| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
Human Endogenous Metabolite; EP
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在 VEGF (20 ng/mL) 存在的情况下,前列腺素 E1 (1 nM-10 μM;48 小时)浓度依赖性降低 HUVEC 增殖(高达 100% 的抑制),IC50 为 400 nM[2]。前列腺素E1 (1-5 μM;12-18小时)以浓度悬浮方式抑制VEGF诱导的HUVEC迁移,IC 为 50 500 nM[2]。 前列腺素E1 (1-5 μM;12-18小时)悬浮细胞生成[2]前列腺素E1 (0.01-10 μM;20分钟) 增加HUVECs中的细胞内cAMP水平[2]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
支架素 E1 (20 ng/动物/天;皮下注射 4 天) 显着抑制小鼠 FGF 诱导的血管生成[2]。 动物模型:C57/bl6 雌性小鼠(6-8 周)注射补充有 aFGF 的 Matrigel和肝素[2] 剂量:20 ng/天/动物 给药方法:皮下放置微型泵 4 天 结果:明显减少新血管形成过程。
|
| 酶活实验 |
前列腺素受体的稳定表达和配体结合分析[1]
先前已经描述了稳定表达DP、EP1、EP2、EP3、EP4和IP受体的CHO细胞系(Sugimoto等人,1992;Watabe等人,1993;Hirata等人,1994;Namba等人,1994,Nishigaki等人,1995;Katsuyama等人,1995)。表达TP和FP受体的细胞系的建立如前所述(Sugimoto等人,1992)。Brie′y、FP受体cDNA的2.4kb EcoRI片段(Sugimoto等人,1994)或TP受体cDNA ML36的EcoRI片段被亚克隆到pdKCR-dhfr中,pdKCR-dhfr是一种真核表达载体,含有小鼠二氢叶酸还原酶基因作为选择标记。然后通过脂质转染法将质粒转染到二氢叶酸还原酶活性低的CHO-dhfr7细胞中。在缺乏核糖核苷酸和脱氧核糖核苷酸的Eagle培养基(a-MEM)的amodi®阳离子中选择表达FP或TP受体以及二氢叶酸还原酶的细胞群。然后通过单细胞克隆分离表达每种受体的克隆细胞系。每条CHO细胞系在含有10%胎牛血清的aMEM中培养至接近有效。用不含二价阳离子的Dulbecco's磷酸盐缓冲盐水(PBS(7))洗涤细胞后,用含有5mM EDTA的PBS(7。通过离心将细胞制成颗粒,并在含有25 mM Tris.HCl、pH 7.5、10 mM MgCl2、1 mM EDTA和0.1 mM苯甲基磺酰脲的0.25 M蔗糖中均质化。如前所述制备膜(Namba等人,1994)。TP、IP、DP、FP受体和EP受体的四种亚型分别被测定为[3H]-S-145、[3H]-iloprost、[3H]-PGD2、[3H][PGF2a和[3H]-PGE2结合活性。Scatchard分析在含有25 mM Tris.HCl、pH 7.0、10 mM MgCl2、1mM EDTA、0.1 mM苯甲基磺酰脲、每种CHO细胞膜100 mg蛋白质和总体积为200 ml的各种浓度的相应放射性配体的测定混合物中进行。Nonspeci®c结合被确定为在非标记配体超过相应放射性配体500倍的情况下的结合。除了用表达DP受体的膜进行的实验外,在308℃下孵育60分钟;这些实验在48℃下进行120分钟,因为在308℃下孵育会导致[3H]-PGD2与该膜的高非特异性®c结合(Hirata等人,1994)。通过加入冰冷的5mM Tris-HCl(pH 7.0)终止孵育。通过Whatman GF/C®过滤器真空过滤混合物。用上述步骤洗涤®lter五次,但EP1受体结合测定除外,该测定洗涤两次。然后在Triton甲苯闪烁体中测定®过滤器上的放射性(Ushikubi等人,1989)。在置换实验中,在每种放射性配体存在的情况下,在测定混合物中包含不同浓度的化合物,其使用浓度是Scatchard分析获得的Kd值的两倍。 |
| 细胞实验 |
增殖试验[2]
将HUVEC以2×104个细胞孔-1的密度铺在96孔板上,用PGE1/α-环糊精预处理30分钟,然后在药物存在下用20 ng ml-1 VEGF或20 ng ml-1bFGF刺激48小时。在培养的最后6小时加入[3H]-胸苷(1μCi孔-1;比活2 Ci mmol-1)。在10%TCA提取和NaOH增溶后,测量了与TCA不溶部分相关的放射性。 体外血管生成试验[2] 血管样结构的形成是在从Engelbreth Holm Swarm小鼠肉瘤中提取的增溶基底膜制剂(Matrigel)上评估的,该制剂常用于评估体外血管生成(综述见Baatout,1997;Benelli&Albini,1999)。24孔板涂有Matrigel,细胞以5×104个细胞孔-1的密度接种在聚合基质上。VEGF(10 ng ml-1)和bFGF(10 ng ml-1)被用作血管生成刺激物。在培养过程中,PGE1/α-环糊精存在于培养基中。在37°C的5%CO2中放置12-18小时后,将细胞固定在4%多聚甲醛中,并使用带有PCO SuperVGA SensiCam的Axiovert显微镜采集图像。通过使用美国国立卫生研究院(NIH)图像程序测量每个井的五个随机区域中管子所占的面积来量化脐带形成的程度。 细胞内cAMP的测定[2] HUVEC以1-1.5×105个细胞孔-1的密度铺在24孔板上,在199培养基中用1 mm异丁基甲基黄嘌呤(IBMX)预孵育10分钟,然后在37°C下用PGE1/α-环糊精刺激20分钟。通过抽吸培养基然后加入0.5 ml冷无水乙醇来终止反应。在-20°C下冷冻过夜后,干燥乙醇上清液,用商业试剂盒评估细胞内cAMP水平。 |
| 动物实验 |
C57/bl6 female mice (6-8 weeks) were injected with Matrigel supplemented with aFGF and heparin
20 ng/day/animal Minipump placed subcutaneously for 4 days PGE1/α-cyclodextrin (20 ng day−1) was systemically administered by means of osmotic pumps (Alzet, Charles River) implanted subcutaneously in the back of the animals, posterior to the scapulae. The pumps continuously delivered the drug at controlled rates, with a pumping rate of 0.5 μl h−1. The control animals were implanted with the same pumps, filled with saline. After 4 days, mice were killed, the Matrigel pellets were collected and their haemoglobin content was evaluated using a Drabkin reagent kit. Animal care was in accordance with the Italian State regulation governing the care and the treatment of laboratory animals (permission n° 14/2001).[2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
