| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
c-Met(H1094R) (Ki = 0.5 nM); c-Met(V1092I) (Ki = 1.1 nM); c-Met(Human) (Ki = 1.2 nM); c-Met(Mouse) (Ki = 2.0 nM); c-Met(D1228H) (Ki = 2.2 nM)
AMG-458 is a highly selective inhibitor of c-MET (mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor) tyrosine kinase, with no significant activity against other kinases. Specific IC50 values: - Recombinant human c-MET kinase: IC50 = 1.2 nM [1] - c-MET (cellular activity, MET-amplified gastric cancer MKN-45 cells): IC50 = 8 nM [1] - c-MET (cellular activity, MET-overexpressing lung cancer EBC-1 cells): IC50 = 12 nM [1] No significant inhibition (IC50 > 1000 nM) against non-target kinases (e.g., EGFR, VEGFR2, PDGFRα, ALK, c-Kit) [1] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
AMG 458 还抑制 PC3 和 CT26 细胞中 HGF 介导的 c-Met 磷酸化,IC50 分别为 60 和 120 nM。据观察,在缺乏 NADPH 的情况下,AMG 458 可与大鼠和人类的肝微粒体蛋白共价结合。据信 AMG 458 与蛋白质中的硫醇基团反应,产生甲氧基喹啉硫醚缀合物。最近的一项研究表明,AMG 458 消除了 H441 中 c-Met 的组成型磷酸化。AMG 458 减弱了 A549 中 c-Met 的基础和 HGF 诱导的磷酸化。发现放射治疗和 AMG 458 治疗相结合通过降低 p-Akt 和 p-Erk 水平来协同增加 H441 细胞系的凋亡,但在 A549 中则不然。激酶测定:AMG 458 是一种有效的 c-Met 抑制剂,Ki 为 1 nM ~ 2.0 nM。研究发现 AMG-458 可显着抑制 NIH3T3/TPR-Met 和 U-87 MG 异种移植模型中的肿瘤生长,且对体重没有不利影响。细胞测定:AMG 458 还抑制 PC3 和 CT26 细胞中 HGF 介导的 c-Met 磷酸化,IC50 分别为 60 和 120 nM。
1. 对MET驱动肿瘤的抗增殖活性: - AMG-458抑制MET扩增胃癌细胞:MKN-45(IC50 = 8 nM)、NCI-N87(IC50 = 10 nM)[1] - 对MET过表达肺癌细胞:EBC-1(IC50 = 12 nM)、H441(IC50 = 15 nM)[1] - 对MET低表达/阴性细胞(A549肺癌、MCF-7乳腺癌),IC50 > 1000 nM(无活性)[1] 2. 信号通路抑制: - 用AMG-458(30 nM,处理1.5小时)处理MKN-45细胞后,p-c-MET(Tyr1234/1235)降低96%,下游p-AKT(Ser473)和p-ERK1/2(Thr202/Tyr204)抑制率分别为93%和91%(Western blot检测)[1] 3. 放射增敏活性: - 在EBC-1细胞中,AMG-458(20 nM)+放疗(2 Gy)使细胞存活率降至28%(单独放疗为55%,单独AMG-458为72%)[3] - 联合处理使凋亡率(Annexin V阳性细胞)从单独放疗的18.5%升至42.3% [3] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
AMG 458 在小鼠、大鼠、狗、猴子和人的肝微粒体中代谢稳定,内在清除率较低(Clint:分别<5、62、8、8、18 (μL/min)/mg)。口服给药时,AMG 458 在所有测试物种中均实现了非常高的生物利用度。口服 AMG 458 可抑制 HGF 介导的 c-Met 磷酸化,其 ED90 约为 30 mg/kg,6 小时时相关血浆暴露约为 15 μM。 AMG 458 在 NIH3T3/TPR-Met 和 U-87 MG 异种移植模型中以 30 和 100 mg/kg qd 以及 30 mg/kg bid 的剂量显着抑制肿瘤生长,对体重没有不利影响。某些器官中高浓度的 AMG 458 可能会通过氧化应激产生毒性。
1. MET扩增胃癌异种移植模型(MKN-45,文献[1]): - 6~8周龄雌性裸鼠口服AMG-458(25 mg/kg、50 mg/kg,每日1次,连续21天)。 - 25 mg/kg组肿瘤体积较溶媒组减少78%;50 mg/kg组减少90%,中位生存期从对照组26天延长至58天 [1] 2. 放疗联合异种移植模型(EBC-1,文献[3]): - 小鼠口服AMG-458(50 mg/kg,每日)+放疗(4 Gy,每周1次,共3次)。 - 肿瘤体积抑制率:联合组92%(单独放疗58%,单独AMG-45880%);肿瘤重量减少94%(联合组)[3] |
| 酶活实验 |
AMG 458 的 Ki 为 1 nM ~ 2.0 nM,使其成为强效的 c-Met 抑制剂。在 NIH3T3/TPR-Met 和 U-87 MG 异种移植模型中,发现 AMG-458 显着抑制肿瘤生长,而不对体重产生负面影响。
重组c-MET激酶活性实验: 1. 制备总体积50 μL的反应体系:50 mM HEPES缓冲液(pH 7.4,含10 mM MgCl₂、1 mM DTT、0.01% BSA)、重组人c-MET激酶结构域(30 ng)、AMG-458(0.0005~100 nM)、10 μM [γ-³²P]ATP、20 μM c-MET特异性肽底物(序列:CGGGYVVPQPQLPYPGENL)。 2. 30°C孵育45分钟,启动激酶反应。 3. 加入25 μL 30%三氯乙酸(TCA)终止反应,冰上孵育15分钟以沉淀磷酸化肽。 4. 取50 μL反应液转移至P81磷酸纤维素滤板,用0.5% TCA(每孔500 μL)洗涤滤板3次,去除未结合的ATP。 5. 50°C烘干滤板30分钟,每孔加入50 μL闪烁液,液体闪烁计数器测定放射性强度。 6. 与溶媒对照组比较计算抑制率,数据拟合四参数模型获得IC50(1.2 nM)[1] |
