| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
PDGFR; WT KIT (IC50 = 4 nM); D816H KIT (IC50 = 5 nM); V654A KIT (IC50 = 8 nM); D816V KIT (IC50 = 14 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
c-Kit-IN-1是c-Kit和c-Met的抑制剂,取自专利2010051373A1,化合物实施例45,IC50 <200 nM。 c-Kit-IN-1 还抑制 KDR、PDGFR α 和 β,IC50 分别为 <2 μM、<10 μM 和 <10 μM[1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在 GIST T1 异种移植模型中,以 50 mg/kg 剂量施用 DCC-2618 会产生 KIT 磷酸化抑制的 ED90,相当于大约 470 ng/mL 的 EC90 浓度。每天服用两次,这种口服剂量几乎可以使肿瘤完全停滞。在 KIT 外显子 17 N822K AML 异种移植模型和表达 KIT 外显子 11 delW557K558/外显子 17 Y823D 的患者来源异种移植 (PDX) GIST 中,该剂量的 DCC-2618 可导致肿瘤消退[1]。 DCC-2618 在异种移植研究中抑制 PDGFRA 和 KIT 驱动的肿瘤生长,包括 AML (N822K)、GIST (Y823D) 和肥大细胞增多症 (D816V) 模型中存在的 KIT 外显子 17 突变体[3]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
为了评估 KIT 和 BTK 信号传导,将 ROSAKIT WT、ROSAKIT D816V、HMC-1.1 和 HMC-1.2 细胞在对照培养基或 DCC-2618 (0.5–5 μM) 中于 37°C 孵育 4 小时。蛋白质印迹基本上是根据其他说明进行的。为了评估 KIT 的下游信号通路,HMC-1.1、HMC-1.2、ROSAKIT WT 和 ROSAKIT D816V 细胞最初在不含干细胞因子和胎儿的 Iscove 改良 Dulbecco 培养基中预培养一整夜。小牛血清。然后,将 DCC-2618 (0.001–10 μM) 在 37°C 下作用于每行 106 个细胞,持续 90 分钟。治疗过程结束后,使用转染鼠 scf (kl) 基因 (CHO-KL) 的中国仓鼠卵巢细胞上清液的 10% 在室温下刺激 ROSAKIT WT 细胞 10 分钟。然后基本上以与前述相同的方式进行蛋白质印迹。
|
| 细胞实验 |
为了评估 KIT 和 BTK 信号传导,将 HMC-1.1、HMC-1.2、ROSA (KIT WT) 和 ROSA (KIT D816V) 细胞在对照培养基或 DCC-2618 (0.5– 5μM)。使用的一种方法是蛋白质印迹法。
使用标准PK/LDH偶联分光光度法测试Ripretinib(DCC-2618)对KIT亚型的抑制作用。CHO细胞被瞬时转染以表达突变KIT或PDGFRα构建体。转染的细胞用一系列DCC-2618处理,通过ELISA或蛋白质印迹测定细胞裂解物中磷酸化KIT或PDGFRα的水平。使用荧光染料刃天青测量了几种细胞系的细胞增殖。实验一式三份。[1] 蛋白质印迹[2] 为了评估KIT和BTK信号传导,将HMC-1.1、HMC-1.2、ROSAKIT WT和ROSAKIT D816V细胞在对照培养基或Ripretinib(DCC-2618)(0.5-5μM)中在37°C下孵育4小时。蛋白质印迹基本上如别处所述进行。为了评估KIT的下游信号通路,HMC-1.1、HMC-1.2、ROSAKIT WT和ROSAKIT D816V细胞首先在不含胎牛血清和干细胞因子的Iscove改良Dulbecco培养基中预孵育过夜。然后,用DCC-2618(0.001-10μM)在37°C下处理来自每条线的细胞(106)90分钟。在治疗结束时,用转染有小鼠scf(kl)基因(CHO-kl)的中国仓鼠卵巢细胞的含干细胞因子的上清液(10%)在室温下刺激ROSAKIT WT细胞10分钟。此后,基本上如前所述进行蛋白质印迹。 |
| 动物实验 |
xenograft models (mice)
100 mg/kg/day or 25 mg/kg/day or 50 mg/kg BID oral |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption
Ripretinib is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract and Tmax is achieved in 4 hours, with steady-state concentrations reached within 14 days. Route of Elimination Ripretinib is 34% excreted in the feces and 0.2% excreted in the urine. Volume of Distribution The mean volume of distribution of ripretinib is 307 L. Clearance The mean apparent clearance of ripretinib is 15.3 L/hour. Metabolism / Metabolites Ripretinib is metabolized by the CYP3A subfamily of enzymes with contributions from CYP2D6 and CYP2E1 to its active metabolite, DP-5439. Biological Half-Life The average half-life of ripretinib is 14.8 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In the prelicensure placebo-controlled clinical trial in patients with refractory and extensively treated GIST, ALT elevations arose in 13% of ripretinib- vs 5% of placebo-treated subjects. ALT elevations were generally transient and mild, and were above 5 times the ULN in only 1% of treated patients and did not require dose modification or discontinuation. Bilirubin elevations were reported in 22% of ripretinib treated patients but only 7.5% of placebo controls. The bilirubin elevations were transient and mild, but were not characterized as to their timing, severity and whether conjugated or unconjugated (direct or indirect). In the open label and controlled trials supporting the approval of ripretinib, there were no instances of clinically apparent liver injury, hepatic failure, or deaths from liver injury. Since its approval in the United States and Europe, there have been no reported cases of clinically apparent liver injury associated with ripretinib therapy. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the use of ripretinib during breastfeeding. Because ripretinib and its metabolite are more than 99% bound to plasma proteins, the amounts in milk are likely to be low. However, their half-lives are long. The manufacturer recommends that mothers should not breastfeed during treatment with ripretinib and for 1 week after the final dose. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Ripretinib is over 99% bound to albumin and alpha-1 acid glycoprotein. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Ripretinib is a kinase inhibitor used for the treatment of advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) that has not adequately responded to other kinase inhibitors such as [sunitinib] and [imatinib]. Ripretinib, also known as Qinlock, is manufactured by Deciphera Pharmaceuticals and was initially approved by the FDA on May 15, 2020. It is the first drug approved as a fourth-line therapy in the specific setting of prior treatment with a minimum of 3 other kinase inhibitors.
Ripretinib is a Kinase Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of ripretinib is as a Stem Cell Factor (KIT) Receptor Inhibitor, and Platelet-derived Growth Factor alpha Receptor Inhibitor, and Cytochrome P450 2C8 Inhibitor, and P-Glycoprotein Inhibitor, and Breast Cancer Resistance Protein Inhibitor. Ripretinib is a multikinase inhibitor that is used to treat refractory forms of advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Serum aminotransferase elevations occur in a small proportion of patients treated with ripretinib, but episodes of clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice have not been reported with its use. Ripretinib is an orally bioavailable switch pocket control inhibitor of wild-type and mutated forms of the tumor-associated antigens (TAA) mast/stem cell factor receptor (SCFR) KIT and platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFR-alpha; PDGFRa), with potential antineoplastic activity. Upon oral administration, ripretinib targets and binds to both wild-type and mutant forms of KIT and PDGFRa specifically at their switch pocket binding sites, thereby preventing the switch from inactive to active conformations of these kinases and inactivating their wild-type and mutant forms. This abrogates KIT/PDGFRa-mediated tumor cell signaling and prevents proliferation in KIT/PDGFRa-driven cancers. DCC-2618 also inhibits several other kinases, including vascular endothelial growth factor receptor type 2 (VEGFR2; KDR), angiopoietin-1 receptor (TIE2; TEK), PDGFR-beta and macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (FMS; CSF1R), thereby further inhibiting tumor cell growth. KIT and PDGFRa are tyrosine kinase receptors that are upregulated or mutated in a variety of cancer cell types; mutated forms play a key role in the regulation of tumor cell proliferation and resistance to chemotherapy. Drug Indication Ripretinib is indicated to treat adults diagnosed with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) who have had prior therapy with at least 3 kinase inhibitors, including with [imatinib]. Qinlock is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumour (GIST) who have received prior treatment with three or more kinase inhibitors, including imatinib. View More
Pharmacodynamics