In patients with erectile dysfunction given 20 μg of alprostadil intracavernously, the systemic plasma concentrations of prostaglandin E1 increased from a baseline of 0.8 pg/mL to a Cmax of 16.8 pg/mL (corrected for baseline). The tmax and AUC for this group of patients were 4.8 min and 173 pg⋅min/mL, respectively. In patients given 20 μg of alprostadil intravenously, AUC was similar to the one detected in patients that received alprostadil intracavernously (174 pg⋅min/mL); however, they had a higher tmax (25.5 min) and a lower Cmax (7.09 pg/mL). Compared to the same dose given by a short-term intravenous infusion, the absolute bioavailability of alprostadil estimated from systemic exposure was about 98%. Following the degradation of alprostadil by beta- and omega-oxidation, metabolites are excreted primarily by the kidney, and excretion is essentially complete within 24 hours after administration (92%). Approximately 88% and 12% of alprostadil metabolites are excreted through urine and feces, respectively, over 72 hours. Alprostadil and its metabolites are not retained in tissues, and unchanged alprostadil has not been detected in urine. The volume of distribution of alprostadil has yet to be determined. In patients with erectile dysfunction given an intravenous infusion of alprostadil (20 μg), the total body clearance was 115 L/min. Metabolism / Metabolites Alprostadil is rapidly metabolized in the human body. Following intracavernous administration, alprostadil is metabolized in the corpus cavernosum, and a smaller portion is absorbed from the penis into systemic circulation. After intravenous or arterial administration, alprostadil is metabolized and distributed throughout the entire body except for the central nervous system. As much as 60-90% of the circulating alprostadil may be metabolized in the lungs through first-pass pulmonary elimination, in a process known as beta- and omega-oxidation. The enzymatic oxidation of the C15-hydroxy group of alprostadil leads to the formation of 15-keto-PGE1, while the reduction of the C13, 14-double bond produces 15-keto-PGE0, and 13,14-dihydro-PGE1 (PGE0). The 15-keto metabolites are inactive, but the PGE0 metabolite has a similar potency to alprostadil in isolated animal organs. The major metabolite of alprostadil is 15-keto-PGE0. Biological Half-Life In healthy adults and neonates given a single intravenous dose of alprostadil, half-life goes from 5 to 10 minutes. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
Alprostadil is bound in plasma primarily to albumin (81% bound) and, to a lesser extent, alpha-globulin IV-4 fraction (55% bound). |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Prostaglandin E1 is a prostaglandins E. It has a role as a platelet aggregation inhibitor, a vasodilator agent, an anticoagulant and a human metabolite. It is a conjugate acid of a prostaglandin E1(1-).