| 细胞实验 |
AMG 458 抑制 PC3 和 CT26 细胞中 HGF 介导的 c-Met 磷酸化的 IC50 分别为 60 和 120 nM。
1. 细胞增殖实验(MTT法,文献[1]): - 将靶细胞(MKN-45、EBC-1)以5×10³细胞/孔接种于96孔板,在含10%胎牛血清、1%青霉素-链霉素的RPMI 1640培养基中,37°C、5% CO₂孵育过夜。 - 向每孔加入AMG-458(0.01~1000 nM,每个浓度3个复孔),设溶媒对照(0.1% DMSO)。 - 孵育72小时后,每孔加入10 μL MTT试剂(5 mg/mL PBS溶液),继续孵育4小时。 - 吸弃培养基,每孔加入150 μL DMSO溶解甲臜结晶,振荡10分钟,酶标仪在570 nm处测定吸光度,通过GraphPad Prism计算IC50 [1] 2. 放射增敏集落形成实验: - EBC-1细胞以2×10³细胞/孔接种于6孔板,孵育24小时。 - AMG-458(20 nM)处理2小时后,暴露于0~6 Gy放疗。 - 孵育14天,0.1%结晶紫染色,计数直径>50 μm的集落。 - 存活分数(SF2):联合组0.28(单独放疗0.55)[3] |
| 动物实验 |
NIH-3T3/TPR-Met model and U-87 MG human glioblastoma xenograft model.
10, 30, 100 mg/kg. Orally q.d. or b.i.d. 1. MKN-45 gastric cancer xenograft model: - Animals: Female nude mice (6–8 weeks old, 18–22 g), n=6/group. - Tumor induction: Subcutaneous injection of 5×10⁶ MKN-45 cells (0.2 mL PBS/Matrigel 1:1) into right flank. - Drug formulation: AMG-458 dissolved in 0.5% methylcellulose + 0.2% Tween 80 (final DMSO <1%). - Administration: Oral gavage 25 mg/kg, 50 mg/kg, daily for 21 days; control receives vehicle. - Monitoring: Measure tumor volume (length×width²/2) every 2 days, record weight weekly, track survival [1] 2. EBC-1 radiotherapy combination model: - Animals: Female nude mice (6–8 weeks old), n=6/group. - Tumor induction: Subcutaneous injection of 4×10⁶ EBC-1 cells (0.2 mL PBS/Matrigel 1:1). - Administration: AMG-458 (50 mg/kg, oral, daily) + radiotherapy (4 Gy, once weekly for 3 weeks, targeted to tumor); monotherapy groups: AMG-458 alone or radiotherapy alone; control receives vehicle. - Endpoint: Euthanize mice, excise tumors, weigh, analyze proliferation (Ki-67 staining) [3] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
1. Oral pharmacokinetics in mice:
- Male C57BL/6 mice (n=3/time point) receive AMG-458 (50 mg/kg, oral). - Collect plasma at 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 24 hours post-dosing, centrifuge (3500 rpm, 4°C, 10 minutes) to separate plasma. - Analyze via LC-MS/MS (mobile phase: acetonitrile/water with 0.1% formic acid; column: C18). - Key parameters: Cmax = 1120 ng/mL, Tmax = 1.0 hour, AUC0-24h = 6200 ng·h/mL, t1/2 = 8.2 hours, oral bioavailability = 52% [2] 2. Metabolism: - In mouse liver microsomes: AMG-458 (1 μM) is metabolized to 3 major metabolites (M1: N-demethylation; M2: phenyl hydroxylation; M3: piperazine oxidation); metabolic half-life = 5.6 hours [2] - Tissue distribution (2 hours post 50 mg/kg oral dose): Liver (3850 ng/g), tumor (3220 ng/g), kidneys (2980 ng/g), spleen (2550 ng/g), brain (78 ng/g) [2] 3. Plasma protein binding: - Ultrafiltration assay: AMG-458 (10–1000 ng/mL) in mouse/rat/human plasma, 37°C incubate 1 hour. - Protein binding rate: >99% in all species and concentrations [2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
1. Acute toxicity in mice:
- Male/female C57BL/6 mice (n=3/sex/dose) receive AMG-458 (oral, 200–500 mg/kg). - No mortality at 200/300/400 mg/kg; 500 mg/kg causes transient lethargy (recovers in 48 hours); oral LD50 >500 mg/kg [2] 2. Subacute toxicity (28-day, mice,): - Doses: 25 mg/kg, 50 mg/kg, 75 mg/kg (oral, daily). - 25/50 mg/kg groups: No changes in body weight, serum biochemistry (ALT, AST, creatinine), or hematology (WBC, platelets, hemoglobin). - 75 mg/kg group: Mild ALT elevation (1.4× control); no histopathological damage to liver/kidneys [2] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
1. Therapeutic background: AMG-458 is a potent, selective c-MET tyrosine kinase inhibitor developed for MET-driven solid tumors (gastric cancer, non-small cell lung cancer) and as a radiosensitizer to enhance radiotherapy efficacy [1][3]
2. Mechanism of action: It competitively binds to c-MET’s ATP pocket, inhibiting c-MET autophosphorylation and downstream PI3K-AKT/ERK pathways. When combined with radiotherapy, it blocks DNA repair in tumor cells, enhancing radiosensitivity [1][3] 3. Metabolism feature: Its major metabolites (M1–M3) show no c-MET inhibitory activity, indicating low off-target metabolic risk [2] 4. Research significance: It validated the feasibility of c-MET inhibitors as radiosensitizers, providing a new strategy for treating radioresistant MET-driven tumors [3] |
| 分子式 |
C30H29N5O5
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
539.58
|
|
| 精确质量 |
539.216
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 66.78; H, 5.42; N, 12.98; O, 14.83
|
|
| CAS号 |
913376-83-7
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
24764449
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Off-white to pink solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.672
|
|
| LogP |
3.02
|
|
| tPSA |
123.99
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
40
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
951
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
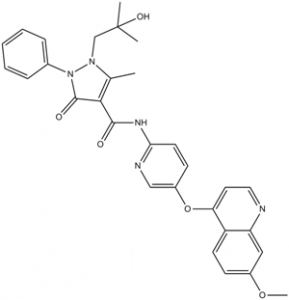
| SMILES |
O=C(C1=C(C)N(CC(C)(C)O)N(C2C=CC=CC=2)C1=O)NC1C=CC(OC2C3C(=CC(=CC=3)OC)N=CC=2)=CN=1
|
|
| InChi Key |
GLBZSOQDAOLMGC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C30H29N5O5/c1-19-27(29(37)35(20-8-6-5-7-9-20)34(19)18-30(2,3)38)28(36)33-26-13-11-22(17-32-26)40-25-14-15-31-24-16-21(39-4)10-12-23(24)25/h5-17,38H,18H2,1-4H3,(H,32,33,36)
|
|
| 化学名 |
1-(2-hydroxy-2-methylpropyl)-N-[5-(7-methoxyquinolin-4-yl)oxypyridin-2-yl]-5-methyl-3-oxo-2-phenylpyrazole-4-carboxamide
|
|
| 别名 |
AMG-458; AMG 458; AMG458
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|---|
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8533 mL | 9.2665 mL | 18.5329 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3707 mL | 1.8533 mL | 3.7066 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1853 mL | 0.9266 mL | 1.8533 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 3688–3691 |
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2008, 21, 2216–2222 |