量依赖性抗肿瘤功效。 BYL719 的半衰期较短,为 8.5 小时,Cmax 个体间差异较低,在人体中暴露剂量在 30 mg/d 至 450 mg/d 之间按比例增加。 BYL719(270 mg/d)临床疗效的第一个迹象包括 1 名 ER+ 乳腺癌患者确认有部分缓解,在评估的 17 名患者中,有 8 名患者出现显着 PET 缓解 (PMR) 和/或肿瘤缩小。
NVP-BYL719/Alpelisib在PI3Kα驱动的肿瘤中显示出强有力的PK/PD/疗效关系[3] 为了检测NVP-BYL719在PI3Kα依赖性体内模型中抑制PI3K/Akt通路的能力,在Rat1-myr-p110α机制肿瘤携带小鼠模型中评估了其药代动力学/药效学(PK/PD)关系。每只雌性无胸腺小鼠接受单次或重复剂量的NVP-BYL719(12.5、25或50mg/kg,口服),并在不同时间点收集血浆和肿瘤样本进行PK和PD分析。在这里,NVP-BYL719治疗与PI3K/Akt通路的剂量和时间依赖性抑制有关,这与肿瘤和血浆中的时间依赖性药物暴露显著平行(图1A)。 为了确定剂量和时间依赖性途径抑制是否与抗肿瘤活性有关,Rat1-myr-p110α荷瘤裸鼠每天口服该化合物,连续8天(图1B)。12.5、25和50mg/kg的治疗耐受良好,并产生了剂量依赖性和统计学上显著的抗肿瘤作用,T/C分别为14.1%和9.6%和65.2%。为了评估体内PI3K的相对选择性,我们在相应的Rate1-myr-p110δ模型中进一步测试了NVP-BYL719。当每天口服50mg/kg的最佳剂量进行测试时,NVP-BYL719仅显示出适度的抗肿瘤作用(T/C为30%;图1C)。 接下来,我们试图更好地了解抗肿瘤疗效所需的PI3Kα抑制程度。为此,我们首先通过使用RPPA测量Akt磷酸化的程度以及来自多个动物和多个时间点的匹配样本中的特定肿瘤药物浓度,确定了给予50%(体内IC50)和80%(体内IC80)S473P-Akt抑制的肿瘤浓度(分别为0.4和4μmol/L)(图1D)。有趣的是,当校正小鼠体内NVP-BYL719的血浆蛋白结合率(PPB=91.2%)时,体内IC50(35 nmol/L)和IC80(352 nmol/L)值分别大致接近74和301 nmol/L的体外细胞IC50和IC80值。接下来,我们试图确定暴露(通过体内IC80的时间测量)与抗肿瘤疗效之间的关系。在这里,我们发现IC80的抗肿瘤疗效幅度和药物暴露时间之间几乎呈线性关系(R2=0.80,P<0.001,n=11;图1E)。从这种关系来看,NVP-BYL719诱导肿瘤停滞需要在至少29%的给药间隔内对Akt磷酸化进行80%的抑制,并且这种途径抑制水平必须在至少45%的给药时间间隔内持续,才能在携带Rat1-myr-p110α肿瘤的裸小鼠中产生30%的肿瘤消退。相比之下,在Rat1-myr-p110δ荷瘤裸鼠中,NVP-BYL719暴露水平没有达到Akt磷酸化的80%抑制率(体内IC80=29μmol/L;小鼠IC80=2552μmol/L中校正了NVP-BYL719血浆蛋白结合),这很可能解释了观察到的适度抗肿瘤作用,并与化合物对p110δ的适度活性相一致。为了排除我们的发现可能是Rat1小鼠肿瘤模型特异性的可能性,将NVP-BYL719以不同剂量在体内给药于裸鼠和携带不同范围癌症细胞系来源的肿瘤异种移植物的裸鼠。在这里,我们还发现IC80的抗肿瘤疗效幅度与药物暴露持续时间之间几乎呈线性关系(R2=0.77,P<0.001,n=27,补充图S4和表S5)。这些数据表明,NVP-BYL719需要在给药间隔的一小部分时间内持续抑制PI3K/Akt通路,才能产生强大的抗肿瘤作用。 与泛I级抑制相比,NVP-BYL719/Alpelisib显示出更高的安全性[3] 抗PI3K治疗的预期靶向副作用是胰岛素抵抗和高血糖。为了评估NVP-BYL719是否扰乱葡萄糖稳态,测量了血浆胰岛素和血糖水平,并将其与来自多个动物和多个时间点的匹配样本中的血浆药物浓度进行了比较。这里的数据显示,胰岛素血浆水平与NVP-BYL719血浆浓度成比例增加,而血糖水平在NVP-BYL719高达20μmol/L时保持接近正常水平(图2A和B)。然而,当浓度超过20μmol/L时,我们观察到化合物浓度依赖性的葡萄糖增加,尽管胰岛素血浆水平升高,但仍导致高血糖。因此,我们将20μmol/L定义为小鼠NVP-BYL719相关的高血糖阈值。 PIK3CA的基因改变预测NVP-BYL719/Alpelisib体内疗效[3] 接下来,将NVP-BYL719以50 mg/kg的剂量(每天,p.o.)体内给药于携带不同遗传背景的癌症细胞系衍生的肿瘤异种移植物的小鼠(图5A和补充表S5),包括先前描述的决策树的预测特征。大多数携带PIK3CA突变或扩增的肿瘤模型对NVP-BYL719有反应(反应定义为T/C<20%)。相比之下,在大多数携带PTEN突变或PIK3CA野生型的肿瘤模型中,我们观察到疾病进展。在体内,预测因子也显著富集了应答者(阳性预测值=89%)。这些数据表明,从CCLE的体外分析和分析中得出的NVP-BYL719预测特征似乎与预测体内反应有关(P=0.01,Fisher检验)。 BYL719/Alpelisib在两种骨肉瘤小鼠模型中同时减少肿瘤生长和肿瘤异位骨形成,并略微调节全身骨参数[4] 接下来,我们测试了BYL719在骨肉瘤小鼠MOS-J同源模型中的作用。与赋形剂组相比,BYL719以剂量依赖的方式显著减少了肿瘤体积(图2a;p<0.01和p<0.001,分别为12.5和50mg/kg BYL719)。事实上,平均肿瘤体积从对照组的1747 mm3降至50 mg/kg BYL719治疗组的938 mm3(图2a,p < 0.001). 此外,对每只小鼠的肿瘤胫骨和对侧胫骨(正常骨)进行µCT分析。胫骨肿瘤的显微CT分析显示肿瘤细胞沉积的异位骨形成,并清楚地表明BYL719显著减少了这种肿瘤异位骨(图2b,左图)。通过测量钙化组织参数,证实了BYL719的益处(图2b,右图)。50mg/kg BYL719显著降低了骨体积(BV),7.08±0.6至4.37±0.21 mm3(p<0.001),骨表面(BS)为99.65±5.74 mm2至63.91±2.3 mm2(p<0.001)。研究了对侧胫骨的组织形态计量学参数,以确定BYL719对无任何肿瘤的正常骨重塑的系统影响(支持信息数据7)。50 mg/(kg·day-1)的BYL719对任何研究的骨小梁参数都没有影响(支持信息数据7)。然而,它显著降低了几个皮质骨参数,包括TV(组织体积)、BV、BV/TV、BS/TV和CTh(p<0.01)(支持信息数据7)。组织学研究显示,BYL719降低了TRAP+破骨细胞的表面,而不影响osterix+细胞的数量(图3a和3b)。此外,BYL719的治疗效果因KI67+细胞数量减少(图3c)和肿瘤血管化减少(图3d)而增强。 基于这些结果,在骨肉瘤异种模型中分析了BYL719的治疗潜力。患有人HOS肿瘤的裸小鼠用50mg/(kg day-1)的BYL719治疗。与MOS-J模型一样,BYL719在治疗期结束时显著减少了肿瘤体积,从对照组的1445 mm3减少到治疗组的650 mm3(图2c;p < 0.01). 这些结果证实了BYL719在第二种临床前骨肉瘤模型中的抑制作用。