| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
EGFR (IC50 = 6 nM); ErbB2 (IC50 = 45.7 nM); ErbB4 (IC50 = 73.7 nM)
- Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) (Ki values in the low nanomolar range for various EGFR mutants) - ERBB2 (also known as HER2) - ERBB family members in general, as it is a pan - ERBB inhibitor [1] Dacomitinib (PF-00299804, PF-299) irreversibly inhibits EGFR (IC₅₀ = 6 nM), HER2 (IC₅₀ = 45.7 nM), and HER4 (IC₅₀ = 73.7 nM) tyrosine kinases [1] It potently inhibits EGFR T790M mutant (IC₅₀ = 7 nM) and EGFR L858R/T790M double mutant (IC₅₀ = 11 nM), with weak activity against wild-type EGFR (IC₅₀ = 65 nM) [1] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
PF299804 是 ERBB 激酶家族的特异性抑制剂。 PF299804 抑制 EGFR 信号传导并诱导含有 EGFR T790M 的 H3255 GR 细胞系凋亡。 PF299804 对吉非替尼敏感和吉非替尼耐药的 NSCLC 细胞系有效。 PF299804 抑制 H3255 和 HCC827 细胞的生长,这些细胞经过改造可表达 EGFR T790M。 PF299804 在存在 T790M 突变的情况下抑制 EGFR 磷酸化。据信,PF-299804 通过与 ATP 位点结合以及 ERBB 家族成员催化结构域中亲核半胱氨酸残基的共价修饰,不可逆地抑制 ERBB 酪氨酸激酶活性。 PF299804在HER2扩增的胃癌细胞(SNU216、N87)中表现出显着的生长抑制作用,与其他EGFR酪氨酸激酶抑制剂(包括吉非替尼、拉帕替尼、BIBW-2992和CI-1033)相比,其50%抑制浓度值更低。 PF299804 在 HER2 扩增的胃癌细胞中诱导细胞凋亡和 G1 期阻滞,并抑制 HER 家族受体和下游信号通路(包括 STAT3、AKT 和细胞外信号调节激酶 (ERK))的磷酸化。 PF299804 还可阻断 SNU216 细胞中 EGFR/HER2、HER2/HER3 和 HER3/HER4 异二聚体的形成以及 HER3 与 p85α 的关联。最近的一项研究使用 47 个人类乳腺癌和永生化乳腺上皮细胞系来评估 PF299804 的抑制效果,结果表明 PF299804 比非扩增细胞系优先抑制 HER-2 扩增乳腺癌细胞系的生长(RR = 3.39,p < 0.0001)。 PF299804 降低大多数敏感细胞系中 HER2、EGFR、HER4、AKT 和 ERK 的磷酸化。 PF299804 通过联合 G0/G1 阻滞和诱导细胞凋亡来发挥其抗增殖作用。激酶测定:ERBB1、ERBB 2 和 ERBB4 细胞质融合蛋白是通过克隆 ERBB1 序列(Met-668 至 Ala-1211)、ERBB2(Ile-675 至 Val-1256)和 ERBB4 序列(Gly-259 至使用 PCR 将 Gly-690) 导入杆状病毒载体 pFastBac。蛋白质在杆状病毒感染的 Sf9 昆虫细胞中表达为 GST 融合蛋白。使用谷胱甘肽琼脂糖珠通过亲和层析纯化蛋白质。使用基于 ELISA 的受体酪氨酸激酶测定法评估 ERBB 酪氨酸激酶活性的抑制。