| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Influenza virus[1] Cap-dependent endonuclease (CEN)[1][2]
Influenza virus RNA polymerase PA subunit endonuclease (active form: Baloxavir, BXA): - Recombinant influenza A virus (H5N1) PA endonuclease: Dissociation constant (Ki) = 0.15 μM [3] - Influenza A virus (H1N1 pdm09, H3N2) PA endonuclease: Half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC₅₀) = 0.3-0.8 μM [6] - Influenza B virus (Yamagata/Victoria lineages) PA endonuclease: IC₅₀ = 0.9-1.2 μM [6] - Influenza A virus (H1N1, I38T mutant, oseltamivir-resistant) PA endonuclease: IC₅₀ = 0.08 μM [5] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:Baloxavir marboxil(也称为 BXM 或 S-033188)是 Baloxavir(商品名 Xofluza;也称为 Baloxavir Acid、BXA 或 S-033447)的前药。它是由罗氏和盐野义开发的一种口服小分子帽依赖性核酸内切酶抑制剂。巴洛沙韦是基于多替拉韦 (DTG) 的双金属药效团概念,通过合理的分子设计发现的,多替拉韦 (DTG) 是一种人类免疫缺陷病毒 (HIV) 整合酶的链转移抑制剂。 Baloxavir 有效且选择性地抑制甲型和乙型流感病毒聚合酶 PA 亚基内的帽子依赖性核酸内切酶。 2018年2月,巴洛沙韦在日本获得全球首个批准,用于治疗甲型或乙型流感病毒感染。美国、欧盟和其他国家正在进行该适应症的 III 期开发。该药物通过抑制 mRNA 合成的起始来阻止流感病毒的增殖。在临床试验中,单剂量的巴洛沙韦可显着降低病毒滴度并减轻流感症状。 PA I38T 取代是降低 BXA 敏感性的主要途径,A 型病毒和 B 型病毒的 EC50 变化分别为 30 至 50 倍和 7 倍。带有 I38T 取代的病毒在细胞中表现出严重受损的复制适应性,并相应地降低了体外核酸内切酶活性。激酶测定:奥司他韦酸在 MES 测定缓冲液中连续稀释 [32.5 mmol/L MES 和 4 mmol/L CaCl2,溶于 DW(用 4 N NaOH 调节 pH 6.5)]。为了制备 NA 酶溶液,用 0.1% NP-40 灭活病毒原液,并用 MES 测定缓冲液稀释。 10 μL 奥司他韦酸溶液和 10 μL NA 酶溶液混合,37℃孵育 30 分钟,然后加入 30 μL 100 μmol/L 2'-(4-甲基伞形基)-α-DN -乙酰神经氨酸钠盐水合物(MUNANA;Sigma-Aldrich Co., Ltd.)。反应混合物在37℃下孵育60分钟,加入150μL终止液[0.1mol/L甘氨酸和25%乙醇(用4N NaOH调节pH 10.7)]终止反应。使用酶标仪EnVision 2103 (PerkinElmer Inc.)在激发波长355 nm和发射波长460 nm下测量荧光强度,然后使用XLfit软件计算IC50值。 FC是通过将每种测试病毒的IC50除以同源野生型病毒的IC50来计算的。细胞测定:犬肾MDCK细胞获自欧洲细胞培养物保藏中心。人准二倍体肿瘤RPMI2650和人胚胎肾293 T细胞由美国典型培养物保藏中心提供。 MDCK 和 RPMI2650 细胞维持在补充有 10% 胎牛血清 (FBS) 和 100 µg/mL 卡那霉素 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) 的基本必需培养基 (MEM) 中。 293 T 细胞在含有 10% FBS 和 100 µg/mL 卡那霉素的 Dulbecco 改良 Eagle 培养基中培养。采用基于八个质粒的反向遗传学技术来产生所描述的重组病毒。 rgA/WSN/33 (H1N1) 质粒组和空载体 pHW2000 由 St. Jude 儿童研究医院的 Robert Webster 博士提供。用于生成 rgA/Victoria/3/75 和 rgB/Maryland 病毒的质粒是通过标准分子生物学技术用 pHW2000 构建的。所使用的引物序列可根据要求提供。 MDCK 和 293 T 细胞的共培养物用八种质粒转染并孵育 48 至 72 小时,然后在 MDCK 细胞中繁殖病毒。重组病毒的PA序列通过Sanger测序进行验证。通过MDCK细胞中的标准组织培养感染剂量(TCID)50测定或空斑形成单位(PFU)测定来测定病毒滴度。
抗甲型/乙型流感病毒活性: - 感染甲型流感(H1N1 pdm09)的MDCK细胞:Baloxavir marboxil(代谢为BXA)呈剂量依赖性降低病毒产量,半数有效浓度(EC₅₀)= 0.008 μM;0.1 μM时病毒滴度较溶剂对照组降低>99% [6] - 感染奥司他韦耐药甲型流感(H1N1,H275Y突变株)的MDCK细胞:EC₅₀ = 0.009 μM,与野生型毒株活性相当 [6] - 感染乙型流感(山形系)的MDCK细胞:EC₅₀ = 0.015 μM;0.1 μM Baloxavir marboxil降低病毒产量约97% [6] - 感染甲型流感(H1N1,I38T突变株)的MDCK细胞:EC₅₀ = 0.08 μM,较野生型升高10倍,但仍低于细胞毒性浓度 [5] - 抑制病毒转录: - 感染甲型流感(H1N1)的A549细胞中,Baloxavir marboxil代谢产生的BXA(0.1 μM)在感染后8小时降低病毒M1和NP mRNA水平(qPCR检测),分别降低约85%和80%,证实病毒mRNA合成受阻 [6] - 低细胞毒性: - 在MDCK、A549和HepG2细胞中,Baloxavir marboxil的半数细胞毒性浓度(CC₅₀)>10 μM,对所有测试流感毒株的选择指数(SI = CC₅₀/EC₅₀)>1000 [6] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
病毒神经氨酸酶抑制剂对感染人分离的H7N9甲型流感病毒的小鼠疗效有限。尽管baloxavir marboxil/巴洛韦马博西可保护小鼠免受从人身上分离的低致病性H7N9禽流感病毒的致命攻击感染,但其对最近感染高致病性H7N9人分离株的小鼠的功效尚不清楚。本实验研究了baloxavir marboxil对感染高致病性人H7N9病毒a /Guangdong/17SF003/2016的小鼠的疗效。用单次1.5 mg/kg剂量的baloxavir marboxil治疗感染小鼠,保护小鼠免受高致病性人H7N9病毒感染的效果与奥司他韦50 mg/kg剂量的治疗相同,每天两次,连续5天。以15或50 mg/kg的剂量每日治疗5天,显示出卓越的治疗效果,在很大程度上阻止了病毒在呼吸器官中的复制。这些结果表明,baloxavir marboxil是人类高致病性H7N9病毒感染患者有价值的候选治疗药物。[6]
在临床试验中,单剂量的巴洛沙韦可显着降低病毒滴度并减轻流感症状。 动物模型临床前疗效: - 甲型流感(H1N1 pdm09)感染小鼠模型:6-8周龄雄性ICR小鼠经鼻感染100× LD₅₀病毒。Baloxavir marboxil(0.1/0.3/1 mg/kg)口服给药,每日1次,连续3天(感染后24小时开始)。1 mg/kg剂量组:感染后7天体重下降仅-5%(溶剂对照组-25%);存活率100%(溶剂对照组20%);感染后4天肺病毒滴度从10⁶.⁵ PFU/g降至10².³ PFU/g [1] - 甲型流感(H1N1 pdm09)感染雪貂模型及传播实验:雪貂经鼻感染10⁶ PFU病毒,感染后1天单次口服Baloxavir marboxil(1 mg/kg),感染后3天鼻洗液病毒滴度降低10⁴倍;病毒向未感染雪貂的传播率从100%(溶剂对照组)降至50% [6] - 人体临床疗效: - 成人无并发症流感患者(18-64岁):单次口服Baloxavir marboxil(体重<80kg者40mg,≥80kg者80mg),症状缓解中位时间较奥司他韦组缩短1.0天(53.7小时 vs 73.2小时),病毒RNA清除时间缩短2.0天(2.5天 vs 4.5天)[4] - 儿童/青少年患者(12-18岁):单次口服Baloxavir marboxil(体重<40kg者40mg,≥40kg者80mg),症状缓解中位时间53.5小时,病毒清除时间2.0天,无剂量限制性毒性 [5] |
| 酶活实验 |
奥司他韦酸在 MES 测定缓冲液中连续稀释 [32.5 mmol/L MES 和 4 mmol/L CaCl2,溶于 DW(用 4 N NaOH 调节 pH 6.5)]。为了制备 NA 酶溶液,用 0.1% NP-40 灭活病毒原液,并用 MES 测定缓冲液稀释。 10 μL 奥司他韦酸溶液和 10 μL NA 酶溶液混合,37℃孵育 30 分钟,然后加入 30 μL 100 μmol/L 2'-(4-甲基伞形基)-α-DN -乙酰神经氨酸钠盐水合物(MUNANA;Sigma-Aldrich Co., Ltd.)。反应混合物在37℃下孵育60分钟,加入150μL终止液[0.1mol/L甘氨酸和25%乙醇(用4N NaOH调节pH 10.7)]终止反应。使用酶标仪EnVision 2103 (PerkinElmer Inc.)在激发波长355 nm和发射波长460 nm下测量荧光强度,然后使用XLfit软件计算IC50值。 FC是通过将每种测试病毒的IC50除以同源野生型病毒的IC50来计算的。
重组PA内切酶活性测定(荧光底物法): - 50 μL反应体系含20 mM Tris-HCl(pH7.5)、5 mM MgCl₂、1 mM DTT、0.1 mg/mL BSA、50 nM重组PA蛋白及1 μM荧光标记DNA底物(模拟宿主mRNA 5'-帽结构)。加入Baloxavir marboxil的活性形式BXA(0.01-10 μM),37°C孵育60分钟,检测激发485nm/发射520nm荧光强度以量化底物切割率。通过切割率与BXA浓度的剂量-效应曲线计算IC₅₀ [6] - PA内切酶Ki值测定(竞争性抑制实验): - 采用上述反应体系,调整底物浓度(0.25-2 μM)和BXA浓度(0.05-0.5 μM),测定初始反应速率并绘制Lineweaver-Burk双倒数图。根据图中直线交点计算H5N1 PA的Ki=0.15 μM,证实BXA对PA内切酶的竞争性抑制作用 [3] |
| 细胞实验 |
犬肾 MDCK 细胞获自欧洲细胞培养物保藏中心。人准二倍体肿瘤RPMI2650和人胚胎肾293 T细胞由美国典型培养物保藏中心提供。 MDCK 和 RPMI2650 细胞维持在补充有 10% 胎牛血清 (FBS) 和 100 µg/mL 卡那霉素 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) 的基本必需培养基 (MEM) 中。 293 T 细胞在含有 10% FBS 和 100 µg/mL 卡那霉素的 Dulbecco 改良 Eagle 培养基中培养。采用基于八个质粒的反向遗传学技术来产生所描述的重组病毒。 rgA/WSN/33 (H1N1) 质粒组和空载体 pHW2000 由 St. Jude 儿童研究医院的 Robert Webster 博士提供。用于生成 rgA/Victoria/3/75 和 rgB/Maryland 病毒的质粒是通过标准分子生物学技术用 pHW2000 构建的。所使用的引物序列可根据要求提供。 MDCK 和 293 T 细胞的共培养物用八种质粒转染并孵育 48 至 72 小时,然后在 MDCK 细胞中繁殖病毒。重组病毒的PA序列通过Sanger测序进行验证。通过MDCK细胞中的标准组织培养感染剂量(TCID)50测定或空斑形成单位(PFU)测定来测定病毒滴度。
MDCK细胞流感病毒产量测定: - MDCK细胞以5×10⁴个/孔接种24孔板,过夜培养。用流感病毒(感染复数MOI=0.01)37°C感染1小时,移除病毒液后加入含Baloxavir marboxil(0.0001-10 μM)的培养基,37°C(5% CO₂)孵育48小时。收集上清液,通过空斑实验测定病毒滴度,EC₅₀定义为使病毒滴度较溶剂对照组降低50%的药物浓度 [6] - A549细胞病毒mRNA qPCR检测: - A549细胞(2×10⁵个/孔,6孔板)用甲型流感(H1N1,MOI=1)感染1小时,加入Baloxavir marboxil(0.1 μM)处理后37°C孵育。感染后4/8/12小时提取总RNA,逆转录合成cDNA,用病毒M1/NP基因特异性引物进行qPCR(GAPDH为内参),通过2⁻ΔΔCt法计算相对mRNA水平 [6] - 细胞毒性MTT实验: - MDCK/A549/HepG2细胞以1×10⁴个/孔接种96孔板,过夜培养。用Baloxavir marboxil(0.1-100 μM)处理72小时,每孔加入10 μL MTT试剂(5mg/mL),37°C孵育4小时。DMSO溶解甲臜结晶后,检测570nm处吸光度,CC₅₀为使细胞活力降低50%的药物浓度 [6] |
| 动物实验 |
To evaluate the efficacy of baloxavir marboxil in vivo infection with the H7N9 virus, baloxavir marboxil was orally administered to mice at 5 and 50 mg/kg twice a day for five days and was shown to have completely protected them from lethal challenge infection with a low pathogenic avian H7N9 human isolate, A/Anhui/1/2013. Highly pathogenic A/Guangdong/17SF003/2016 virus, which possesses enhanced polymerase activity in mammals due to PB2-482R, PB2-588V, and PA-497R is more pathogenic than A/Anhui/1/2013 because it causes a systemic infection in mice, ferrets, and macaques; this greater pathogenicity may affect the efficacy of baloxavir marboxil. Although A/Guangdong/17SF003/2016 showed reduced growth in human bronchial epithelial cells, this virus possesses the A100V, R262K, V387I, N394D, I465V, and K497R mutations in PA that may affect sensitivity to baloxavir marboxil compared with A/Anhui/1/2013. Accordingly, here, we assessed the efficacy of baloxavir marboxil against this highly pathogenic human H7N9 virus in vitro and in vivo.[6]
Next, we assessed the efficacy of baloxavir marboxil in mice infected with the highly pathogenic human H7N9 virus. Six-week-old female mice (BALB/c, Japan SLC Inc.) were anesthetized with isoflurane and intranasally infected with 10 mouse lethal dose 50 (MLD50; 104.3 PFU) of highly pathogenic A/Guangdong/17SF003/2016 (H7N9) possessing NA-294R (arginine at position 294 of NA indicates sensitive to NA inhibitors). Five infected mice per group were orally treated with oseltamivir phosphate at 5 or 50 mg/kg twice a day for 5 days or with baloxavir marboxil at 1.5, 15, or 50 mg/kg once or twice a day for 5 days. The negative control mice received 0.5% methylcellulose because this reagent was used as a solvent. Body weight changes of these mice were monitored for 14 days and mice that lost 25% or more of their initial body weight were scored as dead and euthanized according to institutional guidelines. All animal experiments were conducted in accordance with the University of Tokyo’s Regulations for Animal Care and Use, which were approved by the Animal Experiment Committee of the Institute of Medical Science, the University of Tokyo (approval no. PA15-12). Mice given methylcellulose exhibited immediate body weight loss and died up to 8 days after infection. Oseltamivir phosphate treatment at 5 mg/kg for 5 days slightly improved the survival time of the infected mice (p = 0.009, log-rank test) but failed to protect them from the lethal challenge infection. Oseltamivir phosphate treatment at 50 mg/kg for 5 days showed 80% protection with severe body weight loss. In contrast, 60% of mice treated once with baloxavir marboxil at 1.5 mg/kg survived for 14 days, whereas all of the mice in the other baloxavir-treated groups survived without any body weight loss (p = 0.0016, log-rank test). These results show that a single dose of baloxavir marboxil with 15 mg/kg is sufficient to protect mice from infection with a highly pathogenic human