胫骨肿瘤的显微CT分析显示,BYL719减少了异位骨基质的沉积,骨参数值从64.91±5.2降至36.4±0.70 mm2(p<0.001),从6.2±0.33降至4.0±0.08 mm3(p<0.001) < 0.001), 分别适用于BS和BV(图2d,右侧面板)。通过对侧胫骨的µCT评估BYL719对正常骨的影响,没有任何肿瘤,证实了同基因MOS-J模型中获得的结果(支持信息数据8)。MicroCT证实了BYL719对C57Bl5J小鼠皮质骨的影响。 BYL719/Alpelisib与常规化疗药物联合使用的治疗益处[4] 由于BYL719在骨肉瘤细胞中显示出抑制细胞生长的作用,我们随后评估了将BYL719与异环磷酰胺(用于体外实验的mafosfamide)联合治疗骨肉瘤的疗效,异环磷酰胺是一种常规化疗药物。为了确定这种效应是相加的还是协同的,根据Chou和Talalay的中值效应原理,进行了恒定比率设计的剂量依赖效应和组合指数(CI)值的计算。图4a和4b显示了剂量-反应曲线(联合治疗、BYL719或镁磷酰胺单药治疗)和联合指数图,表明BYL719协同增强了镁磷酰胺对肿瘤细胞生长的影响(图4a和4b)。然后,我们进行了集落形成试验,以评估BYL719±mafosfamide治疗2天后的恢复能力。虽然BYL719没有改变菌落数量,但与对照组相比,镁磷酰胺减少了菌落形成(图4c)。然而,与单独使用每种药物相比,BYL719与镁磷酰胺的组合显著诱导了集落形成的最大减少(图4c)。此外,BYL719增强了mafosfamide诱导细胞凋亡的作用,如切割的PARP表达的增加所示(图4d)。 然后,我们研究了BYL719(50mg/(kg day−1))与次优剂量的异环磷酰胺(IFOS,30mg/(kg day-1),持续3天)联合使用的效果,如前所述的同源小鼠模型(图4e)。正如预期的那样,与对照组相比,50mg/kg BYL719对肿瘤发展具有显著的抑制作用。相比之下,与单独使用IFOS(1746 mm3)或单独使用BYL719(1421 mm3)相比,将次优剂量的IFOS与50 mg/(kg day-1)的BYL719联合治疗显著降低了肿瘤生长(1011 mm3)(图4e)。肿瘤骨的MicroCT分析显示,联合治疗对BYL719的治疗反应没有影响,甚至对形成的异位骨也没有观察到协同或相加作用(图4f和4g)。这些结果强烈表明,将BYL719与常规化疗药物联合使用具有治疗意义,可以显著延缓肿瘤生长和肿瘤异位骨形成。 |
| 酶活实验 |
为了评估Alpelisib(NVP-BYL719)在基于细胞的系统中的亚型特异性效力,如参考文献17所述,在Rat1成纤维细胞中表达了每种PI3K IA类亚型的N-末端肉豆蔻酰化形式。生成了含有人p110α、p110β和p110δ的逆转录病毒表达质粒pBabePuro,其具有N-末端肉豆蔻酰化(myr)信号和HA标签。在含有4μg/mL嘌呤霉素的培养基中选择成功感染的Rat1细胞,扩增并表征p110亚型的表达(2006年)。肉豆蔻酰化蛋白的转基因表达通过磷酸化Akt水平的增加得到证实。D.Kwiatkowski博士于2007年获得了mTORC1本构激活的TSC1-/-零MEFs机理模型。[3]
Alpelisib (NVP-BYL719) 有效抑制 2 种最常见的 PIK3CA 体细胞突变(H1047R、E545K;IC50~4 nM)。 Alpelisib (NVP-BYL719) 有效抑制 PI3Kα 转化细胞中的 Akt 磷酸化 (IC50=74±15 nM),并在 PI3Kβ 或 PI3Kδ 异构体转化细胞中显示出显着降低的抑制活性(与 PI3Kα 相比≥15 倍)。 |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞生长和存活率,克隆形成试验[4]
将2000个肿瘤细胞接种到96孔板中,第二天,用Alpelisib(BLY-719;Piqray;NVP-BYL719)(1-50µmol/L)处理细胞72小时。使用3′[1-(苯氨基羰基)-3,4-四唑鎓]-双(4-甲氧基-6-硝基)苯磺酸水合物的比色测定法测定细胞生长/存活率。在490 nm处读取吸光度。细胞活力也通过台盼蓝排斥试验测定;在处理24和48小时后手动计数活细胞和非活细胞。对于克隆形成试验,肿瘤细胞在96孔板中用或不用25µM BYL预处理6小时,然后用/不用5µg/mL甲氟霜胺处理48小时。然后,在6孔板中分裂肿瘤细胞,500个细胞/孔,不治疗7天。结晶紫染色后计数菌落数。 半胱天冬酶活性[4] 将20万个细胞接种在6孔板中,与或不与Alpelisib(BLY-719;Piqray;NVP-BYL719)一起培养3-48小时(25µM)。根据制造商的建议,使用CaspACE检测系统试剂盒评估Caspase活性。结果以任意单位表示,根据BCA定量的蛋白质浓度进行校正。将用1µg/mL星孢菌素(Invitrogen)处理过夜的细胞裂解物用作阳性对照。 细胞周期分析[4] 将亚流培养物与或不与25µM的Alpelisib(BLY-719;Piqray;NVP-BYL719)一起孵育18小时,胰蛋白酶化,洗涤,并在含有0.12%Triton X-100、0.12 mM EDTA和100µg/mL无DNA酶核糖核酸酶A的PBS中孵育。然后,加入50µg/mL碘化丙啶20分钟。通过流式细胞术测定细胞周期分布,并通过DNA细胞周期分析软件进行分析。 蛋白质印迹[4] 用25µM的Alpelisib(BLY-719;Piqray;NVP-BYL719)处理20万个细胞3-24小时,然后在RIPA缓冲液(150 mmol/L NaCl,5%Tris,pH 7.4,1%NP-40,0.25%脱氧胆酸钠,1 mmol/L Na3VO4,0.5 mmol/L PMSF,10 mg/mL亮肽,10 mg/mL抑肽酶)中裂解。使用BCA试剂盒测定的总细胞裂解物(40μg)在10%SDS-PAGE上运行,并电泳转移到Immobilon-P膜上。用PBS、0.05%吐温20和3%BSA中的抗体(支持信息数据1)印迹膜。使用增强化学发光系统观察抗体结合。 Alpelisib (0–1000 nM) 以逐渐升高的浓度作用于细胞,持续 72 小时。使用 CyQuant 测定法测量细胞活力。 |
| 动物实验 |
Female athymic nu/nu mice