激酶反应(50 mM HEPES,pH 7.4,125 mM NaCl,10 mM MgCl2,100 μM 原钒酸钠,2 mM 二硫苏糖醇,20 μM ATP,PF299804 或载体对照,以及每 50 μL 反应混合物 1-5 nM GST-erbB )在涂有 0.25 mg/mL 聚-Glu-Tyr 的 96 孔板中运行。将反应物在室温下孵育 6 分钟,同时摇动。通过去除反应混合物来终止激酶反应,然后用洗涤缓冲液(0.1% Tween 20 的 PBS 溶液)洗涤孔。通过添加 0.2 μg/mL 抗磷酸酪氨酸抗体(Oncogene Ab-4;50 μL/孔)与稀释在含有 3% BSA 和 0.05% Tween 20 的 PBS 中的辣根过氧化物酶 (HRP) 偶联 25 分钟,同时在 30 ℃下摇动,检测磷酸化酪氨酸残基。室内温度。除去抗体,并用洗涤缓冲液洗涤板。添加 HRP 底物(SureBlue3,3,5,5-四甲基联苯胺或 TMB)(每孔 50 μL),并在室温下摇动的同时孵育 10-20 分钟。添加 50 μL 终止溶液 (0.09 N H2SO4) 终止 TMB 反应。通过测量 450 nm 处的吸光度来量化信号。使用中值效应法测定 PF299804 的 IC50 值。细胞测定:通过5-(3-羧基甲氧基苯基)-2-(4-磺基苯基)-2H-四唑(MTS)测定评估生长和生长抑制。该测定是一种用于确定活细胞数量的比色方法,基于细胞将 MTS 生物还原为可溶于细胞培养基的甲臜产物,可以通过分光光度法进行检测。细胞接受处理 72 小时,每次实验使用的细胞数量根据经验确定。所有实验点设置在6至12个孔中,并且所有实验至少重复三次。使用适用于 Windows 的 GraphPad Prism 3.00 版(GraphPad 软件)以图形方式显示数据。使用具有 S 形剂量响应的非线性回归模型来拟合曲线。
- 在体外有效抑制EGFR激活突变以及EGFR T790M耐药突变的活性。在基于细胞的实验中,它对EGFR突变体的磷酸化表现出显著抑制作用,阻断了与细胞增殖相关的下游信号通路,如MAPK和AKT通路。例如,在具有EGFR激活突变或T790M耐药突变的肺癌细胞系中,达可替尼处理导致细胞活力和增殖呈剂量依赖性下降 [1] - 抑制对Anti - Human HER2和GW572016耐药的HER2扩增乳腺癌细胞系的增殖。在HER2扩增的乳腺癌细胞系中,达可替尼处理以剂量依赖的方式抑制细胞生长。它还能有效降低HER2及其下游信号分子(如AKT和ERK)的磷酸化水平,这些分子对细胞存活和增殖至关重要 [2] 达可替尼(PF-00299804, PF-299)剂量依赖性抑制携带EGFR突变的ZD1839耐药非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)细胞系增殖,包括NCI-H1975(EGFR L858R/T790M,IC₅₀=0.04μM)和HCC827/T790M(EGFR del19/T790M,IC₅₀=0.03μM)。浓度≥0.1μM时,可阻断EGFR/HER2磷酸化及下游AKT/ERK1/2信号通路[1] 在对曲妥珠单抗和拉帕替尼耐药的HER2扩增乳腺癌细胞系(如JIMT-1,IC₅₀=0.08μM;BT474-HR,IC₅₀=0.06μM)中,该药物抑制细胞增殖并诱导G1期细胞周期阻滞,同时下调周期蛋白D1并上调p27的表达[2] 达可替尼(PF-00299804, PF-299)诱导NCI-H1975细胞凋亡,EC₅₀=0.12μM,增加切割型caspase-3和PARP的水平,抑制耐药NSCLC细胞的克隆形成能力(IC₅₀=0.05μM)[1] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
口服 PF299804 可有效抑制 HCC827 Del/T790M 异种移植物的生长。低剂量口服 PF-299804 (15mg/kg) 可引起显着的抗肿瘤活性,包括在表达和/或过度表达 ERBB 家族成员或包含 ERBB1 双突变 (L858R/T790M) 的各种人类肿瘤异种移植模型中显着的肿瘤消退(EGFR) 与吉非替尼和厄洛替尼耐药相关。
