| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
HDAC3 (IC50 = 67 nM); HDAC10 (IC50 = 78 nM); HDAC1 (IC50 = 95 nM); HDAC2 (IC50 = 160 nM); HDAC11 (IC50 = 432 nM); HDAC8 (IC50 = 733 nM)
Chidamide, at low nanomolar concentrations, inhibits both class IIb HDAC10 and class I HDACs 1-3. Both human PBMC and HeLa cervical adenocarcinoma cells exhibit a significant increase in histone H3 acetylation upon exposure to chidamide. Chidamide and MS-275 similarly inhibit the in vitro growth of most tumor cells, but not all of them, in the low micromolar concentration range, according to studies on cell growth inhibition carried out with 18 human-derived tumor cell lines. Nonetheless, normal cells from human fetal kidney (CCC-HEK) and liver (CCC-HEL) are significantly less toxic to chidamide and, to a lesser extent, MS-275, suggesting that normal cells and cancerous cells respond to chidamide differently in terms of cytotoxicity[1]. |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:Chidamide(以前称为 CS055、Tucidinostat 和 HBI-8000)是一种有效的口服苯甲酰胺型组蛋白脱乙酰酶 (HDAC) 抑制剂,对 HDAC1、HDAC2、HDAC3 的 IC50 分别为 95、160、67 和 78 nM西达本胺已被中国FDA批准用于治疗复发或难治性外周T细胞淋巴瘤(PTCL),在日本具有孤儿药地位,截至2015年4月仅在中国获得批准。西达本胺选择性结合并抑制HDAC 导致组蛋白 H3 乙酰化水平增加。它还抑制 PI3K/Akt 和 MAPK/Ras 信号通路中信号激酶的表达,可能导致细胞周期停滞和诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡,从而抑制肿瘤细胞凋亡。敏感肿瘤细胞中的肿瘤细胞增殖。西达本胺正在研究作为胰腺癌的治疗方法。但是,美国 FDA 尚未批准它用于治疗胰腺癌。激酶测定:HDAC 活性按照比色 HDAC 活性测定试剂盒中的描述进行检测。每个反应液 (100 μL) 含有白血病细胞的核蛋白 (50 μg) 提取物和 HDAC 底物。为了测试 HDACis 的效果,将 Chidamide (CS055) 和 MS-275 添加到混合物中并在 37°C 下孵育 1 小时。 HDAC 活性通过酶标仪在 405 nm 处测量。阳性对照(仅核提取物和载体)设置为 100%,含有 10 μM Trichostatin A(一种已知的强 HDACi)的双蒸水用作阴性对照并设置为 0%。细胞测定:使用CCK-8测定评估PaTu8988细胞的增殖。将PaTu8988细胞随机分为4组,并在不存在或存在浓度为0、1.25、2.5和5μM的西达本胺的情况下孵育48小时。随后,每孔加入10 μL CCK-8,孵育2 h。然后用酶标仪在 450 nm 处测量每个孔的光密度。细胞存活率的计算公式为:细胞存活率(%)=1-(ODctrl-ODsample)/ODctrl×100%。
Chidamide 对一系列人重组HDAC蛋白表现出抑制活性,对HDAC1、2、3和10具有低纳摩尔级的效力。它对HDAC4、8和11的活性弱得多,对HDAC5、6、7和9在高达30 µM的浓度下均未显示出显著抑制。[1] 用chidamide处理可显著诱导HeLa宫颈腺癌细胞中的组蛋白H3乙酰化。用1 µM chidamide处理后,乙酰化早在30-60分钟就开始增加,并在24-72小时达到最高水平。在离体用chidamide处理的健康人外周血单个核细胞(PBMC)中也观察到类似的组蛋白H3乙酰化诱导作用。[1] 使用18种人肿瘤来源细胞系进行的细胞生长抑制研究表明,chidamide在低微摩尔浓度范围内抑制大多数肿瘤细胞的体外生长(Gl₅₀值从0.4 µM到>50 µM不等)。值得注意的是,chidamide对正常人胎儿肾细胞(CCC-HEK)和肝细胞(CCC-HEL)的毒性显著较低(Gl₅₀ >100 µM),表明其对正常细胞和癌细胞的细胞毒性反应存在差异。[1] 用纳摩尔浓度的chidamide(100 nM处理48小时为最佳条件)离体处理健康供体的PBMC,能显著增强其对K562人髓系白血病靶细胞的细胞毒性。当仅用chidamide预处理靶细胞K562时,未观察到这种增强的裂解作用。当效应细胞(PBMC)和靶细胞均被处理时,增强作用最大。[1] 流式细胞术分析显示,用100 nM chidamide处理PBMC 48小时,可上调涉及自然杀伤(NK)细胞功能的蛋白质表达,包括激活受体CD16和NKG2D,以及细胞毒性酶颗粒酶A(GZMA)。[1] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
观察到西达本胺 (CS055) 治疗对肿瘤生长的抑制作用呈剂量依赖性,这证明了西达本胺的抗肿瘤活性。 20天后,对照肿瘤平均生长至14.51 cm3,而西达本胺治疗的肿瘤生长至11.68、11.05和8.45 cm3,分别对应于19.54%、23.83%和41.80%的生长抑制。用赋形剂治疗的动物中的平均肿瘤质量为9.4±2.7g,用低剂量西达本胺治疗的动物中的平均肿瘤质量为8.4±2.4g。中剂量西达本胺治疗的动物肿瘤质量为7.6±1.6 g,而接受高剂量西达本胺治疗的动物肿瘤质量为5.4±1.5 g(P<0.01)。此外,西达本胺治疗可延长携带 HL60 异种移植物的裸鼠的存活时间。此外,随着西达本胺的治疗,肿瘤组织中脂质过氧化产物(MDA)的水平增加,这是ROS介导的损伤的推定指标,这表明西达本胺诱导的ROS生成可能发挥了作用。
Chidamide的体内抗肿瘤活性在皮下接种人肿瘤异种移植物的裸鼠中进行评估。每日一次口服chidamide,持续20-28天,显示出剂量依赖性的抗肿瘤功效。[1] 在HCT-8结直肠癌异种移植模型中,与载体对照组相比,12.5、25和50 mg/kg剂量的chidamide能显著减小肿瘤体积和肿瘤重量。50 mg/kg剂量的疗效与对照药物MS-275(25 mg/kg)和5-氟尿嘧啶(5-FU,20 mg/kg)相似或更优。重要的是,chidamide在这些剂量下耐受性良好,未引起显著的体重减轻,而对照药物则导致了体重减轻。[1] 在携带A549肺癌、BEL-7402肝癌和MCF-7乳腺癌异种移植物的裸鼠模型中,也观察到chidamide(12.5和25 mg/kg)具有类似的显著且剂量依赖性的抗肿瘤作用,且在治疗期间未观察到明显的体重减轻。[1] |
| 酶活实验 |
按照比色 HDAC 活性测定试剂盒的说明检测 HDAC 活性。将来自白血病细胞的 HDAC 底物和核蛋白 (50 μg) 提取物添加到每个反应 (100 μL) 中。将西达本胺 (CS055) 和 MS-275 添加到混合物中并在 37°C 下孵育一小时,以测试 HDACis 的影响。使用酶标仪测量 405 nm 处的 HDAC 活性。含有 10 μM Trichostatin A(一种已知的强 HDACi)的双蒸水用作阴性对照并设置为 0%,而阳性对照(仅核提取物和载体)设置为 100%。
使用人重组HDAC蛋白分析chidamide对HDAC亚型的抑制作用。酶反应在含有牛血清白蛋白、HDAC底物、纯化的重组HDAC酶以及预定浓度测试化合物的缓冲液中进行。反应在室温下孵育17小时。孵育后,向每孔中加入显色剂溶液,再将板孵育20分钟。然后使用酶标仪测量荧光强度。通过分析浓度-反应抑制曲线来确定IC50值。每个化合物浓度进行复孔测试。[1] |
| 细胞实验 |
将西达本胺以不同的浓度 (0-400 nM) 添加到 6 孔板中的分离的 PBMC 效应细胞中(6 x 106 细胞/孔),持续不同的时间(24-72 小时)。
对于体外细胞生长抑制实验,将肿瘤细胞接种到96孔板中。24小时后,加入不同浓度的测试化合物,继续培养72小时。然后通过加入试剂,在37°C下孵育2小时,并测量490 nm处的吸光度来评估细胞活力。计算抑制细胞生长50%的浓度(Gl₅₀)。所有化合物溶解于DMSO中并稀释使用。样品进行复孔评估,实验至少重复三次。[1] 对于组蛋白乙酰化分析,用化合物处理HeLa细胞。通过裂解、洗涤、酸提取和沉淀等一系列步骤从细胞沉淀中分离组蛋白。将提取的组蛋白溶解并定量蛋白浓度。对于蛋白质印迹分析,将蛋白质转移到膜上,用抗乙酰化H3抗体孵育,再用抗总组蛋白H3抗体重新孵育。使用辣根过氧化物酶偶联的二抗和增强化学发光法进行检测。[1] 对于细胞毒性实验,从健康供体中分离外周血单个核细胞(PBMC),并在培养板中用chidamide处理。处理后,洗涤PBMC,并与K562靶细胞以不同的效靶比在37°C下共孵育4小时。使用标准的乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)释放检测试剂盒分析细胞毒性。在修正自发释放后,计算特异性裂解百分比。[1] 对于流式细胞术分析,将经chidamide处理或未处理的PBMC与针对特定表面蛋白(如CD16、NKG2D、GZMA)的荧光标记单克隆抗体或相应的同型对照一起孵育。然后在流式细胞仪上分析细胞,并计算特异性荧光指数。[1] |
| 动物实验 |
Athymic nude mice (BALB/c-nu)
12.5-50 mg/kg oral Athymic nude mice (BALB/c-nu), 6-8 weeks old, were used for in vivo antitumor studies. Human tumor cells (HCT-8, A549, MCF-7, Bel-7402) were passaged in vivo and then transplanted subcutaneously into the flank of mice as tumor fragments. Treatment began 3 days after tumor inoculation. Chidamide was dissolved in a vehicle containing 0.2% carboxymethyl cellulose and 0.1% Tween 80. It was administered orally, once daily, for 20 to 28 consecutive days, depending on the tumor model. Tumor dimensions (length and width) were measured every 3 days to calculate tumor volume. At the end of the experiment, mice were euthanized, and tumors were excised and weighed. Each experimental group consisted of 8-10 mice.[1] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
The literature states that chidamide is orally bioavailable.[1]
|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
In vitro, chidamide showed significantly lower toxicity (Gl₅₀ > 100 µM) against normal human fetal kidney and liver cells compared to many tumor cell lines.[1]
In vivo, oral administration of chidamide at doses up to 50 mg/kg/day for several weeks was well-tolerated in tumor-bearing nude mice, with no observed gross body weight loss, whereas control drugs (MS-275 and 5-FU) caused significant weight loss at their effective doses.[1] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Chidamide is a member of benzamides.
Tucidinostat is an investigational drug that is being studied as part of a strategy to cure HIV infection. Tucidinostat belongs to a group of HIV drugs called latency-reversing agents. Tucidinostat is an orally bioavailable benzamide-type inhibitor of histone deacetylase (HDAC) isoenzymes 1, 2, 3 and 10, with potential antineoplastic activity. Upon administration, tucidinostat binds to and inhibits HDACs, leading to an increase of acetylation levels of histone proteins. This agent also inhibits the expression of kinases in the PI3K/Akt and MAPK/Ras signaling pathways and may result in cell cycle arrest and the induction of tumor cell apoptosis. This may inhibit tumor cell proliferation in susceptible tumor cells. HDACs, a class of enzymes that deacetylate chromatin histone proteins, are upregulated in many tumor types and play key roles in gene expression. Compared to some other benzamide-type HDAC inhibitors, chidamide is more stable, more resistant to degradation and has a longer half-life. Drug Indication Investigated for use/treatment in cancer/tumors (unspecified). Mechanism of Action Chidamide is an orally bioavailable histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor derived from the benzamide class. Histone deacetylase inhibitors are a class of cancer drugs that induce selective regulation of gene expression in cancer cells. [HUYA Biosciences Press Release] Chidamide is a new histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor of the benzamide class, discovered using a computer-aided rational drug design approach.[1] Its primary mechanism of action involves the inhibition of Class I HDACs (1, 2, 3) and Class IIb HDAC10, leading to increased histone acetylation and altered gene expression.[1] In addition to direct antitumor effects, chidamide enhances immune cell-mediated cytotoxicity by upregulating the expression of proteins and genes involved in natural killer (NK) cell functions in peripheral blood mononuclear cells.[1] Microarray gene expression studies on peripheral white blood cells from T-cell lymphoma patients treated with chidamide showed upregulated expression of genes related to immune cell-mediated antitumor activity, including NK-activating receptors, cytotoxic enzymes, and apoptosis mediators.[1] Chidamide demonstrated broad-spectrum antitumor activity in preclinical models and is under clinical development for cancer indications.[1] |
| 分子式 |
C22H19FN4O2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
390.41
|
|
| 精确质量 |
390.149
|
|
| CAS号 |
1616493-44-7
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Tucidinostat-d4
|
|
| PubChem CID |
12136798
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid
|
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
602.1±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
317.9±31.5 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.691
|
|
| LogP |
2.4
|
|
| tPSA |
97.1
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
29
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
577
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
FC1C=CC(=C(C=1)N)NC(C1C=CC(=CC=1)CNC(/C=C/C1C=NC=CC=1)=O)=O
|
|
| InChi Key |
SZMJVTADHFNAIS-BJMVGYQFSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H19FN4O2/c23-18-8-9-20(19(24)12-18)27-22(29)17-6-3-16(4-7-17)14-26-21(28)10-5-15-2-1-11-25-13-15/h1-13H,14,24H2,(H,26,28)(H,27,29)/b10-5+
|
|
| 化学名 |
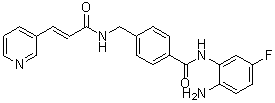
N-(2-amino-4-fluorophenyl)-4-[[[(E)-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enoyl]amino]methyl]benzamide
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.40 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.40 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.40 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 1% CMC Na: 30mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5614 mL | 12.8070 mL | 25.6141 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5123 mL | 2.5614 mL | 5.1228 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2561 mL | 1.2807 mL | 2.5614 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT05140616 | Recruiting | Drug: Chidamide | Safety and Efficacy | The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University |
May 31, 2021 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
| NCT05951855 | Recruiting | Drug: Selinexor Drug: Chidamide |
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (Relapsed/Refractory) |
The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University |
October 19, 2022 | Phase 2 |
| NCT05330364 | Recruiting | Drug: Chidamide Drug: Cladribine |
Acute Myeloid Leukemia | Ge Zheng | June 1, 2021 | Phase 2 |
| NCT05270200 | Recruiting | Drug: Azacitidine Drug: Chidamide |
Leukemia, Myeloid, Acute | Zhujiang Hospital | February 1, 2022 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
| NCT04994210 | Recruiting | Drug: Sintilimab Drug: Chidamide |
Safety and Efficacy | Sun Yat-sen University | October 4, 2021 | Phase 2 |
 Expression levels of MEG3 and methylation related genes in different stages of CML and in healthy donors and the methylation status of MEG3 in different stages of CML and in healthy donors.EBioMedicine.2018 Aug;34:61-75. |
|---|
 Changes in mRNA and protein levels in CML blast cells after chidamide treatment.EBioMedicine.2018 Aug;34:61-75. |
 Changes in mRNA and protein levels in CML blast cells after chidamide treatment.EBioMedicine.2018 Aug;34:61-75. |