Mechanism of Action Protein kinases play important roles in cellular function, and their dysregulation can lead to carcinogenesis. Ripretinib inhibits protein kinases including wild type and mutant platelet-derived growth factor receptor A (PDGFRA) and KIT that cause the majority of gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST). In vitro, ripretinib has been shown to inhibit PDGFRB, BRAF, VEGF, and TIE2 genes. Ripretinib binds to KIT and PDGFRA receptors with mutations on the exons 9, 11, 13, 14, 17 and 18 (for KIT mutations), and exons 12, 14 and 18 (for PDGFRA mutations). The “switch pocket” of a protein kinase is normally bound to the activation loop, acting as an “on-off switch” of a kinase. Ripretinib boasts a unique dual mechanism of action of binding to the kinase switch pocket as well as the activation loop, thereby turning off the kinase and its ability to cause dysregulated cell growth. DCC-2618 inhibited various forms of KIT with nanomolar potency: WT (IC50 4 nM), V654A (8 nM), T670I (18 nM), D816H (5 nM), D816V (14 nM). In CHO cells transiently transfected with both single and double (primary/secondary) KIT mutants, DCC-2618 robustly inhibited exon 17, exon 9/13, exon 9/14, and exon 9/17 KIT mutants, as well as exon 11/17 KIT mutants, including exon 17 D816V, D816G, D820A, D820E, D820Y, N822K, N822Y, N822H, and Y823D primary or secondary mutations. DCC-2618 inhibited wild type KIT phosphorylation in the MO7e cell line (IC50 36 nM). DCC-2618 potently inhibited KIT activation in human GIST cell lines, including GIST T1 (exon 11 deletion, IC50 2 nM), GIST 430 (exon 11 deletion/exon 13 V654A, IC50 7 nM), and GIST 48 (exon 11 V560D/exon 17 D820A, IC50 53 nM). In the murine mastocytosis P815 cell line expressing the exon 17 D816Y mutation, DCC-2618 potently inhibited cell proliferation (IC50 2 nM). In vivo, DCC-2618 administration at 50 mg/kg afforded an ED90 for inhibition of KIT phosphorylation in the GIST T1 xenograft model, corresponding to an EC90 concentration of ∼ 470 ng/mL. When give twice daily, this oral dose resulted in almost complete tumor stasis. This dose of DCC-2618 produced tumor regressions in a patient derived xenograft (PDX) GIST expressing KIT exon 11 delW557K558/exon 17 Y823D, and also in a KIT exon 17 N822K AML xenograft model. Conclusion: DCC-2618 is a potent inhibitor of singly and doubly mutated KIT characterized by primary exon 9 or exon 11 mutations paired with secondary mutations in exons 13, 14 or 17. DCC-2618 inhibits exon 17 mutations, including the D816V mutation refractory to currently marketed KIT inhibitors. DCC-2618 has the potential to treat KIT mutant-driven cancers including GIST, systemic mastocytosis, AML, or melanoma. DCC-2618 has been selected for formal IND-enabling clinical development.[1] Systemic mastocytosis is a complex disease defined by abnormal growth and accumulation of neoplastic mast cells in various organs. Most patients exhibit a D816V-mutated variant of KIT, which confers resistance against imatinib. Clinical problems in systemic mastocytosis arise from mediator-related symptoms and/or organ destruction caused by malignant expansion of neoplastic mast cells and/or other myeloid cells in various organ systems. DCC-2618 is a spectrum-selective pan KIT and PDGFRA inhibitor which blocks KIT D816V and multiple other kinase targets relevant to systemic mastocytosis. We found that DCC-2618 inhibits the proliferation and survival of various human mast cell lines (HMC-1, ROSA, MCPV-1) as well as primary neoplastic mast cells obtained from patients with advanced systemic mastocytosis (IC50 <1 μM). Moreover, DCC-2618 decreased growth and survival of primary neoplastic eosinophils obtained from patients with systemic mastocytosis or eosinophilic leukemia, leukemic monocytes obtained