- 在对ZD1839(吉非替尼)耐药的具有EGFR和ERBB2突变的肺癌模型中显示出有效性。在具有EGFR激活突变或ERBB2突变的肺癌异种移植小鼠模型中,口服给予达可替尼导致肿瘤显著消退。与对照组相比,肿瘤生长受到抑制,小鼠的总生存期得到改善。该药物通过抑制肿瘤组织中EGFR和ERBB2的激活,减少促存活和促增殖因子的产生来实现这一效果 [1] 达可替尼(PF-00299804, PF-299)以15mg/kg/天的剂量口服给药21天,显著抑制裸鼠NCI-H1975异种移植瘤生长。与对照组相比,肿瘤体积减少约80%,瘤内EGFR T790M磷酸化水平几乎完全被阻断[1] 在HER2扩增的曲妥珠单抗耐药乳腺癌小鼠模型(JIMT-1异种移植瘤)中,该药物(20mg/kg/天,口服28天)的肿瘤生长抑制率达75%,中位生存期延长40%[2] 在HCC827/T790M异种移植瘤模型中表现出剂量依赖性抗肿瘤效果,25mg/kg/天(口服)给药24天,肿瘤重量减少70%[1] |
| 酶活实验 |
使用 PCR 将 ERBB1 序列(Met-668 至 Ala-1211)、ERBB2 序列(Ile-675 至 Val-1256)和 ERBB4 序列(Gly-259 至 Gly-690)克隆到杆状病毒载体 pFastBac 中以创建 ERBB1 、ERBB2 和 ERBB4 细胞质融合蛋白。在感染杆状病毒的Sf9昆虫细胞中,蛋白质表达为GST融合蛋白。谷胱甘肽琼脂糖珠用于亲和层析纯化蛋白质。基于 ELISA 的受体酪氨酸激酶测定用于测量 ERBB 酪氨酸激酶活性的抑制。在涂有 0.25 mg/mL 聚 Glu-Tyr 的 96 孔板中,在以下条件下进行激酶反应:50 mM HEPES,pH 7.4,125 mM NaCl,10 mM MgCl2,100每 50 μL 反应混合物含有 μM 原钒酸钠、2 mM 二硫苏糖醇、20 μM ATP、PF299804 或载体对照,以及 1–5 nM GST-erbB。摇动反应物并在室温下孵育六分钟。除去反应混合物以停止激酶反应后,使用洗涤缓冲液(PBS 中的 0.1% Tween 20)清洁孔。磷酸化酪氨酸残基的检测涉及在含有 3% BSA 和 0.05% Tween 20 的 PBS 中添加 0.2 μg/mL 抗磷酸酪氨酸抗体(Oncogene Ab-4;50 μL/孔)以及稀释的辣根过氧化物酶 (HRP)。然后在室温下摇动25分钟。消除抗体后,使用洗涤缓冲液洗涤板。每孔中加入 50 μL HRP 底物(SureBlue3,3,5,5-四甲基联苯胺,或 TMB),并在室温下摇动孵育 10 至 20 分钟。将 50 μL 终止溶液 (0.09 N H2SO4) 添加到 TMB 反应中以终止反应。 450 nm 处的吸光度用于量化信号。使用中值效应法来确定 PF299804 的 IC50 值。
将重组EGFR(野生型、T790M、L858R/T790M)、HER2和HER4激酶结构域分别与ATP及特异性多肽底物在系列稀释的达可替尼(PF-00299804, PF-299)(0.001-100μM)存在下孵育,反应在37°C下进行60分钟,采用放射免疫法检测磷酸化底物。通过与溶媒对照组的放射性对比计算抑制率,从量效曲线中得出IC₅₀值[1] 为证实不可逆结合特性,将药物与EGFR T790M激酶结构域预孵育30分钟后再加入ATP和底物。加入终止缓冲液终止反应,定量磷酸化水平以验证时间依赖性抑制活性[1] |
| 细胞实验 |
在 24 孔板中,以每孔 5×10 3 至 5×10 4 细胞接种重复细胞,并计算生长抑制数据。简而言之,通过添加 10 μM 达克替尼并在铺板后第二天在 12 个浓度范围内进行 2 倍稀释来生成剂量反应曲线。还接种了不含药物的对照孔。在第一天添加药物时对细胞进行计数,并在实验结束(即六天后)时再次对细胞进行计数。使用 Coulter Z1 粒子计数器,在胰蛋白酶消化后将细胞放入等酮溶液中后立即进行计数。使用 Coulter Vi-Cell 计数器对悬浮培养物进行计数 [2]。
