| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Following oral administration of cefuroxime axetil in pediatric patients with acute otitis media with effusion or with chronic or recurrent otitis media with effusion, cefuroxime is distributed into middle ear effusions. In a study in pediatric patients 1-4 years of age with acute otitis media with effusion who received a single 15 mg/kg dose of cefuroxime as cefuroxime axetil oral suspension, cefuroxime concentrations in middle ear effusions 2-5 hours after a dose ranged from 0.2-3.6 ug/mL; concurrent serum concentrations were 2.8-7.3 ug/mL. In pharmacokinetic studies of cefuroxime axetil oral suspension in children, the drug was administered postprandially or with food; no data are available regarding absorption of the suspension in fasting children. Following oral administration to children 3 months to 12 years of age (mean age: 23 months) of a single 10-, 15-, or 20-mg/kg dose of commercially available cefuroxime axetil oral suspension concomitantly with milk or milk products, peak serum cefuroxime concentrations are attained approximately 3.6, 2.7, or 3.1 hours after the dose, respectively, and average 3.3, 5.1, or 7 mcg/mL, respectively. Results of a study in healthy adults indicate that cefuroxime axetil oral suspensions containing 125 mg/5 mL or 250 mg/5 mL are bioequivalent. In healthy adults who received a 250-mg dose of cefuroxime axetil given as a suspension containing 125 mg/5 mL or 250 mg/5 mL with food, peak plasma concentrations of cefuroxime were 2.4 or 2.2 aug/mL, respectively, and were attained 3 hours after the dose. Following oral administration in adults of a single 125-mg, 250-mg, 500-mg, or 1-g dose of commercially available cefuroxime axetil tablets immediately following a meal, peak serum cefuroxime concentrations are attained approximately 2-3 hours after the dose and average 2.1, 4.1, 7, or 13.6 ug/mL, respectively; serum concentrations 6 hours after the dose average 0.3, 0.7, 2.2, or 3.4 ug/mL, respectively. AUC of the drug in these individuals averaged 6.7, 12.9, 27.4, or 50 mcg-h/mL, respectively. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Cefuroxime axetil (13 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Following oral administration, cefuroxime axetil is rapidly hydrolyzed to cefuroxime by nonspecific esterases in the intestinal mucosa and blood; the axetil moiety is metabolized to acetaldehyde and acetic acid. Cefuroxime is not metabolized and is excreted unchanged principally in urine by both glomerular filtration and tubular secretion. Biological Half-Life In neonates and children, the serum half-life of cefuroxime is inversely proportional to age.6 25 30 Following oral administration of cefuroxime axetil oral suspension in children 3 months to 12 years of age, the serum half-life of cefuroxime averages 1.4-1.9 hours. In adults, the serum or plasma half-life of cefuroxime following oral administration of commercially available cefuroxime axetil tablets or oral suspension ranges from 1.2-1.6 hours. Because cefuroxime is renally excreted, the serum half-life is prolonged in patients with reduced renal function. In a study of 20 elderly patients (mean age = 83.9 years) having a mean creatinine clearance of 34.9 mL/min, the mean serum elimination half-life was 3.5 hours. |
|---|---|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Interactions
Drugs that reduce gastric acidity may result in a lower bioavailability of Ceftin compared with that of fasting state and tend to cancel the effect of postprandial absorption. Oral probenecid administered shortly before or concomitantly with cefuroxime usually slows the rate of tubular secretion of cefuroxime and produces higher and more prolonged serum concentrations of cefuroxime. This effect is usually used to therapeutic advantage in the treatment of gonorrhea. Peak serum concentrations of cefuroxime and the half-life of the drug are reportedly increased by up to 30% when probenecid is administered concomitantly; the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) of cefuroxime is increased by about 50%. Concomitant administration of probenecid also reportedly decreases the apparent volume of distribution of cefuroxime by about 20%. Cefuroxime axetil may affect gut flora, leading to decreased estrogen reabsorption and reduced efficacy of oral contraceptives containing estrogen and progestin. The manufacturers state that cefuroxime should be used with caution in patients receiving diuretics because concurrent use of these drugs may increase the risk of adverse renal effects. In vitro studies indicate that the antibacterial activity of cefuroxime and aminoglycosides may be additive or synergistic against some organisms including Enterobacter, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Proteus mirabilis, and Serratia marcescens. Concurrent use of aminoglycosides and certain cephalosporins reportedly may increase the risk of nephrotoxicity during therapy. Although this effect has not been reported to date with cefuroxime, the possibility that nephrotoxicity may be potentiated should be considered if the drug is used concomitantly with an aminoglycoside. Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Rabbit oral 200 mg/kg LD50 Mouse sc 1840 mg/kg LD50 Mouse ip 510 mg/kg LD50 Rat sc 2500 mg/kg LD50 Rat ip 950 mg/kg |
| 其他信息 |
Cefuroxime axetil is a cephalosporin.
