| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g | |||
| Other Sizes |

| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:阿齐沙坦酯是一种前药,口服后吸收过程中,通过肠道和血浆中的酯水解,迅速转化为活性部分阿齐沙坦 (TAK-536)。阿齐沙坦选择性阻断血管紧张素 II 与血管平滑肌和肾上腺中的 AT1(血管紧张素 II 1 型)受体的结合,从而促进血管舒张并降低醛固酮的作用。 Azilsartan 是一种高度选择性的 AT1 受体拮抗剂,IC50 为 2.6 nM,对 AT1 受体的亲和力是 AT2 受体的 10,000 倍以上,并且对其他心脏受体或离子通道没有表现出亲和力。洗去游离化合物后,阿齐沙坦的抑制作用仍然存在(IC50 值为 7.4 nM)。在基于细胞的测定中,Azilsartan 还抑制血管紧张素 II 诱导的肌醇 1-磷酸 (IP1) 的积累,IC50 值为 9.2 nM,并且这种作用具有抗冲洗作用(IC50 值为 81.3 nM)。激酶测定:放射性配体结合测定是通过使用含有 4.4 至 6.2 fmol 受体/孔(10 μg 膜蛋白/孔)的人 AT1 受体包被的微孔板进行的。将膜包被的孔与含有不同浓度测试化合物的 45 μl 测定缓冲液(50 mM Tris-HCl、5 mM MgCl2、1 mM EDTA 和 0.005% CHAPS,pH 7.4)在室温下孵育。 90 分钟后,将 5 μl 溶解在测定缓冲液中的 125I-Sar1-Ile8-AII(终浓度 0.6 nM)添加到孔中,并将板孵育 5 小时。在每个步骤中,将板在板振荡器上短暂且轻轻地摇动。细胞测定:1-磷酸肌醇积累的测量。用表达人 AT1 的质粒转染 24 小时后,通过将培养基更换为饥饿缓冲液(1 mM CaCl2、0.5 mM MgCl2、4.2 mM KCl、146 mM NaCl、5.5 mM 葡萄糖和 10 mM HEPES,pH 7.3)。然后,将 5 μl/孔溶解在饥饿缓冲液中的测试化合物以指定浓度添加到细胞中,并将它们预处理指定时间。饥饿后两小时,添加 LiCl 至终浓度 50 mM,并添加或不添加 10 nM 血管紧张素 II,并将细胞在 37°C 下进一步孵育指定时间。在清洗实验中,在用血管紧张素 II 刺激之前,用 100 μl/孔的饥饿缓冲液清洗细胞一次,以去除未结合的化合物。使用 IP-One Tb 试剂盒测量肌醇 1-磷酸 (IP1) 的积累。在酶标仪上测量荧光共振能量转移信号。
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在 Koletsky 大鼠中,阿齐沙坦治疗可降低血压、基础血浆胰岛素浓度和稳态模型评估的胰岛素抵抗指数,并抑制口服葡萄糖耐量试验期间血浆葡萄糖和胰岛素浓度的过度升高。 Azilsartan 下调 11β-羟基类固醇脱氢酶 1 型表达。
|
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
During absorption, azilsartan medoxomil is hydrolyzed to azilsartan. The parent drug is not detectable in plasma after oral administration. The absolute bioavailability of azilsartan is estimated to be 60%. Tmax ranges from 1.5 to three hours. Steady-state levels of azilsartan are achieved within five days, and no accumulation in plasma occurs with repeated once-daily dosing. Following oral administration of 14C-labeled azilsartan medoxomil, approximately 55% of radioactivity was recovered in feces and approximately 42% in urine. Of the recovered dose in urine, about 15% was excreted as azilsartan. The volume of distribution of azilsartan is approximately 16 L. In rats, a minimal amount of radiolabelled drug crossed the blood-brain barrier. Azilsartan crossed the placental barrier in pregnant rats and was distributed to the fetus. Renal clearance of azilsartan is approximately 2.3 mL/min. Metabolism / Metabolites After azilsartan medoxomil is hydrolyzed into its active metabolite, azilsartan is metabolized to two primary metabolites, which are pharmacologically inactive. The major metabolite in plasma is metabolite M-II, which is formed via O-dealkylation mediated by CYP2C9. The minor metabolite is metabolite M-I, which is formed via decarboxylation mediated by CYP2C8 and CYP2B6. MII has approximately 50% systemic exposure of azilsartan, and MI has less than 1% systemic exposure of azilsartan. Biological Half-Life The elimination half-life of azilsartan is approximately 11 hours. |
||
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
Azilsartan is >99% bound to human plasma proteins, mainly serum albumin. Protein binding is constant at azilsartan plasma concentrations well above the range achieved with recommended doses. |
||
| 参考文献 |
J Pharmacol Exp Ther.2011 Mar;336(3):801-8;Am J Hypertens.2007 May;20(5):579-86.