- 对于肺癌细胞系:将具有不同EGFR突变(如激活突变和T790M耐药突变)的肺癌细胞系培养在合适的生长培养基中。将细胞以特定密度接种于96孔板中。过夜孵育使细胞贴壁后,将不同浓度(范围从低纳摩尔到微摩尔水平)的达可替尼加入孔中。在一定的孵育时间(通常为48 - 72小时)后,使用如MTT法或基于ATP的细胞活力测定法测量细胞活力。根据这些测定获得的吸光度或发光值计算细胞增殖的抑制率,并生成剂量 - 反应曲线以确定IC50值 [1] - 对于乳腺癌细胞系:将HER2扩增的乳腺癌细胞系培养在合适的培养基中。将细胞铺在96孔板中。细胞贴壁后,加入不同浓度的达可替尼。随时间监测细胞生长情况,例如,在特定时间点(如24、48和72小时)使用细胞计数器计数细胞数量,或使用如XTT法测量细胞的代谢活性。在达可替尼处理后,还对细胞裂解物进行蛋白质免疫印迹分析。通过在合适的裂解缓冲液中裂解细胞来制备细胞裂解物。蛋白质通过SDS - PAGE电泳分离,然后转移到硝酸纤维素膜上。用针对HER2、磷酸化HER2、AKT、磷酸化AKT、ERK和磷酸化ERK的抗体对膜进行检测,以评估达可替尼对HER2信号通路的影响 [2] 将NCI-H1975、HCC827/T790M、JIMT-1和BT474-HR细胞以5×10³个细胞/孔接种到96孔板中,用达可替尼(PF-00299804, PF-299)(0.01-1μM)处理72小时,采用四唑盐法检测细胞活性并计算IC₅₀值[1,2] 用0.05-0.2μM药物处理细胞24小时,裂解后通过蛋白质印迹法检测磷酸化EGFR/HER2、AKT、ERK1/2、周期蛋白D1、p27、切割型caspase-3、PARP和GAPDH的表达[1,2] 用0.08-0.2μM药物处理JIMT-1细胞24小时,进行细胞周期分析。细胞经70%乙醇固定,碘化丙啶染色后通过流式细胞术分析[2] 用0.03-0.1μM药物处理NCI-H1975细胞14天,进行克隆形成实验,随后固定、染色并计数克隆数[1] |
| 动物实验 |
Mice: In vivo studies employ 6-to 8-week-old nude mice (nu/nu). Each mouse's lower-right flank is s.c.-injected with a suspension of 5×10 6 HCC827-GFP or HCC827-Del/T790M lung cancer cells (in 0.2 mL of PBS). Group ZD1839 treatment involves inoculating five mice with either HCC827-GFP or HCC827-Del/T790M cells. Using calipers, tumor measurements are taken twice a week. The formula for calculating volume is length×width 2 ×0.52. The body weight and general health of the mice are checked every day. At a mean tumor volume of 400 to 500 mm3, mice are randomized to receive one of two treatments. ZD1839 is taken orally once a day at a dose of 150 mg/kg/d. Dacomitinib is taken orally once a day at a dose of 10 mg/kg/d. When the control tumors' mean size reached 2000 mm 3 , the experiment was stopped.