Ceftin has been reported in Apis cerana with data available. Cefuroxime Axetil is a second generation semi-synthetic cephalosporin and a beta-lactam antibiotic with bactericidal activity. Cefuroxime's effect is dependent on its binding to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located in the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane. Binding results in the inhibition of the transpeptidase enzymes, thereby preventing cross-linking of the pentaglycine bridge with the fourth residue of the pentapeptide and interrupting consequent synthesis of peptidoglycan chains. As a result, cefuroxime inhibits bacterial septum and cell wall synthesis formation. See also: Cefuroxime (has active moiety); Cefuroxime axetil, (E)- (annotation moved to). Mechanism of Action Cefuroxime is usually bactericidal in action.Like other cephalosporins, the antibacterial activity of the drug results from inhibition of mucopeptide synthesis in the bacterial cell wall. Therapeutic Uses Anti-Bacterial Agent Ceftin tablets and oral suspension /are indicated for/ acute bacterial otitis media caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilusinfluenzae(including beta-lactamase-producing strains), Moraxellacatarrhalis (including beta-lactamase-producing strains), or Streptococcus pyogenes. /Included in US product label/ Ceftin tablets and oral suspension /are indicated for/ pharyngitis/tonsillitis caused by Streptococcus pyogenes. NOTE: The usual drug of choice in the treatment and prevention of streptococcal infections, including the prophylaxis of rheumatic fever, is penicillin given by the intramuscular route. Ceftin Tablets are generally effective in the eradication of streptococci from the nasopharynx; however, substantial data establishing the efficacy of cefuroxime in the subsequent prevention of rheumatic fever are not available. Please also note that in all clinical trials, all isolates had to be sensitive to both penicillin and cefuroxime. There are no data from adequate and well-controlled trials to demonstrate the effectiveness of cefuroxime in the treatment of penicillin-resistant strains of Streptococcus pyogenes. /Included in US product label/ Ceftin tablets /are indicated for/ acute bacterial maxillary sinusitis caused by Streptococcus pneumoniaeorHaemophilusinfluenzae (non-beta-lactamase-producing strains only). NOTE: In view of the insufficient numbers of isolates of beta-lactamase-producing strains of Haemophilusinfluenzae and Moraxellacatarrhalis that were obtained from clinical trials with Ceftin Tablets for patients with acute bacterial maxillary sinusitis, it was not possible to adequately evaluate the effectiveness of Ceftin Tablets for sinus infections known, suspected, or considered potentially to be caused by beta-lactamase-producing Haemophilusinfluenzae or Moraxellacatarrhalis. /Included in US product label/ For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Cefuroxime axetil (15 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings Patients should be advised that antibacterials (including cefuroxime) should only be used to treat bacterial infections and not used to treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). Patients also should be advised about the importance of completing the full course of therapy, even if feeling better after a few days, and that skipping doses or not completing therapy may decrease effectiveness and increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable with cefuroxime or other antibacterials in the future. To reduce development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain effectiveness of cefuroxime and other antibacterials, the drug should be used only for the treatment or prevention of infections proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When