Alprostadil is a chemically-identical synthetic form of prostaglandin E1 (PGE1), a potent vasodilator produced endogenously. In 1996, the FDA approved the use of alprostadil, administered either with an intracavernosal injection or an intraurethral suppository, for the treatment of erectile dysfunction, and it is used in men for whom oral treatment is either contraindicated or ineffective. After administration, alprostadil promotes smooth muscle relaxation of the corpus cavernosal. Alprostadil is also used in neonatal patients with congenital heart defects that depend on a patent ductus for survival until corrective or palliative surgery can be performed. This drug causes vasodilation by directly affecting vascular and ductus arteriosus (DA) smooth muscle, preventing or reversing the functional closure of the DA that occurs shortly after birth. This results in increased pulmonary or systemic blood flow in infants. Alprostadil is a Prostaglandin Analog and Prostaglandin E1 Agonist. The mechanism of action of alprostadil is as a Prostaglandin Receptor Agonist. The physiologic effect of alprostadil is by means of Genitourinary Arterial Vasodilation and Venous Vasodilation. Alprostadil has been reported in Populus balsamifera, Populus candicans, and other organisms with data available. Alprostadil is the naturally occurring prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) which displays a variety of pharmacologic actions. Alprostadil is a potent vasodilator agent that increases peripheral blood flow, inhibits platelet aggregation, and induces bronchodilation. Used in the treatment of erectile dysfunction, this agent produces corporal smooth muscle relaxation by binding to PGE receptors, resulting in the activation of adenylate cyclase and the subsequent accumulation of 3'5'-cAMP. A potent vasodilator agent that increases peripheral blood flow. Drug Indication Alprostadil is indicated for palliative, not definitive, therapy to temporarily maintain the patency of the ductus arteriosus until corrective or palliative surgery can be performed in neonates who have congenital heart defects and who depend upon the patent ductus for survival. It is also indicated for the treatment of erectile dysfunction due to neurogenic, vasculogenic, psychogenic, or mixed etiology, and as an adjunct to other diagnostic tests in the diagnosis of erectile dysfunction. Mechanism of Action Alprostadil is a smooth muscle relaxant that promotes vasodilation and platelet aggregation inhibition. In neonatal patients with ductus arteriosus patency, alprostadil relaxes the ductus arteriosus (DA) smooth muscle, preventing or reversing the functional closure of the DA that occurs shortly after birth. This results in increased pulmonary or systemic blood flow in infants. Alprostadil appears to be most effective within 96 hours after birth since the DA rapidly loses its responsiveness to alprostadil. When administered by intracavernosal injection or as an intraurethral suppository, alprostadil acts locally to relax the trabecular smooth muscle of the corpora cavernosa and the cavernosal arteries. Swelling, elongation, and rigidity of the penis result when arterial blood rapidly flows into the corpus cavernosum to expand the lacunar spaces. The entrapped blood reduces the venous blood outflow as sinusoids compress against the tunica albuginea leading to penile rigidity. This is referred to as the corporal veno-occlusive mechanism. Pharmacodynamics Prostaglandin E1 is produced endogenously to relax vascular smooth muscle and cause vasodilation. As a synthetic form of prostaglandin E1, alprostadil has the same pharmacodynamic effects. Alprostadil inhibits platelet aggregation, has anti-inflammatory effects, interferes with immune responses, and stimulates factor X, a blood coagulation enzyme. In adult males, the use of alprostadil may lead to prolonged erection and priapism, penile fibrosis, hypotension, and