from patients with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia with or without concomitant systemic mastocytosis, and blast cells obtained from patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Furthermore, DCC-2618 was found to suppress the proliferation of endothelial cells, suggesting additional drug effects on systemic mastocytosis-related angiogenesis. Finally, DCC-2618 was found to downregulate IgE-mediated histamine release from basophils and tryptase release from mast cells. Together, DCC-2618 inhibits growth, survival and activation of multiple cell types relevant to advanced systemic mastocytosis. Whether DCC-2618 is effective in vivo in patients with advanced systemic mastocytosis is currently under investigation in clinical trials.[2] |
| 分子式 |
C26H21F2N5O3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
489.4735
|
| 精确质量 |
489.161
|
| CAS号 |
1225278-16-9
|
| 相关CAS号 |
1442472-39-0
|
| PubChem CID |
46208890
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.40±0.1 g/cm3 (20 ºC 760 Torr)
|
| LogP |
5.632
|
| tPSA |
101.63
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
36
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
794
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
WWOXKWLDMLMYQY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C26H21F2N5O3/c1-33-15-16(14-30-33)21-11-18(7-10-29-21)36-23-13-19(27)22(12-20(23)28)32-25(35)26(8-9-26)24(34)31-17-5-3-2-4-6-17/h2-7,10-15H,8-9H2,1H3,(H,31,34)(H,32,35)
|
| 化学名 |
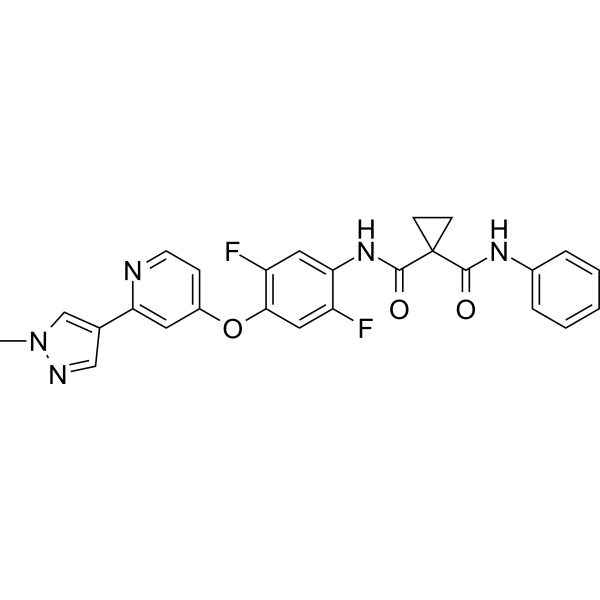
1-N'-[2,5-difluoro-4-[2-(1-methylpyrazol-4-yl)pyridin-4-yl]oxyphenyl]-1-N-phenylcyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxamide
|
| 别名 |
1225278-16-9; c-Kit-IN-1; 1-N'-[2,5-difluoro-4-[2-(1-methylpyrazol-4-yl)pyridin-4-yl]oxyphenyl]-1-N-phenylcyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxamide; N-(2,5-Difluoro-4-((2-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)pyridin-4-yl)oxy)phenyl)-N-phenylcyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxamide; N'1-(2,5-DIFLUORO-4-{[2-(1-METHYLPYRAZOL-4-YL)PYRIDIN-4-YL]OXY}PHENYL)-N1-PHENYLCYCLOPROPANE-1,1-DICARBOXAMIDE; PDGFR inhibitor 1; SCHEMBL2450218; CHEMBL4303619;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~204.30 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.11 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.11 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.11 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0430 mL | 10.2151 mL | 20.4303 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4086 mL | 2.0430 mL | 4.0861 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2043 mL | 1.0215 mL | 2.0430 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT03673501 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: DCC-2618 Tablets Drug: Sunitinib |
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors | Deciphera Pharmaceuticals LLC | February 11, 2019 | Phase 3 |
| NCT05697107 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Ripretinib Oral Tablet | Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors | Peking University | May 20, 2021 | |
| NCT05132738 | Recruiting | Drug: Ripretinib treatment | Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors | RenJi Hospital | August 1, 2021 | Not Applicable |
| NCT05734105 | Recruiting | Drug: Ripretinib Drug: Sunitinib |
GIST | Deciphera Pharmaceuticals LLC | November 2023 | Phase 3 |
| NCT05957367 | Recruiting | Drug: Ripretinib Drug: DCC-3116 |
GIST Colorectal Cancer |
Deciphera Pharmaceuticals LLC | September 28, 2023 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |