| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
LXRα (IC50 = 68 nM); LXRβ (IC50 = 14 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在人全血中,发现 ATP 结合转运蛋白 ABCA1 和 ABCG1 受到 LXR 选择性部分激动剂 BMS-779788 的强烈诱导(EC50=1.2 μM,55% 有效性)[2]。
为了提高分子的效力,制备了苯基取代的替代品,得到了苄基咪唑,如16和17,它们都提高了LXRβ激动剂的效力。对苄基取代的进一步研究提供了宝石二甲基类似物18/BMS-779788。这些苄基咪唑保持了适度的LXRβ结合选择性和15-38%的部分LXRα激动剂效力,其中LXRβ的效力为43-72%(表2)。重要的是,18/BMS-779788在ABCA1 hWBA中的效力有所提高(EC50=1.2μM),部分疗效(55%),与2a(hWBA EC50=4.6μM,56%)相比是有利的。同样,当在10μM下对14个NHR进行测试时,18/BMS-779788是一种高度选择性的LXR激动剂,仅对PXR显示激动剂活性(EC50=2μM)。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在体内诱导血液中 LXR 靶基因时,BMS-779788 与其体外血液基因诱导具有相似的效力 (EC50=610 nM)。在增加血浆甘油三酯和 LDL 胆固醇方面,BMS-779788 的作用分别比完全激动剂 T0901317 低 29 倍和 12 倍。血浆胆固醇酯转移蛋白和载脂蛋白 B 也观察到类似的结果 [1]。 BMS-779788 通过以 3 和 10 mpk 的剂量在小鼠中外周诱导 ABCA1,表现出比完全激动剂更好的诱导作用,而不会导致这些水平的血浆或肝脏甘油三酯明显增加。情况[2]。
肝X受体(LXRs)α和β是调节参与胆固醇逆向转运(RCT)的多个基因的核激素受体,是动脉粥样硬化的潜在药物靶点。然而,全泛激动剂也会激活脂肪生成基因,导致血浆和肝脏脂质升高。我们报告了BMS-779788[2-(2-(1-(2-氯苯基)-1-甲基乙基)-1-(3'-(甲基磺酰基)-4-联苯基)-1H-咪唑-4-基)-2-丙醇]的药理学,这是一种具有LXRβ选择性的强效部分LXR激动剂,与全泛激动剂相比,它在食蟹猴中的治疗窗口有所改善BMS-779788在体内诱导血液中的LXR靶基因,EC50=610 nM,该值与其体外血液基因诱导效力相似BMS-779788在升高血浆甘油三酯和低密度脂蛋白胆固醇方面的效力分别比完全激动剂T0901317低29倍和12倍,血浆胆固醇酯转移蛋白和载脂蛋白B的结果相似。然而,对RCT至关重要的血液中ABCA1和ABCG1 mRNA的诱导是可比的。在最高测试剂量下用BMS-779788治疗7天后,观察到肝脏甘油三酯升高,与血浆甘油三酯的剂量反应几乎相同,这与肝脏LXR在这些脂肪生成作用中的核心作用一致。在BMS-779788治疗的动物中,胆汁胆固醇的剂量依赖性增加以及磷脂和胆汁酸的减少,与小鼠中报告的LXR激动剂作用相似。总之,在食蟹猴中,部分LXRβ选择性激动剂BMS-779788与全泛激动剂相比,其脂肪生成潜力降低,在诱导已知刺激RCT的基因方面具有相似的效力。这为非人类灵长类动物通过限制LXRα活性来改善LXR激动剂治疗窗口提供了支持。[2] |
| 酶活实验 |
人体全血检测。将人全血收集在含EDTA的试管中,立即将0.5mL等分试样与0.5%DMSO中适当稀释的试验化合物BMS-779788混合在96孔块中。样品在37°C下恒定旋转孵育4小时。细胞裂解后,纯化总RNA,合成cDNA,并在ABI Prism 7900HT序列检测系统上使用SYBR Green定量PCR(Q-PCR)对mRNA进行定量。[2]
利用闪烁邻近结合试验分别测定LXRα和LXRβ的结合亲和力,该试验采用昆虫细胞中表达的RXRα-LXRα和RXRα-XXRβ异二聚体。在转录激活试验中评估了同种型选择性激动剂活性,其中LXRα或LXRβ与萤光素酶报告基因LXREx1-tk-luc共转染CV-1细胞。为了观察对基因转录的总体影响,在HeLa细胞的ABCA1 LXREx3报告分析中,使用内源性LXRα和LXRβ受体对化合物进行了分析。用ABCA1x3-tk-luc报告基因和pCMXβ半乳糖苷酶质粒转染HeLa细胞,并如上所述检测萤光素酶活性[2]。 |
| 动物实验 |
Study Design: [1]
The study utilizes male cynomolgus monkeys. Single-Dose PK-PD Study: Two animals each receive either a vehicle control (0.5% carboxymethyl cellulose and 2% Tween 80 in purified water) or 1 mg/kg BMS-779788. 7-Day PD Study: Eighteen animals (3–6 kg) are randomized into six treatment groups (N=3 per group). From day 1 to day 7, each group receives daily oral gavage at 7 AM with one of the following treatments: Vehicle control 10 mg/kg/day T0901317 0.3, 1, 3, or 10 mg/kg/day BMS-779788 Mice were dosed (n = 3) by oral gavage with suspension dosing of drug BMS-779788 in 0.75% CMC/0.1% Tween 80 in water. [2] Mice (C57BL/6) were dosed in vehicle containing 0.75% carboxymethyl cellulose and 0.1% Tween 80 in deionized water for 7 days. ABC transporter mRNA was measured at 5 h post dose last dose. Triglycerides and liver SREBP1c and FAS mRNAs were measured at 24 h post last dose. Pan-agonist 3c was used as a control in the experiment.[2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Both 16 and 18/BMS-779788 had high 5–6 μM 4 h plasma exposures in mouse PK with low 24 h liver exposures (Table 3), indicating they would not have a long liver residence time that might result in increased hepatic triglyceride production. [2]
|
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
BMS-779788 is a small molecule drug with a maximum clinical trial phase of I and has 1 investigational indication.
A series of biaryl pyrazole and imidazole Liver X Receptor (LXR) partial agonists has been synthesized displaying LXRβ selectivity. The LXRβ selective partial agonist 18 was identified with potent induction of ATP binding transporters ABCA1 and ABCG1 in human whole blood (EC50=1.2μM, 55% efficacy). In mice 18 displayed peripheral induction of ABCA1 at 3 and 10mpk doses with no significant elevation of plasma or hepatic triglycerides at these doses, showing an improved profile compared to a full pan-agonist.[2] Based on the hWBA potency, partial LXRα agonism and LXRβ selectivity, mice were dosed with 18/BMS-779788 for 7 days at 0.3, 1, 3, 10 and 30 mpk per day to assess the ABCA1 and ABCG1 blood cell gene induction, as well as plasma and liver triglyceride levels (Fig. 3).37, 38 Significant ABCA1 inductions were observed at the 3, 10 and 30 mpk doses, with ABCG1 showing a similar pattern, and 5 h drug exposures of 0.05, 0.20 and 2.0 μM, respectively. The mouse in vitro EC50 to induce ABCA1 in whole blood was 0.12 μM, which was similar to the plasma drug exposures needed for ABCA1 induction in vivo. The 3 and 10 mpk doses of 18/BMS-779788 gave significant ABCA1 mRNA inductions with no significant plasma or hepatic triglyceride elevation. Plasma triglycerides were significantly elevated 74–108% at only the 30 mpk dose, and no significant hepatic triglyceride elevations were observed at any dose in contrast to the control pan agonist, which had 4.8 fold increase in hepatic triglyceride compared to vehicle. The reduced induction of LXR target genes SREBP1c and FAS in the liver likely accounts for the reduced lipogenic profile of 18/BMS-779788. In the liver SREBP1c was significantly induced to 2.7 and 3.5 fold over vehicle at 10 and 30 mpk, compared to 7.7 fold induction with 3c treatment; whereas FAS had no significant changes up to 30 mpk. [2] These undesirable effects on plasma lipids have been the major impediment for the development of LXR agonist therapeutics. It is likely that LXRα is the isoform that mediates most of the hepatic effects, at least in mice, because LXRα null mice have reduced lipogenic responses to pan agonists (Lund et al., 2006; Quinet et al., 2006). Furthermore, LXR pan agonists inhibit atherosclerosis in these mice, indicating that LXRβ is sufficient to bring about the beneficial effects (Bradley et al., 2007). Thus, one approach to limit lipogenesis is to selectively target LXRβ. However, this approach has not been adequately tested in primates. We report here the in vivo pharmacology in cynomolgus monkeys of BMS-779788, a novel partial, LXRβ-selective LXR agonist. This compound has decreased lipogenic potential compared with a full pan agonist while maintaining similar induction of genes known to enhance RCT. [1] |
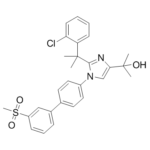
| 分子式 |
C28H29CLN2O3S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
509.0595
|
| 精确质量 |
508.158
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 66.06; H, 5.74; Cl, 6.96; N, 5.50; O, 9.43; S, 6.30
|
| CAS号 |
918348-67-1
|
| PubChem CID |
59251511
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
738.7±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
400.6±35.7 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.6 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.605
|
| LogP |
4.85
|
| tPSA |
80.6
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
35
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
819
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
ClC1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C1C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])C1=NC(=C([H])N1C1C([H])=C([H])C(C2C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C(C=2[H])S(C([H])([H])[H])(=O)=O)=C([H])C=1[H])C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])O[H]
|
| InChi Key |
JLPURTXCSILYLW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C28H29ClN2O3S/c1-27(2,23-11-6-7-12-24(23)29)26-30-25(28(3,4)32)18-31(26)21-15-13-19(14-16-21)20-9-8-10-22(17-20)35(5,33)34/h6-18,32H,1-5H3
|
| 化学名 |
2-(2-(2-(2-chlorophenyl)propan-2-yl)-1-(3'-(methylsulfonyl)-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-1H-imidazol-4-yl)propan-2-ol
|
| 别名 |
XL-652; XL652; BMS-779,788; 918348-67-1; BMS 788; FB7ZTJ8M8A; XL-014; EXEL 04286,652; EXEL-04286,652; XL652; EXEL 04286652; EXEL04286652; EXEL-04286652; BMS-779788; BMS 779788; BMS779788; BMS-788; BMS 788; BMS788
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~196.44 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (4.91 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浮液;超声助溶。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.91 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9644 mL | 9.8220 mL | 19.6440 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3929 mL | 1.9644 mL | 3.9288 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1964 mL | 0.9822 mL | 1.9644 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。