40 mg/kg o.g. Xenograft Studies[3] CW2 cells were re-suspended in serum-free RPMI and Growth Factor-Reduced Matrigel (1:1 ratio) and injected subcutaneously into the right flank of 4–6 week old female athymic nu/nu mic. When the average tumor volume reached ~200 mm3, mice received daily doses of vehicle (0.5% Methylcellulose + 0.4% Tween 80, orogastric gavage), neratinib (40 mg/kg; orogastric gavage), alpelisib (30 mg/kg; orogastric gavage), or neratinib + alpelisib . In our previous studies, we have found neratinib to cause anorexia and moderate body weight loss. To avoid these toxicities, all mice were prophylactically supplemented with DietGel 76A (Clear H2O) in addition to regular chow. Tumor diameters were measured twice weekly using calipers and tumor volumes were calculated using the formula: volume = width2 x length/2. Cell lines–derived tumor models.[3] All in life experimentation and efficacy studies were conducted as described previously. Tumor xenografts were grown subcutaneously or orthotopically in nude mice or nude Rowett rats by injection of 3 × 106 to 1 × 107 cells or implantation of tumor fragments of approximately 50 mg. Tumor-bearing animals mice were treated with either vehicle control, alpelisib/NVP-BYL719 , or NVP-BKM120 (p.o., every day) at the doses indicated. Patient-derived tumor models.[3] Patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models were established by implanting surgical tumor tissues from treatment-naïve cancer patients into nude mice. All samples were anonymized and obtained with informed consent and under the approval of the institutional review boards of the tissue providers and Novartis. All PDX models were histologically characterized and external diagnosis was independently confirmed by in-house pathologists and were genetically profiled using various technology platforms after serial passages in mice. PIK3CA mutation was determined by both RNA and DNA deep sequencing technologies and PIK3CA amplification was determined by SNP array 6.0. For efficacy studies, tumor-bearing animals were enrolled when subcutaneously implanted tumors reached about 200 mm3 and treated with alpelisib/NVP-BYL719 at 50 mg/kg daily. The response is reported as percentage change in tumor volume at last day of treatment relative to day 0 (start of treatment). Formulation used for in vivo experiments: alpelisib/NVP-BYL719 was formulated for oral administration in solution by solving the compound in N-methyl pyrrolidone, polyethylene glycol 300, solutol HS15, and water (10%:30%:20%:40%, v/v) or in suspension in 1% (w/v) carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) + 0.5% (w/v) Tween 80 similar to NVP-BKM120.[3] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Alpelisib reached a peak concentration in plasma of 1320±912ng/mL after 2 hours. Alpelisib has an AUClast of 11,100±3760h ng/mL and an AUCINF of 11,100±3770h ng/mL. A large, high fat meal increases the AUC by 73% and Cmax by 84% while a small, low fat meal increases the AUC by 77% and Cmax by 145%. 36% of an oral dose is eliminated as unchanged drug in the feces and 32% as the primary metabolite BZG791 in the feces. About 2% of an oral dose is eliminated in the urine as unchanged drug and 7.1% as the primary metabolite BZG791. In total 81% of an oral dose is eliminated in the feces and 14% is eliminated in the urine. The apparent volume of distribution at steady state is 114L. The mean apparent oral clearance was 39.0L/h. The predicted clearance is 9.2L/hr under fed conditions. Metabolism / Metabolites Alpelisib