| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
GSK-3β (IC50 = 0.58 nM); GSK-3α (IC50 = 0.65 nM); cdc2 (IC50 = 3700 nM)
Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 (GSK3), including both GSK3α and GSK3β isoforms. For GSK3β, the IC₅₀ value was determined to be ~0.7 nM; for GSK3α, the IC₅₀ value was ~0.6 nM. The compound exhibited high selectivity for GSK3: it showed minimal inhibitory activity against other kinases, with IC₅₀ values >100 nM for cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2), extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 (ERK2), and protein kinase B (Akt) [2] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
CHIR-98014 抑制人 GSK-3β,Ki 为 0.87 nM。 CHIR-98014 对于预防小鼠和大鼠 GSK-3 非常有效。尽管 CHIR-98014 作为 ATP 结合的直接竞争性抑制剂,但与 20 种其他蛋白激酶(例如 Cdc2、ERK2、Tie-2 和 KDR)相比,CHIR-98014 对 GSK-3 的选择性高出 500 倍至 >1000 倍。 CHIR-98014 抑制 Cdc2 的 IC50 为 3.7 M。值得注意的是,CHIR 98014 仅区分 GSK-3 及其最接近的同源物 CDC2 和 ERK2,尽管它对 GSK-3 的高度同源性和亚型表现出相似的效力。当抑制剂 CHIR98014 以不断增加的浓度应用于表达胰岛素受体的 CHO-IR 细胞或原代大鼠肝细胞时,会产生高于基础值 2 至 3 倍的 GS 活性比刺激。对于大鼠肝细胞和 CHO-IR,引起半最大 GS 刺激 (EC50) 的 CHIR-98014 浓度为 107 nM。[1]
1. 在分化的L6大鼠骨骼肌肌管细胞中,用CHIR-98014(0.1 nM-1 μM,处理24小时)处理后,通过[¹⁴C]-葡萄糖掺入法检测发现,该药物呈剂量依赖性促进糖原合成。在10 nM浓度下,糖原合成较溶剂对照组增加约2.3倍。此效应与糖原合成酶(GS)在Ser⁶⁴¹位点的磷酸化水平升高(该位点磷酸化抑制GS活性,去磷酸化则激活)相关,通过Western blot可检测到这一变化。此外,CHIR-98014(10 nM)可增强胰岛素诱导的糖原合成:在1 nM胰岛素存在时,该药物可使糖原积累量较单独使用胰岛素时再增加约1.8倍 [2] 2. 在3T3-L1小鼠脂肪细胞中,CHIR-98014(1 nM-100 nM,处理16小时)通过[³H]-2-脱氧葡萄糖摄取实验检测显示,可促进葡萄糖转运。在10 nM浓度下,葡萄糖转运较对照组增加约1.9倍。该药物还能增强胰岛素刺激的葡萄糖转运:与10 nM胰岛素联合使用时,葡萄糖摄取量较单独使用胰岛素时高约2.5倍。Western blot分析表明,CHIR-98014(10 nM)可增加Akt在Ser⁴⁷³位点的磷酸化(胰岛素信号通路的下游效应分子),并降低GSK3β在Ser⁹位点的磷酸化(GSK3β抑制的标志物) [2] 3. 在转染了β-连环蛋白响应性荧光素酶报告基因(TOPFlash)的HEK293细胞中,CHIR-98014(0.1 nM-1 μM)呈剂量依赖性激活Wnt/β-连环蛋白通路,EC₅₀约为2 nM。在10 nM浓度下,荧光素酶活性较对照组高约8倍,同时伴随β-连环蛋白在细胞核内的积累(免疫荧光染色) [2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
GSK-3 抑制剂 CHIR-98014 可激活胰岛素敏感瘦 Zucker 大鼠和胰岛素抵抗 ZDF 大鼠分离的 I 型骨骼肌中的 GS 活性比。从 ZDF 大鼠中分离的比目鱼肌显示出对激活 GS 的胰岛素具有显着抵抗性,但对 500 nM CHIR-98014 的反应程度与来自瘦 Zucker 大鼠的肌肉相同程度(增加 40%)。值得注意的是,胰岛素加 CHIR-98014 的 GS 激活对瘦 Zucker 大鼠的肌肉具有附加作用,并且比 ZDF 大鼠的肌肉具有更大的附加作用。这些细胞和肌肉中的总 GS 活性不会被 CHIR-98014 或胰岛素改变。同时,CHIR-98014 不会影响瘦动物肌肉中的胰岛素剂量反应。高血糖的降低和葡萄糖处理的改善不仅限于db/db小鼠和ZDF大鼠,在ob/ob小鼠、饮食诱导的糖尿病C57BL/6小鼠和用CHIR-治疗的葡萄糖不耐症SHHF大鼠中也观察到类似的结果。 98014。此外,CHIR-98014 还可降低出生后大鼠皮质和海马中 tau 蛋白的磷酸化 (Ser396)。
1. 在雄性ob/ob小鼠(2型糖尿病遗传模型,8-10周龄)中,口服给予CHIR-98014(1 mg/kg、3 mg/kg、10 mg/kg,每日1次,连续7天),呈剂量依赖性降低空腹血糖(FBG)。在10 mg/kg剂量下,第7天的FBG从溶剂组的24.3 mM降至15.7 mM(降低约35%)。该药物还能增加肝脏和骨骼肌中的糖原含量:在10 mg/kg剂量下,肝糖原较对照组高约2.1倍,腓肠肌糖原较对照组高约1.8倍 [2] 2. 在雄性db/db小鼠(另一种2型糖尿病模型)中,单次口服CHIR-98014(10 mg/kg)后,餐后血糖(PBG)在给药2小时时降低约40%,效应可持续长达6小时。胰岛素耐量试验(ITTs)显示,CHIR-98014(3 mg/kg,口服3天)可改善胰岛素敏感性:ITT期间的血糖曲线下面积(AUC)较溶剂组降低约25% [2] |
| 酶活实验 |
聚丙烯 96 孔板每孔填充 300 μL 含有激酶的缓冲液(50 mM tris HCl、10 mM MgCl2、1 mM EGTA、1 mM 二硫苏糖醇、25 mM β-甘油磷酸、1 mM NaF、0.01% BSA,pH 7.5) 、肽底物和任何活化剂。在所有无细胞测定中,将 CHIR-98014 或对照添加到 3.5 μL DMSO 中,然后添加 50 μL ATP 库存,以产生 1 μM ATP 的终浓度。孵育后,将一式三份的 100 L 等分试样添加到 Combiplate 8 板中,其中每孔含有 100 µL 浓度的 50 mM ATP 和 20 mM EDTA。将孔用 PBS 冲洗五次,填充 200 L 闪烁液,密封,放置 30 分钟,然后在第一小时后在闪烁计数器中计数。整个过程在室温下进行。
1. GSK3β激酶活性检测:将重组人GSK3β(5 ng)与合成肽底物(序列:YRRAAVPPSPSLSRHSSPHQpSEDEEE,50 μM)在含20 mM Tris-HCl(pH 7.5)、10 mM氯化镁(MgCl₂)、1 mM二硫苏糖醇(DTT)和10 μM [γ-³³P]-ATP的反应缓冲液中孵育。加入CHIR-98014(0.01 nM-1 μM)后,混合物在30°C孵育60分钟。取20 μL反应液点样于磷酸纤维素纸上终止反应,用1%磷酸洗涤3次以去除未掺入的[γ-³³P]-ATP。通过液体闪烁计数测定放射性,根据剂量-反应曲线(抑制率vs.对数浓度)计算IC₅₀ [2] 2. GSK3α激酶活性检测:实验流程与GSK3β检测一致,仅替换为重组人GSK3α(5 ng)。使用相同剂量范围的CHIR-98014和数据分析方法确定GSK3α的IC₅₀ [2] 3. 激酶选择性检测:对于其他激酶(CDK2、ERK2、Akt),将重组酶(5-10 ng)与其各自的肽底物、[γ-³³P]-ATP和CHIR-98014(0.1 nM-10 μM)在激酶特异性反应缓冲液中孵育。按上述方法测定放射性,计算IC₅₀以评估选择性 [2] |
| 细胞实验 |
表达人胰岛素受体的 CHO-IR 细胞在含有 10% 胎牛血清且不含次黄嘌呤的 Hamm's F12 培养基中生长至 80% 汇合。将胰蛋白酶处理的细胞以 1 × 106 个细胞/孔的密度接种在 2 mL 不含胎牛血清的培养基中的 6 孔板中。 24 小时后,用 1 mL 含有 GSK-3 抑制剂 CHIR 98014 或对照(最终 DMSO 浓度 0.1%)的无血清培养基替换培养基,在 37 °C 下培养 30 分钟。将细胞在含有 1 mM EDTA、1 mM DTT、100 mM NaF、1 mM 苯甲基磺酰氟和 25 g/mL 亮抑肽素(缓冲液 A)的 50 mM tris (pH 7.8) 中冷冻/解冻,并在 30 ℃ 离心 15 分钟。 4°C/14000 克。使用不存在时的 GS 活性来计算 GS 的活性比。
1. L6肌管细胞糖原合成实验:将L6细胞接种于24孔板,在含2%马血清的DMEM中培养7天分化为肌管细胞。肌管细胞饥饿血清16小时后,用CHIR-98014(0.1 nM-1 μM)±胰岛素(1 nM)处理24小时。在处理的最后4小时加入[¹⁴C]-葡萄糖(0.5 μCi/mL)。用冷PBS洗涤细胞,用10%三氯乙酸(TCA)裂解细胞,糖原在4°C沉淀过夜。沉淀的糖原用乙醇洗涤,溶解于水中,通过液体闪烁计数测定放射性,以量化糖原合成 [2] 2. 3T3-L1脂肪细胞葡萄糖转运实验:3T3-L1前脂肪细胞通过胰岛素、地塞米松和IBMX处理8天分化为脂肪细胞。脂肪细胞饥饿血清4小时后,用CHIR-98014(1 nM-100 nM)±胰岛素(10 nM)处理16小时。加入[³H]-2-脱氧葡萄糖(0.1 μCi/mL)孵育10分钟,用含200 μM根皮素(抑制葡萄糖转运体)的冷PBS洗涤细胞。用0.1% SDS裂解细胞,测定放射性以确定葡萄糖摄取量 [2] 3. β-连环蛋白报告基因实验:使用转染试剂将TOPFlash(β-连环蛋白响应性荧光素酶质粒)和pRL-TK(海肾荧光素酶质粒,内参对照)转染至HEK293细胞。转染24小时后,用CHIR-98014(0.1 nM-1 μM)处理细胞24小时。采用双荧光素酶报告基因检测系统测定荧光素酶活性,将萤火虫荧光素酶活性归一化为海肾荧光素酶活性 [2] |
| 动物实验 |
Drugs and drug administration[2]
SB216763 (30 mg kg−1) and CHIR98014 (30 mg kg−1) were re-suspended in DMSO and injected i.v. AR-A014418 (30 mg kg−1), was dissolved in 100% PEG400 and administered per os (p.o.) Indirubin-3′-monoxime (20 mg kg−1) and Alsterpaullone (20 mg kg−1) were dissolved in 20% DMSO/25% Tween-80 and injected i.p. and s.c., respectively. All drug studies were conducted using P12 rats from the same litter. Control animals were dosed with the respective vehicle and both groups were killed after 1, 2 and 4 h for brain exposure measurements (see the next section), western blotting and GSK-3β activity assays. Experiments measuring the efficacy of each compound were performed at least three times and at a time point determined by brain exposure data. LiCl (100 and 200 mg kg−1) was dissolved in sterile water, and administered p.o. to animals. P12 rats were killed 8 h after injection. Some of the littermates were used as the control group and dosed with NaCl (100 or 200 mg kg−1, p.o.) dissolved in sterile water.[2] Brain exposure measurements[2] Rat brain homogenates were analysed for exposure levels of SB216763, Indirubin-3′-monoxime, Alsterpaullone, CHIR98014 and AR-A014418 using turbulent flow chromatography (HTLC) followed by detection by Tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS). Four times 70% v w−1acetonitrile was added to the sample and homogenized in an autogizer robot. The brain homogenate was centrifuged at 6000 g for 15 min at 5 °C, and the supernatant was analysed. Calibration curves (1–1000 ng ml−1 brain homogenate) for each compound were prepared using brain homogenate from untreated rats. A total of 25 μl of 10% MeOH with internal standard (citalopram) was added to either 25 μl of brain homogenate or calibration standard, followed by centrifugation at 6000 g for 20 min at 5 °C). Ten microlitres of each sample was injected into the HTLC system using a HTS PAL autosampler. Samples with AR-A014418 were purified using 0.1% HCOOH in water for 15 s (2 ml min−1) using a Cyclone HTLC column (0.5 × 50 mm, 50 μm). The compounds were extracted from the HTLC using 100 μl 0.1% HCOOH/90% acetonitrile placed in the loop and transferred to the analytical column, X-Terra MS C8 (20 × 2.1 mm, 3.5 μm) with 0.1% HCOOH in water over 120 s (0.08 ml min−1) and eluted from the analytical column using a gradient from 0.1% HCOOH/2% MeCN to 0.1% HCOOH/98% acetonitrile for 45 s, followed by elution with 0.1% HCOOH/98% acetonitrile for 120 s flow 0.5 ml min−1). Detection of the compound was performed using Ultima triple-quadropole mass spectrometer (Waters) and positive ionization using multiple reaction monitoring set at optimal conditions. For AR-A014418 the transition 308.9 → 121.7 was used. Blood is obtained by shallow tail snipping at lidocaine-anesthetized tips. Blood glucose is measured directly or heparinized plasma is collected for measurement of glucose or insulin. Animals are prebled and randomly assigned to vehicle control or GSK-3 inhibitor treatment groups. For glucose tolerance tests (GTTs), animals are fasted throughout the procedure with food removal early in the morning, 3 h before the first prebleed (db/db mice), or the previous night, 16 h before the bleed (ZDF rats). Food is taken away 16 hours prior to the test agent being administered when determining the time course of plasma glucose and insulin changes in fasting ZDF rats. The GS activity ratio is calculated as the GS activity in the presence of 5 mM glucose-6-phosphate divided by the activity in the absence of glucose-6-phosphate. 1. ob/ob mouse chronic treatment protocol: Male ob/ob mice (8-10 weeks old, weighing 40-45 g) were randomly divided into 4 groups (n=6/group): vehicle (0.5% methylcellulose), CHIR-98014 1 mg/kg, 3 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg. The drug was suspended in 0.5% methylcellulose and administered via oral gavage once daily for 7 days. Mice were fasted for 6 hours before FBG measurement (tail vein blood, glucose meter) on day 0 (baseline) and day 7. On day 7, mice were euthanized; liver (left lobe) and gastrocnemius muscle were harvested, frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at -80°C. Glycogen content in tissues was measured via a colorimetric assay (glycogen hydrolysis to glucose, followed by glucose oxidase detection) [2] 2. db/db mouse acute glucose-lowering protocol: Male db/db mice (10-12 weeks old) received a single oral dose of CHIR-98014 (10 mg/kg, suspended in 0.5% methylcellulose) or vehicle. PBG was measured at 0, 1, 2, 4, 6 hours post-dosing (fed state). For ITT, mice were treated with CHIR-98014 (3 mg/kg) or vehicle orally for 3 days, then fasted for 4 hours. Insulin (0.75 U/kg) was injected intraperitoneally, and blood glucose was measured at 0, 15, 30, 60, 120 minutes post-insulin to calculate glucose AUC [2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
1. In male CD-1 mice, oral administration of CHIR-98014 (10 mg/kg) showed an oral bioavailability of ~30%. The peak plasma concentration (Cₘₐₓ) was ~85 ng/mL, achieved at ~1 hour (Tₘₐₓ) post-dosing. The elimination half-life (t₁/₂) was ~2.1 hours. Tissue distribution analysis showed that the drug accumulated in the liver (peak concentration ~240 ng/g) and skeletal muscle (peak concentration ~120 ng/g) at 1 hour post-dosing [2]
|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
1. In acute toxicity studies in CD-1 mice, single oral doses of CHIR-98014 up to 100 mg/kg caused no mortality or overt signs of toxicity (e.g., lethargy, ataxia) over 7 days. Body weight gain was similar between drug-treated and vehicle groups [2]
2. In the 7-day chronic study in ob/ob mice (1-10 mg/kg, oral), CHIR-98014 had no significant effect on serum alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), creatinine, or urea nitrogen (markers of liver and kidney function) compared to vehicle [2] 3. Plasma protein binding of CHIR-98014 was ~95% in mouse, rat, and human plasma (measured via equilibrium dialysis) [2] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
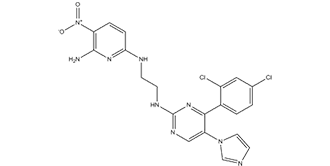
CHIR-98014 is a member of the class of aminopyrimidines that is pyrimidine substituted by {2-[(6-amino-5-nitropyridin-2-yl)amino]ethyl}amino, 2,4-dichlorophenyl, and 1H-imidazol-1-yl groups at positions 2, 4 and 5, respectively. It is a potent ATP-competitive inhibitor of GSK3alpha and GSK3beta (IC50 values of 0.65 and 0.58 nM, respectively). It has a role as an EC 2.7.11.26 (tau-protein kinase) inhibitor, an apoptosis inducer, an antineoplastic agent, a hypoglycemic agent, a Wnt signalling activator and a tau aggregation inhibitor. It is a secondary amino compound, a dichlorobenzene, a member of imidazoles, a diaminopyridine, an aminopyrimidine and a C-nitro compound.