H7N9 virus[6]. Mouse influenza infection model: - Male ICR mice (20-25 g, 6-8 weeks old) were randomly divided into 4 groups (n=10): vehicle control and Baloxavir marboxil (0.1/0.3/1 mg/kg). Baloxavir marboxil was dissolved in 0.5% methylcellulose + 0.1% Tween 80 in distilled water. Mice were anesthetized with isoflurane and intranasally infected with influenza A (H1N1 pdm09, 100 μL, 100× LD₅₀). Drug was administered via oral gavage once daily for 3 days (starting 24 h post-infection). Body weight and survival were monitored for 14 days; 3 mice per group were euthanized on day 4 to measure lung virus titer [1] - Ferret influenza infection and transmission model: - Female ferrets (1-1.5 kg, 6-8 months old) were acclimated for 1 week. Ferrets were anesthetized with ketamine/xylazine and intranasally infected with influenza A (H1N1 pdm09, 1 mL, 10⁶ PFU). A single oral dose of Baloxavir marboxil (1 mg/kg, dissolved in 0.5% methylcellulose + 0.1% Tween 80) was given on day 1 post-infection. Nasal washes were collected daily for 7 days to measure virus titer. For transmission experiments, infected ferrets were housed with naive ferrets (1:1) for 7 days, and naive ferret nasal washes were tested for virus [6] - Rat pharmacokinetic study: - Male SD rats (250-300 g) received a single oral dose of Baloxavir marboxil (10 mg/kg, dissolved in 0.5% sodium carboxymethylcellulose). Blood samples were collected at 0.25/0.5/1/2/4/8/12/24 h post-dose. Plasma BXA concentration was measured via LC-MS/MS, and pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated: elimination half-life (t₁/₂) = 6.5 h, oral bioavailability = 75% [3] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Following oral administration of 40 mg baloxavir marboxil in adolescents and adults aged 12 years and older, the AUC was 5520 ng x hr/mL and the Cmax was 68.9 ng/mL. Following a 80 mg dose, the the AUC was 6930 ng x hr/mL and the Cmax was 82.5 ng/mL. The Tmax is about four hours. Food decreased Cmax by 48% and AUC0-inf by 36%. In pediatric patients aged five to 12 years of age weighing less than 20 kg, the AUCinf was 5830 ng x hr/mL and the Cmax was 148 ng/mL following a 2 mg/kg dose. The AUCinf was 4360 ng x hr/mL and the Cmax was 81.1 ng/mL following a 40 mg dose in pediatric patients who weigh greater than or equal to 20 kg. The Tmax ranged from 3.5 to 4.5 hours. Baloxavir is primarily eliminated by biliary excretion. About 80.1% of the total dose is excreted in feces. About 14.7% of the dose is excreted in urine, where 3.3% of the recovered dose is the unchanged parent drug. The volume of distribution is 1180 L. Clearance of baloxavir is 10.3 L/h. Metabolism / Metabolites Baloxavir predominantly undergoes UGT1A3-mediated metabolism to form glucuronic acid conjugate. It is subsequently metabolized by CYP3A4 to form sulfoxide. Biological Half-Life The apparent terminal elimination half-life of baloxavir is 79.1 hours. Absorption: - Oral bioavailability: ~70% in mice (1 