is metabolized by hydrolysis reactions to form the primary metabolite. It is also metabolized by CYP3A4. The full metabolism of Alpelisib has yet to be determined but a series of reactions have been proposed. The main metabolic reaction is the substitution of an amine group on alpelisib for a hydroxyl group to form a metabolite known as M4 or BZG791. Alpelisib can also be glucuronidated to form the M1 and M12 metabolites. Biological Half-Life The mean half life of alprelisib is 8 to 9 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In the prelicensure clinical trials of alpelisib in patients with cancer, liver test abnormalities were frequent although usually transient, asymptomatic, and mild-to-moderate in severity. Some degree of ALT elevation arose in up to 44% of alpelisib- and fulvestrant-treated patients, but were above 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) in only 3% to 4%. The aminotransferase elevations rarely necessitated dose modifications or interruptions, and only slightly lower rates of enzyme elevations occurred in patients taking fulvestrant without alpelisib. In these trials that enrolled less than 1000 patients, there were several reports of marked serum aminotransferase elevations that led to early discontinuation. However, the nature and clinical features of the liver injury were not provided and there were no cases of clinically apparent liver injury. Skin rashes were also common with alpelisib therapy, and patients are often given prophylactic antihistamines which appear to result in fewer and milder rashes. However, moderate-to-severe rash can occur and some are accompanied by drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic signs (DRESS) syndrome, some degree of liver injury (usually anicteric and asymptomatic) being a part of the manifestations. Likelihood score: E* (unproven but suspected rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on alpelisib during breastfeeding. The manufacturer recommends that breastfeeding be discontinued during alpelisib therapy and for 1 week after the final dose. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Alpelisib is 89% protein bound. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
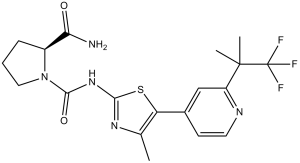
Pharmacodynamics
Alpelisib does not prolong the QTcF interval. Patients taking alpelisib experience a dose dependent benefit from treatment with a 51% advantage of a 200mg daily dose over a 100mg dose and a 22% advantage of 300mg once daily over 150mg twice daily. This suggests patients requiring a lower dose may benefit from twice daily dosing. (2S)-N1-[4-methyl-5-[2-(1,1,1-trifluoro-2-methylpropan-2-yl)-4-pyridinyl]-2-thiazolyl]pyrrolidine-1,2-dicarboxamide is a proline derivative. Alpelisib is a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor with potent antitumor activity. It works by selectively inhibiting class I PI3K p110α, which is the catalytic subunit of PI3K, a lipid kinase that plays a role in various biological processes, including proliferation, survival, differentiation, and metabolism. Alpelisib was designed to target this enzyme that appears