injection site bleeding. In patients treated up to 24 months with alprostadil, the incidence of prolonged erections (>4 hours long) was 4% of all, and the incidence of priapism (erections greater than 6 hours in duration) was <1%. Patients with preexisting cardiovascular disease treated with alprostadil may also have higher cardiac risk. Neonates with congenital heart defects treated with alprostadil may experience apnea. Apnea is experienced by 10-12% of neonates and is more common in those weighing less than 2 kg at birth. The administration of alprostadil to neonates may also result in gastric outlet obstruction secondary to antral hyperplasia. |
| 分子式 |
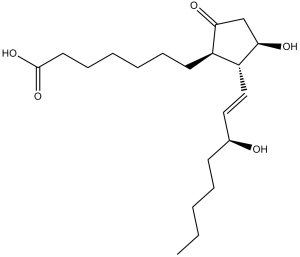
C20H34O5
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
354.48
|
|
| 精确质量 |
354.24
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 67.77; H, 9.67; O, 22.57
|
|
| CAS号 |
745-65-3
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Prostaglandin E1-d4;211105-33-8;Prostaglandin E1-d9;2342573-59-3; 745-65-3 (free acid); 27930-45-6 (sodium); 217182-28-0 (isopropyl ester); 35900-16-4 (ethyl ester)
|
|
| PubChem CID |
5280723
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.1±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
529.3±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
115-116 °C
|
|
| 闪点 |
288.0±26.6 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±3.2 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.546
|
|
| LogP |
2.24
|
|
| tPSA |
94.83
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
13
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
25
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
432
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
4
|
|
| SMILES |
CCCCC[C@H](O)/C=C/[C@@H]1[C@H](C(C[C@H]1O)=O)CCCCCCC(O)=O
|
|
| InChi Key |
GMVPRGQOIOIIMI-DWKJAMRDSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C20H34O5/c1-2-3-6-9-15(21)12-13-17-16(18(22)14-19(17)23)10-7-4-5-8-11-20(24)25/h12-13,15-17,19,21,23H,2-11,14H2,1H3,(H,24,25)/b13-12+/t15-,16+,17+,19+/m0/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
7-[(1R,2R,3R)-3-hydroxy-2-[(E,3S)-3-hydroxyoct-1-enyl]-5-oxocyclopentyl]heptanoic acid
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.05 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.05 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.05 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.05 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% EtOH + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 EtOH 储备液加入400 μL PEG300 中,混匀;再向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;然后加入450 μL 生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 5 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.05 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% EtOH + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100μL 25.0mg/mL澄清EtOH储备液加入到900μL 20%SBE-β-CD生理盐水中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8210 mL | 14.1052 mL | 28.2103 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5642 mL | 2.8210 mL | 5.6421 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2821 mL | 1.4105 mL | 2.8210 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT00610051 | Not yet recruiting | Drug: Alfuzosin | Heart Failure | Biopeutics Co., Ltd | October 2023 | Phase 3 |
| NCT05475717 | Completed | Drug: Alprostadil liposome injection |
Contrast-induced Acute Kidney Injury |
CSPC ZhongQi Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd. |
October 20, 2022 | Phase 2 |
| NCT00324948 | Completed | Drug: Topical alprostadil (PGE-1) |
Sexual Dysfunction, Physiological | VIVUS LLC | September 2004 | Phase 2 |
| NCT02889822 | Completed | Drug: Alprostadil Liposomes for Injection |
Cardiovascular Diseases | Guangzhou Yipinhong Pharmaceutical CO.,LTD |
March 2010 | Phase 1 |
| NCT02628106 | Completed | Drug: Lipo-PGE1 | Diabetic Nephropathy | West China Hospital | December 2015 | Phase 4 |
|
|
|