|
||
| 其他信息 |
Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamic effects of azilsartan medoxomil are mediated by its active metabolite, azilsartan. Azilsartan inhibits the pressor effects of an angiotensin II infusion in a dose-related manner. At a single 32 mg dose, azilsartan inhibited the maximal pressor effect by approximately 90% at peak plasma concentrations and by 60% at 24 hours after administration. In healthy subjects receiving single and repeated doses of azilsartan medoxomil, plasma angiotensin I and II concentrations and plasma renin activity increased, while plasma aldosterone concentrations decreased. Like other ARBs, azilsartan causes dose-dependent decrease in peripheral resistance and decreases smooth muscle vascular tone. As azilsartan blocks the angiotensin II receptor, the negative regulatory feedback of angiotensin II on renin secretion is inhibited; however, the resulting increased plasma renin activity and angiotensin II circulating levels do not overcome the blood pressure-lowering effect of azilsartan. Blood pressure-lowering effects of antihypertensive agents can be reduced in patients of African descent. However, there are no recommended dosage adjustment of azilsartan on the basis of a patient’s sex, race, or degree of renal or hepatic impairment. Azilsartan medoxomil has negligible effects on serum potassium or sodium levels. Azilsartan does not affect the biosynthesis of angiotensin II nor bradykinin levels. It also does not bind to any ion channels that are involved in cardiovascular regulation. |
| 分子式 |
C30H24N4O8
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
568.53
|
| 精确质量 |
568.159
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 63.38; H, 4.26; N, 9.85; O, 22.51
|
| CAS号 |
863031-21-4
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Azilsartan;147403-03-0;Azilsartan-d5;1346599-45-8;Azilsartan medoxomil monopotassium;863031-24-7
|
| PubChem CID |
135409642
|
| 外观&性状 |
Solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.5±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
748.0±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
406.2±35.7 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.5 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.680
|
| LogP |
5.73
|
| tPSA |
155.59
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
10
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
10
|
| 重原子数目 |
42
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1100
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
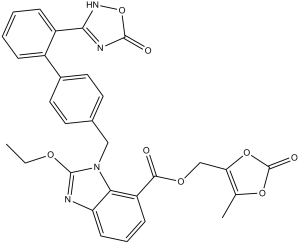
| SMILES |
O=C1OC(COC(C2C3=C(N=C(N3CC3C=CC(C4C(C5NC(=O)ON=5)=CC=CC=4)=CC=3)OCC)C=CC=2)=O)=C(C)O1
|
| InChi Key |
QJFSABGVXDWMIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C30H24N4O8/c1-3-38-28-31-23-10-6-9-22(27(35)39-16-24-17(2)40-30(37)41-24)25(23)34(28)15-18-11-13-19(14-12-18)20-7-4-5-8-21(20)26-32-29(36)42-33-26/h4-14H,3,15-16H2,1-2H3,(H,32,33,36)
|
| 化学名 |
(5-methyl-2-oxo-1,3-dioxol-4-yl)methyl 2-ethoxy-1-((2-(5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)-[1,1-biphenyl]-4-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-7-carboxylate
|
| 别名 |
TAK-491; TAK 491; TAK491; Azilsartan medoxomil; Azilsartan medoxomil potassium; trade name: Edarbi. Ipreziv.
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.66 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.66 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7589 mL | 8.7946 mL | 17.5892 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3518 mL | 1.7589 mL | 3.5178 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1759 mL | 0.8795 mL | 1.7589 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。