to be mutated at a rate of nearly 30% in human cancers, leading to hyperactivation. There are several isoform-specific PI3K inhibitors that are under clinical development or currently approved, such as [idelalisib] used for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Approved by the FDA in May 2019, alpelisib is the first approved PI3K inhibitor indicated for the treatment of hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative, PIK3CA-mutated, advanced or metastatic breast cancer in combination with [fulvestrant] for postmenopausal women and male patients. To initiate alpelisib therapy, it is required that the presence of a PIK3CA mutation in the tissue and/or liquid biopsy sample collection should be confirmed via FDA-approved diagnostic tests. Alpelisib is marketed under the trade name Piqray and is available as oral tablets. Studies evaluating the therapeutic effectiveness of alpelisib in other cancers, such as ovarian cancer and colorectal cancer, are under ongoing investigations. Alpelisib was granted FDA approval on 24 May 2019. In April 2022, the FDA granted the use of alpelisib in the treatment of PIK3CA-Related Overgrowth Spectrum (PROS) in adults and children who require systemic therapy. Alpelisib is an oral selective inhibitor of the phosphoinositol-3-kinase (PIK3) which is mutated in several forms of solid tumors and is approved for use in specific forms of advanced or metastatic breast cancer. Serum aminotransferase elevations are common during alpelisib therapy but clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice has not been reported with its use and must be rare, if it occurs at all. Alpelisib is an orally bioavailable phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor with potential antineoplastic activity. Alpelisib specifically inhibits PI3K in the PI3K/AKT kinase (or protein kinase B) signaling pathway, thereby inhibiting the activation of the PI3K signaling pathway. This may result in inhibition of tumor cell growth and survival in susceptible tumor cell populations. Activation of the PI3K signaling pathway is frequently associated with tumorigenesis. Dysregulated PI3K signaling may contribute to tumor resistance to a variety of antineoplastic agents. ALPELISIB is a small molecule drug with a maximum clinical trial phase of IV (across all indications) that was first approved in 2019 and has 5 approved and 17 investigational indications. Open Targets Activating mutations in HER2 (ERBB2) drive the growth of a subset of breast and other cancers and tend to co-occur with HER3 (ERBB3) missense mutations. The HER2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor neratinib has shown clinical activity against HER2-mutant tumors. To characterize the role of HER3 mutations in HER2-mutant tumors, we integrate computational structural modeling with biochemical and cell biological analyses. Computational modeling predicts that the frequent HER3E928G kinase domain mutation enhances the affinity of HER2/HER3 and reduces binding of HER2 to its inhibitor neratinib. Co-expression of mutant HER2/HER3 enhances HER2/HER3 co-immunoprecipitation and ligand-independent activation of HER2/HER3 and PI3K/AKT, resulting in enhanced growth, invasiveness, and resistance to HER2-targeted therapies, which can be reversed by combined treatment with PI3Kα inhibitors. Our results provide a mechanistic rationale for the evolutionary selection of co-occurring HER2/HER3 mutations and the recent clinical observations that HER3 mutations are associated with a poor response to neratinib in HER2-mutant cancers.