| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
5-HT1D ( pKi = 7.9 ); 5-HT1A ( pKi = 7.7 ); 5-HT2B ( pKi = 7.4 ); 5-HT2A ( pKi = 6.6 ); 5-HT7 ( pKi = 6.3 )
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:BRL-15572 对 h5-HT1D 受体表现出高亲和力和选择性。 BRL-15572 对 h5-HT1D 的亲和力比 5-HT1B 受体高 60 倍。 BRL-15572 与 h5-HT1B 和 h5-HT1D 受体结合,pKB 分别小于 6 和 7.1。 BRL-15572 刺激两种细胞系中的 [35S]GTP γ S 结合,其效力与其在 h5-HT1B 和 h5-HT1D 受体表达细胞系中的受体结合亲和力相关。 BRL-15572 揭示了对 5-HT1A、5-HT1B、5-HT1E、5-HT1F、5-HT2A、5-HT2B、5-HT2C、5-HT6 和 5-HT7 的受体结合亲和力,pKi 为 7.7、6.1、分别为 5.2、6.0、6.6、7.4、6.2、5.9 和 6.3。在 h5-HT1D 细胞系中,两种 BRL-15572 (1 µM) 均会改变 5-HT 浓度响应曲线,pKB 分别为 7.1。 BRL-15572 对人类 5-HT1A 和 5-HT2B 受体具有中等高的亲和力。在人心耳中,电诱发的氚溢出被 5-HT 抑制,其方式容易受到 BRL-15572(300 nM;h5-HT1D 受体 Ki 的 23 倍)的拮抗作用。 5-HT 对 K+ 引起的谷氨酸溢出的抑制作用被 h5-HT1D 受体配体 BRL-15572 拮抗。 BRL-15572 (1 μM) 无法改变 5-HT 对自身受体调节 [3H]5-HT 释放的影响。选择性 5-HT1D/1B 受体拮抗剂 BRL 15572 抑制激动剂 L-694 247 的作用。细胞测定:[35S]GTPγS 结合研究。在表达 h5-HT1B 或 h5-HT1D 受体的 CHO 细胞中进行 [35S]GTPγS 结合研究。简而言之,将 1 × 106 个细胞的膜在含有 GDP 的 HEPES 缓冲液(HEPES [20 mM]、MgCl2 [3 mM]、NaCl [100 mM]、抗坏血酸 [0.2 mM])中预孵育 30 分钟。 (10 µ M),有或没有 BRL-15572。通过添加 10 µL [35S]GTPγS(100 pM,测定浓度)开始反应,然后在 30°C 下进一步孵育 30 分钟。在添加细胞之前,通过添加未标记的 GTPγS (10 µM) 来确定非特异性结合。使用 Whatman GF/B 级过滤器快速过滤,然后用冰冷的 HEPES 缓冲液洗涤五次,从而终止反应。放射性通过液体闪烁光谱法测定。
|
||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在糖尿病大鼠中,给予选择性 5-HT1D 受体拮抗剂 BRL-15572 (2 mg/kg) 不会改变迷走神经电刺激引起的 HR 降低。 L-694,247 (50 μg/kg)(一种非啮齿动物 5-HT1B 和 5-HT1D 受体的选择性激动剂)在用 BRL-15572 预处理后对迷走神经诱导的心动过缓的影响并不明显。
|
||
| 酶活实验 |
尽管h5-HT1B和h5-HT1D受体氨基酸序列之间只有适度的同源性,但这些受体显示出非常相似的药理学。迄今为止,很少有化合物能区分这些受体亚型和那些具有一定选择性的化合物,如酮色林,对其他5-HT受体亚型具有更大的亲和力。我们现在报告了两种化合物,SB-216641(N-[3-(2-二甲氨基)乙氧基-4-甲氧基苯基]-2'-甲基-4'-(5-甲基-1,2,4-恶二唑-3-基)-(1,1'-联苯)-4-甲酰胺)和BRL-155723-[4-(3-氯苯基)哌嗪-1-基]-1,1-二苯基-2-丙醇),它们分别对h5-HT1B和h5-HT1D受体显示出高亲和力和选择性。在CHO细胞中表达的人受体的受体结合研究中,SB-216641对h5-HT1B受体具有高亲和力(pKi=9.0),对h5-HT1D受体的亲和力低25倍。相比之下,BRL-15572对h5-HT1D(pKi=7.9)的亲和力比5-HT1B受体高60倍。在豚鼠纹状体的天然组织5-HT1B受体上测定了这些化合物的类似亲和力。在[35S]GTPγS结合试验和重组h5-HT1B和h5-HT1D受体上的cAMP积累试验中测量了SB-216641和BRL-15572的功能活性。这两种化合物在这些高受体表达系统中都是部分激动剂,其效力和选择性与其受体结合亲和力相关。在cAMP积累测定中,化合物的pK(B)测量结果再次与受体结合亲和力相关(SB-216641,pK(B)=9.3和7.3BRL-15572,pK(B)=<6,h5-HT1B和h5-HT1D受体分别为7.1)。这些化合物将成为表征5-HT1B和5-HT1D受体介导反应的有用药理学试剂[1]。
|
||
| 细胞实验 |
[35S]GTPγS 结合研究。 [35S]GTPγS 结合研究是在表达 h5-HT1B 或 h5-HT1D 受体的 CHO 细胞中进行的。总之,1 × 106 细胞膜在 HEPES 缓冲液中预孵育(HEPES [20 mM]、MgCl2 [3 mM]、NaCl [100 mM]、抗坏血酸 [ 0.2 mM]),含 GDP (10 µ M),含或不含 BRL-15572,30°C 30 分钟。以 10 µL 增量添加 100 pM 测定浓度的 [35S]GTPγS 以启动反应,然后在 30°C 下再孵育 30 分钟。非特异性结合的测定是通过首先添加未标记的 GTPγS (10 µM),然后添加细胞来实现的。使用 Whatman GF/B 级过滤器快速过滤掉反应物,然后进行五次冰冷 HEPES 缓冲液洗涤。液体闪烁光谱用于测量放射性。
|
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1997 Sep;356(3):312-20. [2]. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1997 Sep;356(3):321-7. [3]. Br J Pharmacol. 1999 Feb;126(3):607-12. [4]. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2005 Oct;32(10):894-900. [5]. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007 Nov;34(11):1199-206. [6]. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2004 Jul;370(1):46-53. |
||
| 其他信息 |