- In the lung cancer xenograft models: Human lung cancer cell lines with EGFR or ERBB2 mutations were subcutaneously injected into the flanks of nude mice. Once the tumors reached a certain volume (usually around 100 - 200 mm³), the mice were randomly divided into treatment and control groups. Dacomitinib was formulated in a suitable vehicle (such as a mixture of DMSO and PEG 400 in saline). The drug was administered orally to the treatment group mice at a specific dose (e.g., 10 - 50 mg/kg) once daily for a defined period (usually 2 - 4 weeks). Tumor volumes were measured twice a week using calipers, and the body weights of the mice were also monitored. Tumor volume was calculated using the formula: volume = length × width² × 0.5. At the end of the treatment period, the mice were sacrificed, and tumors were excised for further analysis, such as immunohistochemistry to assess the expression of EGFR, ERBB2, and their phosphorylated forms [1] Nude mice bearing NCI-H1975 xenografts (100-150 mm³) were randomly divided into control and treatment groups. Dacomitinib (PF-00299804, PF-299) was suspended in 0.5% carboxymethylcellulose and administered orally at 15 mg/kg/day for 21 days. Tumor volume was measured every 3 days, and mice were euthanized to collect tumors for Western blot analysis of EGFR phosphorylation [1] Nude mice bearing JIMT-1 xenografts were treated with the drug orally at 20 mg/kg/day for 28 days. Survival time was recorded daily, and tumor tissues were processed for immunohistochemical staining of Ki-67 (proliferation marker) [2] For dose-response studies, nude mice with HCC827/T790M xenografts were given Dacomitinib (PF-00299804, PF-299) at 10, 15, or 25 mg/kg/day (oral) for 24 days. Tumor weights were measured at the end of treatment to calculate inhibition rates [1] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Dacomitinib has shown a linear kinetics after single and multiple dose range studies. The absorption and distribution do not seem to be affected by food or the consumption of antacids. The peak plasma concentration after a dosage of 45 mg for 4 days is of 104 ng/ml. The reported AUC0-24h and tmax are of 2213 ng.h/mL and 6 hours, respectively. As well, following oral administration, the absolute oral bioavailability is 80%. From the administered dose, 79% is recovered in feces, from which 20% represents the unmodified form of dacomitinib, and 3% is recovered in urine, from which <1% is represented by the unchanged form. The volume of distribution of dacomitinib was reported to be of 2415 L. The geometric apparent clearance of dacomitinib is 27.06 L/h. Metabolism / Metabolites Dacomitinib presents an oxidative and conjugative metabolism marked mainly by the activity of glutathione and cytochrome P450 enzymes. After metabolism, its major circulating metabolite is an O-desmethyl dacomitinib form named PF-05199265. This metabolite has been shown to be formed by an oxidative step by CYP2D6 and to a smaller extent by CYP2C9. The following steps of the metabolism are mainly mediated by CYP3A4 for the formation of smaller metabolites. From these metabolic studies, it was shown that dacomitinib inhibited strongly the activities of CYP2D6. Biological Half-Life Dacomitinib is reported to have a very large half-life of 70 hours. Dacomitinib (PF-00299804, PF-299) had an oral bioavailability of ~80% in mice after a single dose of 15 mg/kg. The plasma half-life was approximately 9.5 hours, and the maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) was 4.6 μg/mL achieved at 1.5 hours post-administration [1] In rats, oral administration of 20 mg/kg resulted in an AUC₀-24h of 58.3 μg·h/mL. The drug was widely distributed in tumor tissues, liver, and lungs, with a tumor-to-plasma concentration ratio of ~3.0 [2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In large early clinical trials, elevations in serum aminotransferase levels were common during dacomitinib therapy, arising in 40% of patients treated with standard doses. However, most elevations were transient and asymptomatic, and they rarely led to dose modification or discontinuation. Serum ALT elevations above 5 times the ULN occurred in only 1.4% of patients, these rates being lower than with other EGRF inhibitors such as erlotinib and gefitinib. Serum alkaline phosphatase elevations also occurred but were not common. There were no instances of clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice. However, clinical experience with dacomitinib has been limited. Likelihood score: E (unproven but suspected rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the clinical use of dacomitinib during breastfeeding. Because dacomitinib is 98% bound to plasma proteins, the amount in milk is likely to be low. However, because of its potential toxicity in the breastfed infant and its half-life of 70 hours, the manufacturer recommends that breastfeeding be discontinued during dacomitinib therapy and for at least 17 days after the last dose. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Dacomitinib is known to present a protein binding of 98%. Mice treated with Dacomitinib (PF-00299804, PF-299) at 15 mg/kg/day for 21 days showed mild weight loss (~7%) but no significant liver or kidney toxicity. Serum ALT, AST, and creatinine levels were within normal ranges [1] The plasma protein binding rate of the drug was ~94% in human plasma as determined by equilibrium dialysis. In long-term toxicity studies (28 days, 20 mg/kg/day, oral), rats showed no severe hematological or gastrointestinal toxicities [2] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
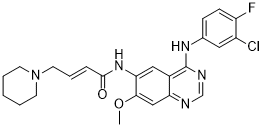
Dacomitinib is a member of the class of quinazolines that is 7-methoxyquinazoline-4,6-diamine in which the amino group at position 4 is substituted by a 3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl group and the amino group at position 6 is substituted by an (E)-4-(piperidin-1-yl)but-2-enoyl group. It has a role as an epidermal growth factor receptor antagonist and an antineoplastic agent. It is a member of quinazolines, a member of piperidines, an enamide, a member of monochlorobenzenes, a member of monofluorobenzenes, a tertiary amino compound, a secondary amino compound and a secondary carboxamide.