[1] Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase α (PI3Kα) is a therapeutic target of high interest in anticancer drug research. On the basis of a binding model rationalizing the high selectivity and potency of a particular series of 2-aminothiazole compounds in inhibiting PI3Kα, a medicinal chemistry program has led to the discovery of the clinical candidate NVP-BYL719. [2] Somatic PIK3CA mutations are frequently found in solid tumors, raising the hypothesis that selective inhibition of PI3Kα may have robust efficacy in PIK3CA-mutant cancers while sparing patients the side-effects associated with broader inhibition of the class I phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) family. Here, we report the biologic properties of the 2-aminothiazole derivative NVP-BYL719, a selective inhibitor of PI3Kα and its most common oncogenic mutant forms. The compound selectivity combined with excellent drug-like properties translates to dose- and time-dependent inhibition of PI3Kα signaling in vivo, resulting in robust therapeutic efficacy and tolerability in PIK3CA-dependent tumors. Novel targeted therapeutics such as NVP-BYL719, designed to modulate aberrant functions elicited by cancer-specific genetic alterations upon which the disease depends, require well-defined patient stratification strategies in order to maximize their therapeutic impact and benefit for the patients. Here, we also describe the application of the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia as a preclinical platform to refine the patient stratification strategy for NVP-BYL719 and found that PIK3CA mutation was the foremost positive predictor of sensitivity while revealing additional positive and negative associations such as PIK3CA amplification and PTEN mutation, respectively. These patient selection determinants are being assayed in the ongoing NVP-BYL719 clinical trials.[3] |
| 分子式 |
C19H22F3N5O2S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
441.47
|
| 精确质量 |
441.144
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 51.69; H, 5.02; F, 12.91; N, 15.86; O, 7.25; S, 7.26
|
| CAS号 |
1217486-61-7
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Alpelisib hydrochloride;1584128-91-5
|
| PubChem CID |
56649450
|
| 外观&性状 |
white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 折射率 |
1.587
|
| LogP |
-0.02
|
| tPSA |
133.93
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
30
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
663
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
S1C(=C(C([H])([H])[H])N=C1N([H])C(N1C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[C@@]1([H])C(N([H])[H])=O)=O)C1C([H])=C([H])N=C(C=1[H])C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])C(F)(F)F