1. In the present study, we investigated how alloxan-induced diabetes affects the ability of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) to modulate bradycardia induced in vivo by electrical stimulation of the vagus nerve in pithed rats. We also analysed the type and/or subtype of 5-HT receptors involved. 2. Diabetes was induced in male Wistar rats with a single injection of alloxan (150 mg/kg, s.c.). Four weeks later, rats were anaesthetized, pretreated with atenolol and pithed. Electrical stimulation (3, 6 and 9 Hz) of the vagus nerve resulted in frequency dependent decreases in heart rate (HR). 3. In diabetic rats, intravenous bolus administration of high doses of 5-HT (100 and 200 microg/kg) increased the bradycardia induced by vagal electrical stimulation. Similarly, low doses (10 microg/kg) of the 5-HT(1/7) receptor agonist 5-carboxamidotryptamine (5-CT), increased vagally induced bradycardia. However, at high doses (50, 100 and 150 microg/kg), 5-CT reduced the bradycardia. Attenuation of the vagally induced bradycardia evoked by the higher doses of 5-CT was reproduced by L-694,247 (50 microg/kg), a selective agonist for the non-rodent 5-HT(1B) and 5-HT(1D) receptors. Enhancement of the vagally induced bradycardia elicited by low doses of 5-CT was reproduced by the selective 5-HT(1A) receptor agonist 8-hydroxydipropylaminotretalin hydrobromide (8-OH-DPAT; 50 microg/kg). These stimulatory and inhibitory actions on vagal stimulation-induced bradycardia in diabetic rats were also observed after administration of exogenous acetylcholine. 4. Vagally induced bradycardia in diabetic rats was not affected by administration of the selective 5-HT(2) receptor agonist alpha-methyl-5-HT (150 microg/kg), the selective 5-HT(3) receptor agonist 1-phenylbiguanide (150 microg/kg) or the selective 5-HT(1B) receptor agonist CGS-12066B (50 microg/kg). 5. Enhancement of the electrical stimulation-induced bradycardia in diabetic rats caused by 5-CT (10 microg/kg) or 8-OH-DPAT (50 microg/kg) was abolished by the selective 5-HT(2/7) receptor antagonist mesulergine (1 mg/kg) and the selective 5-HT(1A) receptor antagonist WAY-100,635 (100 microg/kg), respectively. Similarly, pretreatment with the non-selective 5-HT(1) receptor antagonist methiothepin (0.1 mg/kg) blocked the inhibitory effect of 5-CT (50 microg/kg) on the bradycardia induced by vagal electrical stimulation in diabetic rats. BRL-15572 (2 microg/kg), a selective 5-HT(1D) receptor antagonist, inhibited the action of L-694,247 (50 microg/kg), a selective agonist for the non-rodent 5-HT(1B) and 5-HT(1D) receptors, on the vagally induced bradycardia. 6. In conclusion, in the present study, experimental diabetes evoked changes in both the nature and 5-HT receptor types/subtypes involved in vagally induced bradycardia.[5]
It has previously been suggested that ergotamine produces external carotid vasoconstriction in vagosympathectomised dogs via 5-HT1B/1D receptors and alpha2-adrenoceptors. The present study has reanalysed this suggestion by using more selective antagonists alone and in combination. Fifty-two anaesthetised dogs were prepared for ultrasonic measurements of external carotid blood flow. The animals were divided into thirteen groups (n=4 each) receiving an i.v. bolus injection of, either physiological saline (0.3 ml/kg; control), or the antagonists SB224289 (300 microg/kg; 5-HT1B), BRL15572 (300 microg/kg; 