Dacomitinib, designed as (2E)-N-16-4-(piperidin-1-yl) but-2-enamide, is an oral highly selective quinazalone part of the second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors which are characterized by the irreversible binding at the ATP domain of the epidermal growth factor receptor family kinase domains. Dacomitinib was developed by Pfizer Inc and approved by the FDA on September 27, 2018. Some evidence in the literature suggests the therapeutic potential of dacomitinib in the epithelial ovarian cancer model, although further investigations are needed. Dacomitinib is a multi-kinase receptor inhibitor used in the therapy of cases of non-small cell lung cancer that harbor activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor gene (EGFR). Dacomitinib is associated with high rate of transient serum aminotransferase elevations during therapy but has not been linked to instances of clinically apparent acute liver injury. Dacomitinib is a highly selective, orally bioavailable small-molecule inhibitor of the HER family of tyrosine kinases with potential antineoplastic activity. Dacomitinib specifically and irreversibly binds to and inhibits human Her-1, Her-2, and Her-4, resulting in the proliferation inhibition and apoptosis of tumor cells that overexpress these receptors. Drug Indication Dacomitinib is indicated as the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 19 deletion or exon 21 L858R substitution mutations as verified by an FDA-approved test. Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death and NSCLC accounts for 85% of lung cancer cases. From the cases of NSCLC, approximately 75% of the patients present a late diagnosis with metastatic and advanced disease which produces a survival rate of 5%. The presence of a mutation in EGFR accounts for more than the 60% of the NSCLC cases and the overexpression of EGFR is associated with frequent lymph node metastasis and poor chemosensitivity. FDA Label Vizimpro, as monotherapy, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) activating mutations. Mechanism of Action Dacomitinib is an irreversible small molecule inhibitor of the activity of the human epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) family (EGFR/HER1, HER2, and HER4) tyrosine kinases. It achieves irreversible inhibition via covalent bonding to the cysteine residues in the catalytic domains of the HER receptors. The affinity of dacomitinib has been shown to have an IC50 of 6 nmol/L. The ErbB or epidermal growth factor (EGF) family plays a role in tumor growth, metastasis, and treatment resistance by activating downstream signal transduction pathways such as such as Ras-Raf-MAPK, PLCgamma-PKC-NFkB and PI3K/AKT through the tyrosine kinase-driven phosphorylation at the carboxy-terminus. Around 40% of cases show amplification of EGFR gene and 50% of the cases present the _EGFRvIII_ mutation which represents a deletion that produces a continuous activation of the tyrosine kinase domain of the receptor. Pharmacodynamics Preclinical data suggested that dacomitinib increases the inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor kinase domain as well as the activity in cell lines harboring resistance mutations such as T790M. This activity further produced a significant reduction of EGFR phosphorylation and cell viability. In these studies, non-small cell lymphoma cancer cell lines with L858R/T790M mutations where used and an IC50 of about 280 nmol/L was observed. In clinical trials with patients with advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma who progressed after chemotherapy, there was an objective response rate of 5% with a progression-free survival of 2.8 months and an overall survival of 9.5 months. As well, phase I/II studies showed positive dacomitinib activity despite prior failure with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Phase III clinical