|
| InChi Key |
STUWGJZDJHPWGZ-LBPRGKRZSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C19H22F3N5O2S/c1-10-14(11-6-7-24-13(9-11)18(2,3)19(20,21)22)30-16(25-10)26-17(29)27-8-4-5-12(27)15(23)28/h6-7,9,12H,4-5,8H2,1-3H3,(H2,23,28)(H,25,26,29)/t12-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(2S)-1-N-[4-methyl-5-[2-(1,1,1-trifluoro-2-methylpropan-2-yl)pyridin-4-yl]-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]pyrrolidine-1,2-dicarboxamide
|
| 别名 |
Alpelisib; NVP-BYL-719; 1217486-61-7; BYL-719; BYL719; Piqray; Vijoice; NVP-BYL719; Alpelisib (BYL719); NVP-BYL719; NVP-BYL 719; BYL-719; BYL719; BYL 719
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 5 mg/mL (11.33 mM) (饱和度未知) in 5% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 50% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
*生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 2.08 mg/mL (4.71 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;再向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;然后加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.71 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.71 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入900 μL 玉米油中,混合均匀。 配方 5 中的溶解度: 30% PEG400+0.5% Tween80+5% Propylene glycol : 30mg/mL 配方 6 中的溶解度: 10 mg/mL (22.65 mM) in 0.5% MC 0.5% Tween-80 (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 配方 7 中的溶解度: 10 mg/mL (22.65 mM) in 1% CMC 0.5% Tween-80 (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2652 mL | 11.3258 mL | 22.6516 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4530 mL | 2.2652 mL | 4.5303 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2265 mL | 1.1326 mL | 2.2652 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Targeted Therapy Directed by Genetic Testing in Treating Patients With Locally Advanced or Advanced Solid Tumors, The ComboMATCH Screening Trial
CTID: NCT05564377
Phase: Phase 2 Status: Recruiting
Date: 2024-11-21
 PK/PD/efficacy relationship of NVP-BYL719 in PI3Kα-dependent tumor mouse modelsin vivo.Mol Cancer Ther.2014 May;13(5):1117-29. |
|---|
 Determination of NVP-BYL719 safety profile compared with pan-class I PI3K inhibitors.Mol Cancer Ther.2014 May;13(5):1117-29. |
 PTENmutation andPIK3CAamplification/copy number modulate response to NVP-BYL719.Mol Cancer Ther.2014 May;13(5):1117-29. |
 A, genetic alterations inPIK3CApredict NVP-BYL719in vivoefficacy.B, PDX models carrying aPIK3CAmutation and/or amplification were established by implanting surgical tumor tissues from treatment-naïve cancer patients into athymic mice.Mol Cancer Ther.2014 May;13(5):1117-29. |
|---|
PIK3CAmutation is the top positive predictor for NVP-BYL719 sensitivity. A, NVP-BYL719 sensitivity profile. Scatter plot showingAmax(%) by EC50values expressed in μmol/L of NVP-BYL719 in cell viability assays assessed on 474 cancer cell lines.Mol Cancer Ther.2014 May;13(5):1117-29. |
 Identification of selectivity index of small molecule inhibitors forPIK3CAmutant versusPIK3CAwild-type (WT) cell line populations across ∼1,000 different compounds.Mol Cancer Ther.2014 May;13(5):1117-29. |