selecting or modifying anti-infective therapy, use results of culture and in vitro susceptibility testing. In the absence of such data, consider local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns when selecting anti-infectives for empiric therapy. Prior to initiation of cefuroxime therapy, careful inquiry should be made concerning previous hypersensitivity reactions to cephalosporins, penicillins, or other drugs. Cefuroxime axetil /is/ contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to cefuroxime or other cephalosporins and should be used with caution in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to penicillins. Use of cephalosporins should be avoided in patients who have had an immediate-type (anaphylactic) hypersensitivity reaction to penicillins. Prescribing Ceftin in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Cefuroxime axetil (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
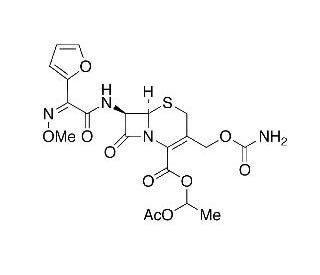
| 分子式 |
C20H22N4O10S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
510.47448
|
| 精确质量 |
510.105
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 47.06; H, 4.34; N, 10.98; O, 31.34; S, 6.28
|
| CAS号 |
64544-07-6
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Cefuroxime sodium;56238-63-2
|
| PubChem CID |
6321416
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to almost white crystalline powder
White powder |
| 密度 |
1.6±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 折射率 |
1.665
|
| LogP |
0.85
|
| tPSA |
214.36
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
12
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
12
|
| 重原子数目 |
35
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
968
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
| SMILES |
CC(OC(OC(C1=C(CS[C@@H]2[C@H](NC(/C(/C3=CC=CO3)=N\OC)=O)C(N12)=O)COC(N)=O)=O)C)=O
|
| InChi Key |
KEJCWVGMRLCZQQ-YJBYXUATSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C20H22N4O10S/c1-9(25)33-10(2)34-19(28)15-11(7-32-20(21)29)8-35-18-14(17(27)24(15)18)22-16(26)13(23-30-3)12-5-4-6-31-12/h4-6,10,14,18H,7-8H2,1-3H3,(H2,21,29)(H,22,26)/b23-13-/t10?,14-,18-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
1-acetyloxyethyl (6R,7R)-3-(carbamoyloxymethyl)-7-[[(2Z)-2-(furan-2-yl)-2-methoxyiminoacetyl]amino]-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate
|
| 别名 |
Cefuroxime axetil; SN 407; DRG-0157; CXM-AX
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~125 mg/mL (~244.87 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.07 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.07 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.07 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9590 mL | 9.7949 mL | 19.5898 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3918 mL | 1.9590 mL | 3.9180 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1959 mL | 0.9795 mL | 1.9590 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT03584919 | Completed | Drug: doxycycline Drug: Cefuroxime Axetil 500Mg Tab Other: control subjects |
Erythema Chronicum Migrans | University Medical Centre Ljubljana | 2006-06-01 | Not Applicable |
| NCT06527560 | Recruiting | Drug: Cefuroxime Drug: Cefuroxime Axetil |
Pyelonephritis in Pregnancy | Hospital de Clinicas de Porto Alegre | 2024-09-09 | Phase 4 |
| NCT03020940 | Unknown status | Drug: Cefuroxime Axetil Dispersible Tablets | Infectious Disease | Jiangsu Famous Medical Technology Co., Ltd. | 2017-01 | |
| NCT01518192 | Completed | Drug: doxycycline Drug: cefuroxime axetil |
Erythema Migrans Post-Lyme Disease Symptoms |
University Medical Centre Ljubljana | 2006-06 | Phase 4 |
| NCT00257049 | Completed | Drug: levofloxacin | Pneumonia | Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research & Development, L.L.C. | 1984-01 | Phase 2 Phase 3 |