mg/kg oral dose), ~75% in rats (10 mg/kg oral dose) [3] - Human pharmacokinetics: Single oral dose of Baloxavir marboxil (40 mg/80 mg) in adults: time to peak concentration (Tmax) = 1.5-2.0 h; peak plasma concentration (Cmax) = 13.6/27.7 ng/mL; area under the concentration-time curve (AUC₀-∞) = 45.3/92.6 ng·h/mL [4] - Distribution: - Tissue penetration: In mice (1 mg/kg oral dose), BXA concentrations at 2 h post-dose: lung = 2.5 μM, nasal mucosa = 3.1 μM, plasma = 1.2 μM (target tissues had higher concentrations) [1] - Plasma protein binding: BXA (active form) had ~90% plasma protein binding in human plasma [2] - Metabolism: - Baloxavir marboxil is a prodrug; it is hydrolyzed by esterases in vivo to active BXA. Minimal hepatic metabolism: <10% of BXA was metabolized in human liver microsomes after 2 h incubation [2][3] - Excretion and elimination: - Elimination half-life (t₁/₂): 6 h in mice, 6.5 h in rats, 7.7-8.8 h in humans [3][4] - Renal excretion: ~20% of BXA was excreted unchanged in human urine within 24 h post-dose [2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In clinical trials, there was little evidence that baloxavir caused liver injury, either in the form of serum enzyme elevations or clinically apparent liver disease. A proportion of patients with acute influenza A may have minor serum enzyme elevations during the acute illness, but these are independent of therapy and do not appear to be exacerbated by baloxavir. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the use of baloxavir marboxil during breastfeeding. Because baloxavir is 93% bound to plasma proteins, the amount in milk is likely to be low. If baloxavir is required by the mother, it is not a reason to discontinue breastfeeding, but an alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Baloxavir, the active metabolite, is 92.9–93.9% bound to human serum proteins. The ratio of blood cell to blood is 48.5–54.4%. Animal toxicity: - Acute toxicity: Mice received oral Baloxavir marboxil up to 200 mg/kg; no mortality or clinical signs (lethargy, weight loss) were observed within 14 days [3] - Subacute toxicity: Rats received oral Baloxavir marboxil (10/30/100 mg/kg/day) for 28 days; no significant changes in body weight, food intake, or serum markers (ALT, AST, BUN, creatinine) vs. control [3] - Clinical safety: - Adult patients: Adverse event (AE) rate was 17.8% (vs. 19.0% for oseltamivir); common AEs included diarrhea (2.1%) and headache (1.8%); no severe AEs [4] - Pediatric/adolescent patients: AE rate was 14.3%; common AEs included vomiting (3.0%) and abdominal pain (1.5%); no hepatotoxicity or nephrotoxicity [5] - Drug-drug interactions: - No significant pharmacokinetic interactions with oseltamivir, ibuprofen, omeprazole, or oral contraceptives; no synergistic toxicity observed [2][4] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Pharmacodynamics
Baloxavir marboxil is an antiviral drug that works against influenza virus to block viral replication. It has an 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 1.4 to 3.1 nM for influenza A viruses and 4.5 to 8.9 nM for influenza B viruses in a polymerase acidic (PA) endonuclease assay. In murine models of influenza and avian influenza A, baloxavir reduced pulmonary viral loads and increased survival rates of mice. The reduction of viral titer was observed within 24 hours of administration, in a dose-dependent manner. Mechanism of action: - Baloxavir marboxil (BXM) is a prodrug that is converted to active Baloxavir (BXA) in vivo. BXA competitively inhibits the endonuclease activity of influenza virus RNA polymerase PA subunit, blocking the cleavage of host mRNA 5'-cap structure (required for viral mRNA synthesis), thereby suppressing viral transcription and replication [2][3] - Indications and regulatory status: - Approved in the US, Japan, and EU since 2018 for the treatment of uncomplicated influenza A/B in patients ≥12 years old (including oseltamivir-resistant infections). Approved in 2020 for patients ≥1 year old in multiple countries [2][5] - Resistance profile: - PA I38T mutation is the main resistance-associated mutation; Baloxavir marboxil has reduced activity against I38T mutant strains (EC₅₀ = 0.08 μM vs. 0.008 μM for wild-type) but remains effective in some patients [5] - Clinical advantages: - Single oral dose improves patient compliance; faster symptom resolution and viral clearance than oseltamivir; broad activity against influenza A/B and oseltamivir-resistant strains [4][5][6] |
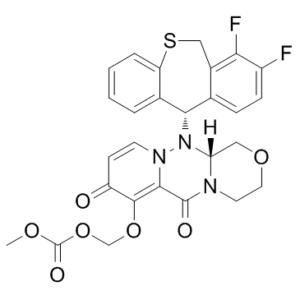
| 分子式 |
C27H23F2N3O7S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
571.55
|
| 精确质量 |
571.122
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 56.74; H, 4.06; F, 6.65; N, 7.35; O, 19.59; S, 5.61
|
| CAS号 |
1985606-14-1
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Baloxavir;1985605-59-1;Baloxavir-d5;Baloxavir-d4;2415027-80-2
|
| PubChem CID |
124081896
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to yellow solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.6±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
712.8±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
384.9±35.7 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.696
|
| LogP |
2.24
|
| tPSA |
123Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
12
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
40
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1090
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
| SMILES |
S1CC2C(=C(C=CC=2[C@@H](C2C=CC=CC1=2)N1[C@@H]2COCCN2C(C2=C(C(C=CN12)=O)OCOC(=O)OC)=O)F)F
|
| InChi Key |
RZVPBGBYGMDSBG-GGAORHGYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C27H23F2N3O7S/c1-36-27(35)39-14-38-25-19(33)8-9-31-24(25)26(34)30-10-11-37-12-21(30)32(31)23-15-6-7-18(28)22(29)17(15)13-40-20-5-3-2-4-16(20)23/h2-9,21,23H,10-14H2,1H3/t21-,23+/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