5-HT1D), rauwolscine (300 microg/kg; alpha2), SB224289 + BRL15572 (300 microg/kg each), SB224289 + rauwolscine (300 microg/kg each), BRL15572 + rauwolscine (300 microg/kg each), rauwolscine (300 microg/kg) + prazosin (100 microg/kg; alpha1), SB224289 (300 microg/kg) + prazosin (100 microg/kg), SB224289 (300 microg/kg) + rauwolscine (300 microg/kg) + prazosin (100 microg/kg), SB224289 (300 microg/kg) + prazosin (100 microg/kg) + BRL44408 (1,000 microg/kg; alpha2A), SB224289 (300 microg/kg) + prazosin (100 microg/kg)+ imiloxan (1,000 microg/kg; alpha2B), or SB224289 (300 microg/kg) + prazosin (100 microg/kg) + MK912 (300 microg/kg; alpha2C). Each group received consecutive 1-min intracarotid infusions of ergotamine (0.56, 1, 1.8, 3.1, 5.6, 10 and 18 microg/min), following a cumulative schedule. In saline-pretreated animals, ergotamine induced dose-dependent decreases in external carotid blood flow without affecting arterial blood pressure or heart rate. These control responses were: unaffected by SB224289, BRL15572, rauwolscine or the combinations of SB224289 + BRL15572, BRL15572 + rauwolscine, rauwolscine + prazosin, SB224289 + prazosin, or SB224289 + prazosin + imiloxan; slightly blocked by SB224289 + rauwolscine; and markedly blocked by SB224289 + rauwolscine + prazosin, SB224289 + prazosin + BRL44408 or SB224289 + prazosin + MK912. Thus, the cranio-selective vasoconstriction elicited by ergotamine in dogs is predominantly mediated by 5-HT1B receptors as well as alpha2A/2C-adrenoceptor subtypes and, to a lesser extent, by alpha1-adrenoceptors.[6] |
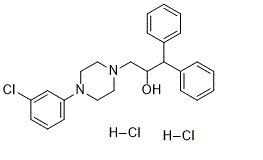
| 分子式 |
C25H29CL3N2O
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
479.87
|
|
| 精确质量 |
478.13
|
|
| CAS号 |
1173022-77-9
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
BRL-15572 hydrochloride; 1173022-77-9
|
|
| PubChem CID |
9891303
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 沸点 |
580.7ºC at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
305ºC
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
2.51E-14mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| LogP |
5.459
|
|
| tPSA |
26.71
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
31
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
451
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
0
|
|
| InChi Key |
WPEXRXMQMPOHIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C25H27ClN2O.2ClH/c26-22-12-7-13-23(18-22)28-16-14-27(15-17-28)19-24(29)25(20-8-3-1-4-9-20)21-10-5-2-6-11-21;;/h1-13,18,24-25,29H,14-17,19H2;2*1H
|
|
| 化学名 |
3-[4-(3-chlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1,1-diphenylpropan-2-ol;dihydrochloride
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.33 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.33 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.33 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 30% Propylene glycol , 5% Tween 80 , 65% D5W: 20 mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0839 mL | 10.4195 mL | 20.8390 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4168 mL | 2.0839 mL | 4.1678 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2084 mL | 1.0419 mL | 2.0839 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
|
|