trials (ARCHER 1050), done in patients suffering from advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung carcinoma with EGFR-activating mutations, reported a significant improvement in progression-free survival when compared with gefitinib. - Dacomitinib is an irreversible pan - ERBB inhibitor. It binds covalently to nucleophilic cysteine residues in the catalytic domains of ERBB family members at the ATP - binding site, leading to irreversible inhibition of their tyrosine kinase activity. This inhibition blocks the downstream signaling cascades that are essential for cell proliferation, survival, and migration, making it a potential therapeutic agent for cancers with mutations and/or amplifications of ERBB family members [1] Dacomitinib (PF-00299804, PF-299) is an irreversible pan-HER tyrosine kinase inhibitor that covalently binds to the ATP-binding pocket of EGFR, HER2, and HER4, blocking downstream signaling pathways involved in tumor proliferation and survival [1] It was developed to overcome resistance to first-generation EGFR inhibitors (e.g., ZD1839) and anti-HER2 therapies (e.g., trastuzumab) in NSCLC and breast cancer. Preclinical data supported its advancement into clinical trials [2] The drug is approved by the FDA for the first-line treatment of metastatic NSCLC with EGFR exon 19 deletion or exon 21 L858R substitution mutations [1] |
| 分子式 |
C24H25CLFN5O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
469.9390
|
| 精确质量 |
469.17
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 61.34; H, 5.36; Cl, 7.54; F, 4.04; N, 14.90; O, 6.81
|
| CAS号 |
1110813-31-4
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Dacomitinib hydrate;1042385-75-0;Dacomitinib-d10 dihydrochloride;Dacomitinib-d10
|
| PubChem CID |
11511120
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
665.7±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
184-187 ºC
|
| 闪点 |
356.4±31.5 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.663
|
| LogP |
4.4
|
| tPSA |
79.4
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
33
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
665
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
COC1=C(C=C2C(=C1)N=CN=C2NC3=CC(=C(C=C3)F)Cl)NC(=O)/C=C/CN4CCCCC4
|
| InChi Key |
LVXJQMNHJWSHET-AATRIKPKSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C24H25ClFN5O2/c1-33-22-14-20-17(24(28-15-27-20)29-16-7-8-19(26)18(25)12-16)13-21(22)30-23(32)6-5-11-31-9-3-2-4-10-31/h5-8,12-15H,2-4,9-11H2,1H3,(H,30,32)(H,27,28,29)/b6-5+
|
| 化学名 |
(E)-N-[4-(3-chloro-4-fluoroanilino)-7-methoxyquinazolin-6-yl]-4-piperidin-1-ylbut-2-enamide
|
| 别名 |
Vizimpro; PF-00299804; PF00299804; PF 00299804; PF-299; PF299804; PF-299804; PF 299804; PF299; PF 299; dacomitinib
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.32 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (5.32 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.32 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 1% DMSO+30% polyethylene glycol+1% Tween 80, pH 9: 10mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1279 mL | 10.6397 mL | 21.2793 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4256 mL | 2.1279 mL | 4.2559 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2128 mL | 1.0640 mL | 2.1279 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Phase-2 Dacomitinib Study on Patients With EGFR-Driven Advanced Solid Tumours With Low EGFR-AS1 IncRNA Expr or Other Novel Emerging Biomarkers
CTID: NCT04946968
Phase: Phase 2 Status: Recruiting
Date: 2024-02-02
Inhibitory concentration and cell type.
Effects of dacomitinib on cell cycle.Cancer Res.2007 Dec 15;67(24):11924-32. |
The effects of dacomitinib on total and phosphorylated HER2, EGFR, HER4, AKT, and ERK.
Chemical structures of investigated molecules in this article.Cancer Res.2007 Dec 15;67(24):11924-32. |
Effects of dacomitinib on apoptosis.Cancer Res.2007 Dec 15;67(24):11924-32. |