({(12aR)-12-[(11S)-7,8-difluoro-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]thiepin-11-yl]-6,8-dioxo-3,4,6,8,12,12ahexahydro-1H-[1,4]oxazino[3,4-c]pyrido[2,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-7-yl}oxy)
|
| 别名 |
Trade name Xofluza; Baloxavir acid; 1985606-14-1; Xofluza; S-033188; baloxavir-marboxil; 505CXM6OHG; Baloxavir marboxil [INN]; UNII-505CXM6OHG; BXA; Baloxavir marboxil; S-033188; S 033188; S033188
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : 33~100 mg/mL ( 58.32~174.96 mM )
Ethanol : 7 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.37 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入900 μL 玉米油中,混合均匀。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 10% DMSO+90% Corn Oil: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.37 mM) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7496 mL | 8.7481 mL | 17.4963 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3499 mL | 1.7496 mL | 3.4993 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1750 mL | 0.8748 mL | 1.7496 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT04712539 | Recruiting | Drug: Baloxavir Marboxil Drug: Oseltamivir |
Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Cell Neoplasm Influenza |
M.D. Anderson Cancer Center | October 11, 2021 | Phase 2 |
| NCT05170009 | Recruiting | Drug: Baloxavir Marboxil Drug: Placebo |
Influenza | Weill Medical College of Cornell University |
April 22, 2022 | Phase 2 Phase 3 |
| NCT06207058 | Not yet recruiting | Drug: Baloxavir Marboxil | Influenza | Tricore, Inc | January 15, 2024 | |
| NCT06205641 | Recruiting | Drug: Xuanfei Baidu Granule Drug: Baloxavir Marboxil Tablet |
Influenza A | Capital Medical University | January 2024 | Not Applicable |
 In vitroendonuclease activity and inhibition of PA variants and thermal stabilization induced by the binding of BXA.Sci Rep.2018 Jun 25;8(1):9633. |
|---|
 BXA binding to influenza A/H1N1 PA endonuclease. BXA interacts with (A) PA-A WT and (B) PA-A I38T by chelating the two manganese ions in the active site.Sci Rep.2018 Jun 25;8(1):9633. |
 Comparison of PA endonuclease from Flu A and Flu B bound to BXA in either WT or I38T form. Superposition of PA-BXA complexes: (A) PA-A WT and PA-A I38T, (B) PA-B WT and PA-B I38T, (C) PA-A WT and PA-B WT, (D) PA-A I38T and PA-B I38T.Sci Rep.2018 Jun 25;8(1):9633. |
 Local interactions of residue 38 in apo- and BXA-bound FluB PA (A) Superposition of ligand-free PA-B WT (PDB:5FML, in hotpink) and bound to BXA (green sticks for BXA, teal sticks/cartoon for PA). (B) Superposition of ligand-free (forest green) and BXA-bound PA-B I38T (light magenta sticks for BXA, orange sticks/cartoon for PA).Sci Rep.2018 Jun 25;8(1):9633. |
 Replicative capacity of variant viruses with indicated AA substitutions in PA protein. Canine MDCK cells (A–C) or human RPMI2650 cells (D,E) were infected with WT or I38x viruses based on rgA/WSN/33 (H1N1) (A,D), rgA/Victoria/3/75 (H3N2) (B,E), or B/Maryland/1/59 (C,F).Sci Rep.2018 Jun 25;8(1):9633. |