1. CHIR-98014 exerts its anti-diabetic effects primarily by inhibiting GSK3: inhibition of GSK3 reduces phosphorylation of GS (activating GS to promote glycogen synthesis) and enhances insulin signaling via increased Akt phosphorylation, thereby improving glucose uptake and glycogen storage in muscle and adipose tissue [2] 2. The activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway by CHIR-98014 (via β-catenin stabilization) suggests potential off-target effects, but in diabetic models, the dominant therapeutic effect is mediated by GSK3 inhibition in metabolic tissues (muscle, liver, adipose) [2] 3. CHIR-98014 shows advantages over earlier GSK3 inhibitors (e.g., SB216763) due to its higher potency (lower IC₅₀ for GSK3) and selectivity for GSK3 over other kinases, reducing the risk of off-target toxicities [2] |
| 分子式 |
C20H17CL2N9O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
486.3141
|
| 精确质量 |
485.088
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 49.39; H, 3.52; Cl, 14.58; N, 25.92; O, 6.58
|
| CAS号 |
252935-94-7
|
| 相关CAS号 |
556813-39-9 (CHIR98024);252935-94-7 (CHIR98014);CHIR98014 HCl;
|
| PubChem CID |
53396311
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to yellow solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.6±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
839.0±75.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
461.2±37.1 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±3.1 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.753
|
| LogP |
3.76
|
| tPSA |
158.85
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
9
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
33
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
645
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
ClC1C([H])=C(C([H])=C([H])C=1C1C(=C([H])N=C(N=1)N([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N([H])C1C([H])=C([H])C(=C(N([H])[H])N=1)[N+](=O)[O-])N1C([H])=NC([H])=C1[H])Cl
|
| InChi Key |
MDZCSIDIPDZWKL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C20H17Cl2N9O2/c21-12-1-2-13(14(22)9-12)18-16(30-8-7-24-11-30)10-27-20(29-18)26-6-5-25-17-4-3-15(31(32)33)19(23)28-17/h1-4,7-11H,5-6H2,(H3,23,25,28)(H,26,27,29)
|
| 化学名 |
6-N-[2-[[4-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-5-imidazol-1-ylpyrimidin-2-yl]amino]ethyl]-3-nitropyridine-2,6-diamine
|
| 别名 |
CT-98014; CT 98014; CT98014; CHIR 98014; CHIR-98014; 252935-94-7; 6-N-[2-[[4-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-5-imidazol-1-ylpyrimidin-2-yl]amino]ethyl]-3-nitropyridine-2,6-diamine; CT-98014; 2,6-PYRIDINEDIAMINE, N6-[2-[[4-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL)-5-(1H-IMIDAZOL-1-YL)-2-PYRIMIDINYL]AMINO]ETHYL]-3-NITRO-; CHEMBL3185148; N2-(2-((4-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-5-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl)amino)ethyl)-5-nitropyridine-2,6-diamine; N6-[2-[[4-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL)-5-(1H-IMIDAZOL-1-YL)-2-PYRIMIDINYL]AMINO]ETHYL]-3-NITRO-2,6-PYRIDINEDIAMINE; CHIR-98014; CHIR98014;CHIR98014 HCl; CHIR-98014 hydrochloride
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~8 mg/mL (~16.5 mM)
Water: <1 mg/mL Ethanol: <1 mg/mL |
|---|
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0563 mL | 10.2815 mL | 20.5630 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4113 mL | 2.0563 mL | 4.1126 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2056 mL | 1.0282 mL | 2.0563 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
The aminopyrimidine GSK-3 inhibitor, CHIR98014, reduced tau phosphorylation in vivo.Br J Pharmacol.2007Nov;152(6):959-79. |
CHIR98014, reduced tau phosphorylation in a dose-dependent manner in vivo.Br J Pharmacol.2007Nov;152(6):959-79. |
Characterization of the postnatal rat model.Br J Pharmacol.2007Nov;152(6):959-79.Characterization of the postnatal rat model. Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Nov;152(6):959-79. |